Econ - Ch 10. Measuring a Nation's Income
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is Economics about?
Scarcity: The limited nature of society’s resources.
What is Macroeconomics?
Study the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole
Goals of Macroeconomics
Define and identify significant economic concepts
Identify the equilibrium within the supply and demand model
Explain the concepts of the business cycle
Analyze the impacts of fiscal and monetary policy on the economic fluctuations
What are the four macro markets
resource market
loanable funds market
foreign exchange market
aggregate goods and services market.
When price (P) changes
Quantity (Q) changes
What is GDP (Y) ?
The market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time.
Total income of everyone in the economy.
Total expenditure on the economy’s output of goods and services.
“income” equals expenditure because every dollar a buyer spends is a dollar of income for the seller
Circular Flow Diagram
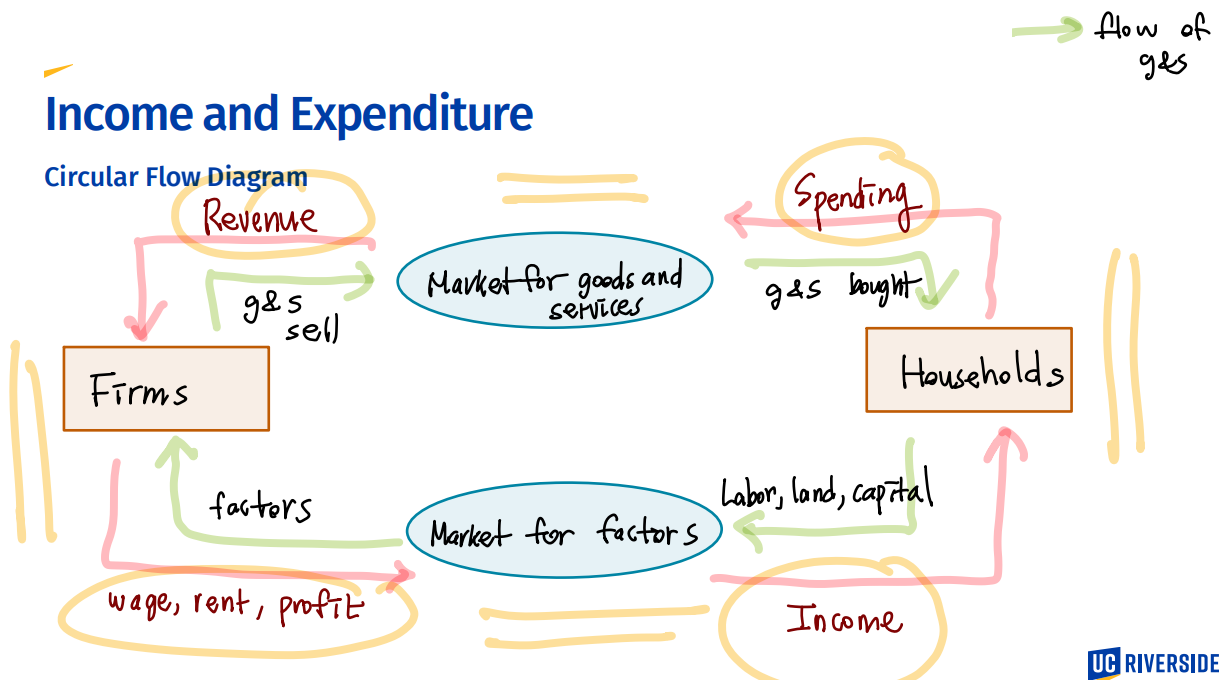
“The market value”
Actual market for the goods and services.
“all final goods and services”
Final goods: Goods whose sale is intended to be for their final purpose.
Intermediate goods: Goods that are bought to be used in the production of another good
NOT a part of GDP
“Produced”
Only goods and services produced by the economy are counted. It does not matter whether the goods are bought, sold, consumed, traded, etc.
NOT items produced in the past
ex) A used 1997 car being transacted in 2025 only counts for the 1997 GDP not 2025 one
“Within a country”
Only measures the value of production that occurs within a country’s borders, whether done by its own citizens or by foreigners located there
“In a given period of time”
Typically a year or quarter. Goods and services that counted toward GDP in a previous calculation do not affect the current calculation.
Components of GDP
C, I, G, NX
(G) Government Expenditures
Government Expenditures - All spending on the goods and services purchased by government at the federal, state, and local levels
Examples of Government Expenditures
• Salaries of government employees
• Contracts to build new roads and bridges
• Military spending
Examples of NOT Government Expenditures
Transfer Payments: Made by the government to households and firms that are not in exchange for goods or services
Unemployment insurance
medicare
social security
ie transaction from the government to the individual (nothing new produced)
(C) Consumption
Total spending by households on goods and services
Notes on Households: (buying house services)
for renters. consumption includes rent
for homeowners, consumption includes the imputed rental value of the house, but not the purchase of new housing or mortgage
(I) Investment/Business spending
Total spending on goods that will be used in the future to produce more goods
Business spending, residential investment, changes in inventory
Investment includes
capital equipment (tools)
structures (purchasing a new house, etc)
inventories (goods produced but not sold)
(NX) Net Exports
Value of exports after taking out the value of imports
NX =
Exports - Imports
What are Exports
Goods and services produced in the US but bought and consumed internationally.
Import
Goods and services produced internationally but bought and consumed in the US.
What is Gross National Product (GNP) ?
The total income earned by a nation’s permanent residents (called nationals).
It differs from GDP. It includes income that our citizens earn abroad and excludes income that foreigners earn here.
GNP =
GDP + any income earned by residents from overseas - income earned by foreigners within the country
What is Economic Growth?
measured as the percentage change in GDP from one year to the next
What is the Percentage Change formula
(This year - Last year) / Last year * 100
What is Nominal GDP?
Measures everything in terms of today
• Can change due to a change in prices or quantities .
Nominal GDP =
Current Prices * Current Quantities
What is Real GDP?
Measures the market value of production using a base year’s prices
• Changes only come from changes in production.
• Standard metric for gauging economic growth.
• Base year can be any year.
Real GDP =
Base Year * Current Quantities
What is GDP Deflator?
Measure of the overall price level in an economy
GDP Deflator =
Nom. GDP / R. GDP * 100
What is Inflation?
The percentage increase in the price level from one year to the next
Inflation Rate =
(GDP Deflator Today - GDP Deflator Last Year) / (GDP Deflator Last Year) * 100
Real GDP per capita is the main indicator for a person’s standard of living but
its not a perfect measure of wellbeing