SLHS 2156Q final exam
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
what is frequency and what variable is it represented by?
the number of cycles per second in hertz (f)
what is period and what variable is it represented by?
the time it takes to complete one cycle in milliseconds (T)
how do you calculate frequency from period?
1/T
how do you calculate period from frequency?
1/f
what is the conversion between hertz and kilohertz?
to get from hertz to kilohertz, divide by 1000
what is the relationship between amplitude and frequency?
they are independent of one another
what is elasticity?
tendency of volume of air to return to its former volume after it has been compressed
what is amplitude?
the maximum displacement of particles from a vibration
how is sound made?
a force sets a source into vibration
the vibration is sustained by the interaction of inertia and elasticity
the vibration of the source sets the molecules of the medium into vibration
the motion creates alternating compressions and rarefractions in the medium
the density changes propagate through the medium
what is one cycle of vibration?
equilibrium → maximum displacement → equilibrium → maximum displacement → equilibrium
what is simple harmonic motion?
characterized as projected uniform circular motion
sinusoidal motion
the quantity varies over time in a way that can be mathematically described by a sine wave
in the projection of uniform circular motion, what is equivalent to one cycle?
rotation through 360 degrees
how is sine found?
opposite over hypotenuse (OH)
what does the sine of the angle correspond to?
percentage of maximum displacement (ex. if sin of the angle =.707, the percentage is 70.7)
what are the five dimensions of the sine wave?
frequency, period, amplitude, phase, wavelength
what is the rms?
root mean square amplitude. meant to capture level of steady sounds; A * 0.707
what is in phase?
two waveforms have the same frequency and same phase
what is out of phase?
two waveforms have the same frequency but different phase
what is wavelength?
the physical distance traveled by the wave during one period
what does wavelength depend on?
frequency of vibration of the source and speed of sound in the medium
what is the formula for wavelength?
wavelength= speed of sound/frequency
what is a nominal scale of measurement?
categorical with no hierarchy among values
what is an ordinal scale of measurement?
hierarchical
what is an interval scale of measurement?
units of equal size (temperature and clock time)
what is a ratio scale of measurement?
successive units are constant ratios of one another. have a base (multiplied by this base)
what type of scale of measurement is the decibel scale?
ratio scale with a base of 10
what occurs when a number is raised to the 0th power?
it equals one
what occurs when a number is raised to the 1st power?
it equals itself
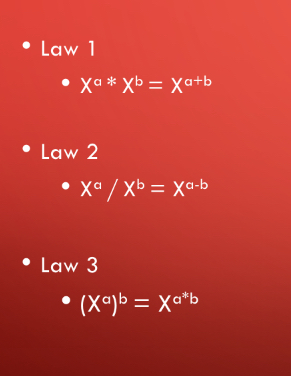
what are the laws of exponents?
conceptually, what is signal and what is noise?
signal is the sound of interest while noise is the sounds of the environment. any sound can be the signal and any sound can be the noise
what is a complex wave?
any wave that is not sinusoidal. complex waves can have repeating patterns.
what is the difference between a periodic and aperiodic wave?
a periodic wave repeats itself over regular intervals while an aperiodic wave does not repeat itself regularly over time. periodic waves can be sinusoidal or complex, while aperiodic waves can only be complex
what do periodic sounds sound like versus aperiodic sounds?
periodic sounds are tonal while aperiodic sounds are either noise like (continuous) or abrupt (transient)
what is fourier’s theorem?
every complex periodic wave is a sum of simple sine waves
how does fundamental frequency/harmonics relate to fourier’s theorem?
fourier’s theorem thinks of a complex periodic wave as a sum of sine waves. a sine wave component of a complex periodic wave will have a frequency that is a whole number multiple of the fundamental frequency.
what are harmonics?
multiples of the fundamental frequency. there does not need to be every harmonic in the series for it to be periodic, just a clear pattern
how would you solve for the period of a complex periodic wave?
the amount of seconds over the amount of cycles (usually it’s over one in a sinusoid cause we know its one frequency, but there will be multiple frequencies so we put the amount of cycles)
what is the difference between a waveform and a spectrum?
a waveform displays vibration in the time domain (amplitude by time), while a spectrum displays vibration in the frequency domain (amplitude by frequency)
what is the shape of a complex waveform dependent on?
the frequency, amplitude, and starting phases of the components
what is an octave?
halving or doubling frequency
where does a sine wave have energy?
at all frequencies
where does a triangle wave have energies?
at odd multiples with a slope of -12 dB/octave
what is a filter?
a frequency selective system. examples include hearing aids, vocal tract, and the outer, middle, and inner ears
what is preamble?
a buzzing sound with a smooth line spectrum that is used as the basis to be altered with resonance/filtering to produce vowels
what occurs when preamble is altered?
no sharp prominences to then an obvious spectral prominence
a periodic force is to an elastic system as…
a tuning fork is to a hard surface
what occurs when the frequency of the applied force is closer to the natural frequency of the elastic system?
the amplitude of the vibration is greater
what does 0 dB mean?
the level of harmonics with greatest amplitude?
at output of systems…
amplitudes vary with frequency
where does the greatest amplitude occur in an elastic system?
fnat
how is the resonance curve achieved?
if amplitude was constant
how is the bandwidth calculated?
upper cutoff - lower cutoff
what happens if you stimulate (drive) a system at many frequencies?
frequencies close to the natural frequency will resonate while those that are very different will dampen
what do even versus odd harmonics sound like?
even harmonics are rich and full. odd harmonics are brighter and hallow.
what are formants?
resonances of the vocal tract
what are the limits of human hearing in reference to the physical stimulus?
the range of hearing in frequency and intensity
what is the approximate frequency range of human hearing?
20-20,000 Hz
what is the approximate dynamic range of human hearing?
~130 dB
what is the absolute threshold?
the minimum detectable level of sound in the absence of any other external sounds
what is being tested when testing for an absolute threshold?
you use certain frequencies to test what db SPL a person’s absolute threshold is for that frequency. the absolute threshold will depend on the frequency
what is the sensitivity of human hearing?
1-6 kHz
what is the method of limits?
experimenter controls the stimulus and the subject responds
what is the method of adjustment?
subject adjusts the stimulus level they are hearing until it is barely audible
what is the method of constant stimuli?
experimenter chooses set of stimuli over range of levels with a chosen increment size and presents them in random order
what is adaptive procedures?
experimenter adjusts level of stimulus present depending on how subject responds to previous stimulus
what is the hughson westlake procedure?
staircase method. down 10 up 5.
how do you calculate the JND (△S)?
constant fraction original stimulus magnitude (△S = constant fraction * S)
how do you convert from db SPL to db HL?
find the RETSPL for that frequency then do what you have minus the reference (current threshold in SPL minus the reference)
how do you convert from db HL to db SPL?
find the RETSPL for that frequency then do what you have plus the reference (current threshold in HL + RETSPL)
what does an audiogram plot?
absolute hearing thresholds. better thresholds are at the top of the graph
what is a “stop”?
air fully stops then it is released.
what is nasal?
the mouth is closed and air flows through the nose
what is fricative?
air flows through a narrow space. involves the creation of turbulent airflow.
what is an approximant?
a looser kind of consonant. closest consonant to a vowel since air flows pretty freely and there’s no stops
what is a affricate?
a stop then fricative
what is a VOT?
voice onset time. time from releasing burst of consonant to onset of vocal folds vibration for the vowel
what is the VOT for voiceless stops?
25 to 100 ms
what is the VOT for voiced stops?
-20 to 20 ms
what letters are voiced?
b, d, g
what letters are voiceless?
p, t, k
what are the acoustic (physical) properties of sound?
frequency
amplitude
phase
duration
what are the perceptual properties of sound?
pitch
loudness
duration
timbre
in the source filter theory, what is the source and what is the filter?
the vocal folds are the source and the vocal tract is the filter
what are examples of sources according to the source filter theory?
fundamental frequency
harmonics (2F/H2)
F0
vocal folds
pitch of the voice
what are examples of filters according to the source filter theory?
formants
oral cavity
F1
resonances
vocal tract
which parameters can be altered with the source alone?
fundamental frequency (pitch) and amplitude (loudness
what is one change the sound filter can elicit acoustically (physically)?
the sound filter can raise or lower formant frequencies
what is one change the sound filter can elicit perceptually?
the sound filter can change which vowel is perceived. it can also change timbre
what does the x axis of a waveform and spectrogram represent?
time
what does the y axis of a waveform represent?
amplitude
what does the y axis of a spectrogram represent?
frequency
what do the acoustic & articulatory features of a speech sound vary depending on?
the adjacent phonemes
what is voicing?
whether or not the vocal folds are vibrating
what are suprasegmentals?
contribute to the intelligibility of speech
what is bilabial?
using both lips (example is p)
what is alveolar?
tongue behind teeth (example is t)
what is velar?
back of tongue (example is k)
what is the dynamic range?
pain threshold minus absolute threshold
what occurs to the dynamic range when hearing loss is conductive?
the value of the dynamic range is the same but where the range is shifts upwards