Biology: Gas Exchange Adaptations in Humans, Fish, and Plants
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Why do multicellular organisms require specialized exchange surfaces for gas exchange?
Due to a larger distance that needs to be crossed because of a higher surface area to volume ratio.
What are the key features of an efficient exchange surface?
Large surface area, thin structure, good blood supply or ventilation to maintain a steep gradient.
What role do root hair cells play in gas exchange?
They provide a large surface area for efficient gas exchange.
What is the primary function of the lungs in mammals?
To facilitate gas exchange with a large surface area located in the chest cavity.
What protects the lungs in the thoracic cavity?
The rib cage.
What is the purpose of the lubricating substance secreted around the lungs?
To prevent friction between the rib cage and lungs during inflation and deflation.
What muscles are involved in the ventilation process?
Intercostal muscles and diaphragm.
How does air enter the lungs?
Through the nose, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
What are the alveoli?
Tiny sacs filled with air where gaseous exchange occurs.
What structural feature of the trachea allows for the passage of food down the esophagus?
Incomplete 'C' shaped rings of cartilage.
What is the composition of the walls of the trachea and bronchi?
Several layers including cartilage, glandular and connective tissue, elastic fibres, smooth muscle, and blood vessels.
What is the function of ciliated epithelium in the respiratory system?
To move mucus along and prevent lung infection.
What do goblet cells secrete and why?
Mucus to trap bacteria and dust, reducing the risk of infection.
How do smooth muscles contribute to the respiratory system?
They contract to control the diameter of the airway, thus regulating airflow.
What is the role of elastic fibres in the lungs?
They stretch during exhalation and recoil during inhalation, controlling airflow.
What are the two stages of ventilation?
Inspiration and expiration.
What happens during inspiration?
External intercostal muscles contract, diaphragm flattens, increasing thoracic volume and decreasing pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs.
What occurs during expiration?
Internal intercostal muscles contract, diaphragm relaxes, decreasing thoracic volume and increasing pressure, forcing air out of the lungs.
What is a spirometer used for?
To measure lung volume.
What is vital capacity?
The maximum volume of air that can be inhaled or exhaled in a single breath.
What is tidal volume?
The volume of air breathed in and out at each breath at rest.
What is residual volume?
The volume of air that is always present in the lungs.
What adaptations do bony fish have for gas exchange?
Four pairs of gills with gill filaments and lamellae for gas exchange.
What is the significance of counter current flow in fish gills?
It enhances gas exchange efficiency by allowing blood and water to flow in opposite directions.
How do insects achieve gas exchange?
Through spiracles and tracheae that deliver oxygen directly to tissues.
What is the function of the upper epidermis in a leaf? and how does it do this
To prevent excessive water evaporation and allow light penetration.
its a waxy, waterproof layer with no chloroplasrs
What is the main site of photosynthesis in a leaf?
Palisade mesophyll, which contains a large number of chloroplasts.
What is the role of stomata in gas exchange?
To regulate the uptake of carbon dioxide and conserve water.
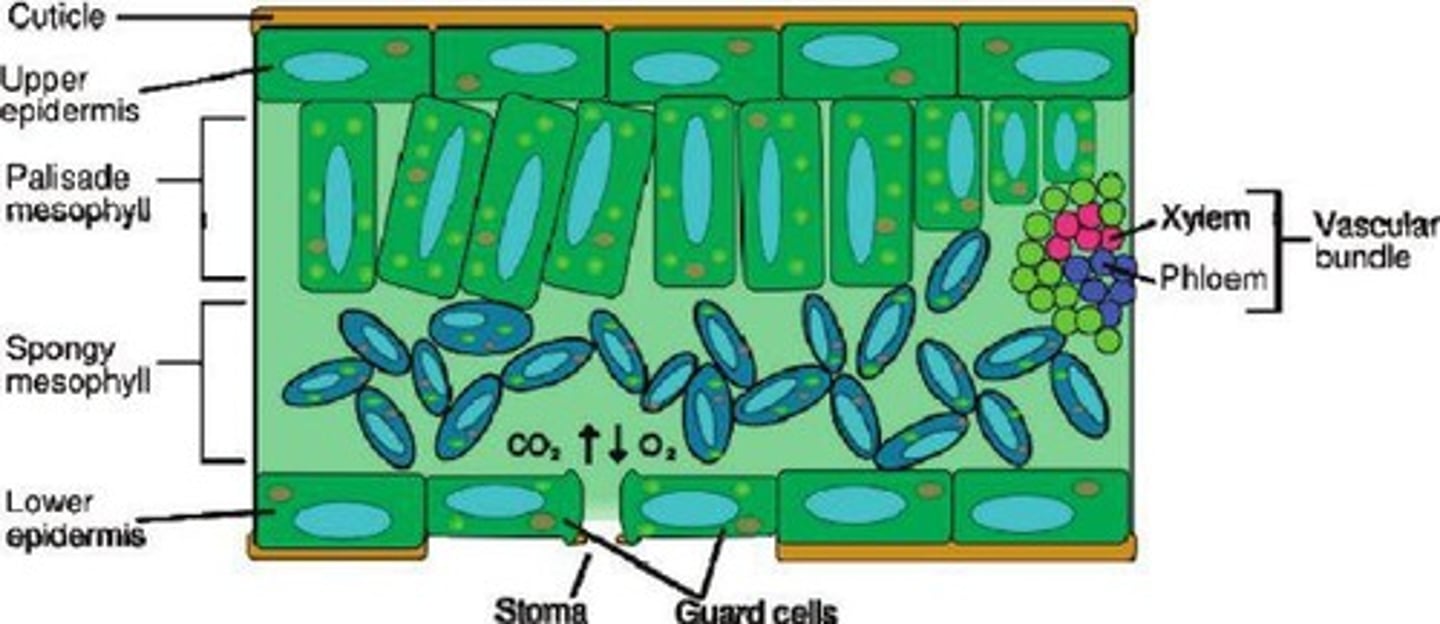
How do guard cells control stomatal opening?
By inflating or deflating in response to turgidity caused by potassium ion concentration.
What triggers stomata to close?
Excess water loss, usually in response to low light levels and reduced photosynthesis.