Chemical Reactions and Equations
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
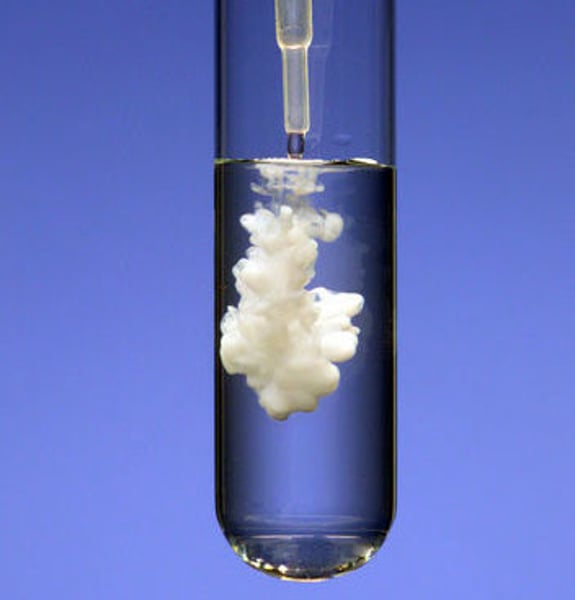
precipitate
insoluble ionic compound

aq
dissolves well, soluble
s
precipitate
spectator ions
don't react in the equation/change, not written in net ionic form
electrolytes
a compound that dissolves in water to give aqueous ions, will conduct electricity
strong electrolytes
completely give ions in water, nothing left of original compound, ex., ionic compounds
strong acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO3, HClO4, dissociate in water
strong bases
group I and II hydroxide compounds
weak electrolytes
dissociate to some extent, but mostly ions stay together, all besides "strong"
solubility
A measure of how much solute can dissolve in a given solvent at a given temperature.
soluble compounds
anything w alkali metal ions or HN4+, nitrates, bicarbonates, chlorates, halides except of Ag+, Hg2+, and Pb2+, sulfates except of Ag+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, alkali metals w Ba2+
insoluble compounds
carbonates, phosphates, chromates, sulfides except when w alkali metals or ammonium, hydroxides
acid base reactions
acid+base---water and salt of most strong acids and bases
aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
solubility
The ability to dissolve in another substance
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
electric conductivity
the measure of the amount of electrical current a material can carry, happens when solute dissociates in solution
acid
Any compound that increases the number of hydronium ions when dissolved in water
molarity
the number of moles of solute in one liter of solution, concentration
stock solution
a solution whose concentration is accurately known
dilution
the procedure for preparing a less concentrated solution from a more concentrated solution
precipitation reaction
a reaction in which a solid, insoluble substance forms and separates from the solution
molecular equation
lists the reactants and products in their molecular form
complete ionic equation
an equation that shows dissolved ionic compounds as dissociated free ions (aq) and may include ppt as (s).
spectator ions
Ions that are not involved in the overall reaction
neutralization reactions
acids and bases neutralize each other to form salt and often water
redox reaction
an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction
oxidation state
The hypothetical charge on an atom assuming that the bonding is completely ionic
oxidation
loss of electrons (OIL)
reduction
gain of electrons (RIG)
oxidizing agent
the chemical that caused something to get oxidized, reactant containing the element that is reduced
reducing agent
the reactant that contains the element that gets oxidized
half-reaction
the two parts of a redox reaction, each representing either reduction or oxidation