Chapter 13: Leadership styles & behaviours
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is leadership?
Use of power & influence to direct activities of followers toward goal achievement
What is leader effectiveness?
Degree to which leader’s actions result in:
achievement of unit’s goals
unit’s employees continued commitment
development of mutual trust, respect, & obligation in leader
What is the great person theory?
Theory of what kind of traits effective leaders possess
External (attractiveness)
Internal (CANOE, personality)
It depends → no set/definite traits → do traits make leader, or does situation manifest traits?
doesn’t describe what leaders do
What is the behavioural approach?
Effective leaderships depends on the situation
leadership behaviours can be learned → not pure personality
What are the 2 day-to-day leadership behaviours?
Initiating structure → give direction, goal accomplishment focus, feedback
directive & task oriented
→ effective only if needed (otherwise, micromanaging)
Consideration → approachable, show concern
supportive & relational oriented
→ effective when employers are stressed/start to develop expertise
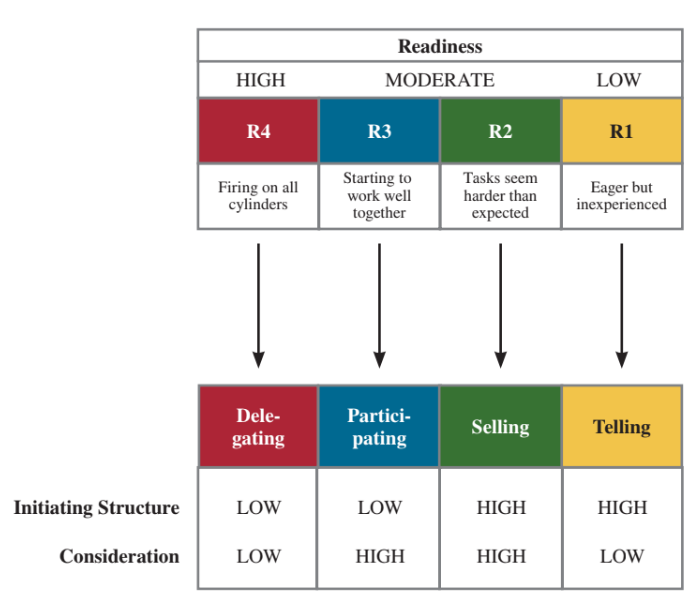
What is the life cycle theory of leadership (situation model)?
The best behaviours based on readiness
Readiness = situation (how able, willing motivated, leader’s impact depends on readiness)
R1 (eager but inexperienced) → telling
R2(tasks seem harder than expected) → selling
R3 (starting to work well together) → participating
R4 (firing on all cylinders) → delegating
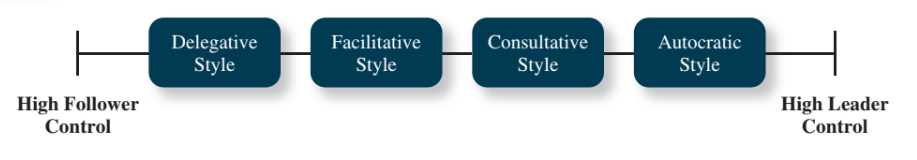
What are the 4 leader decision making styles?
In order of high to low follower control
Delegative style - allow employee to make decision
Facilitative style - leader shares decision-making power with employees
Consultative style - consult employee about decision but ultimately made by leader
Autocratic style - leader makes own decision
When is a high and low follower control more appropriate in leader decision-making styles?
High follower control:
more appropriate when decisions significant, commitment is important, employees have more expertise, work well as team, shared objectives
Low follower control:
more appropriate when decisions less significant, commitment less important, leader has more expertise, work bad as team, own objectives
What are the 7 questions in the time-driven model of leadership?
Leadership is dependent on 7 questions → best way to make decision depends on answers
If high, continue to next question
Decision significance
Importance of commitment
Leader expertise
Likelihood of commitment
Shared objectives
Employee expertise
Teamwork skills
What is the dominant leadership theory: Transactional/transformational leadership?
3 types → contingent reward is default
Contingent reward - most important/effective, meet behaviour, get reward
Management by exception (active) - leader anticipates issues & corrects
Management by exception (passive) - corrects issue only when it occurs (bad)
What is the dominant leadership theory: transformational leadership?
Idealized influence - charismatic/admirable qualities
Inspirational motivation - share an inspirational vision
Intellectual innovation - think outside box, intellectually stimulating
Individualized consideration - instill caring feeling, a mentor
What is leader-member exchange (LMX)?
The quality of work relationship that develops between leader & follower → some employees are treated differently
About exchange → leader has a lot to offer (autonomy), follower offers exceptional performance & emotional support
What are the 2 phases in a high leader-member exchange relationship?
Role taking
leader has expectations & follower meets expectations
leader tests ability & motivation → leader trusts if challenging task is met
→ follower trusts if more delegation
Role making
follower has expectations (after trust is built)
free-flowing exchange of work/resources
What is a high quality LMX?
Leader has different relationships with followers built on trust levels
High quality → the in-group
Low quality → the out-group
high trust, respect, sense of obligation, employee satisfaction, task performance, OCB’s
repeated exchange of favours
unlikely transactional