AP World History Midterm Review
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I made/found questions from our notes about the topics of the documents in the review packets. This is a work in progress, but I have stuff from the first four units.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
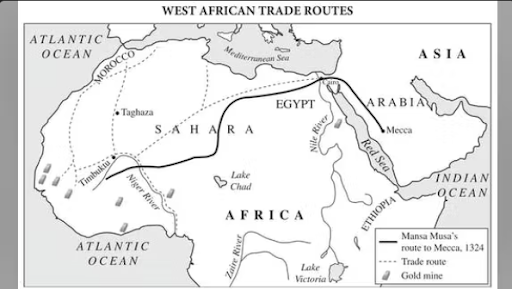
The map below best supports which of the following assertions?
Forced conversion of conquered populations
The spread of Islam facilitating trade relationships
Religious conflict between native African religions
A sectarian split between Sunni and Shi’a in Africa
The spread of Islam facilitating trade relationships
What type of trade route was the Silk Road called?
Relay trade because goods changed hands many times before reaching their final place
How did the geography of Eurasia cause the Silk Road?
The inner part had forest products, while the southern part had agricultural products
What types of goods were traded on the Silk Road?
Luxuries like silk and porcelain
When was the Silk Road the most powerful?
When large/powerful states protected merchants
Who played a significant role in the production and consumption of silk?
Women
Why was silk desired so much?
Its comfort and display of wealth
What is a caravan and what did merchants do?
A caravan is a group of camels/people transporting goods. The merchants walked alongside the camels.
What effect did trade have on empires?
Trade helped empires grow, expand their economy, and gain access to new technology.
What effect did trade have on religion?
Trade helped spread religion around the world.
What was an important innovation for the trans-Saharan trade and why?
Camel saddles because it allowed people to use camels effectively to transport goods\
What caused growth of trade in Eurasia?
Technology, increase in demand, common religion, and strong city-states
How did trade routes help with history?
Travelers wrote about their travels a lot
What contributed to the growth of the Trans-Saharan trade?
The spread of Islam because it unified people, new empires because it provided stability, and technological advances because it made travel possible
Why did trade grow in Eurasia?
Technologies/innovations, new cities/states, and cultural diffusion
Most important inventions before the 17th century
Compass, printing, gunpowder
Where was the Ottoman Empire?
Southern Europe, Middle East, North Africa
What is the Ottoman devshirme an example of?
Recruitment and use of bureaucratic elites and the development of military professionals
Did the Ottoman empire accept diverse populations?
Yes, this is shown by their acceptance of Jews and Christians in their empire
What was Ottoman tax farming?
They auctioned the right to tax to the highest bidder, who could then charge more than needed
Which branch of Islam was the Ottoman empire and what was the result of it?
Sunni, this caused conflict with the Safavid empire because they were Shi’a
What ethnicity were the Ottomans?
Turkish
What was the Ottoman tax system based on?
Ancestry
What groups did the Ottomans threaten?
Europe and Safavids
What was the Ottoman millet system?
Other monotheistic religious groups had autonomy over most of their society, while still providing labor
What was the effect of the devshirme system being expanded?
It allowed everyone to have access to the elite bureaucratic positions that allowed for social mobility
What was the social structure in the Aztec empire?
It was very strict with nobles, commoners, serfs, and slaves. However, people could not be born into slavery.
What was the Spanish social system called?
Caste system
What were the Spanish casta system rankings?
Peninsulares - Spanish born in Spain
Creoles - Spanish born in America
Mestizo - Spanish and Native American
Mulato - Spanish and African
Native Americans and Africans
Why was the casta system established?
People intermingled and the Spanish men didn’t want to have children with Indigenous or Black women and have them seen as lesser.
How did the Spanish use the casta system to build their empire?
They made all other groups “lower” so it was easier for them to obtain power
How did the Spanish change the social structures in the Americas?
They made them based on race instead of occupation. You could also buy your way into a better social class.
What role did European traders play in the capture of enslaved Africans during the trans-Atlantic slave trade?
A. They captured enslaved Africans themselves.
B. They relied on African rulers and traders to capture and bring enslaved Africans to the coast.
C. They purchased enslaved Africans directly from other European nations.
D. They used military force to take enslaved Africans from their communities.
B. They relied on African rulers and traders to capture and bring enslaved Africans to the coast.
How did many African traders acquire captives for the slave trade?
A. By acquiring them as a result of military and political conflict.
B. Through peaceful negotiations with neighboring tribes.
C. Through voluntary agreements with local communities.
D. By purchasing them from European traders.
By acquiring them as a result of military and political conflict.
What was the significance of slavery in some African societies by the early sixteenth century?
A. It was only practiced in coastal regions.
B. It was primarily a punishment for criminals.
C. It was a new concept introduced by European traders.
D. It played a major role and contributed to maritime slave trade systems.
D. It played a major role and contributed to maritime slave trade systems.
What argument do some historians make regarding European traders and existing slave trade systems in Africa?
A. They completely dismantled existing systems.
B. They took advantage of pre-existing slave trade systems to obtain labor.
C. They created new systems that replaced the old ones.
D. They had no impact on the existing systems.
B. They took advantage of pre-existing slave trade systems to obtain labor.
What was a significant characteristic of ethnic identities in Africa during the trans-Atlantic slave trade?
A. They were irrelevant to the slave trade.
B. They were based solely on geographical location.
C. They were influential but did not create a common identity.
D. They unified all groups under a common African identity.
They were influential but did not create a common identity.
What was a common consequence of frequent conflicts among African groups during the trans-Atlantic slave trade?
A. It resulted in the decline of agricultural production.
B. It fostered peaceful relations between neighboring tribes.
C. It led to the unification of all African tribes.
D. It produced captives who could be sold into the slave trade.
D. It produced captives who could be sold into the slave trade.
In what way did European traders influence African societies during the slave trade?
A. They introduced new agricultural practices.
B. They provided education to local populations.
C. They influenced African leaders to supply enslaved Africans for the trans-Atlantic trade.
D. They established democratic governments in African regions.
C. They influenced African leaders to supply enslaved Africans for the trans-Atlantic trade.
How did the presence of slavery in areas where it was not prevalent change due to European demand?
A. It resulted in the establishment of new trade routes.
B. It expanded the presence of the institution and trade.
C. It had no significant impact on local economies.
D. It led to the complete abolition of slavery.
B. It expanded the presence of the institution and trade.
What could African leaders do if the profits from the slave trade did not outweigh the loss of local labor?
A. They could refuse to supply enslaved people.
B. They could seek military assistance from European powers.
C. They had to comply with European demands regardless.
D. They could negotiate better prices with European traders.
A. They could refuse to supply enslaved people.
How did the Trans-Atlantic slave trade change over time?
It started with mostly Great Britain, but then the countries involved began to get more diverse. Spain and France especially began to be in the slave trade. At the end, it was almost only Portugal and Spain
Where did most of the slaves come from and go to?
Most of them came from West Africa and went to the Caribbean
The concept of slavery was not new to Africa or Europe. But, how were the Atlantic slave trade and American slavery different than previous versions of slavery on other continents?
The Atlantic slave trade and American slavery was different because the slaves had even less rights than usual and were unable to obtain their freedom.
Why did African kingdoms participate in the slave trade? (Name at least two factors).
African kingdoms participated in the slave trade by bringing prisoners of war to sell as slaves to Europeans and using slaves to trade with Europe to get goods like guns.
How did Christian Europeans justify slavery, considering it was at odds with their ideologies?
Christian Europeans justified slavery by claiming that Africans were biologically inferior and meant for slavery.
Some of the trade routes described in the map had declined significantly during the period 1450-1750. Which of the following is NOT a strong explanation for that change?
The rise of the Atlantic system as a center for world trade
The damage done to the silk road by the black plague during the 1300’s
The deaths of millions of camels due to disease along the Sahara
The decreasing power of pastoral nomads after the fall of the Mongol empire
The deaths of millions of camels due to disease along the Sahara
How did Europeans extend their power/influence in the Indian Ocean Trade? Was it a change or continuity?
They used the military to control trade, which was a change from the primarily peaceful trade run by merchants
How did Europe get power in the Indian Ocean Trade?
They threatened ships and taxed them.
How did the Spanish having silver impact the Indian Ocean trade?
Other groups, like China and India, wanted silver so they really wanted to trade with Spain
What are natural rights?
Rights that people are born with and cannot be taken away from them, like life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness
Who encouraged the idea of a social contract?
John Locke
What is empiricism?
The idea that true knowledge is gained through senses and experiments
How did Baron de Montesquieu think the government could be preserved from corruption?
Having different branches of government to divide up the power
What did Wollstonecraft advocate for?
Equal rights for women
What was the main idea behind the French Revolution?
The government should be based on what is best for the people and all people must be equal
What government actions caused the French people to revolt?
The government tightened control to pay war debts
What was the main inspiration for the Haitian Revolution?
The French Revolution. They were controlled by France and the slaves thought that everyone being equal was a good idea.
Where did the Industrial Revolution start?
Great Britain
What caused certain countries to industrialize faster than others?
Short Answer: They were positioned well, had lots of resources, and they were in a prosperous era
Long Answer: They were close to waterways to transport goods, had a lot of coal and iron, access to foreign resources through colonies, had improved agricultural output so there was plenty of food, rapid urbanization, made entrepreneurs feel safe about taking risks, and had people with a lot of money
How did the Industrial Revolution impact the jobs people had?
Jobs moved away from specialized labor since many factory workers did repetitive tasks that were easy to do
Which invention helped Industrial Revolution increase more rapidly?
Steam engine
Where did power shift during the Industrial Revolution?
Industrialized states like Great Britain, France, Russia, and US
Which country industrialized way before everyone else?
Great Britain
What was the effect of the steam engine?
Factory machines didn’t have to be powered by water anymore so they could now be built anywhere
Which regions became more developed during the Industrial Revolution?
Internal regions because all of the trade wasn’t happening at sea anymore
How did the Industrial Revolution impact the economy?
It interlinked states more closely into a global economy
Which states’ industrialization was mainly powered by the government?
Egypt, Japan
Why did Japan industrialize?
Noticed that Western powers were dominating other Asian states like China and America threatened them into opening their ports
What was the Meiji Restoration?
Japan sought to escape foreign domination by adopting much of the industrial practices that had made the West powerful
What economic changes were caused by the Industrial Revolution?
Mercantilism decreased and the free market system increased
What was the effect of the industrialization for working class women?
They worked wage-earning jobs since their husbands’ jobs didn’t earn enough money
What was the effect of the industrialization for middle class women?
They did not work and became increasingly viewed as domestic and supposed to support their husband and children
Which European countries were the main players in Indian Ocean trade?
Portugal and Dutch
Why didn’t Japan like Europeans?
They didn’t like Christianity. They allowed the Dutch to continue trade a little because they didn’t focus as much on trade