Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Lecture 2 Exam Study Guide
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Connective Tissue
Tissue type composed largely of nonliving extracellular matrix; important in protection and support
Muscle Tissue
Composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts
Nervous Tissue
Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities. Stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning.
Epithelium Tissue
A thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body,, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs
An epithelium that has several layers, with an apical layer of flattened cells, is called
Stratified and Squamous
The gland type that secretes products such as milk, saliva, bile, or sweat through a duct is
An exocrine gland
Scar tissue is a variety of
Connective Tissue
The primary cell type in connective tissue proper
Fibroblast
The primary cell type in cartilage
Chondroblast
The primary cell type in bone
Osteoblast
The two major components of the extracellular matrix
Ground Substance (subclass: interstitial fluid, proteoglycans, and glycosaminoglycans) and Fibers (subclass: collagen, elastic, reticular)
Forming the soft packing around organs
Areolar
Supporting the ear pinna
Elastic Cartilage
Forming "stretchy" ligaments
Elastic Connective Tissue
Forming the intervertebral discs
Fibrocartilage
Covering the ends of bones at joint surfaces
Hyaline Cartilage
Main component of subcutaneous tissue
Areolar Connective Tissue
The mode of secretion of exocrine glands?
Merocrine Glands are not altered by the secretory process
The first step in tissue repair involves ________.
inflammation
What tissue has lacunae, calcium salts, and blood vessels?
Bone (osseous tissue)
The most importance to goblet cells and other glandular epithelia
Golgi apparatus
Modification of the simple columnar epithelium that allows for efficient absorption along portions of the digestive tract
Dense Microvilli
Three characteristic components of Connective Tissue
Cells, large amounts of amorphous ground substance, and protein fibers
Four characteristic components of Muscle Tissue
Excitability, contractibility, extensibility, and elasticity
Characteristics of the Nervous Tissue
Comprises of neurons and neuroglia. Neurons are specialized cells that help in the communication of signals and stimuli. Neuroglia helps the neuronal functions, protection of neurons, and neuronal nourishment. Is present in the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system
Characteristics of the Epithelium Tissue
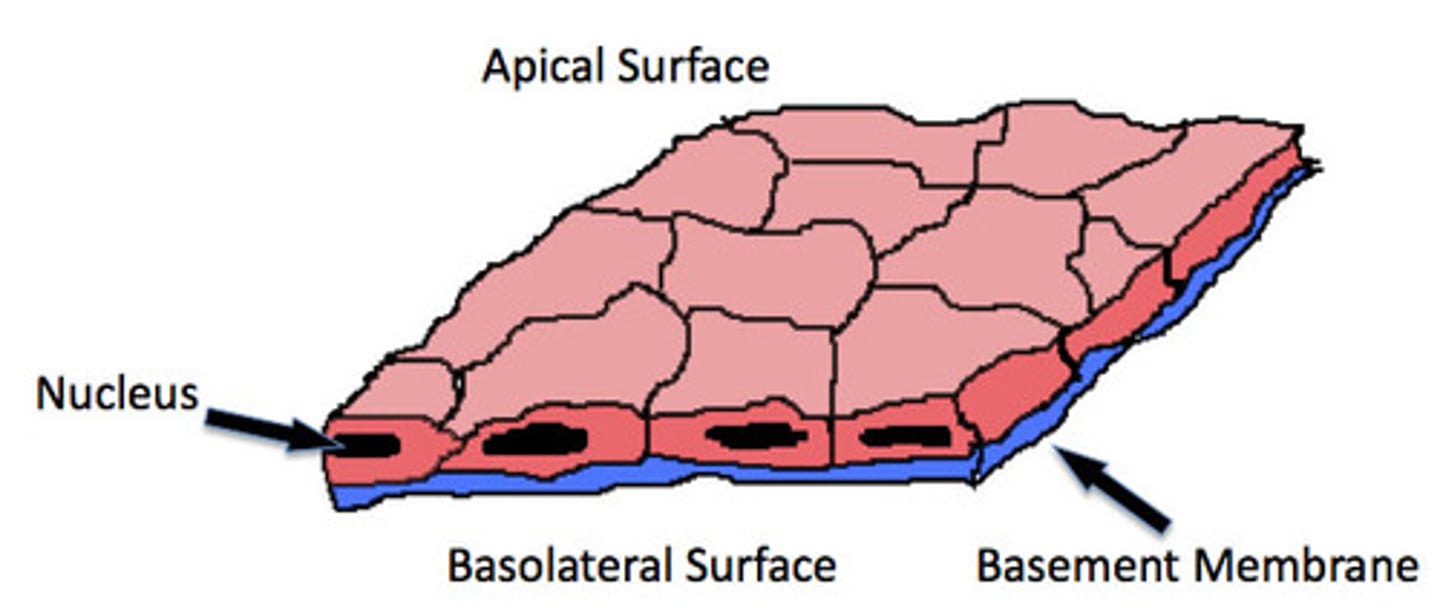
Has only one cell layer where every cell is in direct contact with the underlying basement membrane. Polarized distribution of organelles and membrane-bound proteins between their basal and apical surfaces
What happens to Proteins following ingestion
Hydrochloric acid and enzymes called proteases break down into smaller chains of amino acids
What happens to Fats following ingestion
Fatty acids are passed through the lymph system and then throughout the body via your blood stream to be used or stored for energy, cell repair, and growth. The lymph system also absorbs fatty acids to help fight infection
What happens to Carbohydrates following ingestion
Digestion begins in the mouth, where salivary amylase starts the breakdown, then after breaking down throughout the digestive system, monosaccharides are absorbed into the blood stream. The blood sugar levels increase, stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin
What are the characteristics of Proteins
Glass transition temperature, melting point, isoelectric point, molecular weight, secondary structure, solubility, surface hydrophobicity, and emulsification
What foods are in the Protein Group
Meat, poultry, seafood, beans, peas, eggs, soy products, nuts, and seeds
What are the characteristics of Saturated Fats
Solid at room temperature, do not spoil very quickly, and have high melting points
What foods are in the Saturated Fats Group
Butter, cakes, biscuits, fatty cuts of meats, cheese, bacon
What are the characteristics of Unsaturated Fats
Are liquid at room temperature, spoil relatively quickly, and have low melting points
What foods are in the Unsaturated Fats Group
Avocados, olives, peanut butter, fatty fish, nuts, seeds
What are the characteristics of Carbohydrates
contain only the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and their combustion will yield carbon dioxide plus one or more molecules of water
What foods are in the Carbohydrates Group
Bread, beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, soft drinks, corn
The three states of the body in regard to food are
absorptive (fed), post absorptive (fasting), and starvation
What hormones are prominent in the Absorptive State
Insulin
What hormones are prominent in the Post absorptive State
Glucagon
What hormones are prominent in the Starvation State
Ghrelin
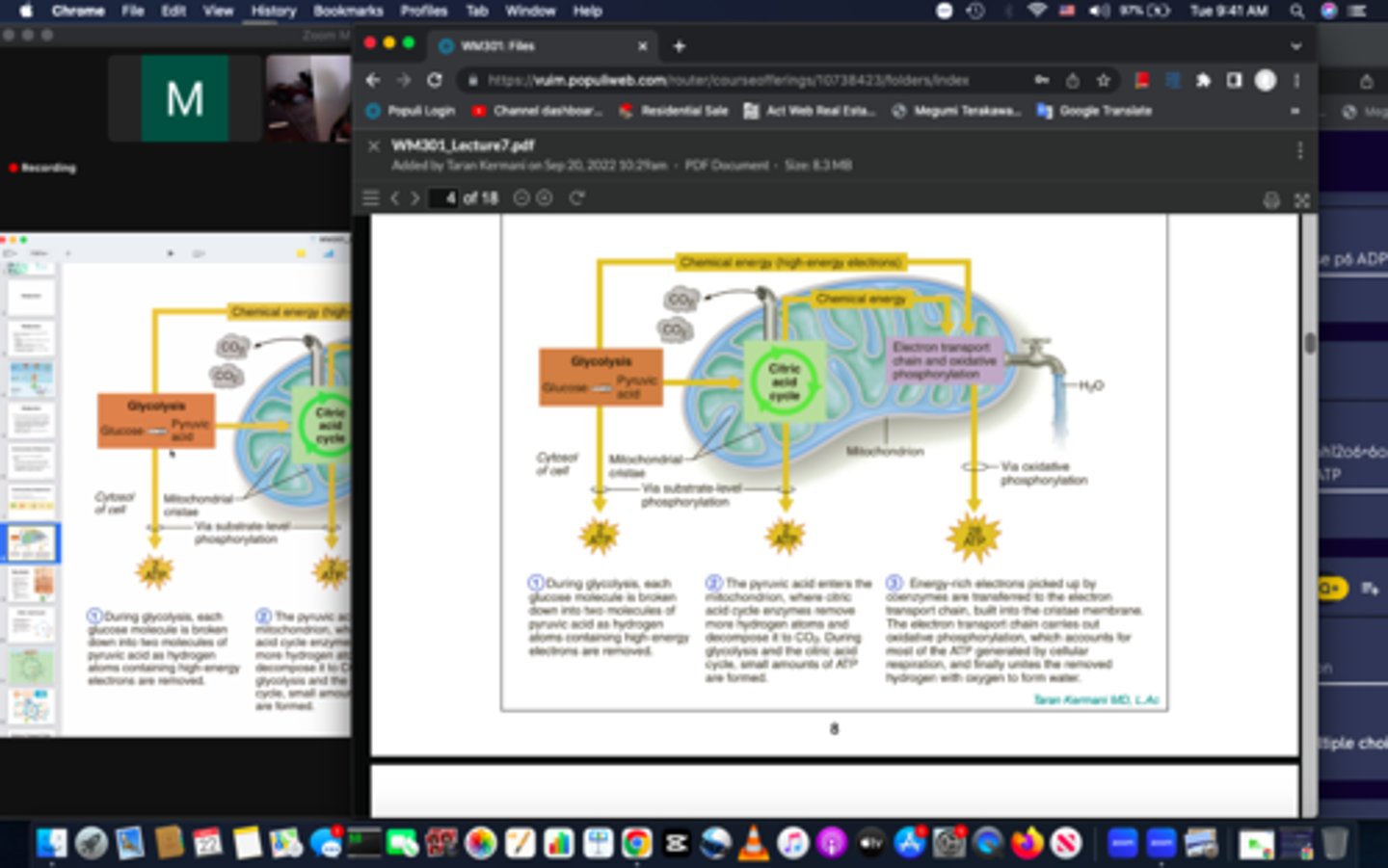
Cellular Respiration
The process in which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds, 38 ATP Molecules, takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA cycle occurs inside the matrix of the mitochondria
Oxidative Respiration
This the fourth step of cellular respiration and produces most of the energy in cellular respiration. There are 30-32 ATP molecules that are generated from the electron transport chain. Glucose oxidizes and releases energy in the human body. This occurs in the mitochondria. It is linked to the processes of the electron transport chain
Describe the effects of Leptin
Decreases body mass and food intake and suppresses hunger. It controls body fat by decreasing triglycerides and decreasing total fat mass as it increases HDL
Describe the effects of Insulin
Causes sugar (glucose) to go from the blood into our body's cells to make fat, sugar, and protein after we eat. In the liver, it helps promote the transport of glucose from the blood into hepatocytes, where it is further converted to glycogen, fatty acids, and triglycerides. In the skeletal muscles, it facilitates the uptake of glucose and amino acids from the bloodstream
What is Glycolysis
A process in which glucose (sugar) is partially broken down by cells in enzyme reactions that do not need oxygen. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH, and water. It takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen; occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms
What is Anabolism
The building of complex molecules from numerous simple ones.
What is Catabolism
The breakdown of complex molecules into numerous simple ones
What are the USDA My Plate guidelines for all groups
Green is for veggies, red for fruits, orange for grains, purple for protein, and blue for dairy. Vegetables 2.5 to 3 cups, Fruits 1.5 to 2 cups, Whole grains about a half a cup, Poultry, fish or meant 5 to 6 ounces, Dairy such as milk or yogurt three cups, Healthy oils 1 to 2 tablespoons
Exocrine Glands
Secrete their substances through ducts onto your body's surfaces
Endocrine Glands
Secrete their substances directly into your bloodstream, called ductless glands, and are part of the endocrine system and secrete hormones
What is Lipolysis and where is it located
Occurs in all tissues and cell types, it is most abundant in white and brown adipose tissue. It is the process of breaking down lipids. Is used to mobilize the stored energy for use by cells
What is Lipogenesis and where is it located
Encompasses the processes of fatty acid synthesis and subsequent triglyceride synthesis, and takes place in both liver and adipose tissue
What is Ketogenesis and where is it located
Occurs primarily in the mitochondria of liver cells. The formation of ketone bodies is an alternative catabolic pathway for active acetates
What is Glycogenesis and where is it located
The process of glycogen synthesis, in which glucose molecules are added to chains of glycogen for storage. This process is activated during rest periods following the Cori cycle in the liver and is also activated by insulin in response to high glucose levels
What is Beta Oxidation and where is it located
It is the oxidation of fatty acids to form acetyl-CoA. Fatty acids will be broken down into acetyl-coA while producing NADH and FADH2 for each 2 carbons it has in the chain. Occurs in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, fatty acids are broken down in the cytosol. IN eukaryotes, it occurs in both mitochondria and peroxisomes
What is Gluconeogenesis and where is it located
Occurs in the liver and kidneys. Supplies the needs for plasma glucose between meals. Is stimulated by the diabetogenic hormones (glucagon, growth hormone, epinephrine, and cortisol)
What is Hyaline Cartilage and it's characteristics
A type of connective tissue, glossy pearl-gray or blue-whit in appearance and resilient, found on surfaces of joints and in the cartilage making up the fetal skeleton
What is Fibrocartilage and it's characteristics
Is a transition tissue that should be viewed as a blend between hyaline cartilage and dense fibrous connective tissue. It is white, densely arranged, opaque, tufted tissue with a mixture of both chondrocytes and fibroblasts. Is found in the meniscus of the knee, in the disk between the vertebrae in the spine. Supports muscles, tendons, and ligaments throughout the body
What is Elastic Cartilage and it's characteristics
Is the most flexible cartilage. Supports parts of your body that need to bend and move to function. Can bounce back its original shape, even after a strong force. It makes up the external ear, the auditory tube of the middle ear, and the epiglottis
Epithelial Simple Squamous
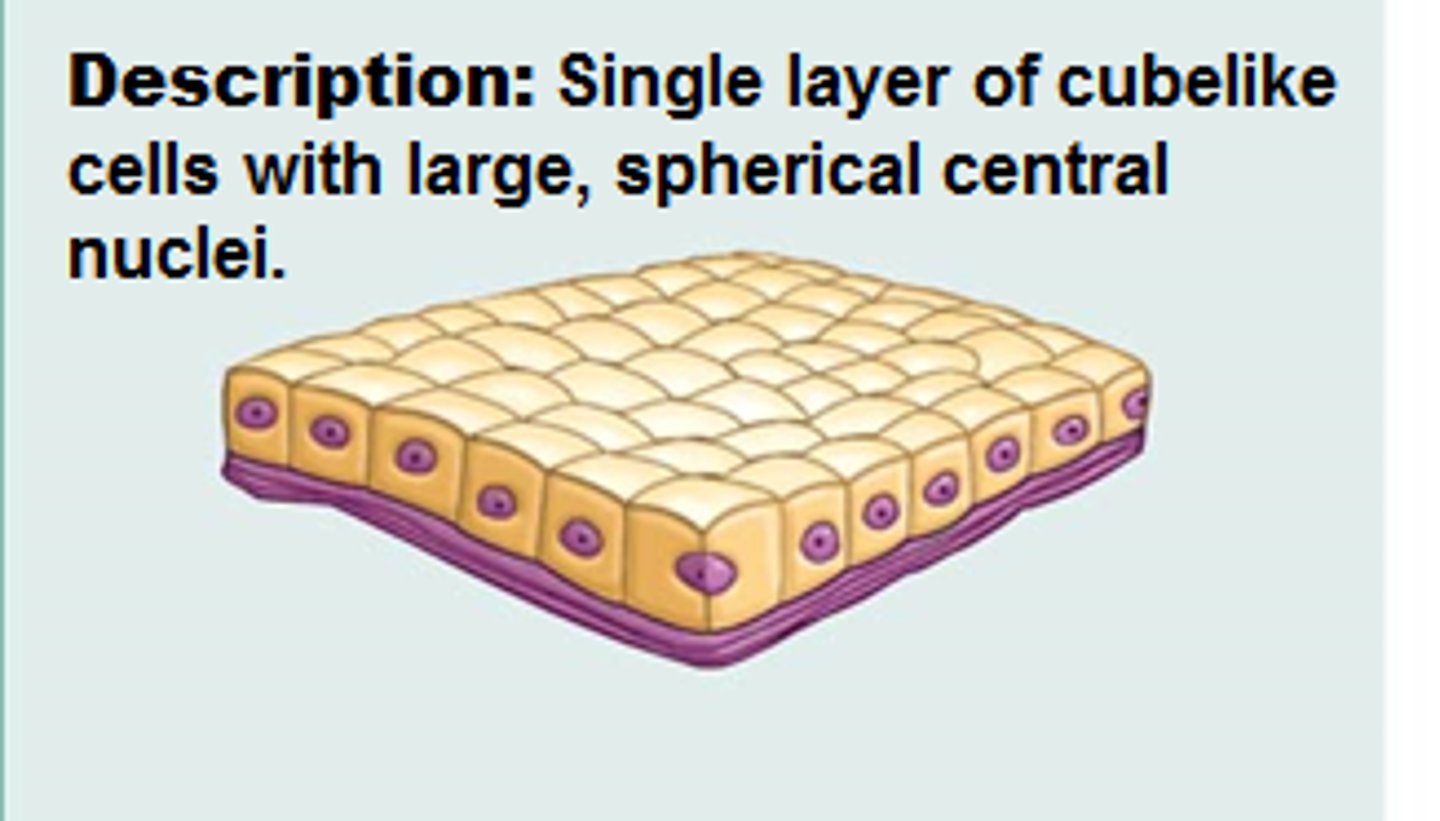
simple cuboidal epithelium
Cardiac
Transitional
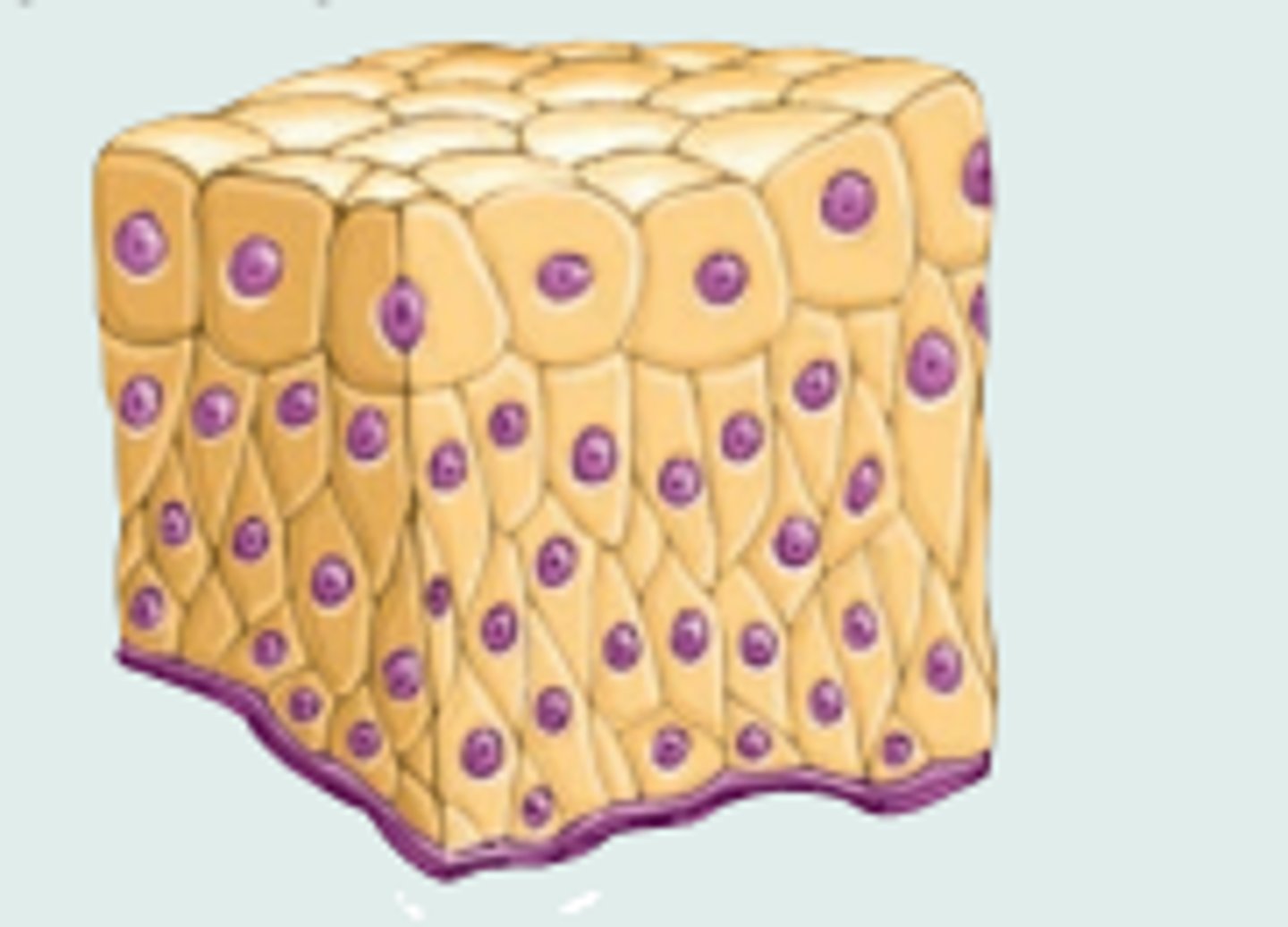
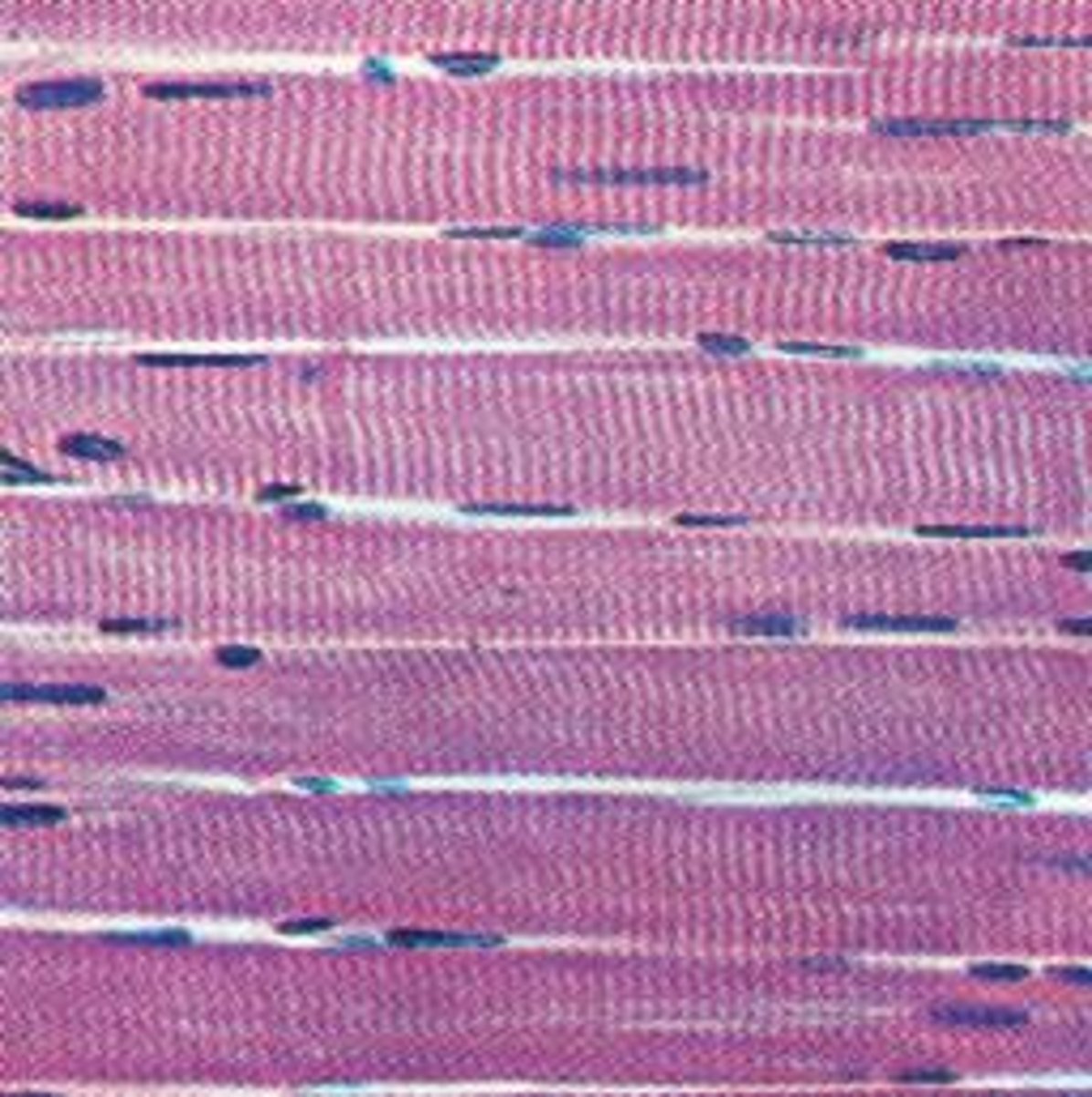
Skeletal
Chemical energy (high-energy electrons)