Thermal Energy PAP Chemistry
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Kinetic Energy at High Temperature
Vibrating fast or high energy
Kinetic Energy at Low Temperature
Vibrating slow or low energy
Sublimation
Solid to Gas
Change from Solid to Gas
A rapid increase in temperature or kinetic energy
Definition of Temperature
Average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance
Change from Gas to Liquid
Condensation
Negative Enthalpy
Exothermic
Change from Liquid to Solid
A decrease in temperature or kinetic energy
Effect of Increased Kinetic Energy in Solid
It might melt but they would definitely move faster
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
Deposition
Gas to Solid
Heat Transfer through Electromagnetic Waves
Radiation
Energy in Chemical Reaction
Heat of rxn
Reaction Absorbing Energy
Endothermic Rxn
Vaporization Process
Endothermic, temperature decreases because the particles need to gain energy to become a gas
Heat and Light from Octane Burning
From forming bonds, chemical potential energy is being released as the rxn occurs
Exothermic Mixing of Chemicals
Heat released into the environment, chemical particles slow, environment particles speed up
Convection
Hot fluid rising and cool fluid sinking due to density
Burning Hand on Hot Pot
Heat is conducted from the pot to your hand. The particles in your hand begin to move faster when the heat is transferred to them
Vaporization Process Name
Vaporization
Element without Boiling Point
None
Latent Heat
increased energy usually shows increase in temp
If ΔG negative, what is K
K>1
If ΔG positive, what is K
K<1
If ΔG negative, what is E
positive (battery galvanic)
if ΔG positive, what is E
negative (electrolyte)
if ΔG positive
nonfavorable, doesn’t happen, a reaction that does not happen to a measurable degree
if ΔG negative
favorable, does happen, a reaction that does happen to a measurable degree
ΔG is -, ΔH is -, ΔS is +
Driving force is both (all temps)
ΔG is +, ΔH is +, ΔS is -
Driving force is none (all temps)
ΔG is +/-, ΔH is -, ΔS is -
Driving force is ΔH
ΔG is +/-, ΔH is +, ΔS is +
Driving force is ΔS
conduction
direct contact, particle motion is transferred, particles vibrate really fast and transfers to the hand that touches pot.
specific heat (c)
amount of energy needed to increase temp of one gram of a substance by 1 C
Law of Conservation of Energy
energy can neither be created or destroyed, it can only be transformed from one form to another
Energy
The capacity of a system to do work or transfer heat
Kinetic energy
The energy form that can object or a particle has by reason of its motion
Example(s) of Kinetic energy
Movement of water molecules in a hot cup of coffee. Falling objects, moving cars, or flowing rivers.
Temperature
A measure of the average kinetic energy or molecules in the systems
Potential energy
The store energy within a system due to its position, structure, or the arrangement of its atoms and molecules.
Example(s) of Potential energy
A drawn bow, water stored in a dam, a rollercoaster at the top, or a compressed spring.
Chemical (potential) energy
The stored energy within the chemical bonds of a substance
Example(s) of Chemical (potential) energy
Batteries, food, gasoline, and explosives
Thermal energy
The energy contained within a system that is responsible for its temperature; high particle motion due to its heat
Heat
Transfer of thermal energy between two objects or systems at different temperatures
Example(s) of Heat
Heating water on a stove.
Specific Heat (c)
The amount of energy needed to increase the temperature of one gram of a substance by 1 degrees Celcius
Specific Heat (c)
A substance’s resistance to changes in temperature
Change in Temperature
Final temp minus initial temp
Specific heat of water (H2O)
4.18 J/g *C
Kilojoule
J x 1KJ/ 1000J = -2.88 KJ
q in MCat
heat
m in MCat
mass
c in MCat
specific heat capacity
ΔT in MCat
Change in temperature
Calorimeter
fa cg styrofoam cup- lets no heat in or out
Step 1 in Calorimetry
Start with H2O and find q (J/energy of H2O)
Step 2 in Calorimetry
Flip sign of the J/energy of H2O and solve for the specific heat of the metal
Characteristics of solids
Vibrate, “no spacing”- as compact as possible, low kinetic energy
Characteristics of liquids
flow, very small spacing, medium-low kinetic energy
Characteristics of gases
Constant random motion, very big spacing, HIGH kinetic energy
Condensation
Gas to liquid
Vaporization
Liquid to gas
Deposition
Gas to solid
Solidification
Liquid to solid
Liquification
Solid to liquid
Sublimation
Solid to gas
EntHalpy
the total energy content of a system
Exothermic enthalpy
Rxn where MORE energy is relation by new bonds forming than was consumed breaking the original bonds
Exothermic enthalpy ________ energy
releases
Endothermic enthalpy
Rxn where LESS energy is relation by new bonds forming than was consumed breaking the original bonds
Endothermic enthalpy ________ energy
Takes in
System
The object being observed
Surroundings
Everything else around the object
Universe
EVERYTHING (system and surroundings)
Heat of Rxn (ΔHrxn)
The energy lost or gained during a rxn
Heat of formation (ΔHf)
The energy lost or gained when 1 mol of a chemical is formed from its ground state (by itself with no charge) element
How to solve enthalpy
ΔH = H(products) - H(reactants)
Exothermic
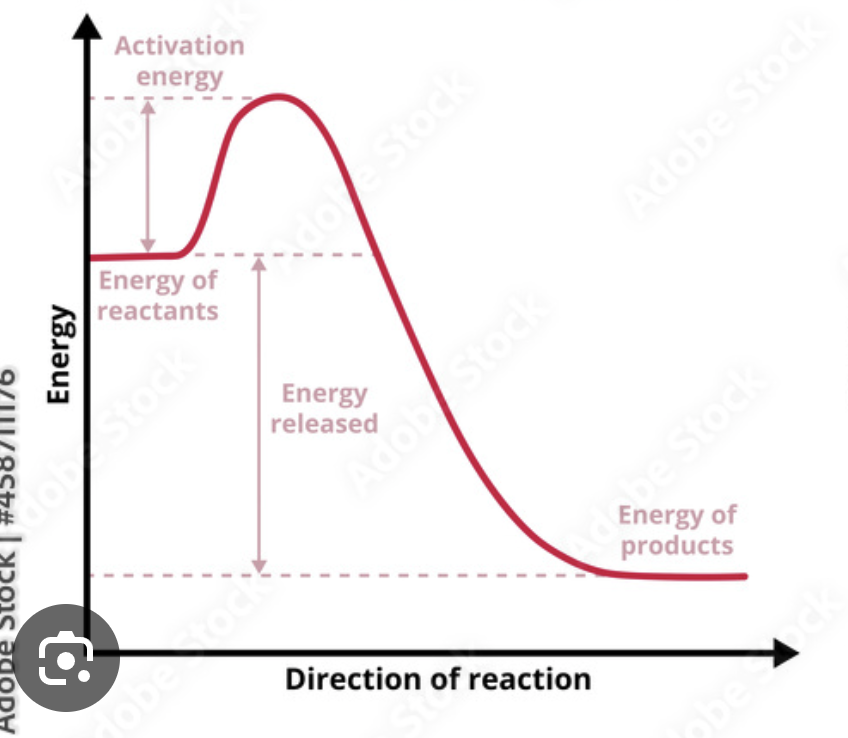
Endothermic
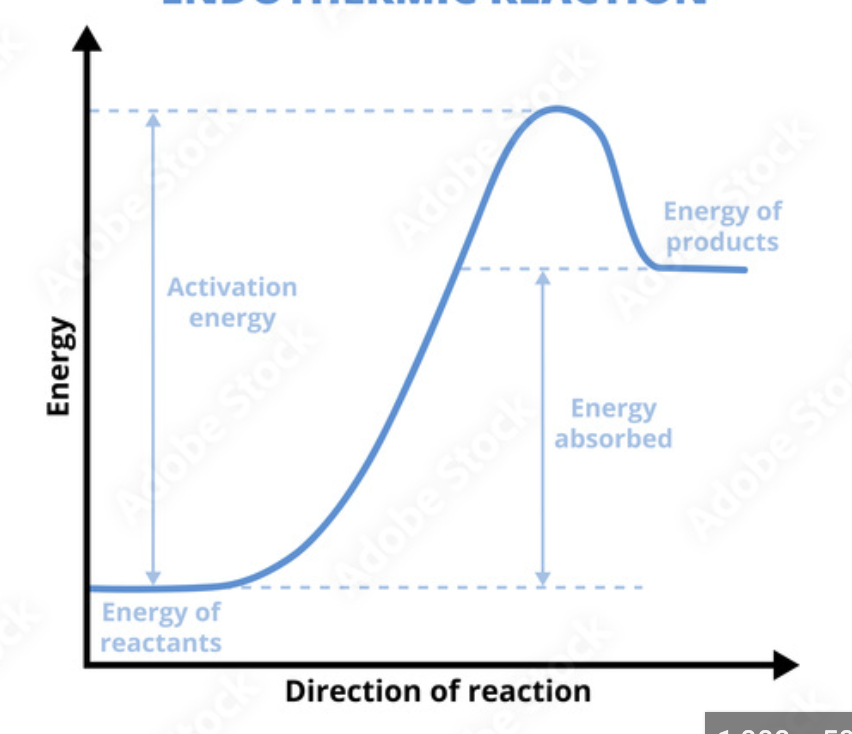
Convection
Heat transfer in fluids
Hot fluids ______ in convection
rise
Cold fluids ______ in convection
sink
Radiation
energy transfer through photons
Conduction
energy transfer through direct contact (fast vibrating particles)