Topic 4 - Chemical changes (without electrolysis)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the pH scale?
A measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is
What are the number scale of the pH scale?
0 - 14
Is a solution acidic of alkaline is it has a pH between 0 - 6?
Acidic
Where is neutral on the pH scale?
7
Is a solution acidic or alkaline if it has a pH between 8 - 14?
Alkaline
3 examples of acids?
Stomach acid
vinegar
lemon juice
3 examples of alkaline?
Bleach
Soap powder
Washing-up liquid
What is an example of neutral substances?
Pure water
How can you measure the pH of a solution?
Using an indicator
Using a pH probe attached to a pH meter
What can an acid be defined as?
An acid is a substance that forms an aqueous solution with pH less than 7 and form H+ ions in water
What can a base be defined as?
A base is any alkali substance that will react with an acid to form a salt and produce water
What is the net ionic equation of all acid-base neutralisations?
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) = H2O(i)
What can an Alkali be defined as?
A base that dissolves in water to form a solution that has a pH grater than 7 and form OH- ions in water.
What is the reaction between acids and bases called?
Neutralisation - the products are neutral - they have a pH of 7
What is the equation for the reaction between an acid and the base?
acid + base = salt + water
What are acid-base titrations?
They can determine exactly how much alkali is needed to neutralize a quantity of acid - and vice versa
How can titrates also be used?
Can be used to prepare salts or other precipitates and redox reactions
What indicators can we use in titration?
Phenolphthalein
Litmus solution
Methyl orange
What color is Phenolphthalein in acid?
Colourless
What color is Phenolphthalein in alkali?
Pink
What color is Phenolphthalein in neutral?
Colourless
What color is Litmus solution in acid?
Red
What color is Litmus solution in alkali?
Blue
What color is Litmus solution in neutral?
Purple
What color is Methyl orange in acid?
Red
What color is Methyl orange in alkali?
Yellow
What color is Methyl orange in neutral?
orange
What equipment are needed to do a titration?
Pipette
Burette
Acid
Scale
Conical flask
What is a Burette?
Burette measure different volumes and let you add the solution drop by drop
What does the conical flask contain in this experiment?
Alkali and indicator
DO TITRATION FLASHCARDS ON PMT
YES OR NO?
What is the objective of the titrations required practical?
To determine the reacting volumes of a strong acid and a strong alkali by titration
What are concordant results?
Concordant results are values that are within 0.1 cm3 of each other.
What should only be considered when calculating a mean titre?
Only concordant results should be used
How to work out moles using concentraiton and volume?
Moles = concentration X volume
What are strong acids?
All of the acid particles in a strong acid produce H^+ ions - they ionise completely in the water
What pHs do strong acids have then?
ph 1 - 3
What are weak acids?
Only a small proportion of acid particles dissociate to release H^+ ions - they don not fully ionise in the solution
Examples of strong acids?
Sulfuric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Nitric acids
Examples of weak acids?
Ethanoic acids
Citric acids
Carbonic acids
Why is the ionisation of weak acids a reversible reaction?
There is an equilibrium between the undissociated and dissociated acid
For every decrease of 1 on the pH scale…
The concentration of H^+ ions increases by a factor of 10
How to work out the H+ ion concentration using the pH?
10-x where x = difference in pH (final pH - start pH)
Word equation for acid + Metal Oxide/Metal hydroxide and Acid + metal carbonate?
Acid + Metal Oxide = Salt + water
Acid + Metal Hydroxide = Salt + water
Acid + Metal Carbonate = Salt + Water + carbon dioxide
What is the reactivity series?
The reactivity series lists metals in order of their reactivity towards other substances
Order of metals in the reactivity series?
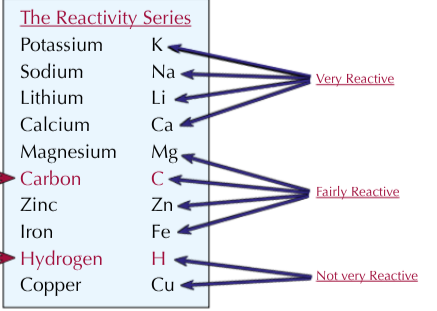
How can metals be extracted from their ores if they are less reactive than carbon?
Reduction with carbon
Which metals will not react with acids?
Metals that are less reactive than hydrogen
What is the equation when acids react with metal?
Acid + Metal = Salt + Hydrogen
How to test to confirm that hydrogen is formed in these reactions?
Use the burning splinter test:
Hold a burning splinter next to the test tube containing hydrogen
If there is hydrogen present - you will hear a squeaky pop
What is the equation when water reacts with metals?
Metal + Water = Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen
Which metals won’t react with water?
Zinc
Iron
Copper
What are the Redox reactions?
OIL RIG:
A loss of electrons is called oxidation
A gain of electrons is called reduction
What determines how reactive a metal is?
How easily it loses electrons to form positive ions
2 examples of Redox reactions?
Metals reacting with acids
Halogen Displacement Reactions
How to know if an atom exists as diatomic?
I
Bring
Clay
For
Our
New
House
What is a spectator ion?
Spectator ions are ions that are present during the reaction but are unchanged by the reaction
What reactants make up a soluble salt?
The reaction of an acid with and an insoluble base
Why is the insoluble reactant added in excess?
To ensure that all the acid has reacted so that any unreacted acid wouldn’t become dangerously concentrated during evaporation and crystallization
How is this excess of insoluble reactant removed?
Filtration
What metals can react with Acid to produce a salt?
Metal above hydrogen in the reactivity series
If the metal is not too reactive, which could result in a dangerous reaction
What is the objective of the soluble salt practical?
To prepare a pure, dry sample of a soluble salt from an insoluble oxide or carbonate using a Bunsen burner and dilute acid
What should the outcome of the practical be?
Regularly shaped bright blue crystals
What is the conclusion of this soluble salt practical
The regularly shaped salt reflects the ionic lattice structure in its bonding