Coasts and fieldwork
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
list the physical landscapes of the UK
Highland Britain
Moor
Mountain
Rugged
High rainfall
water logging
Lowland Britain
Rolling
flat
marsh
fen
water logging
In which area are igneous and metamorphic rocks found
higher places → e.g Scottish highland, lake district, snowdonia
what are waves
waves are formed by wind
Big waves are formed by:
1) strong wind
2) duration of wind
3) Fetch (distance in which wave traveled)
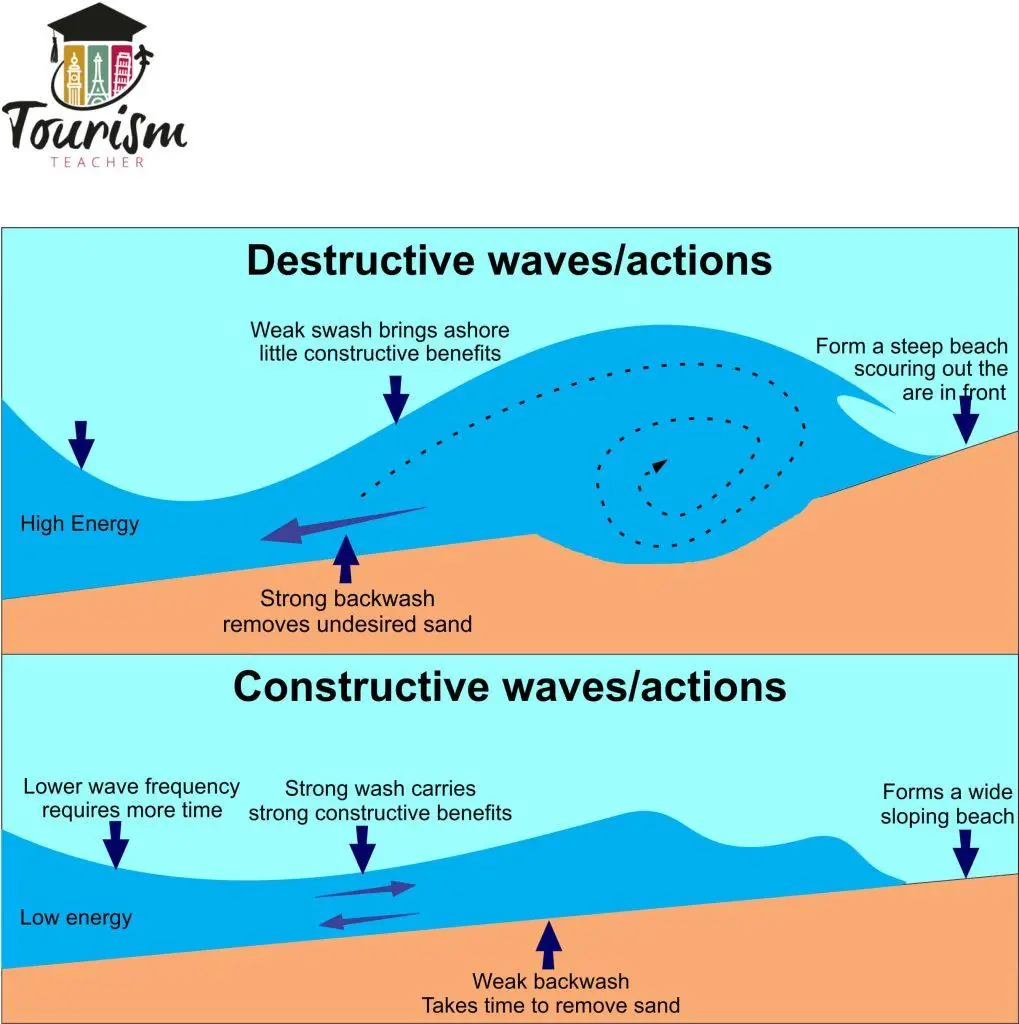
what are the different types of wave
Destructive ( high energy)
Constructive (low energy)
3 things that water does is:
EXACT ORDER
1) Erosion
2) transportation
3) Deposition
define weathering
weathering is the breaking down of rocks in situ.
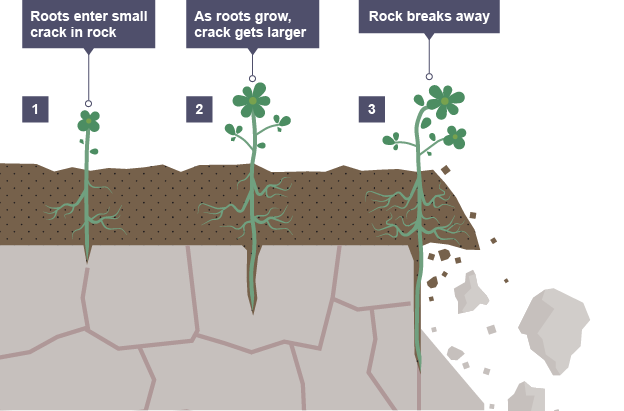
explain how biological weathering works
when roots of trees breaks into rocks
explain how chemical weathering works
cracks in rocks formed by rain as rain is slightly acidic

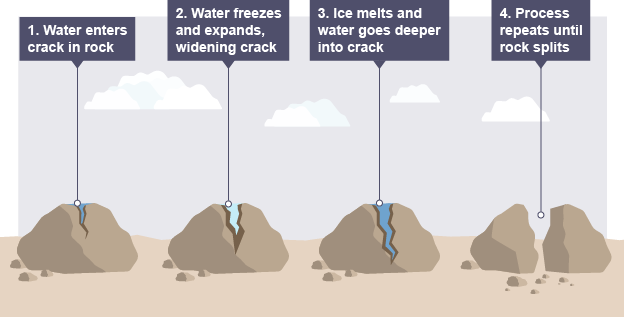
explain how physical (freeze thaw) weathering works
when water seeps into cracks in rocks, the water freezes and expands, the water the melts and this process repeats until rock is split in half
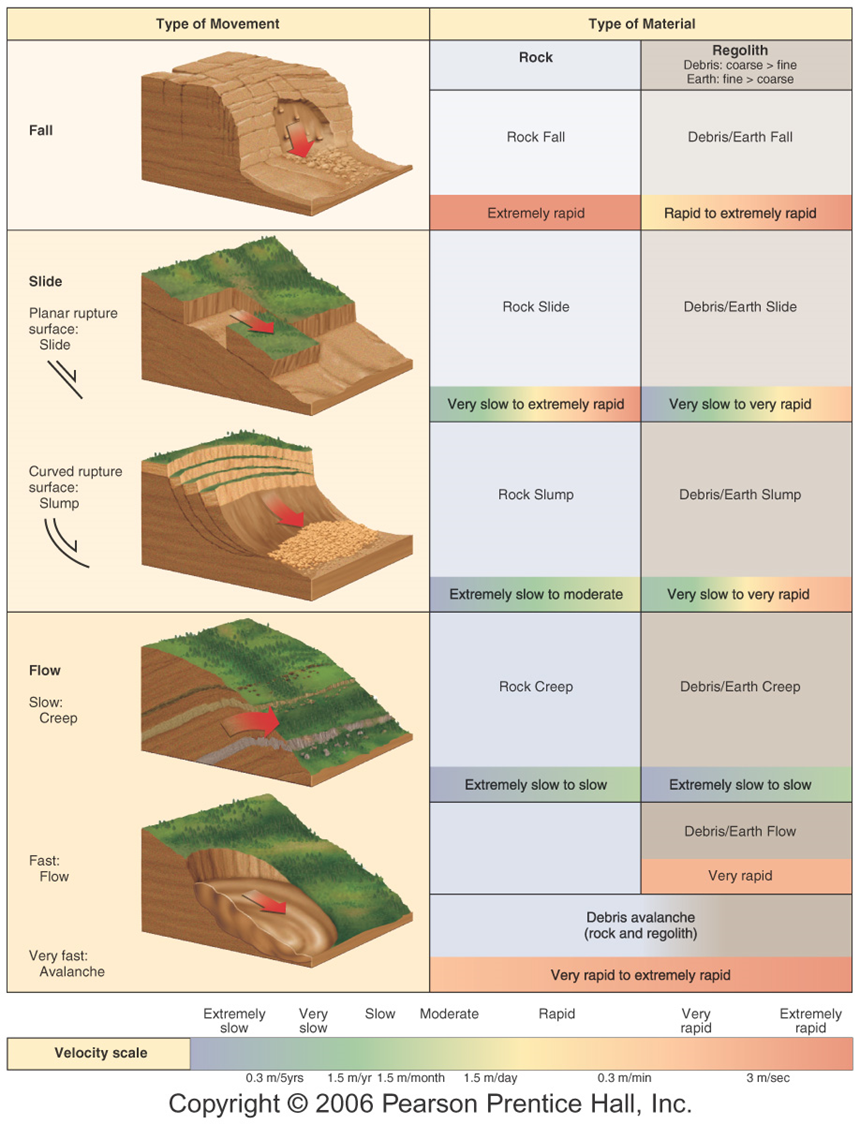
what is mass movement
the sudden movement of a large volume of rock or sediment
list the different types of mass movement
Rockfall
landslide
slumping
what are the different types of erosion
Abrasion → rocks that do the erosion by scraping the sea bed/ hitting cliff
Solution → chemicals dissolve the rock
Hydraulic action → force of water when hits cliff
Attrition → rocks that bang together becoming rounder + smaller
list the different coastal landforms of erosion
headlands and bay
cliffs
caves, arches, stacks
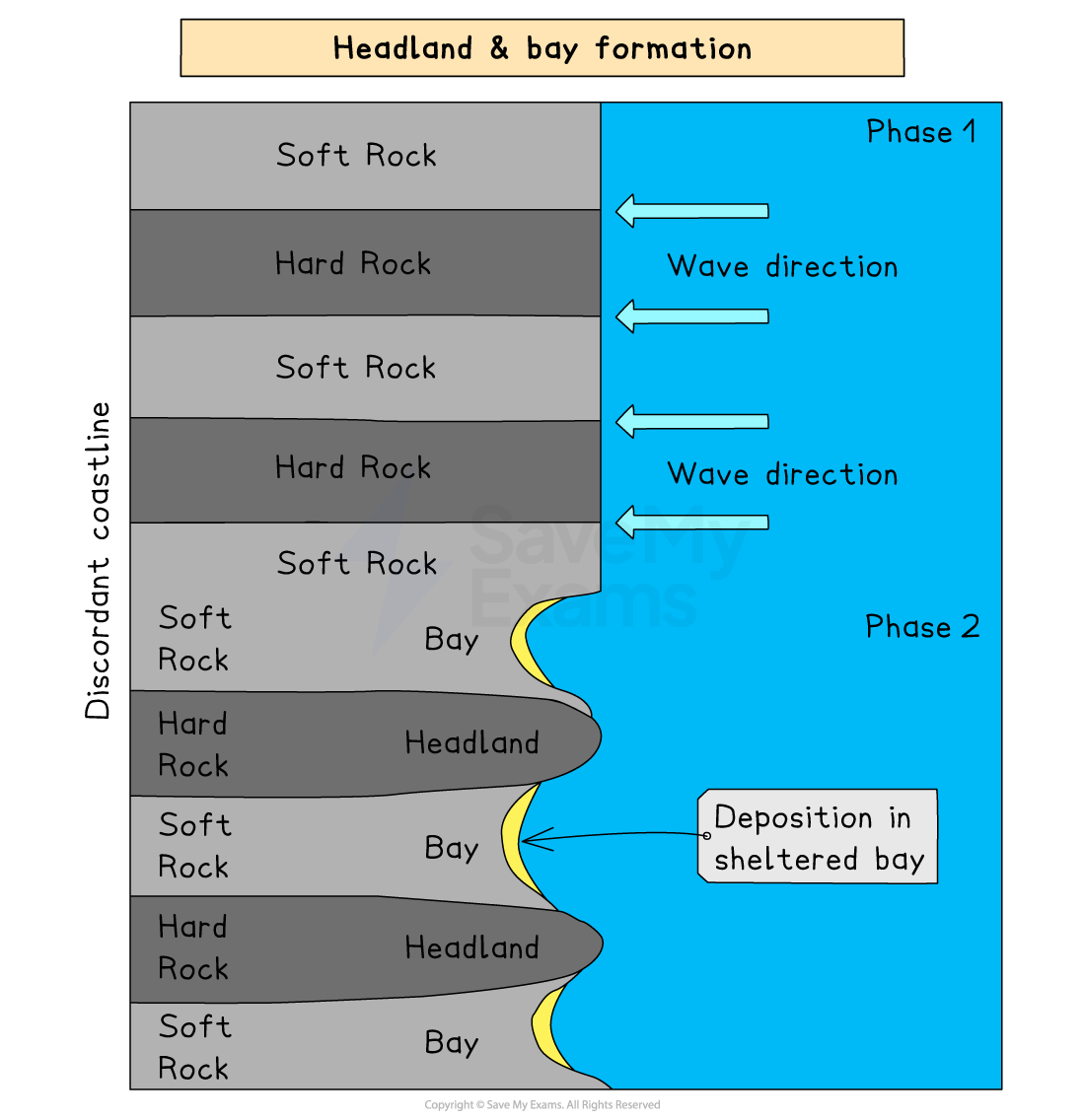
describe how headlands and bays are formed
The coastline has alternating bands of hard and soft rock.
Soft rock (e.g chalk) erodes faster than hard rock (e.g granite)
Erosion processes like hydraulic action and abrasion wear away the soft rock, forming a bay.
The hard rock is more resistant so it erodes slower forming a headland.
Over time, wave energy is focused on headlands, causing more erosion and spread out in bays where deposition often occurs
e.g Swanage bay
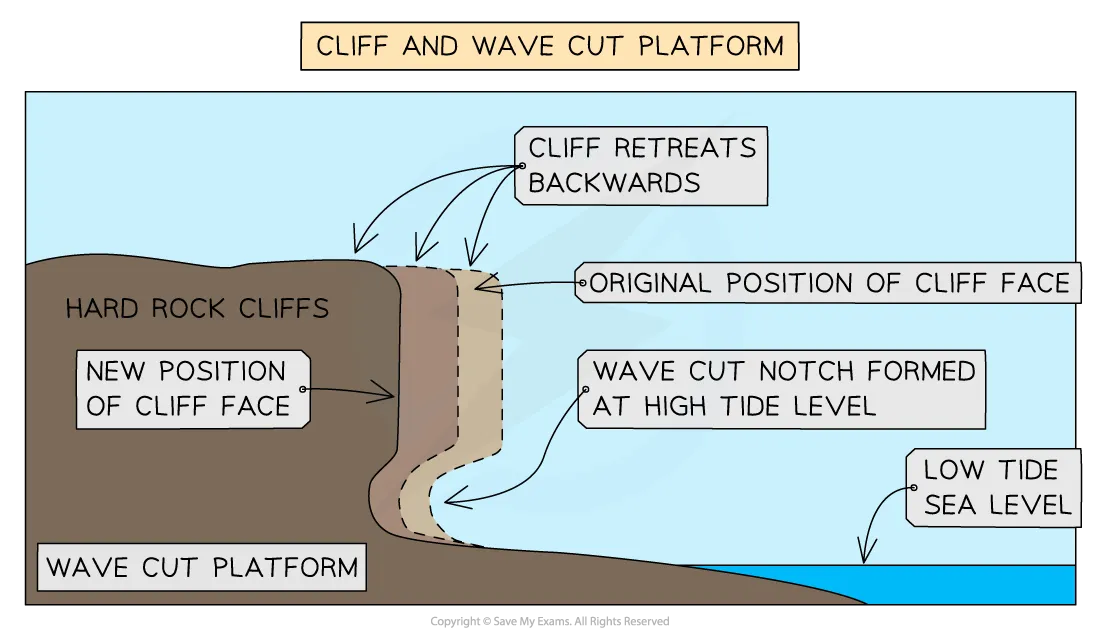
describe how cliffs are formed
formed mainly by erosion and weathering of rock along the coast.
Waves hit the base of the coastline through processes like hydraulic action, abrasion, creating a wave-cut notch at the bottom of the rock face.
As the notch deepens, the overhanging rock above becomes unstable and eventually collapses due to gravity.
The collapsed material is washed away by the sea, and the cliff face retreats inland.
This process repeats over time, leaving behind a steep cliff and a wave-cut platform
Bare off cliff means it is being eroded back
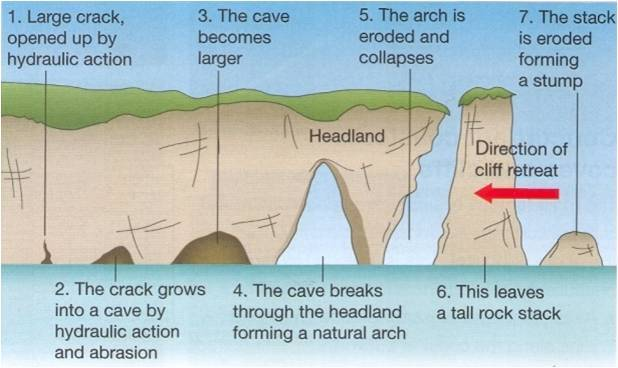
describe how caves, arches, stacks are formed
e.g old harry (Dorset)
what are the characteristics of beaches
1) Composition e.g sand or pebble
2) Angle e.g low or steep
3) width
sandy beaches have a gentle profile - low energy
pebbles and shingle beaches ofter have steeper profile - high energy
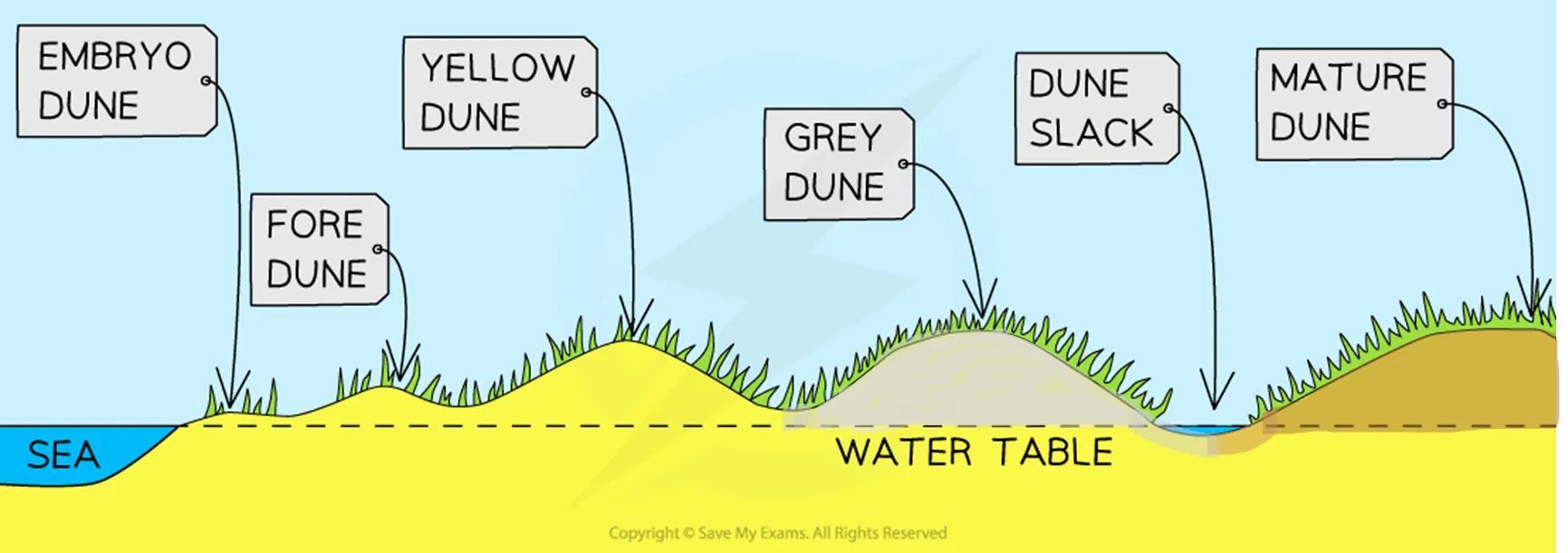
describe how sand dunes are formed
A sand dune need:
large supply of sand
big flat beach
prevailing wind
obstacle for dune to form around e.g seaweed, driftwood
what are the 4 steps of transportation
1) traction
2) saltation
3) suspension
4) solution
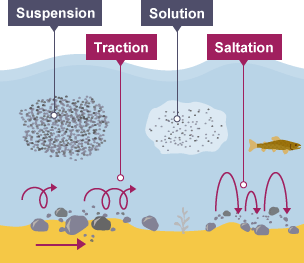
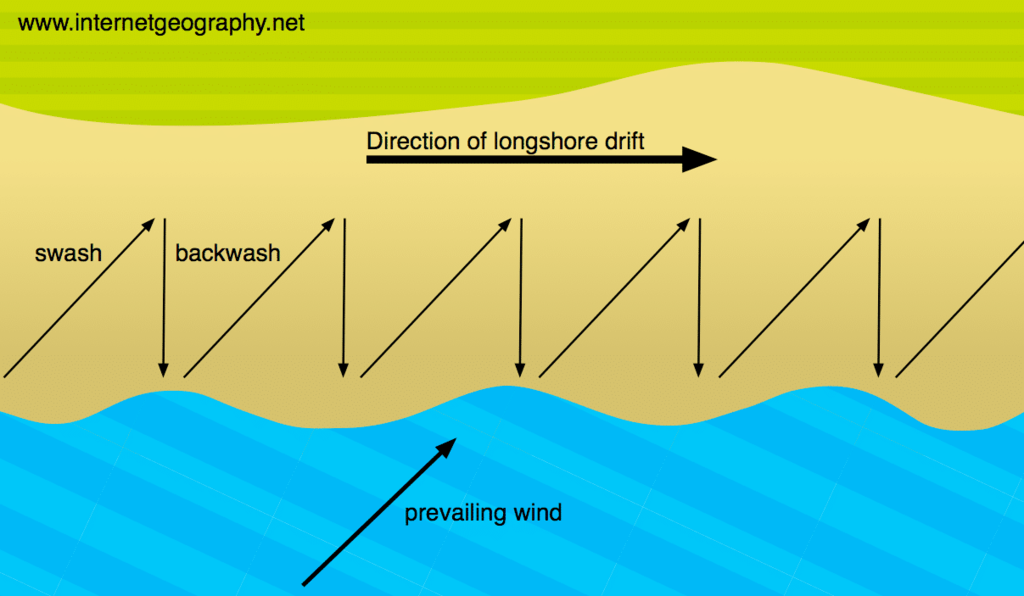
what is longshore drift
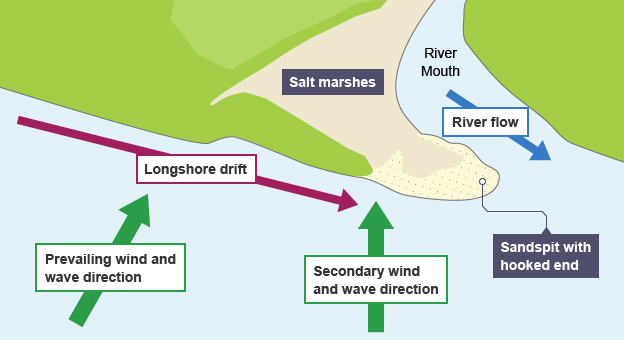
describe the formation of a spit
Longshore drift moves sediment along the coast in the direction of the prevailing wind.
When the sediments meets the mouth of the river, they’re deposited out to sea.
This builds up a narrow ridge of sand or shingle sticking out from the coast — called a spit.
The end of the spit may curve (forming a hook) due to storms
Salt marshes or mudflats often form behind the spit where the water is sheltered and calm.
define hard engineering
putting man-made structures on the coasts to stop it from eroding
list the hard engineering strategies at the coast
sea wall - concrete/rock barrier, reflects energy from waves back to sea
groynes - timber or rock structures built out to sea, stops longshore drift
gabions - wire cages filled with rocks, built up to support cliffs, buffer against sea
rock armour - piles of boulders dumped the foot of the cliff, forces waves to break, absorbing their energy
what are the advantages and disadvantage of the sea wall
Advantage
Reflects wave energy
Disadvantage
high maintenance
expensive £5,000 - 10,000 per metre

what are the advantages and disadvantage of Groynes
Advantage
low maintenance
creates wider beach - reduces wave energy and can be popular with tourists
cheap £150,000 each
Disadvantage
starve beaches further along the coats (terminal groyne syndrome)

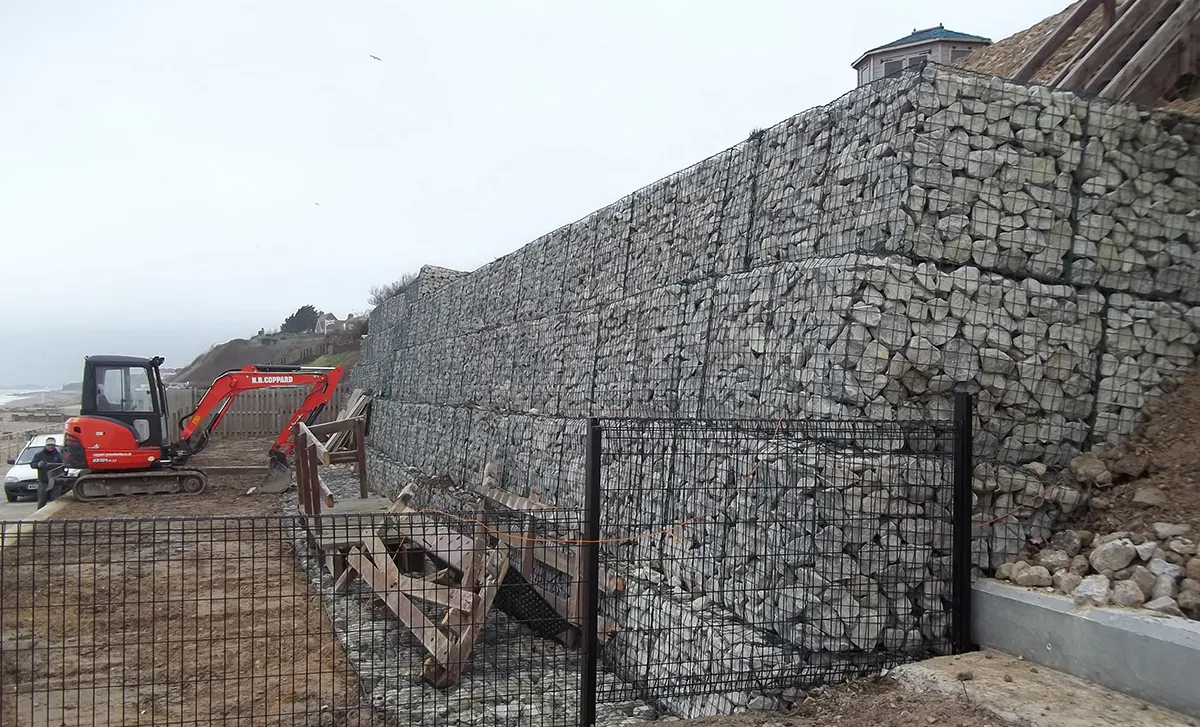
what are the advantages and disadvantage of Gabions
Advantage
cheap to produce £50,000 per 100m
flexible when finished
will become vegetated over time - looks more natural
Disadvantage
looks ugly when first placed
may not be effective against storm weather
cages will rust

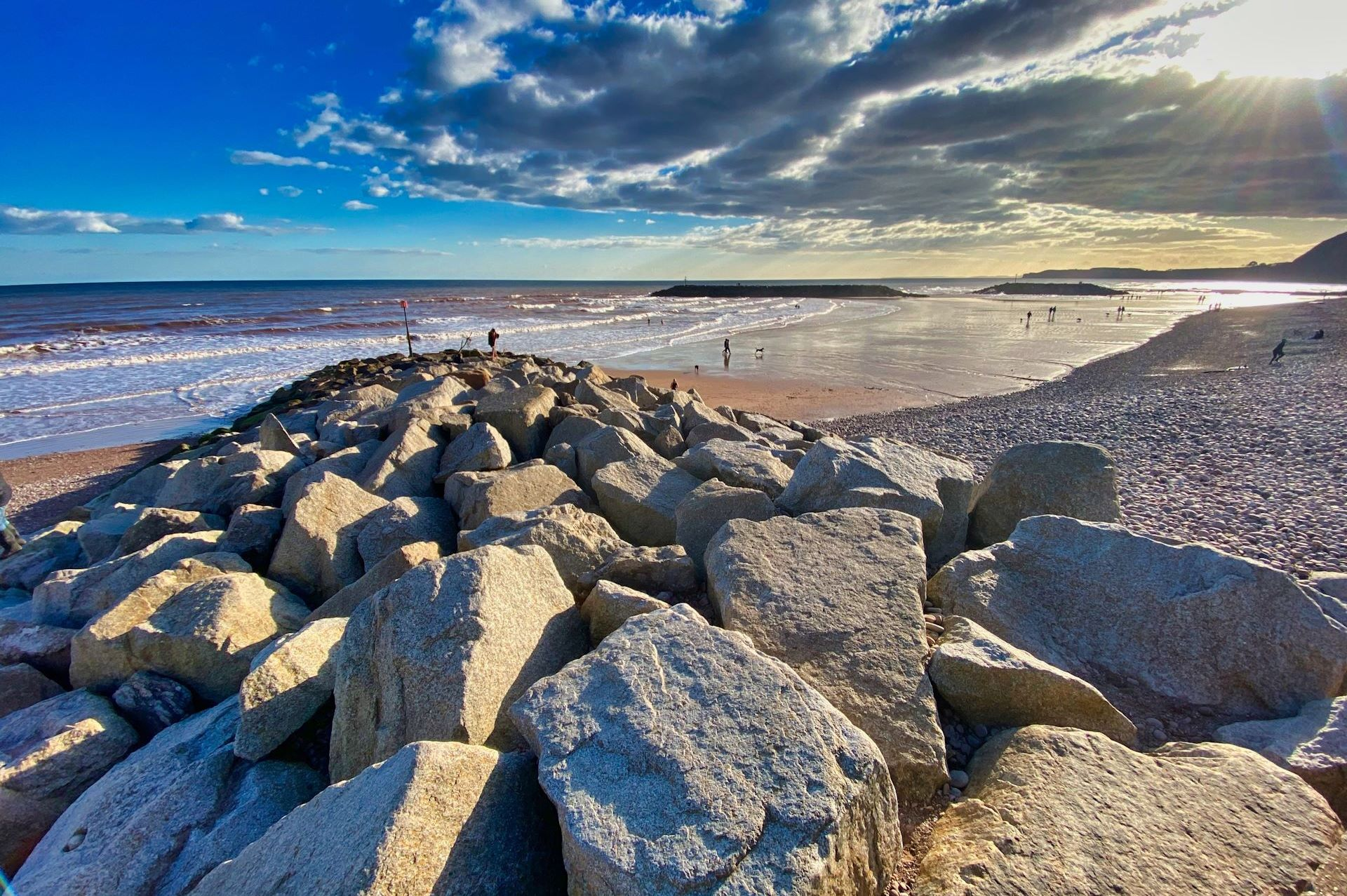
what are the advantages and disadvantage of Rock armour (rip-rap)
Advantage
low maintenance
can provide interest to the coast - fishing
cheaper £200,000 per 100m
Disadvantage
do not fit with local geology
looks ugly
blocks views

what are the 6 stages of fieldwork in order
planning → data collection → presentation → analysis → conclusion → evaluation
list the 4 different sampling techniques
1) random sampling e.g picking up stones from any area
2) stratified sampling e.g surveying 3 residential buildings
3) systematic sampling e.g sampling every 5th groyne
4) pragmatic sampling → we used this at Southworld bc lack of time to measure all groyne (6/7)
what did you see at Southworld
groynes - rock and timber
sea wall - repairing with steel pipes
cliff re-alighnment
what is the hypothesis of our fieldwork
The goynes at Southworld stops longshore drift
give reasons why Southworld was a suitable location for the fieldwork
it’s 2h drive away - distance of abt 70m
it has gryones
what are the risks during the field trip what you did to reduce it
drowning because we are doing it close to the sea - to not be allowed in the water at all
lost in town because we’ve nvr been there before - bring your phone, given a map
what are we measuring in Southworld
we are measuring groyne drop height, from the top of the goyne to the surface of the sand on opposite sides
how did you present your data from Southworld and what are the strength and weakness of it
Strength
easy to draw and understand
shows the amount of sand on each side of the groyne
weakness
needs to be careful when drawing it
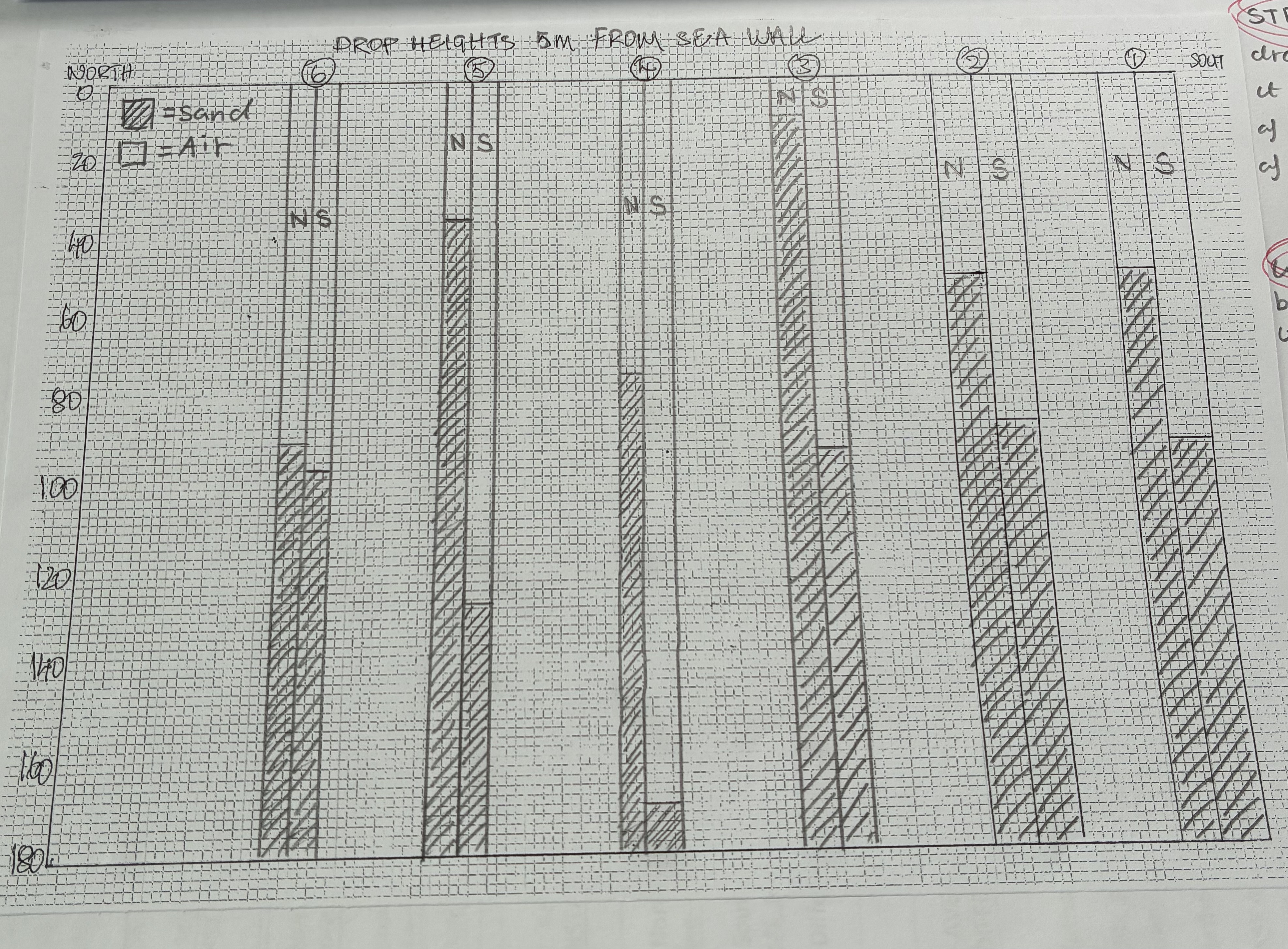

was there any anomoly in the data
none in data but took photo of groyne being covered in sand
what’s another case study we have learnt about managed retreat
Medberry, west sussex
what’s case study have we learnt about holding the land other then Southworld
Bunn leisure in west sussex
what is the managed retreat in Medberry about
largest coastal realignment scheme in UK
done this because they have suffered many floods
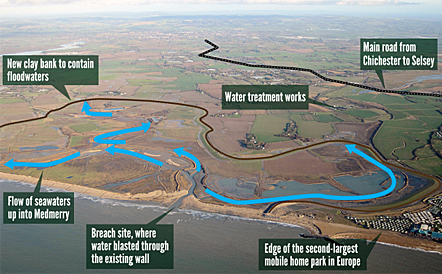
what are the advantages of managed retreat in Medberry
The area now has 10km of footpaths, 7km of bike paths, and 5km of bridleways → provide people with more open space for e.g jogging → improve quality of life
attract green tourists due to salt marsh being a wild bird habitat → tourists spend money on e.g hotel → boost economy
lot’s of biodiversity e.g reed beds → compensates for losses due to development → allowing a diverse of animals to live there attracting e.g bird watchers
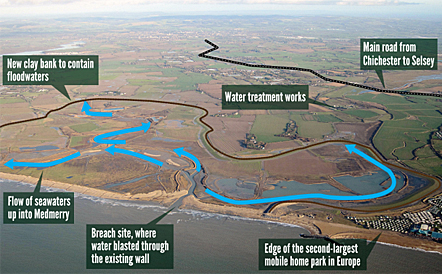
what are some PLC about Medberry managed retreat
Monitored by the Environmental Agency
salt water marsh
good for wildlife
£28m
4miles of new embankment
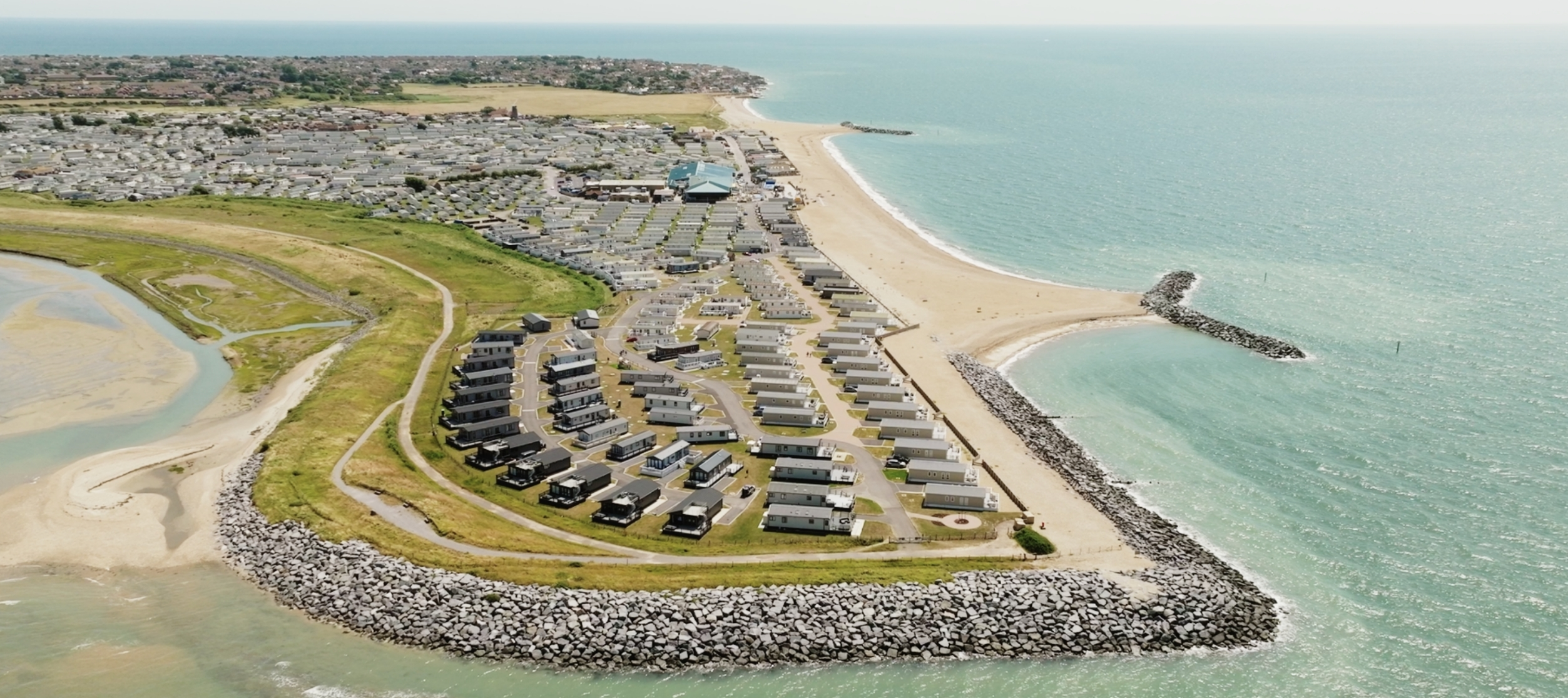
what is the holding the land at Bunn leisure about
beach nourishment + rock groyne
cost £15m
the manager of Bunn leisure doesn’t want his holiday resort to be destroyed by erosion

what are the different types of coastiline
1) concordant e.g Southworld
2) discordant e.g Swanage bay - Dorset
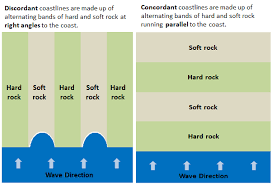
give an example of a UK coastline
The Dorset Coastline
Discordant coastline
differential rate of erosion happen
Give examples of what forms during erosion and give an example of the location
wave cut platforms forms - e.g Kimmeridge bay
Arch - e.g Durdle door
Stack - e.g Old Harry
Headlands and bays - e.g Swanage bay
give examples of what forms during deposition and give an example of the location
sand dunes - e.g Studland
spit - e.g Sandbanks
beach - e.g Swanage
Bar - e.g Chesil Beach