Cells: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, endosymbiosis, cell theory
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Differences of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (6)
Differences:
prokaryotic: bacteria and archaea, eukaryotic: animals, plants and fungi
prokaryotic: DNA free in cytoplasm. eukaryotic: DNA in membrane bound nucleus
prokaryotic: no membrane bound organelles. eukaryotic: membrane bound organelles
prokaryotic has a decreased level in complexity (no membrane bound cells)
prokaryotic cell walls: peptidoglycon eukaryotic: (if any) chitin or cellulose
prokaryotic: smaller (0.1 - 0.5 micrometers) eukaryotic: bigger (up to 100 micrometers)
Cell theory (3)
All organisms are composed of one (unicellular) or more (multicellular) cells
Cells are the structural and functional unit of any living organism, and are where “MRS GREN” resides
All cells arise from prexisting cells via cell division
What are the necessary features of living organisms? (7)
Movement
Respiration
Sensitivity
Growth
Reproduction
Excretion
Nutrition
(MRS GREN)
Organelles
Sub-cellular structures in cells
What is endosymbiotic theory? (3)
Eukaryotic cells evolved due to a mutualistic relationship between 2 or more prokaryotic cells.
A larger prokaryotic cell with a flagellum eats a smaller prokaryotic cell without one. When the larger cell cannot digest the smaller anymore, it takes it into the vacuole
Name the structures in all prokaryotic cells (5)
Cytoplasm
Cell wall
Cell surface membrane
70s ribosomes
Loop of DNA
Name the optional extras of a prokaryotic cell (4)
Flagellum
Mesosome
Plasmid
Slime capsule
What is the consequence of the mutualistic relationship between the larger prokaryotic cell with the flagellum, and the smaller prokaryotic cell
Bigger one keeps the smaller one at the surface (because of flagellum’s grant of motility), for photosynthesis
Smaller carries out photosynthesis and produces oxygen, ATP, and glucose
Function of slime capsule
Protection from phagocytes engulfing cell
Plasmid (2)
Small circular molecule of DNA.
Contains additional genes for antibiotic resistance
Mesosome (2)
Infolding of cell surface membrane
Increases surface area for respiration
Flagellum
Microscopic appendage of cell that allows motility (movement)
Cytoplasm (2)
the solution where all of chemical reactions (metabolism) occur. where proteins are catalysed by enzymes
Prokaryotic cell walls (3)
Made of peptidoglycon
provides mechanical strength and support
prevents osmotic lysis in hypotonic solution
What kind of organisms have Prokaryotic cells (2)
bacteria, archaea
What kind of organisms do eukaryotic cells belong to (4)
Animals, plants, fungi. protoctista
Loop of DNA (3)
in prokaryotic cells
carries generic information in the form of genetic code which controls photosynthesis, and transcription of protein
essential genes involved in metabolism
70S Ribosomes (3)
In prokaryotic cells, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
Carry out translation (formation) of polypeptide chain
site of protein synthesis
Cell surface membrane (prokaryotic)
controls movements of molecules and ions in and out of cell
Evidence for endosymbiotic theory (4)
mitochondria and chloroplasts have:
double membranes
loop of DNA
70S ribosomes
mitochondria is a similar size to prokaryotic cells
Mitochondria function (3)
site of aerobic respiration
produces ATP to be hydrolysed for energy
which is needed for protein synthesis and exocytosis
chloroplast function (3)
site of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water with light = glucose + oxygen
glucose contains 2 molecules of ATP
nucleus function
controls functions of cell
carries DNA in chromatin
contains essential genetic code for protein synthesis
transcription of gene occurs, producing a molecule of mRna
mRna leaves nucleus via nuclear pore
mRna
messenger ribonucleic acid
read by ribosomes and used to synthesis a proteins
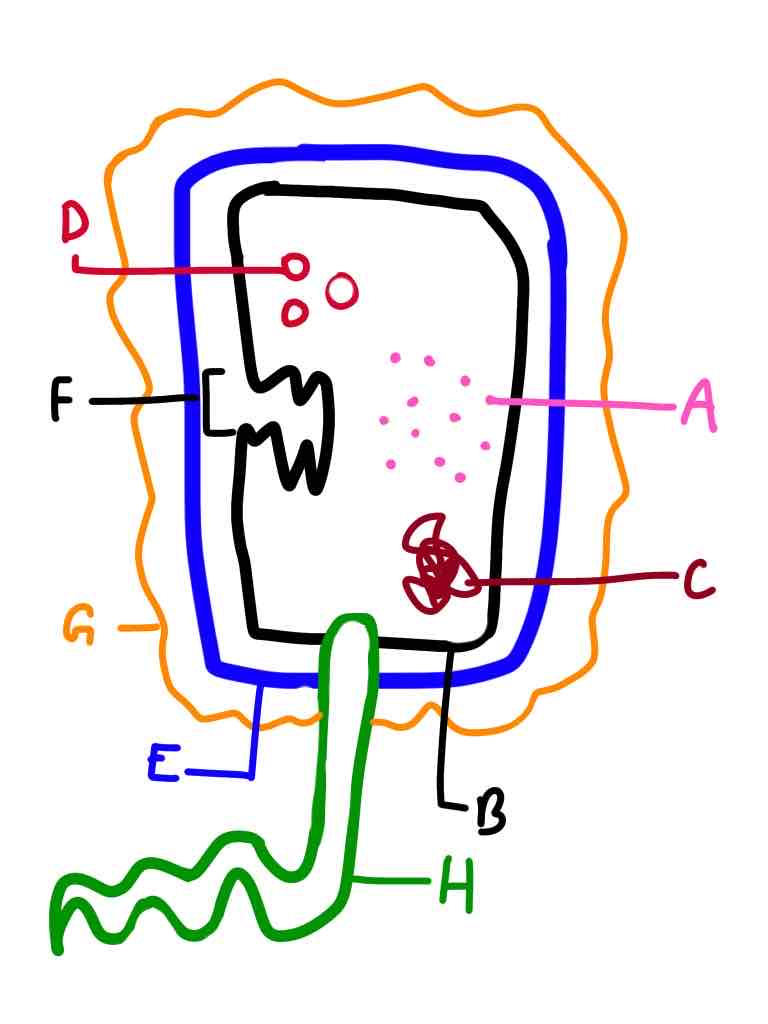
A: 70S Ribosomes
B: Cell surface membrane
C: Loop of DNA
D: Plasmids
E: Cell wall
F: Mesosome
G: Slime capsule
H: Flagellum
Division of labour (3)
eukaryotic cells have many membrane bound organelles
this allows for the COMPARTMENTALISATION of cell
therefore different reactions happen in different organelles
Eukaryotic cell walls (5)
Cellulose / chitin microfibrils
pores are called plasmodenta
Allows cytoplasms of adjacent cells to connect
provided mechanical strength and support
prevents osmotic lysis in hypotonic solutions
Thykaloid (2)
internal membrane in chloroplast which contains chlorophyll to absorb light energy
Granum
Stacks of thylakoids for increased SA for photosynthesis
Smooth endoplastic reticulum (3)
No ribosomes
Cisternae lined to nuclear envelope
synthesises, stores and transports lipids and carbohydrates
Ribosomes (3)
Made of large and small subunit
made of mRna and protein
Site of protein synthesis / translation: mRna is used to make polypeptide chain
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (3)
where folding of polypeptide chain occurs.
forming secondary and tertiary structure of protein
transports polypeptide chain / protein through cell
Vesicles (2)
pinches off of rough endoplasmic reticulum and transfer protein to golgi body
golgi body (3)
where protein is chemically modified and packaged
may involve addition of carbohydrate chain to form glycoprotein
also synthesises lysosomes
Secretory vesicle
transports functional protein to cell surface membrane
cell surface membrane (2)
controls molecules / ions going in and out of cell
vesicles fuse with membrane and release protein by exocytosis
exocytosis
moving large molecules out of cell to cell exterior
lysosome (5)
contains lumen, single membrane
contains hydrolitic enzymes
hydrolyses material digested by phagocytes
releases enzymes out of cell + digests worn out organelles + dead cells
programmed cell death / autolysis
autolysis
aka programmed cell death
breaking down of dead cells