Animal DiversityLAB - Week 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Sagittal Plane
bisects body into right and left halves
Frontal Plane
divides dorsal and ventral sides
Transverse Plane
divides anterior and posterior
Anterior
front or head end
Posterior
tail or hind end
Dorsal
back or uppermost side
Ventral
belly side
Lateral
side of the body
Medial
at or near midline of body
Cephalic/Cranial
head end
Caudal
trail end
Proximal
toward point of attachment
Distal
away from point of attachment
Longitudinal
lengthwise
Peripheral
parts away from the center
Superficial
on or near surface
Oral
mouth or region around mouth
Aboral
away from mouth
Radial Symmetry
any plane passing through longitudinal axis will divide body into like halves
Bilateral Symmetry
only a sagittal plane will divide the body into like halves
Characteristics common to ALL animals
-eukaryotic
-multicellular
-heterotrophic
-lack cell walls
-motile at some point
-sexual reproduction
Characteristics common ONLY to animals
-nervous tissue
-connective tissue
-develop blastula
Zygote → Morula → Blastula → Gastrula
fertilized egg, solid mass, hollow mass, opening forms
Diploblastic
2 germ layers
Triploblastic
3 germ layers
Blastocoel
center of blastula
Blastopore
forms either mouth or anus
Archenteron
hollow tube created by invaginated cells of gastrula
Protostome Characteristics
spiral cleavage, mosaic development, mouth first
Deuterostome Characteristics
radial cleavage, regulative development, anus first
Cladistics
biological system in which things are grouped together based on shared, derived characteristics
Molecular Phylogenetics
any method inferring evolutionary relationships from similarities or differences in molecular structure
Nested Clades
emphasize specificity and differentiation; what fits into what
Phylogenetic Tree
evolutionary history of an organism, relating to all extinct and extant species
Sister Group
two groups that are more closely related to each other than any other group
Outgroup
taxon that is closely related to, but not included within the focal group being studied
Homologous Traits (Shared Derived)
features among different organisms that share a common ancestor
Analogous Traits (Convergent Evolution)
features or structures in different species whose similarities are not due to common evolutionary origin
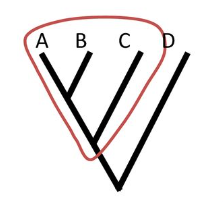
Monophyletic
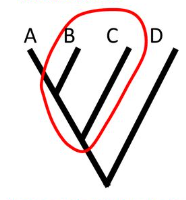
Paraphyletic
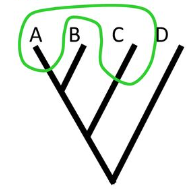
Polyphyletic
Ectoderm
forms nervous system, epidermis, and nasal/oral epithelium
Endoderm
forms GI tract epithelium, digestive organs, and respiratory system
Mesoderm
forms muscle/bone/connective tissue and circulatory system