2.5: Time Dilation and Length Contraction
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Section 2.5 of Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
The time interval between two events occurring at the same position in a system, measured by a clock at rest in the system in called?
The proper time, denoted (T₀).
Mathematically describe the formula for Time Dilation.
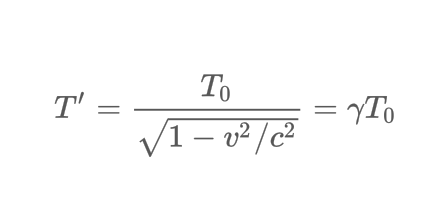
How is time dilation interpreted?
It is interpreted by saying moving clocks run slow by a factor of γ⁻¹.
The actual time interval on a moving clock is what?
Greater than the proper time as measured on a clock at rest.
The proper time is always what?
The smallest possible time interval between two events.
What is defined as proper length?
The length measured at rest.
Mathematically describe the formula for Length Contraction (Lorentz-Fitzgerald Contraction.
This effect like time dilation is reciprocal, and each observer will say one moving length is shorter.

Why is there no length contraction perpendicular to the relative motion?
It is because y’ = y and z’ = z.
How does the effect of length contraction along the direction of travel affect the appearance of two or three dimensional objects.
We see objects when the light reaches our eyes, not when the light leaves the object. So, if objects are moving rapidly, we will not see the as they appear at rest.