vascular plants lab 6
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
characteristics of phylum coniferophyta
branching, woody plants and most genera have long shoots and short shoots
The secondary wood (xylem) is made up of tracheids, rays and resin canals.
The leaves are spirally arranged or opposite (rarely whorled), and needle-like or scale-like, (rarely broad)
The reproductive organs are unisexual cones
The female cones (megastrobili) usually consist of a main axis with bract scales, each subtending or fused with an ovuliferous scale bearing 2 ovules
Pinus taxonomy
Phylum: Coniferophyta
Class: Coniferopsida
Order: Coniferales
Family: Pinaceae
Genus: Pinus
2 kinds of pine leaves
photosynthetic needles
non-photosynthetic scale leaves
short shoots
short lateral branches that have needles
long shoots
twigs and branches that have many short shoots
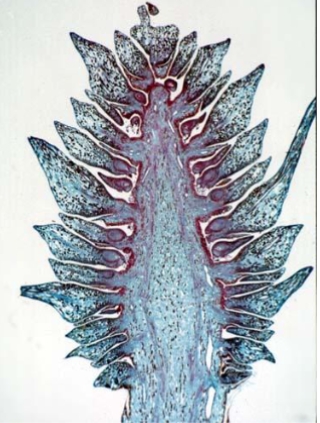
xerophytic traits of pine needles
thick cuticle
sunken stomata
hypodermis
super compact mesophyll tissue
resin canals
found in pine needles and pine stems
lined with cells that make terpenoids (pine sap)
sap acts as anti-herbivory and anti-fungal compounds
transfusion tissue
a specialized tissue in conifer leaves that surrounds the
vascular bundlesfacilitates the radial transport of water and sugars between the
xylem and phloem.
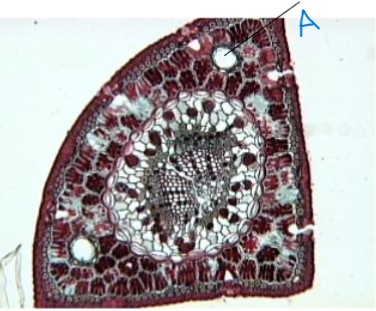
identify the genus
identify the part of the plant
identify a
pinus
leaf
resin canal
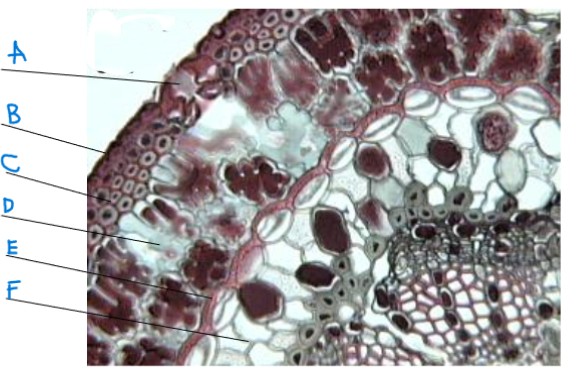
identify the genus'
identify the part of the plant
identify a-f
pinus
leaf
a. sunken stomata
b. epidermis
c. hypodermis
d. mesophyll
e. endodermis
f. transfusion tissue
growth rings
Well-marked concentric zones of secondary xylem
Their width indicates the favorability of the climate during each growing
seasonIn unusually cold or dry years, the rings may be narrow or even
absent, whereas they will be wide in those years which have favourable
weather.
false rings
the production of two growth rings in one year
because a growing season is interrupted by a period of stress e.g.
frost, insect attack, drought, fire or sapsucker damage then growth resumes
after the stress has ended.
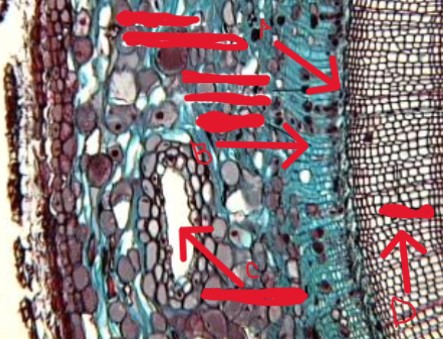
identify the genus
identify the part of the plant
identify a-d
pinus
stem
a. vascular cambium
b. phloem
c. resin canal
d. xylem
characteristics of pinus stems
composed mostly of elongate tracheids
narrow medullary rays (of parenchyma cells) extend radially through the xylem
vascular cambium function
The cambium adds many new cells that mature into secondary
xylem internally and into secondary phloem externally
cork cambium
aka phellogen
is a lateral meristematic tissue responsible for the production of the outer bark, which is a thick protective layer.
forms during secondary growth, replacing the epidermis
producing the periderm on the outside and phelloderm on the inside
periderm
a layer composed of cork cells (phellem) which are dead cells that provide
waterproofing and protection against pathogens and water loss
phelloderm
an extra layer of living cells that are still part of the periderm
medullary rays
radial sheets of parenchyma cells that are in both stems and roots
These rays run vertically and perpendicular to the growth rings, connecting the center to the outer bark
Their main functions are to conduct water and minerals radially (lateral transport) and to store carbohydrates
characteristics of pinus roots
protostelic taproot
vascular core surrounded by a narrow pericycle, a prominent endodermis and cortex, and an epidermis with root hairs
root hair zone limited
undergo secondary growth and become woody

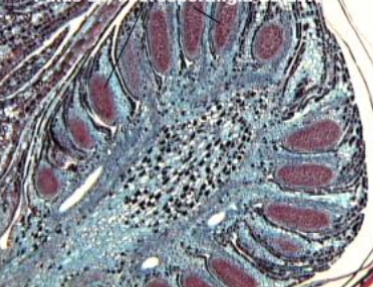
identify the genus
identify the part of the plant
identify a-f
pinus
root
a. periderm
b. cortex
c. phloem
d. xylem
e. resin canal
f. medullary rays
3 cell types in a pollen grain
generative cell
tube cell
prothallial cells
generative cells
produce sperm cells by mitosis
tube cells
grows through the megasporangial wall to make a pathway for the sperm cells to get to the egg
prothallial cells
don’t do anything (they’re vestigial leftovers from
evolution when the microgametophyte was free living)
identify genus
identify part of plant
what are the lines pointing at
pinus
pollen cone
microsporangia
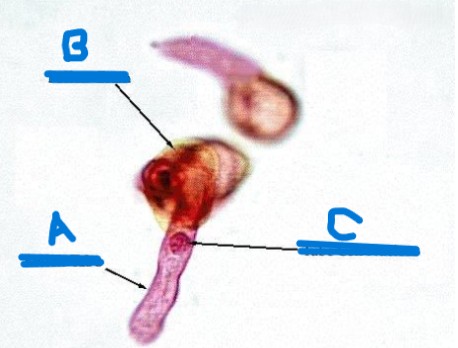
identify a-c
a. pollen tube
b. pollen grain
c. tube cell nucleus
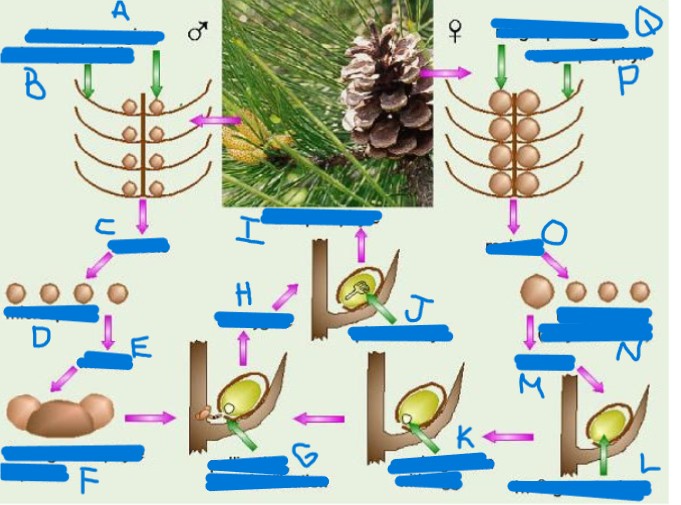
identify a-q
a. microsporangium
b. microsporophyll
c. meiosis
d. microspores
e. mitosis
f. haploid male gametophyte (pollen)
g. pollination then fertilization
h. diploid zygote
i. diploid sporophyte
j. pine embryo
k. archegonium with egg
l. haploid female gametophyte
m. mitosis
n. megaspores (only 1 lives)
o. meiosis
p. megasporophyll
q. megasporangium
identify the genus
identify the part of the plant
pinus
female cone (megastrobilus)
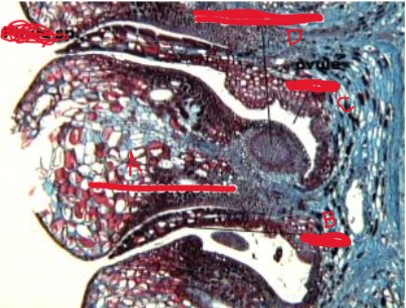
identify a-d
a. ovuliferous scale
b. bract
c. ovule
d. megasporangia
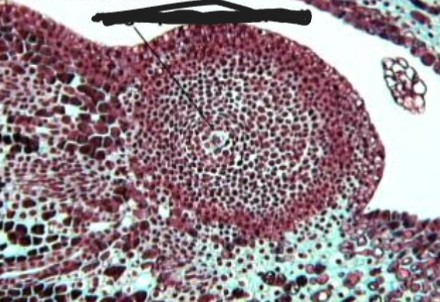
identify the structure
megaspore mother cell
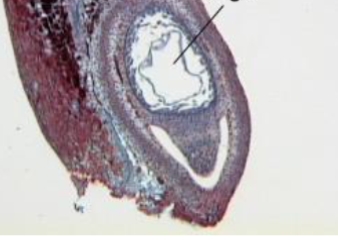
identify stage of female gametophyte development
free nuclear stage
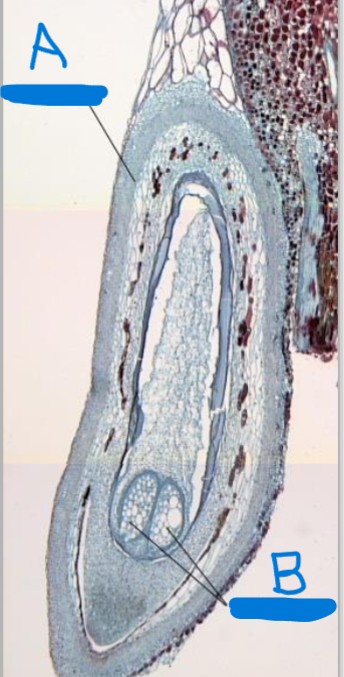
identify life stage and a-b
mature female gametophyte
a. integuments b. arcgegonia
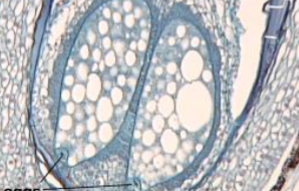
what is the line pointing at
egg cell
suspensor cells
fed embryo nutrients and plant hormones
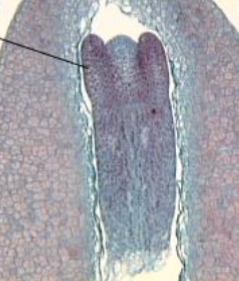
what is the line pointing at
embryo
juniper taxonomy
Phylum: Coniferophyta
Class: Coniferopsida
Order: Coniferales
Family: Cupressaceae
Genus: Juniperus
white cedar taxonomy
Phylum: Coniferophyta
Class: Coniferopsida
Order: Coniferales
Family: Cupressaceae
Genus: Thuja
Characteristics of Juniper
fragrant reddish tinted wood
dioecious (few monoecious)
megastrobili are fleshy and resemble berries (used to make Gin)
White cedar characteristics
fragrant fine-grained wood
rot resistant
yew taxonomy
Phylum: Coniferophyta
Class: Taxoposida
Order: Taxales
Family: Taxaceae
Genus: Taxus
yew characteristics
dioecious
ovules occur singly at the apices of short branches, enclosed in a fleshy aril
megastrobili resemble red berries with opening to display poisonous seed
Ephedra taxonomy
Phylum: Gnetophyta
Order: Ephedrales
Genus: Ephedra
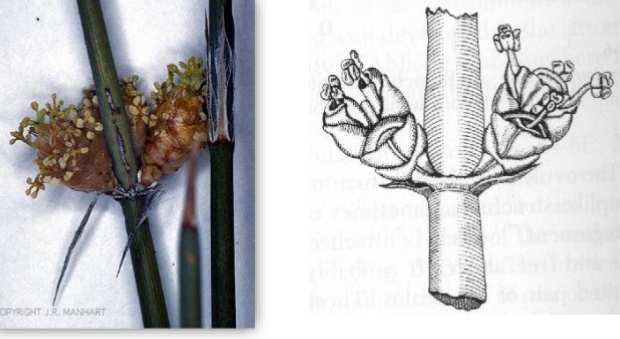
identify the structure
ephedra microsporangia
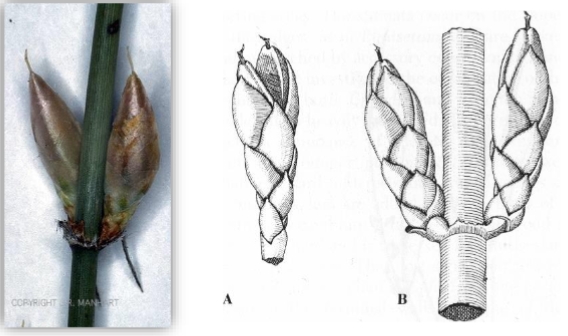
identify the structure
ephedra megasporangium
three orders in Gnetophyta
ephedrales
gnetales
welwichiales

identify the species
ephedra