BIOL 430 3-5 Length-Tension Curve & Muscle Fiber Types
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
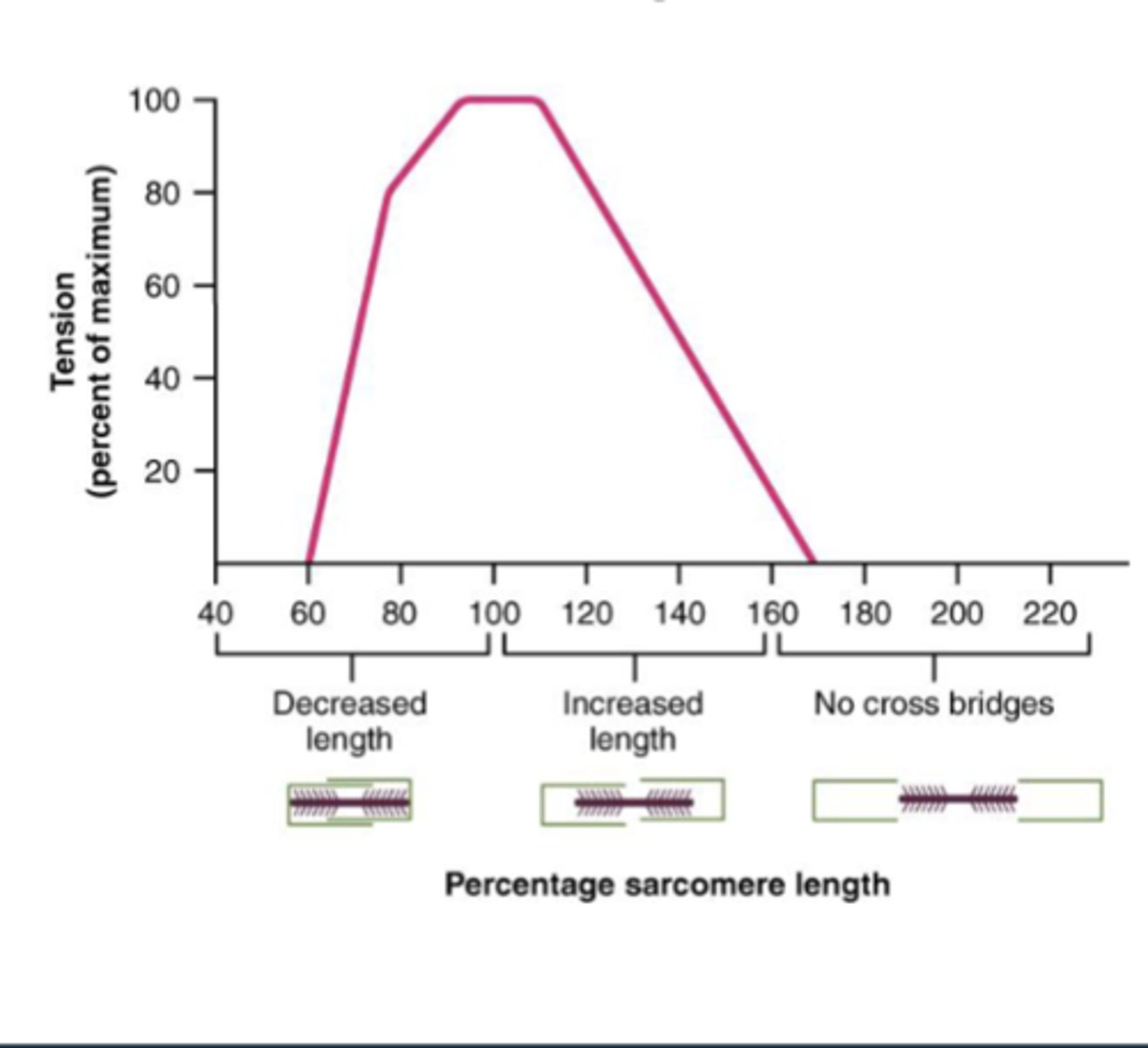
What is the relationship between sarcomere length and tension
-length of sarcomere has influence on force generated when sarcomere is shortened/contracted
-ideal length of sarcomere is about 80-120% of resting length; produces maximum tension
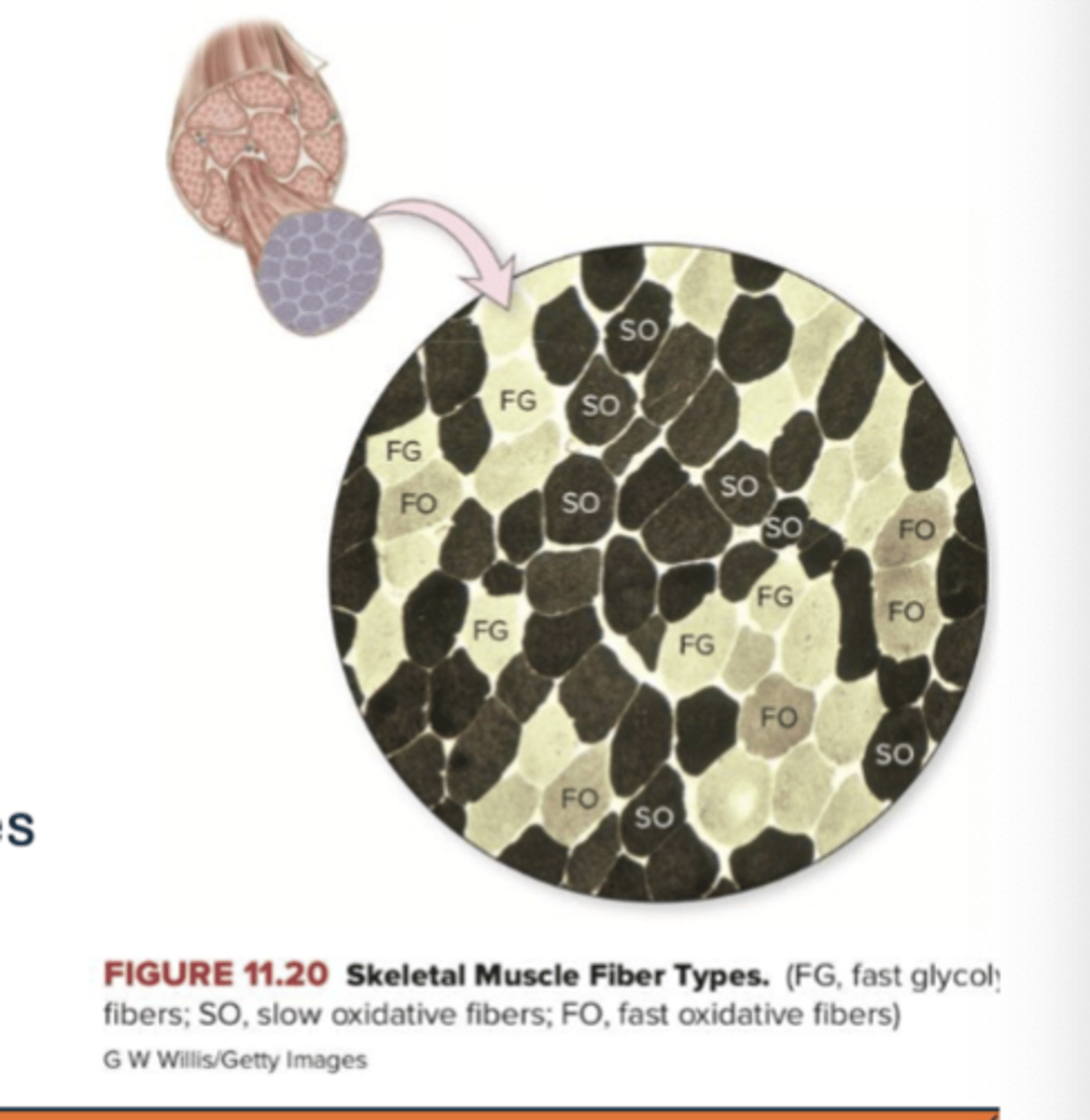
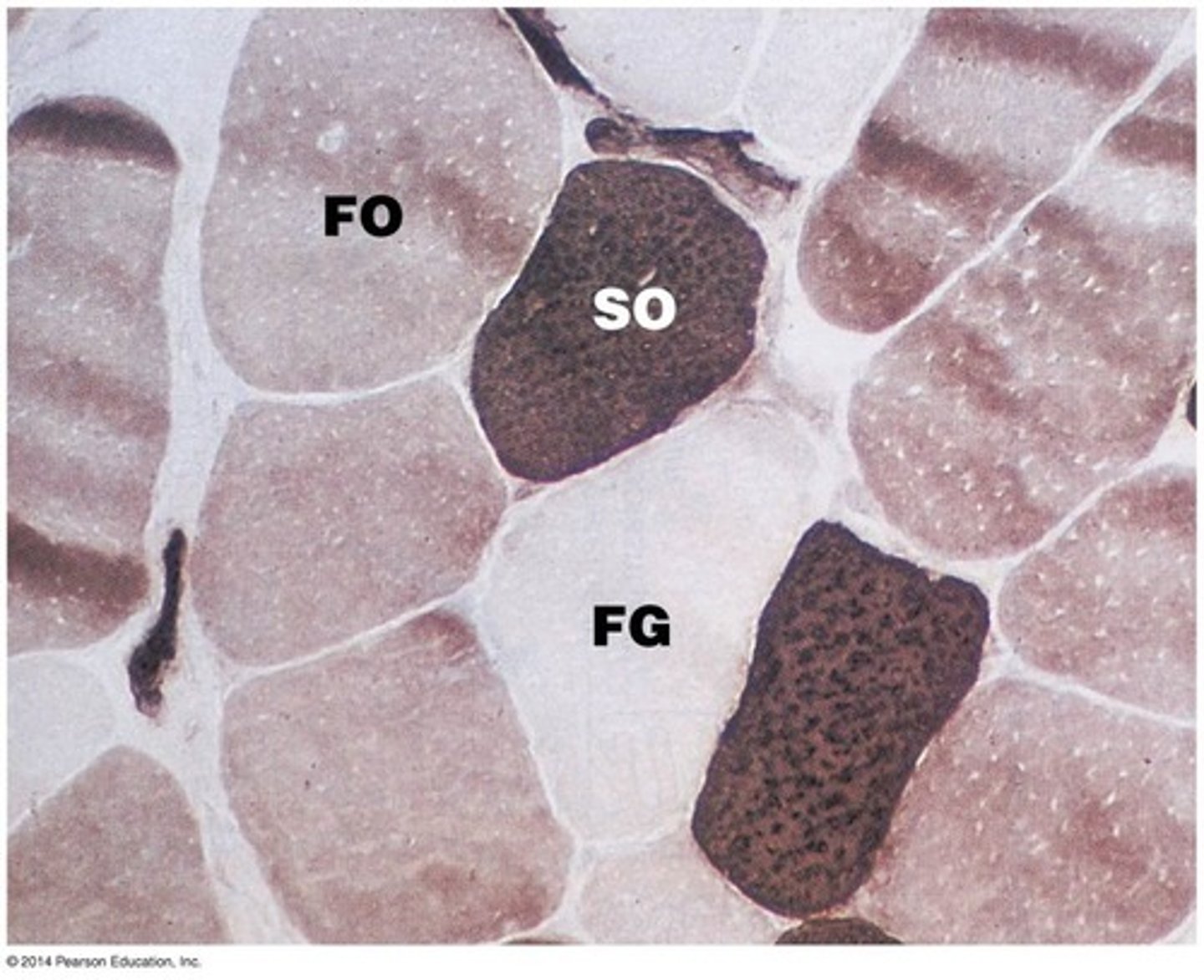
What are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers
-slow oxidative fibers (SO), fast oxidative fibers (FO), and fast glycolytic fibers (FG)
-whole muscles contain all three types w/ diff proportions
Describe slow oxidative fibers
-slow to contract
-aerobic respiration
-gluteus minimus is MAINLY SO fibers
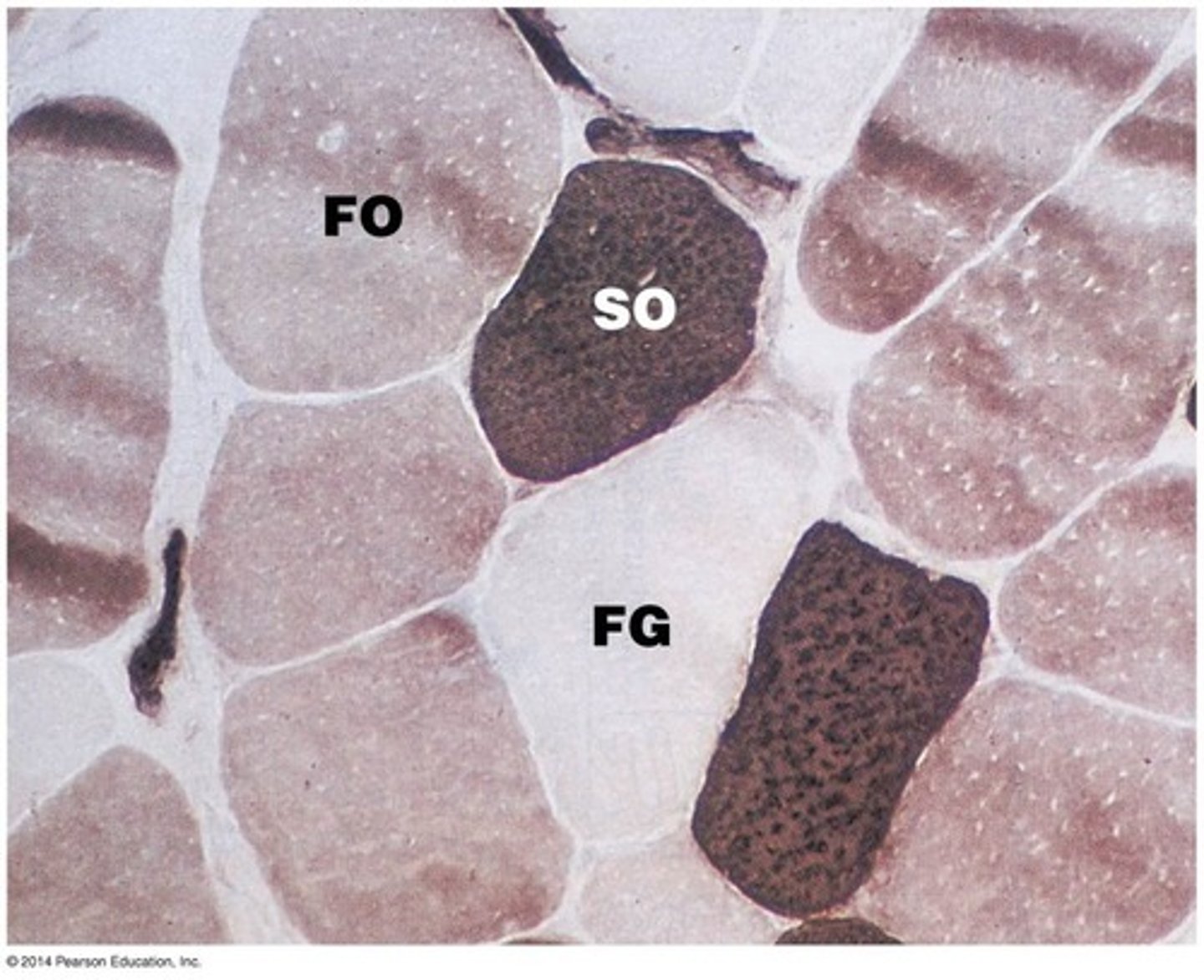
Describe fast oxidative fibers
-fast to contract
-aerobic respiration
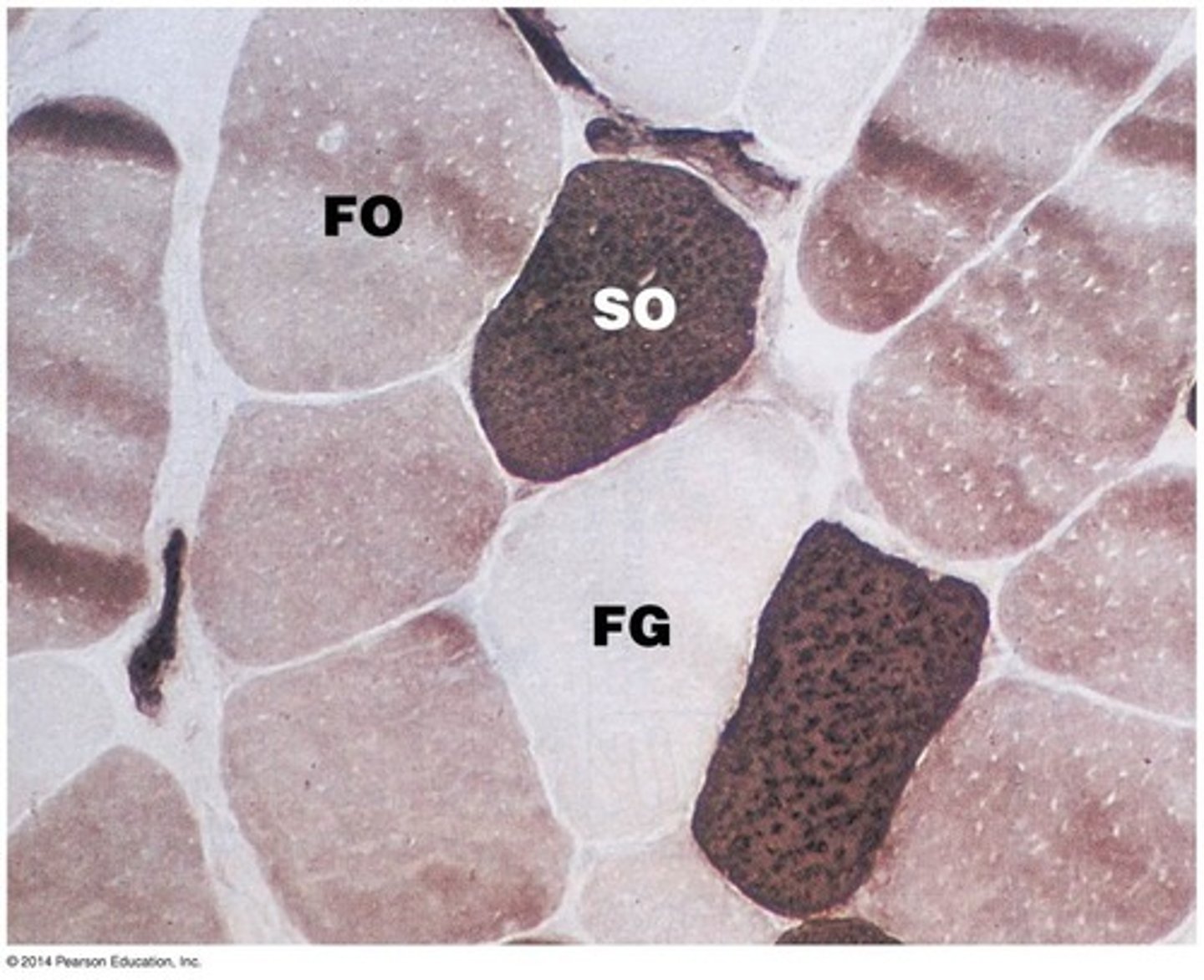
Describe fast glycolytic fibers
-fast to contract
-anaerobic respiration
-gluteus maximus is MAINLY FG fibers
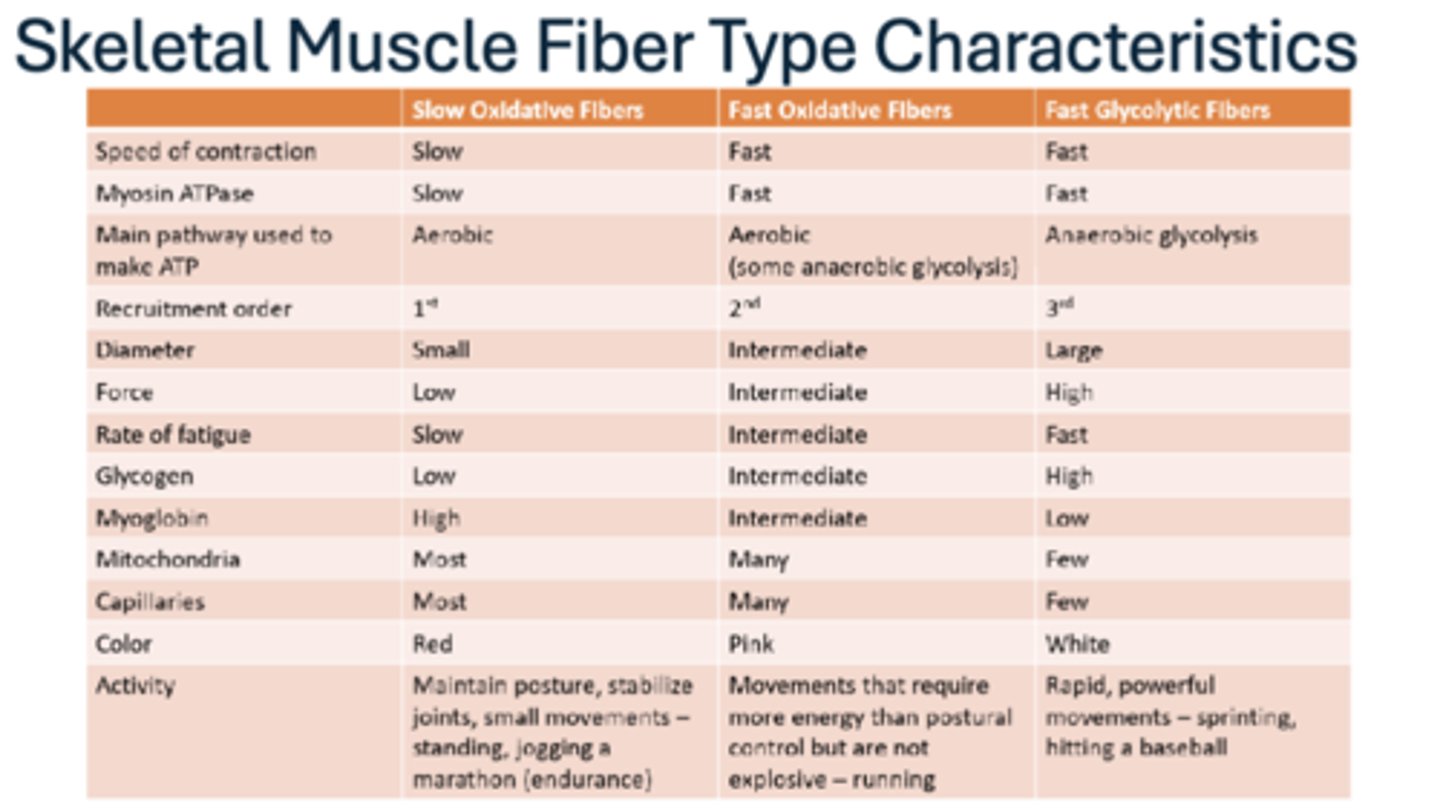
Characteristics of skeletal muscle fibers
refer to image
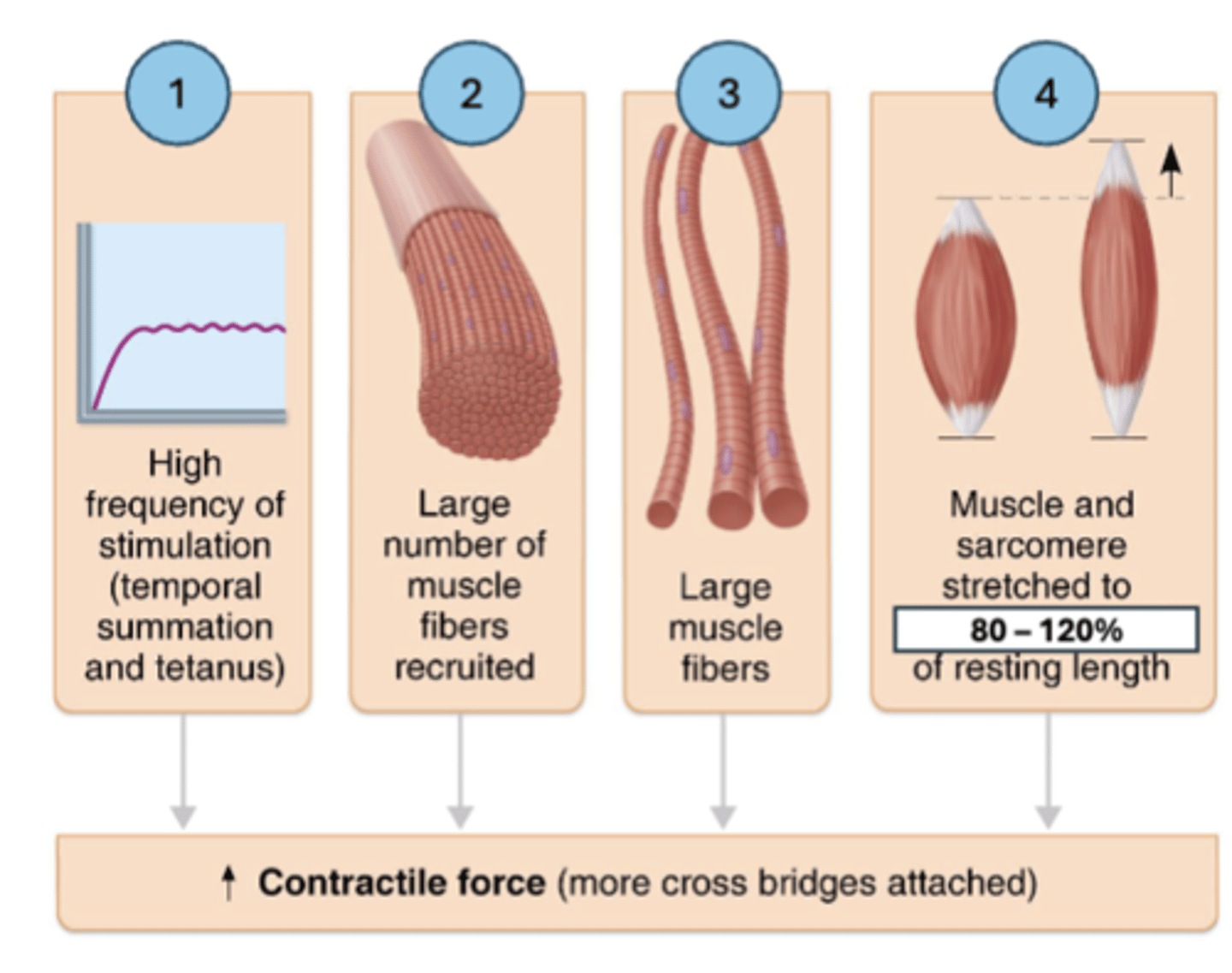
What are the four influencing factors on muscle contraction force
1. Frequency of stimulation (tetanus/wave summation)
2. Number of muscle fibers stimulated(motor unit recruitment)
3. Size of muscle fibers (Diameter)
4. Degree of muscle stretch (80-120%)
Describe the behaviors of muscle performance
-physical training alters appearance of skeletal muscles
-muscles change in size, not # of muscle fibers
-other cellular components of muscle fibers also undergo change in response to muscle use

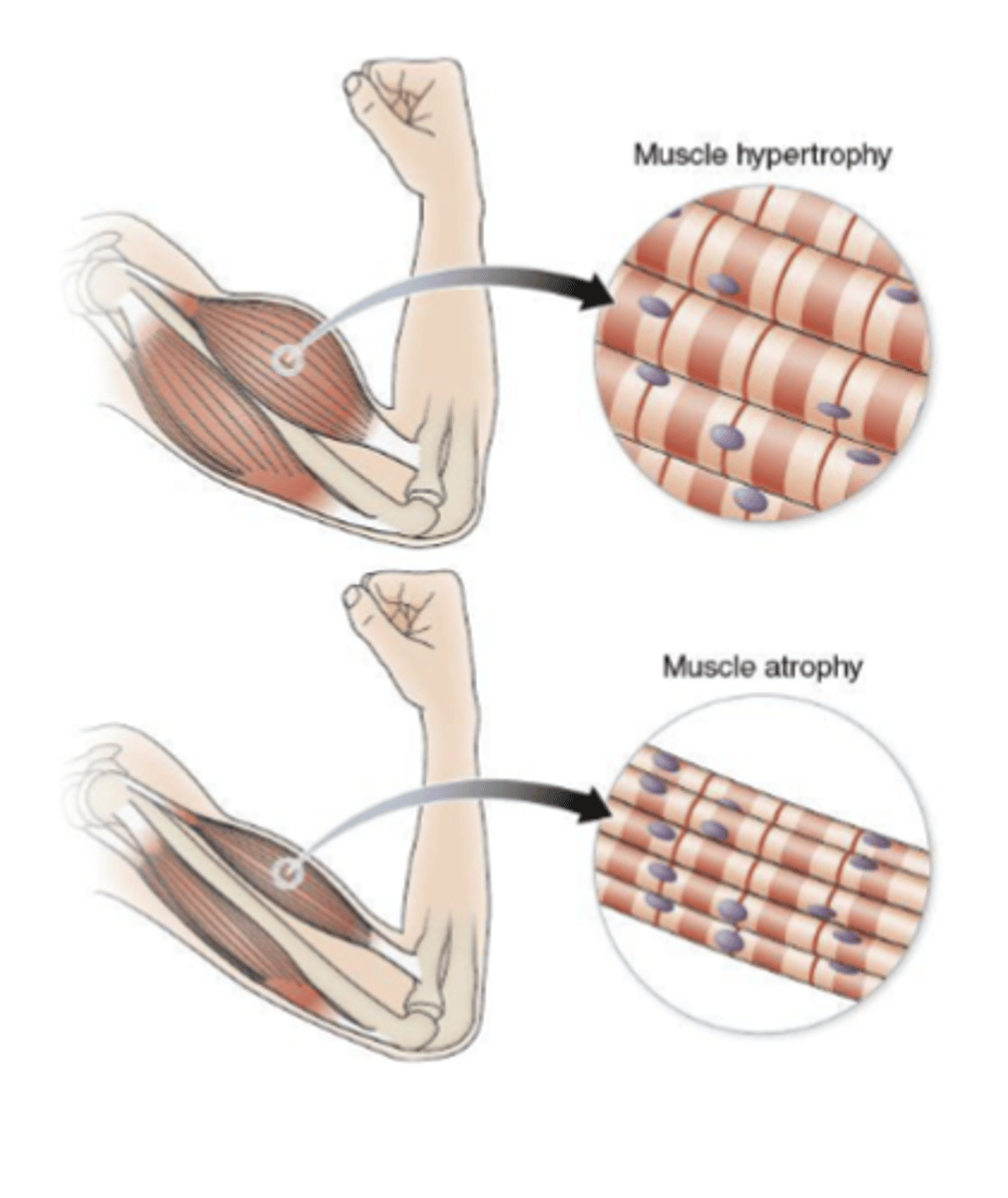
Differentiate hypertrophy and atrophy
-hypertrophy: structural proteins are added to muscle fibers; diameter increase (more myofibrils)
-atrophy; structural proteins are lost; muscle mass decreases
Describe the effects of aerobic/endurance exercise on the muscle
-little force on muscles over multiple repetitions; utilizes oxidative fibers (SO and FO fibers)
-leads to increased # of mitochondria, myoglobin synthesis (carries O2), muscle capillaries/angiogenesis (resists fatigue), conversion of FG to FO (less muscle mass)

Describe the effects of anaerobic/resistance exercise on muscle
-high force on muscles over short period; utilizes high # of fast glycolytic fibers (FG cells)
-leads to increased # of myofibrils (hypertrophy), CT (perimysium, epimysium, endomysium), force production, and conversion of FO to FG

Describe different PED/PES
-anabolic steriods: testosterone -> stimulates muscle formation -> increased mass
-erythropoietin (EPO): hormone (produced in kidney) producing RBC -> more O2 to muscles -> more aerobic respiration/less fatigue
-human growth hormone (hGH): promotes tissue/muscle recovery
-creatine: production of more ATP from the creatine phosphate system and allow more explosive power output
Describe side effects of PED/PES
-anabolic steriods: agression, cardiovascular disease
-erythropoietin (EPO): blood viscous, high BP
-human growth hormone (hGH): unpredictable side effects due to physiological strain
-creatine: NA
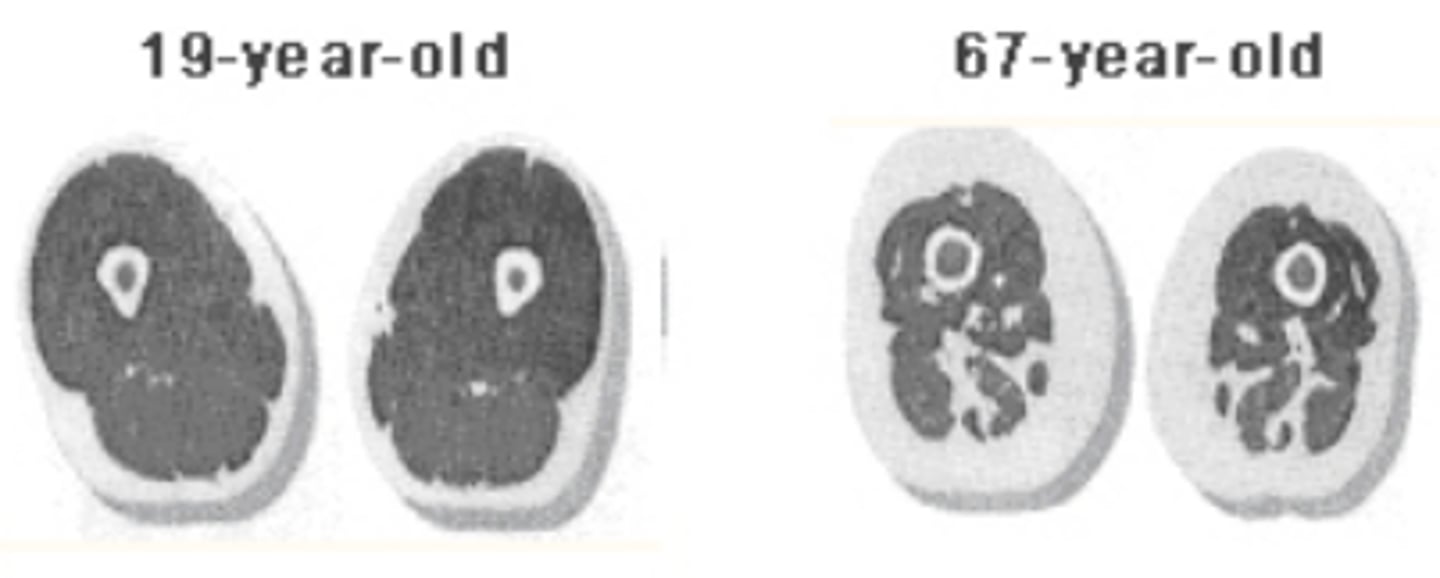
Describe what sarcopenia is
-irreversible muscle atrophy with age (starts around 30-40); why athletic performance decreases
-muscle fibers die and get replaced w/ non-contractile connective tissue (less crossbrdige formations)
-sarcopenia delayed w/ exercise