PH3. Newton's Laws of Motion
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

19 Terms
What is Newton's First Law of Motion?
Objects remain at rest or move with constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant
force
What are drag forces, and what happens when they are absent?
- Drag forces oppose motion through a fluid by slowing objects down, depending on shape, speed, and viscosity
- Without drag, objects move indefinitely at a constant velocity
How is weight related to mass, and why does weight vary with location?
- Weight = mg, so it varies with gravitational field strength
- Mass remains constant as it measures inertia
What is inertia?
Inertia is an object's resistance to changes in its motion, determined by its mass
How is F=ma applied when two unequal forces act on an object in opposite directions?
Resultant force = F1−F2 = ma, so the object accelerates in the direction of the larger force
In what situations can F=ma not be applied?
F=ma cannot be applied when forces are undefined, acceleration isn’t uniform, or mass changes significantly (rockets losing fuel)
Why do you feel less support as an ascending lift stops?
- Deceleration reduces tension in the lift cable (T
What happens to the acceleration of a falling object as it approaches terminal speed?
- As object falls velocity increases due to weight
- As velocity increases air resistance increases so acceleration decreases
- Eventually, air resistance = weight so resultant force and acceleration is 0
- The velocity at which resultant force = 0 is called terminal velocity
Why does the speed of a powered vehicle reach a maximum even when the driving force is still acting?
- As the car drives, the drag force increases with speed, reducing the resultant force
- Acceleration gradually decreases, until terminal speed when drag force equals driving force
- Which means the resultant force is zero, so acceleration is zero and speed remains constant
What role does streamlining play in determining the top speed of a vehicle?
Streamlining reduces drag, allowing higher top speeds for the same engine power
What is thinking distance?
Distance traveled from spotting a hazard to applying brakes = Initial speed×Reaction time = ut
What is braking distance?
Distance traveled from applying brakes to stopping = u²/2a (initial speed, deceleration)
What is stopping distance?
- Total distance traveled from spotting a hazard to stopping the vehicle, including both the thinking distance and braking distance
- Total Distance = Thinking Distance+Braking Distance = ut+u²/2a
What factors influence thinking distance and how can it be minimized?
Factors: Reaction time (affected by distractions, fatigue, drugs/alcohol), speed
Minimization: Stay alert by avoiding distractions, and maintain safe speed
What conditions affect braking distance?
- Wet/icy roads, worn tires and high speeds reduce friction between tires and the road, decreasing deceleration and increasing braking distance
- Dry roads, new tires and low speeds increase friction between tires and the road, increasing deceleration and shortening braking distance
What happens to the force on a moving body if it is suddenly stopped, such as in a road accident?
Sudden stop results in large deceleration, leading to a high impact force, expressed in terms of g (acceleration due to gravity)
(For example, a deceleration of 30m/s² is approximately 3g, meaning the force is three times the weight of the vehicle as F=ma=m(3g))
What should be increased to reduce deceleration from a given speed during an impact?
Impact time is inversely proportional to impact force, so a longer impact time reduces magnitude of deceleration and therefore the impact force
Which design features in modern vehicles aim to increase impact time and reduce deceleration during collisions?
- Crumple zones deform and absorb energy
- Airbags inflate to cushion passengers
- Seat belts stretch slightly
- Energy-absorbing materials in bumpers dissipate impact energy
- These features reduce risk of injury by increasing the contact time over which the passenger's momentum reaches zero, reducing the force exerted on them
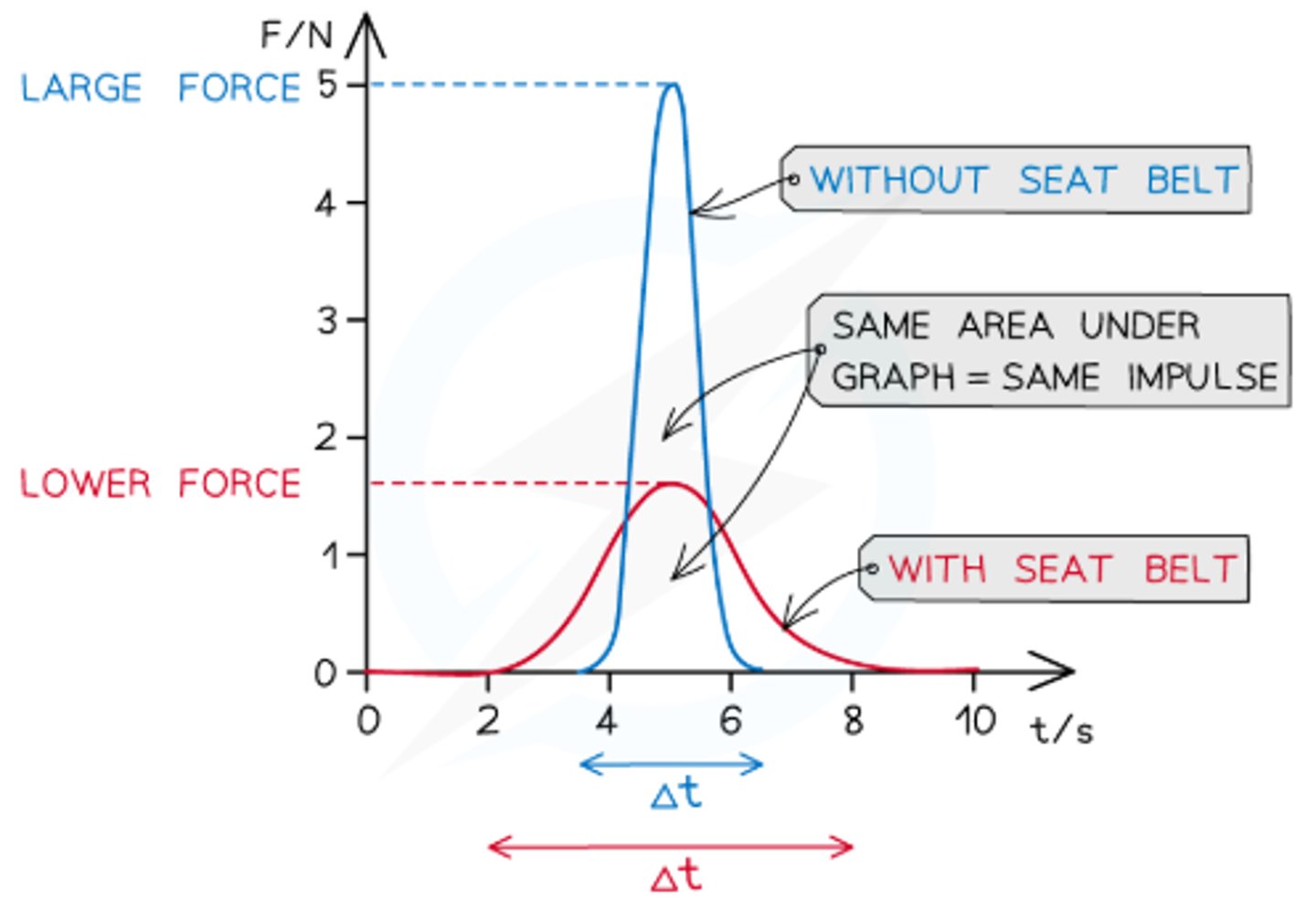
How is impact time related to impact force in a collision?
Impact time can be calculated using t=u+v²s, then used to calculate acceleration (a=tv−u) and impact force (F=ma)