3. modern chemotherapy -protein-protein interactions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
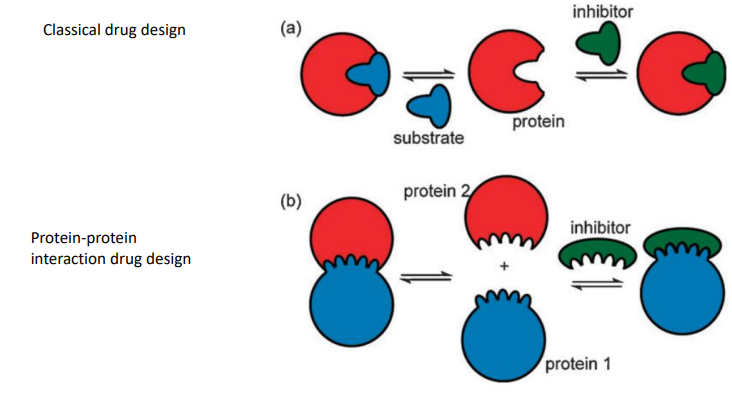
what are protein-protein interactions
the interaction of 2 proteins at their domain interfaces that regulates the function of protein complex
what are 6 potential problems with using protein-protein interactions
affinity acheived from the accumulation of numerous weak interactions
small molecule compared to protein
protein surfaces often flat & featureless
buried surface
hydrophobic nature results in drug that large and hydrophobic - can’t cross BBB
PPPis invlove large S.A - hard to design
what is the Bcl-2 family
B-cell lymphoma 2 family
key regulators in cell apoptosis
some members are pro-survival (Bcl-2, Bcl-x, MCl-1P
some members are pro-death (BAX, BID, BIM, BAD)
what happens with the Bcl-2 family members in cancer
over-expression of pro-survival proteins
prevents pro-death proteins from triggering caspase activation therefore prevents apoptosis
what is the overall aim of targeting the bcl-2 family in cancer
use a small molecule to bind to and inhibit the pro-survival protein therefore restoring apoptosis pathway how
how would we target the BCL-2 family (what technique, binding site)
3D NMR studies reveal the presence of hydrophobic groove on anti-apoptotic pathway
binding site to the a-helicall peptide of pro-apoptotic members w
what are the 3 types of fragment elaboration technique
Elaboration of HTS hit
fragment growing
fragment linking
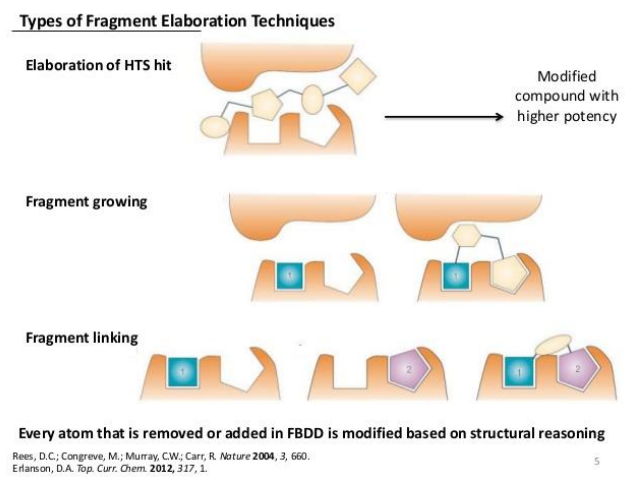
4 features of fragment based drug discovery
screen low affinity fragments at high concentrations
uses structural information to determine bindin mode
less synthetic steps
quick SAR
What is ABT-377
Discovered through high throughput NMR based screen & parallel synthesis
aims to identify small molecules that bind to the hydrophobic grrow of Bcl-2
how does the structure of ABL-377 enable it to bind to the bidnign site
has a polar group in solvent exposed areas - aids water solubitiy
has a long side chain of chloro-biphenyl group- hydrophobic space
what are the effects of a loss or mutation in P53 protein
accumulation of cancer promoting mutations
uncontrolled proliferation
apoptosis evasion
neoangiogenesis
DNA instability
how does MDM2 block P53
Direct Binding and Inhibition:
interferes with the interaction of p53 with transcriptional co-activators and RNA polymerase, inhibiting p53-mediated gene expression.
Ubiquitination and Degradation:
MDM2 has E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, which allows it to ubiquitinate p53.
Ubiquitinated p53 is targeted for degradation by the proteasome, leading to decreased levels of p53 protein in the cell.
Nuclear Export:
MDM2 can shuttle p53 out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where p53 is more susceptible to degradation by the proteasome, further reducing its transcriptional activity.
Phosphorylation of MDM2 or p53 at specific sites can disrupt their binding, leading to activation of p53 and induction of its target genes.
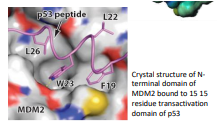
How does P53 bind to MDM2
Binding site on MDM2; deep, hydrophobic groove
P53 binds in a-helical manner
P53 forms 3 critical contacts through the side chains of Phe19, Try23, Leu26
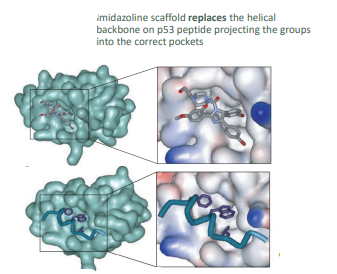
what s the role of the nutrlins
mimics the interaction of p53
displaces P53 from MDM2 w. nanomoleculer affinity
cis-imidizolines
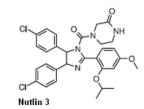
how does the cis-imidazoline interact with P53
one bromophenyl group sits deeply in the Try23 pocket, other occupies Leu26
Ethyl ether side chain is directed towards Phe19
scaffold replaes the helical backbone on P53 projecting the groups into correct pockets