Unit 1 - The Nervous System & Neurons
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
How many neurons are in the brain?
100 billion
How long is a neuron?
10 um
How many watts does the brain use?
20 watts
Resting Voltage
-65mV
CNS
Parts of the nervous system enclosed in bone
PNS
Parts of the nervous system not in bone
Brainstem consists of
Midbrain + pons + medulla
Neuron
Fires action potential + axon
Glial Cells
Creates support
Astrocytes
Maintains ionic environment
Microglia
Clears cellular debris
Oligodendrocytes
Myelinates CNS neurons and wraps around multiple axons
Schwann Cells
Myelinates PNS neurons and wraps around 1 axon
CSF
Aqueous solution surrounding neurons with Na, K, Cl, other ions
What are the main causes of a negative resting potential?
Diffusion and Electrostatic forces
Electrostatic Forces of K
Enough K flows out creating electrostatic attraction, creating equal flow in and out at a negative voltage
Rostral
Upwards
Dorsal
Behind neuraxis
Caudal
Lower
Ventral
Infront of neuraxis
Superior
Above
Posterior
Behind
Inferior
Below
Anterior
In front of
Ipsilateral
Same side
Contralateral
Opposite side
Decussate
Cross midline
Proximal
Close to reference
Distal
Far to reference
Efferent
Leaving from reference
Afferent
Towards reference
Medial
Near midline
Lateral
Far from midline
Coronal
Side to side
Sagittal
Midline
Neuroscience Rules
Symmetry
Localization
Contralaterality
Topography
Localization
Different parts have different functions and spatially separatedq
Contralaterality
Functions for something are crossed
Topography
Neurons are mapped on the brain as the body
Nissl Stain
Shows section of neurons by staining the RNA
How thick is the cerebral cortex in mammals?
2mm
Brodmann’s areas
52 cortical areas identified by the Nissl stain
How is it discovered that everything is through action potentials?
Local anesthesia
Electrical brain stimulation
Strokes
How did Helmhotz measure neuron propagation?
Shocked nerves and seeing the time difference between the muscle contraction
Receptor Potential
Graded tiny potentials that brings neuron to threshold
Depolarization
Voltage becomes positive
Afterhyperpolarization
Past resting potential around -70mV
Threshold Potential
Around -50mV
Na Rushing in because
Postive activation gate on Na gated channels open because it’s no longer attracted to the less negative inside
Na inactivation
Na channel inactivate from the positive gate being repelled from the positive inside
Absolute Refractory Period
Inactivation of Na channels
Falling Phase
K voltage channels open after inactivation from its positive charged gate
Undershoot
K voltage channels close slowly and leaks channels are still open causing hyperpolarization
Lidocaine
Enters Na gated channels and physically blocks them for a certain amount of time
Tetrodoxin
From pufferfish bacteria in ovaries and liver binds to Na channels but remains bounded causing paralysis of lung nerves
Saxitoxin
Butter clam that came in contact with red time made by toxic dinoflagellates which the shells eat causing paralytic poisoning
Voltage Clamp
Measures current voltage and can manipulate the axon’s voltage
Voltage Clamp Set Up
Inserts 2 electrodes into axon, 1 to meausre current and uses a reference as a base, and 2 to add current through
Use of Electrode 2 in Voltage Clamp
Maintains a given voltage, if voltage surpasses threshold, more energy is given to counteract axon’s natural firing
Hodgkin and Huxley
Refined voltage clamp and AP
Nernst Equation
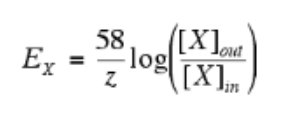
Neuron Conduction Velocity Equation
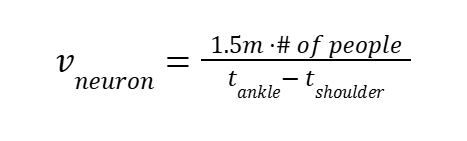
Goldman-Hodgkin Katz Equation
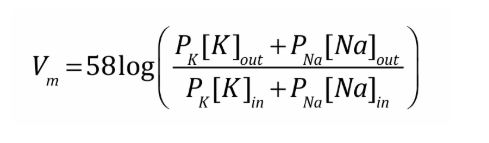
Rising Phase
Na+ ions enter from positively activated gate, when inside is positive enough, Na channel inactivation closes because it’s repelled from the positive inside
Low Membrane Resistance
Na ions coming in repels K ions that goes out leak channels, making it harder to reach AP (leaky)
High Membrane Capacitance
The negative outside of neuron causes positive ions inside to stick to the membrane (sticky)
High Axial Resistance
Thin axons make it hard for ions to move down
What did invertebrates evolve to increase AP conduction?
Wider axons for selected neurons which increases AP but takes up space
What did vertebrates evolve to increase AP conduction?
Myelin which adds distance between charges, and prevents leaking out to replace it with nodes of ranvier
Louis-Antione Ranvier
Discovered the notes of ranvier
Theodor Schwann
Discovered Schwann cells and component that cells are made from cells
Multiple Sclerosis
Autoimmune disease causing loss of function in nervous system that vary day to day from demyelination of oligodendrocytes from antibodies
Multiple Sclerosis Risks
Twice as common in woman, and increases chances if an identical twin has it, compared to fraternal
Guillain Barre Syndrome
Multiple sclerosis but in the PNS, which is rarer but condition and recovery can vary drastically
Camillo Golgi believed in
Proponent of reticular theory where all neurons are physically connected
Santiago y Cajal believed in
Proponent of neuron doctrine where neurons have small gaps between them
Synaptic Cleft
Gap between neurons about 20-40nm wide
Otto Loewi
Tested chemical transmission by putting 2 frog vagus nerve in separate containers connected by solution, and simulation of 1 caused same reaction in other nerve indicated some chemical must’ve been released
Bernard Katz
Took muscle cells and stimulated them to see the mV in trails and found at 0.4mV intervals there was a characteristic peak
Poisson Distribution
Discrete probability distribution that shows the probability of a given number of event within an interval
Synaptic Transmission
Positive charge causes Ca gate to unbind and allow Ca ions to come in
Neurotransmitter Release
Vesicles move near the membrane with help of SNARE complex, and Ca binds to synaptotagmin catalyzing membrane fusion
Synaptotagmin
Ca detector protein on vesicles
Ca Pump
Pumps Ca out using H and ATP
Na/Ca ion Exchanger
Uses Na gradient to pump Ca out
Lily Jan and Yuh Nung Jan
Discovered peptides are neurotransmitters
Glutamate
Common excitatory neurotransmitter
Glumate Receptor Channel
Allosterically binds with glutamate to be equally permeable to K and Na causing overall EPSP
GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in cerebral cortex
GABA Receptor Channel
Selectively permeable to Cl when GABA binds causing IPSP
Glycine
Common inhibitory neurotransmitter in CNS
Driving Force Equation
Ix = gx (Vm - Ex)
If Ix is positive
Outward current, cell loses positive charge, gains negative charge
If Ix is negative
Inwards current, cell loses negative charge or gain positive charge
Spatial Integration
Multiple signals from different neurons
Temporal Integration
Signals from same neuron
Spatial Integration Equation
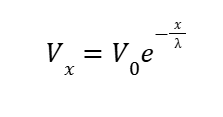
Length Constant
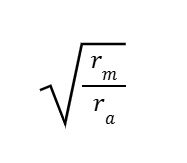
Temporal Integration Equation
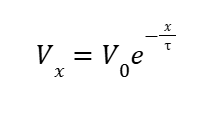
Time Constant
rmcm