Practicle lab 2: Enzymes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are the characteristics of an enzyme?
enzymes are proteins
Each different enzyme reacts with a specific substrate
Enzymes do not require substantial heat to bring about chemical reactions
Enzymes cannot change the equilibrium concentrations for a given reaction, however they do bring the reactants to that point much faster
Enzymes do not affect the free energy changes (total G) of a given reaction
Finally enzymes emerge un altered from reactions ready to act again and again
What is a substrate or reactant?
The substrate/reactant is the substance in which the enzyme acts on.
What are products?
The substance that is the result of the chemical reactions/experiment.
What makes enzyme efficient catalysts?
what makes them efficient catalyst is because they assume precise shapes.
The importance of shape is seen in the active site a crucial part of any enzyme.
What is the active site?
The active site is where chemical reactions happen and take place.
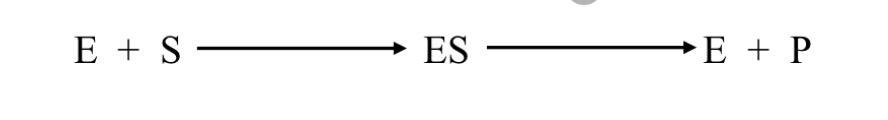
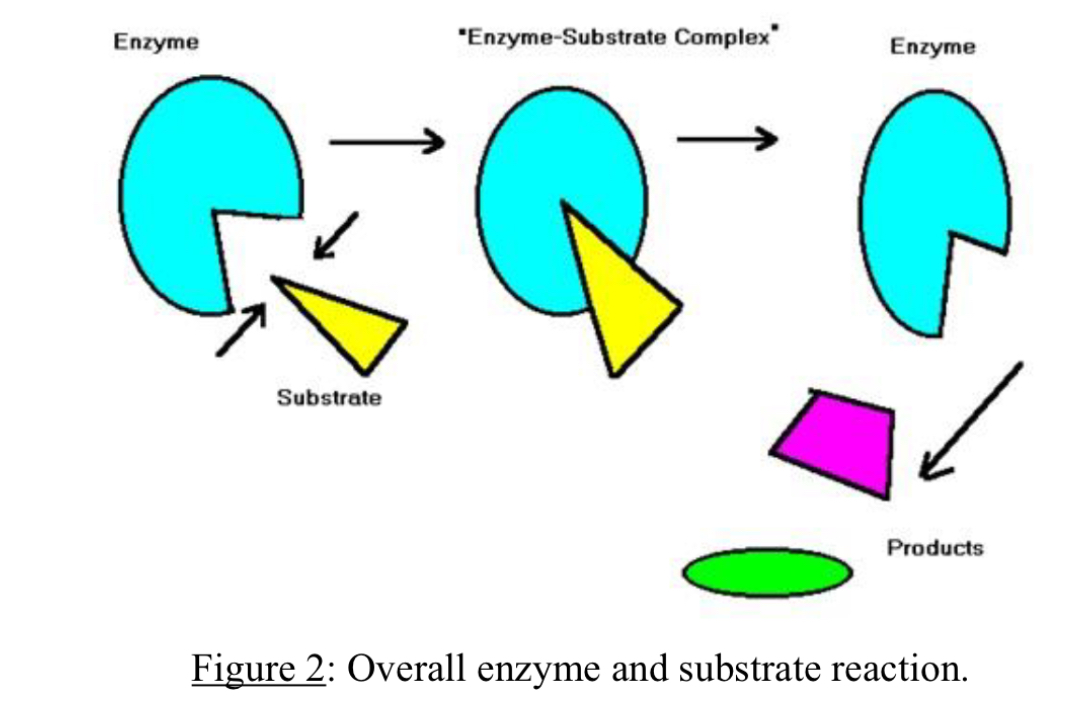
What is the enzyme-substrate complex?
The enzyme-substrate complex is when an enzyme and substrate briefly join at the active site.
What are activators?
Chemicals that must bind for the enzyme to be active/work.
What are co-factors?
Are non-protein substances that usually bind to the active site on the enzyme and are essential for the enzyme to work.
What are coenzymes?
Organic cofactors are called coenzymes but other cofactors are essential metal ions.
What are inhibitors?
Chemicals that interfere with enzyme activity.
can be classified as competitive or non-competitive
What are the two ways to measure enzyme activity?
determine the rate of disappearance of the substrate
Determine the rate of the appearance of the product (we used this method in our lab experiment)
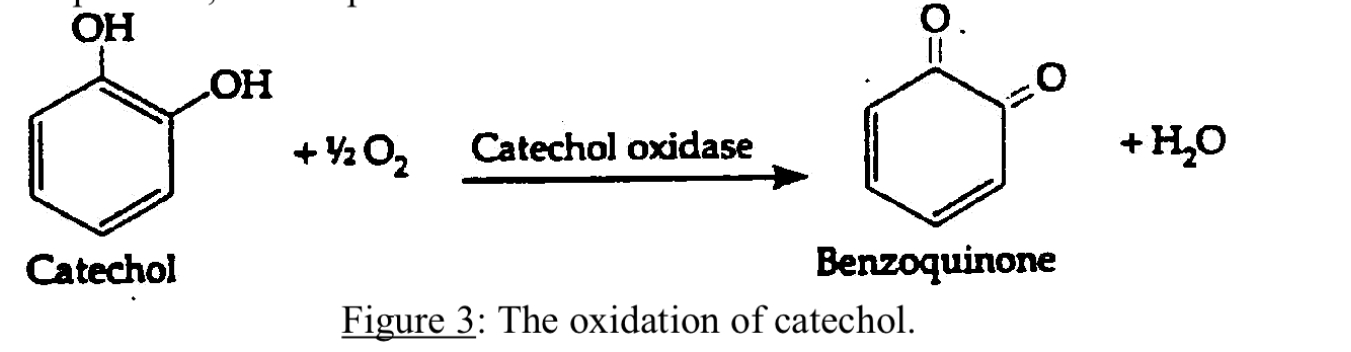
Where is Catechol oxidase found?
It is an enzyme found on potato’s and plants
How is benzoquinone made?
In the presence of oxygen catechol oxidase catalyzes the removal of electrons and hydrogens from catechol, hence converting it to benzoquinone.
the pigment products are responsible for darkening of fruits and vegetable sauce as apples and potatoes, after air exposure.
What is competitive inhibition?
competitive inhibition takes place when a molecule that is structurally similar to the substrate for a particular reaction competes for a position at the active site on the enzyme.
Timing the enzyme up so it isn’t available to the substrate
Competitive inhibition can be reversed with substrate levels being risen/increased while the inhibitor is held constant.
What is a non-competitive inhibition.
In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a site that is not the active site and changes the nature of the enzyme so that its catalytic properties are lost.
can happen by noncompetitve physically blocking the access to the active site or by causing a conformation change in the enzyme resulting in inactivation.
Because the substrate molecules cannot reverse the binding of a noncompetitve inhibitor, increase the concentration of substrate will not reverse the inhibition.