Unit 0: Accuracy and precision, Unit Conversions and Chemistry Lab Equipment
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
How close the measured value is to the true value
Accuracy definition
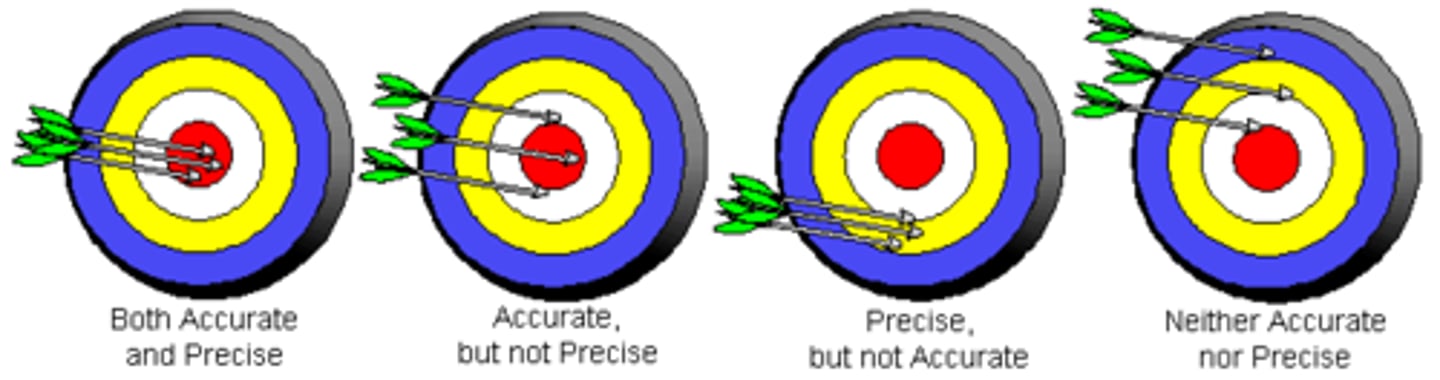
How close the measured points are to each other
Precision definition
Points of measurement that are close together and close to the true value
both precise and accurate

Points of measurement not close to each other and not close to the true value.
neither precise nor accurate
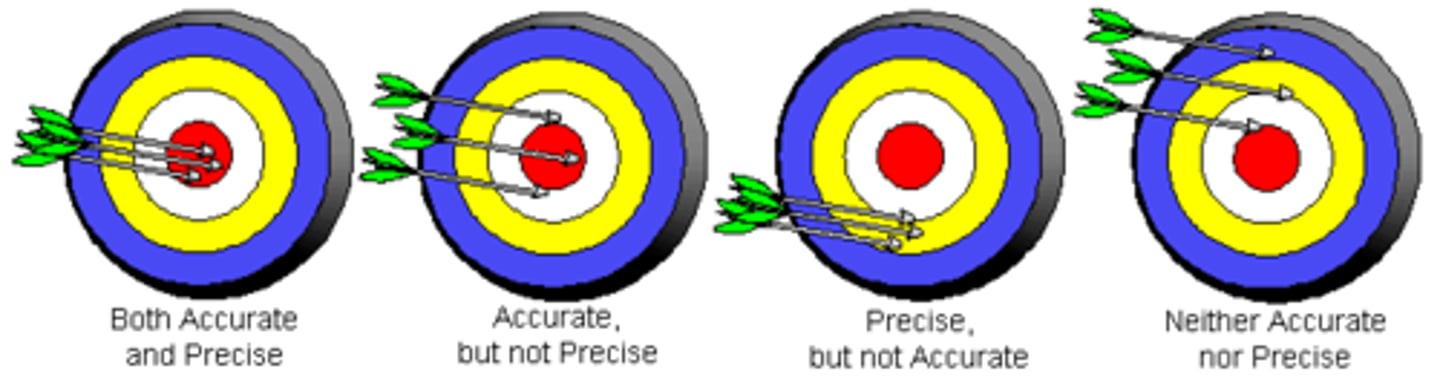
I fire five arrows and all five of them land in the direct center of where was aimed.
Both precise and accurate example

I fire five arrows at a target. They all land close to the desired area but not close together
accurate, but not precise example
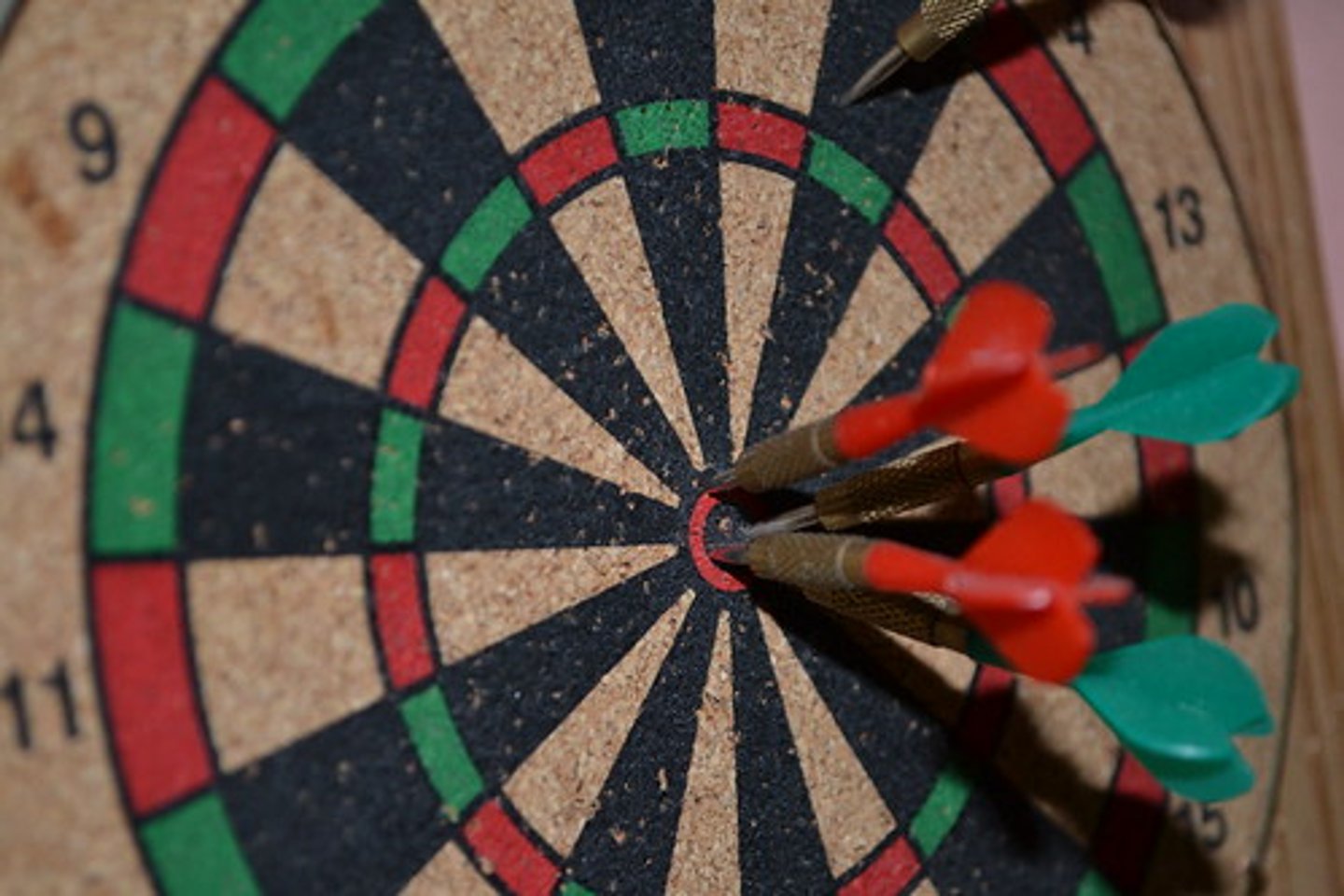

I fire five arrows at a target. they don't land close together or close to the desired area
neither precise nor accurate example
1000 meters =
1 kilometer
1000000 micrometer =
1 meters
3000 g =
3 kg
0.001kg =
1 g
1 millimeter =
0.001 meter
1000 centimeters =
10 meter
1/100 meter =
1 centimeter
20 meters =
2 dekameters
1 cm^3
1 mL
5 meters =
5, 000 millimeters
1 decimeter =
1/100 dekameter
2 kiloliters
2, 000 liters
10 centigrams
1 decigram
This unit is 100 times smaller than a meter
centimeter
This unit is 1,000 times larger than a centimeter
dekameter
Beaker

Erlenmeyer flask

Graduated cylinder

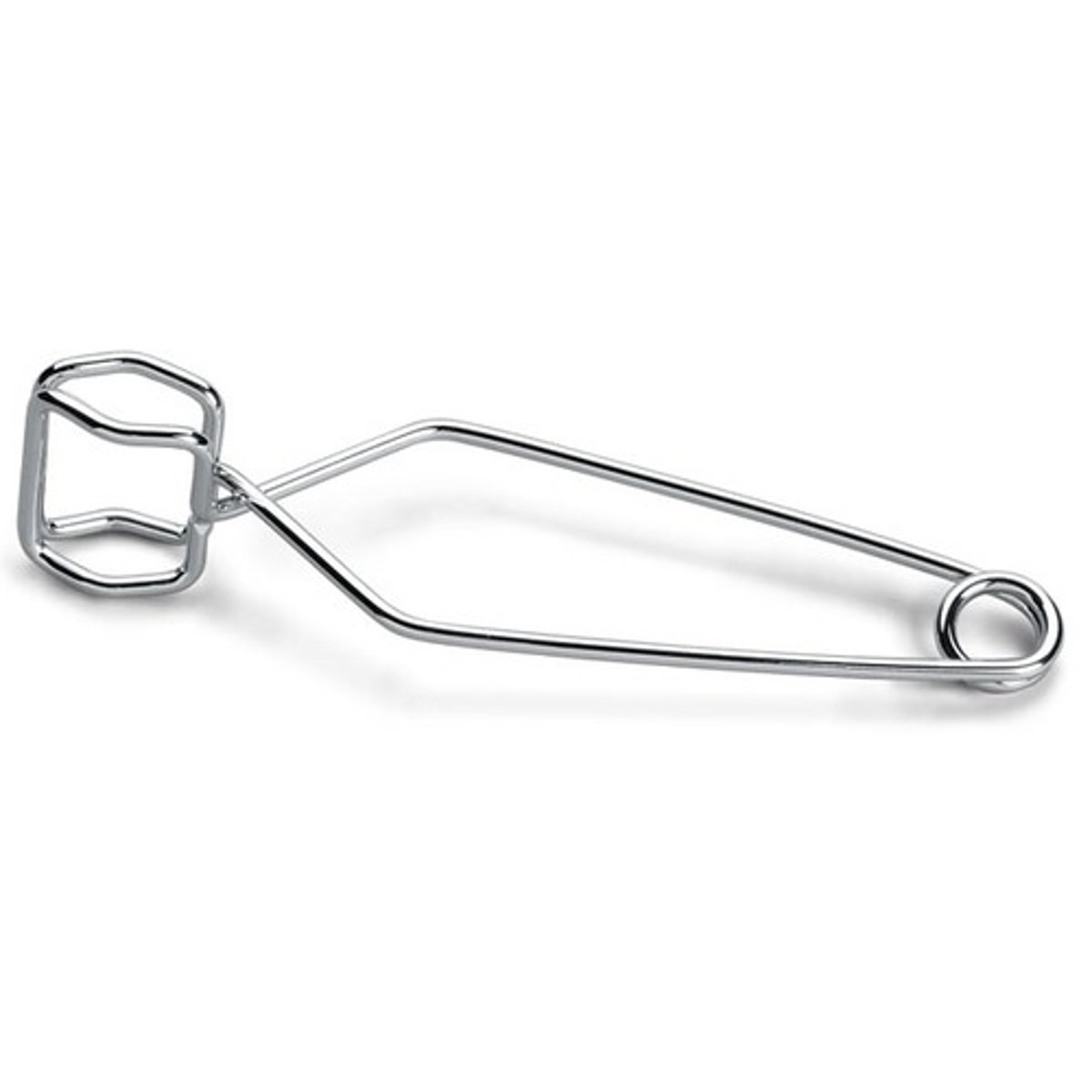
Test tube clamp

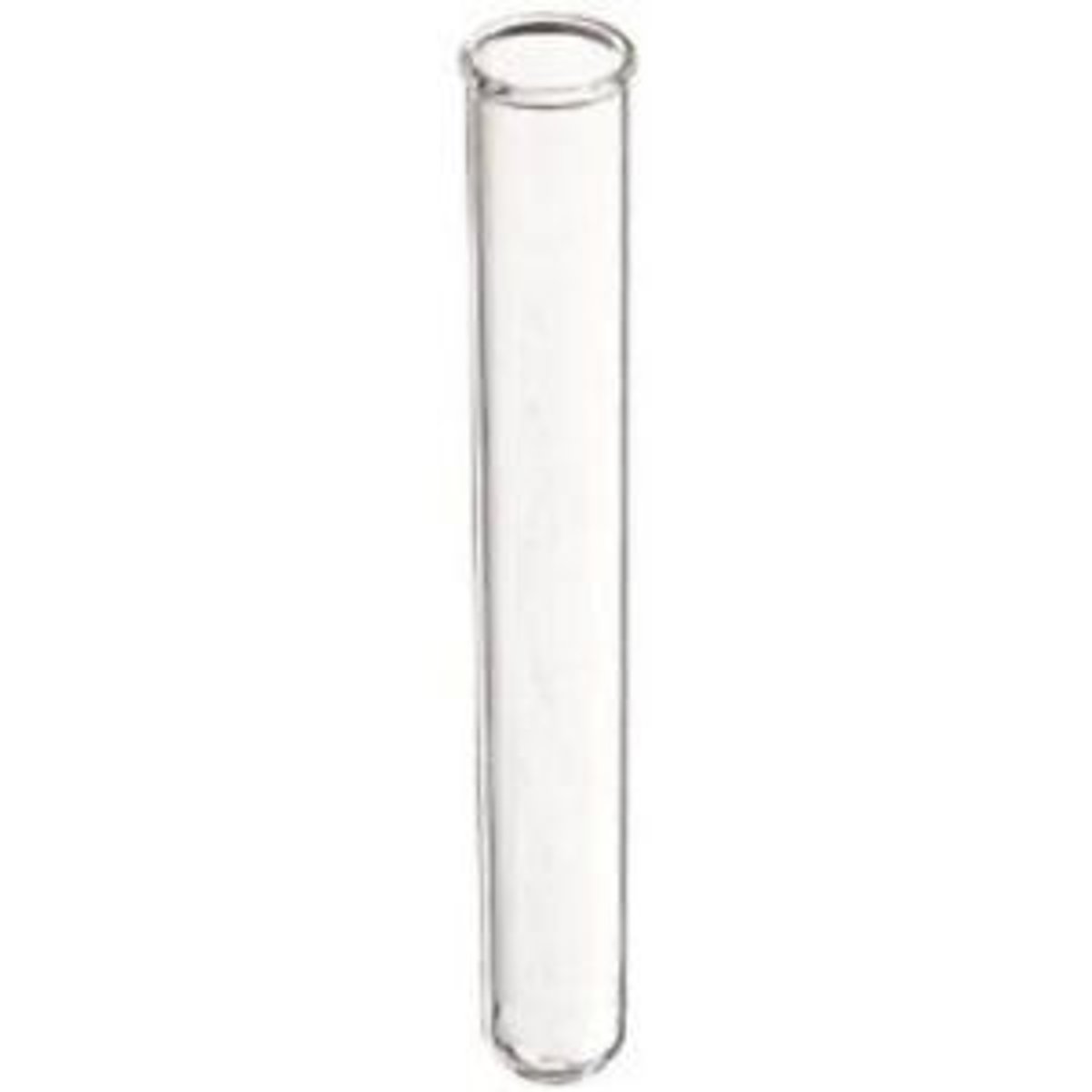
Test tube

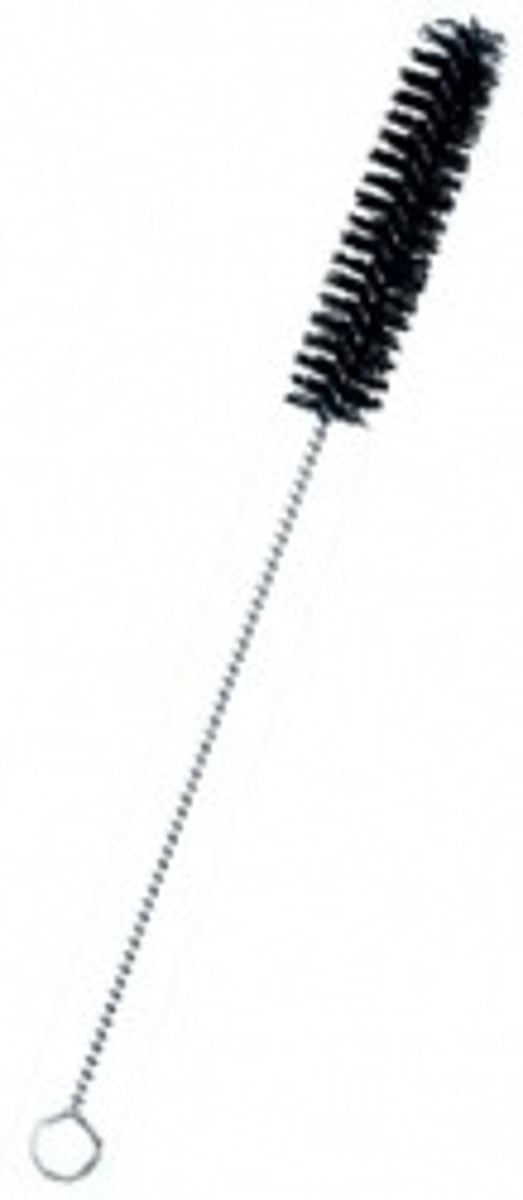
Test tube brush

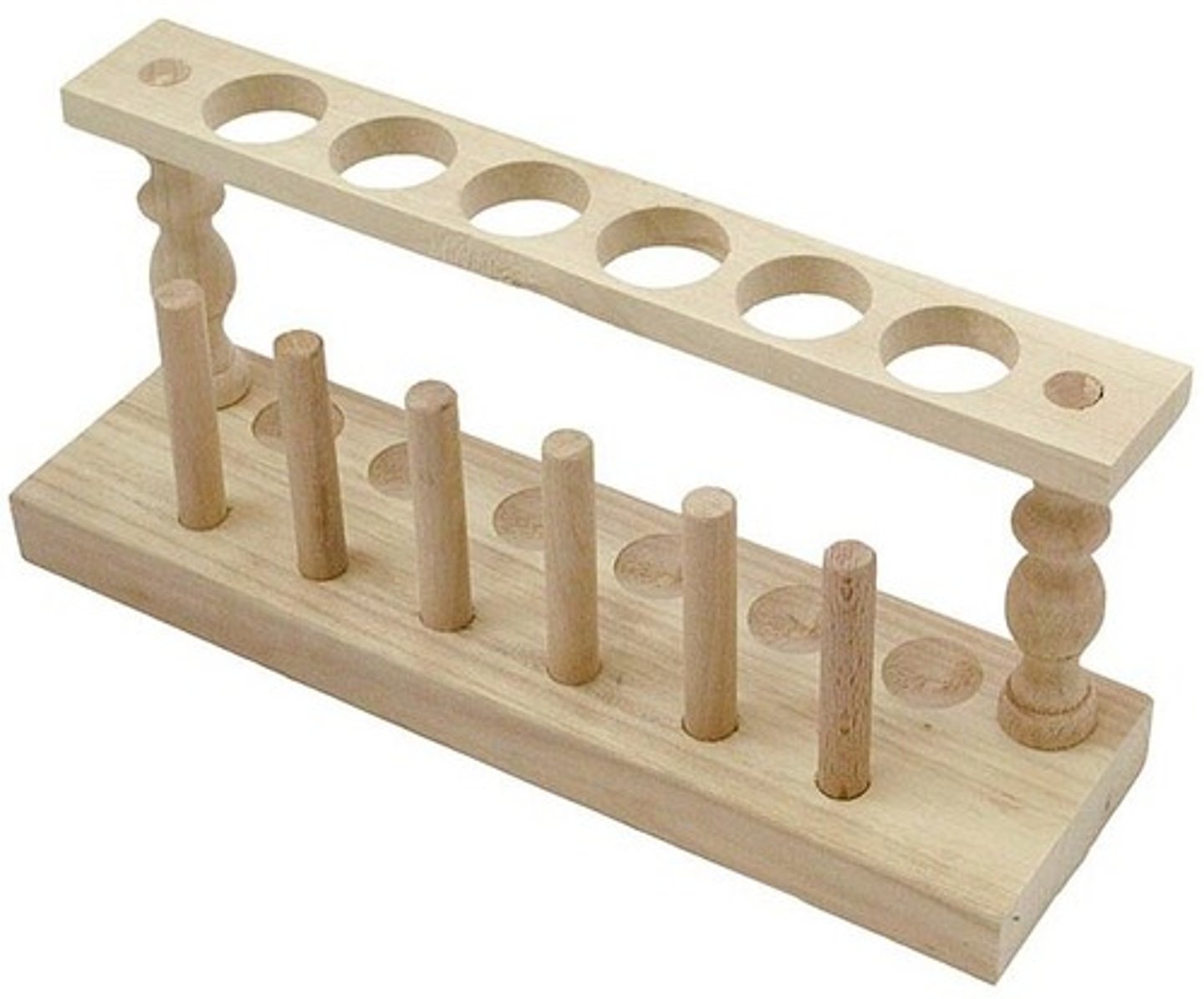
Test tube rack

Rubber stopper

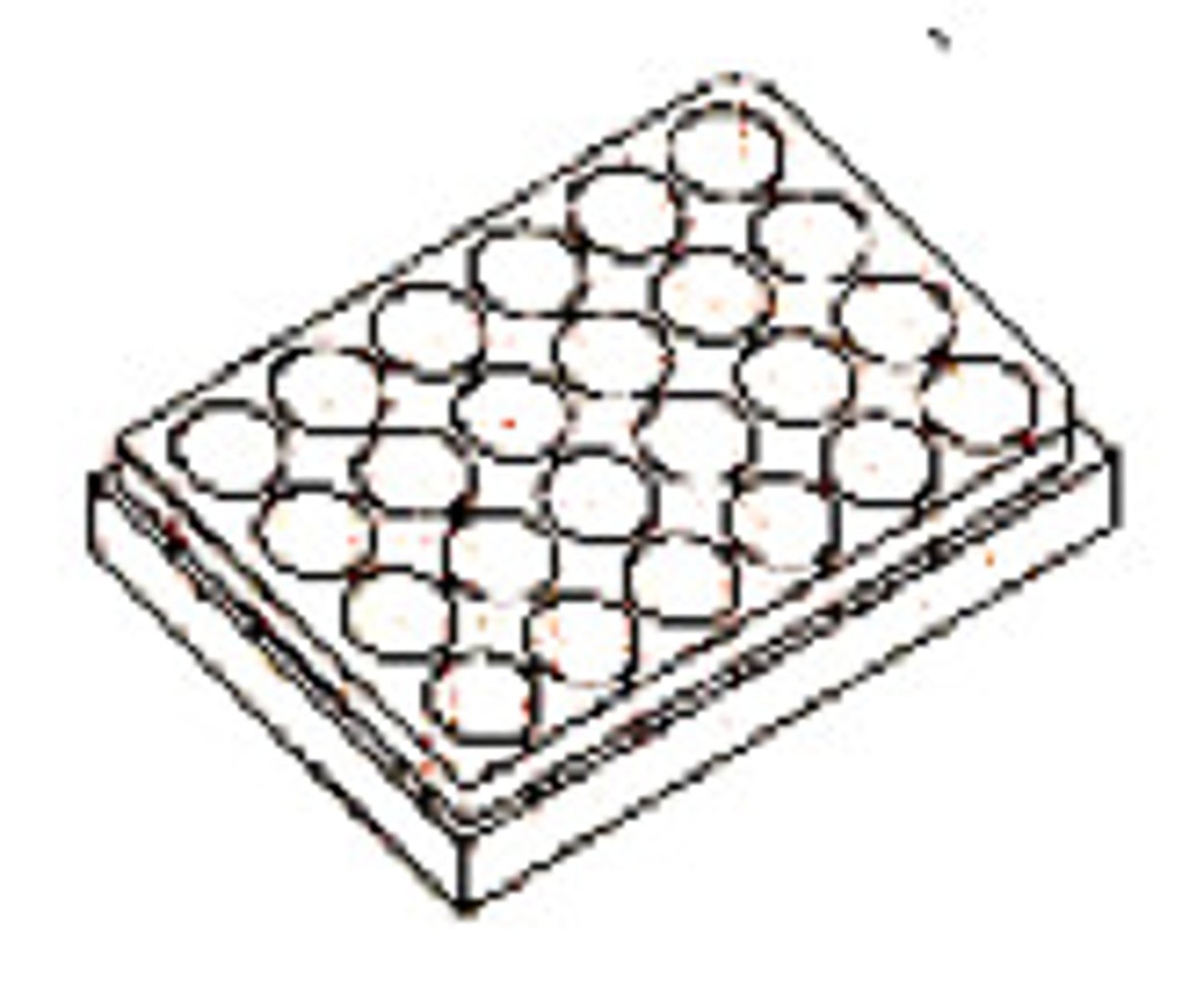
Spot Plate
Watch glass

Glass stir rod

Wire gauze

Funnel

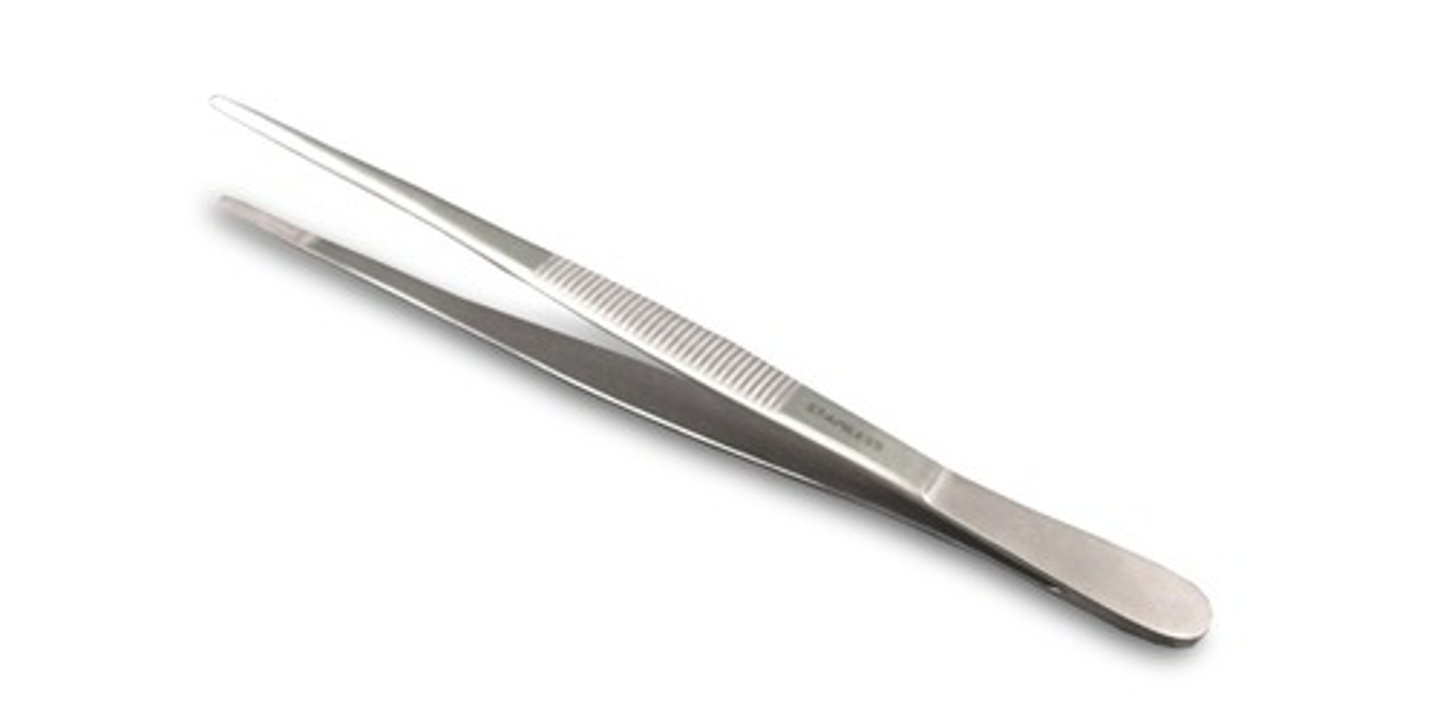
Forceps / tweezers

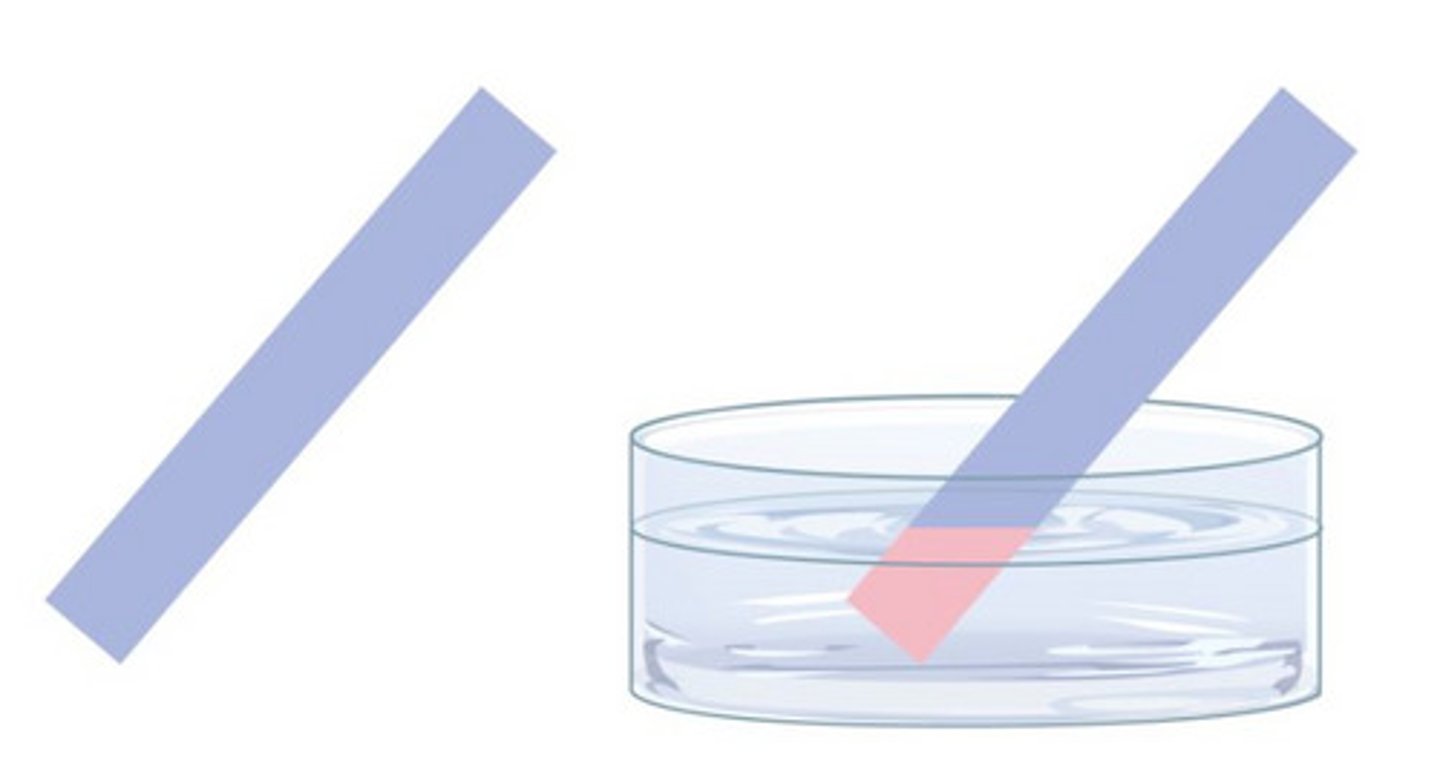
Litmus Paper
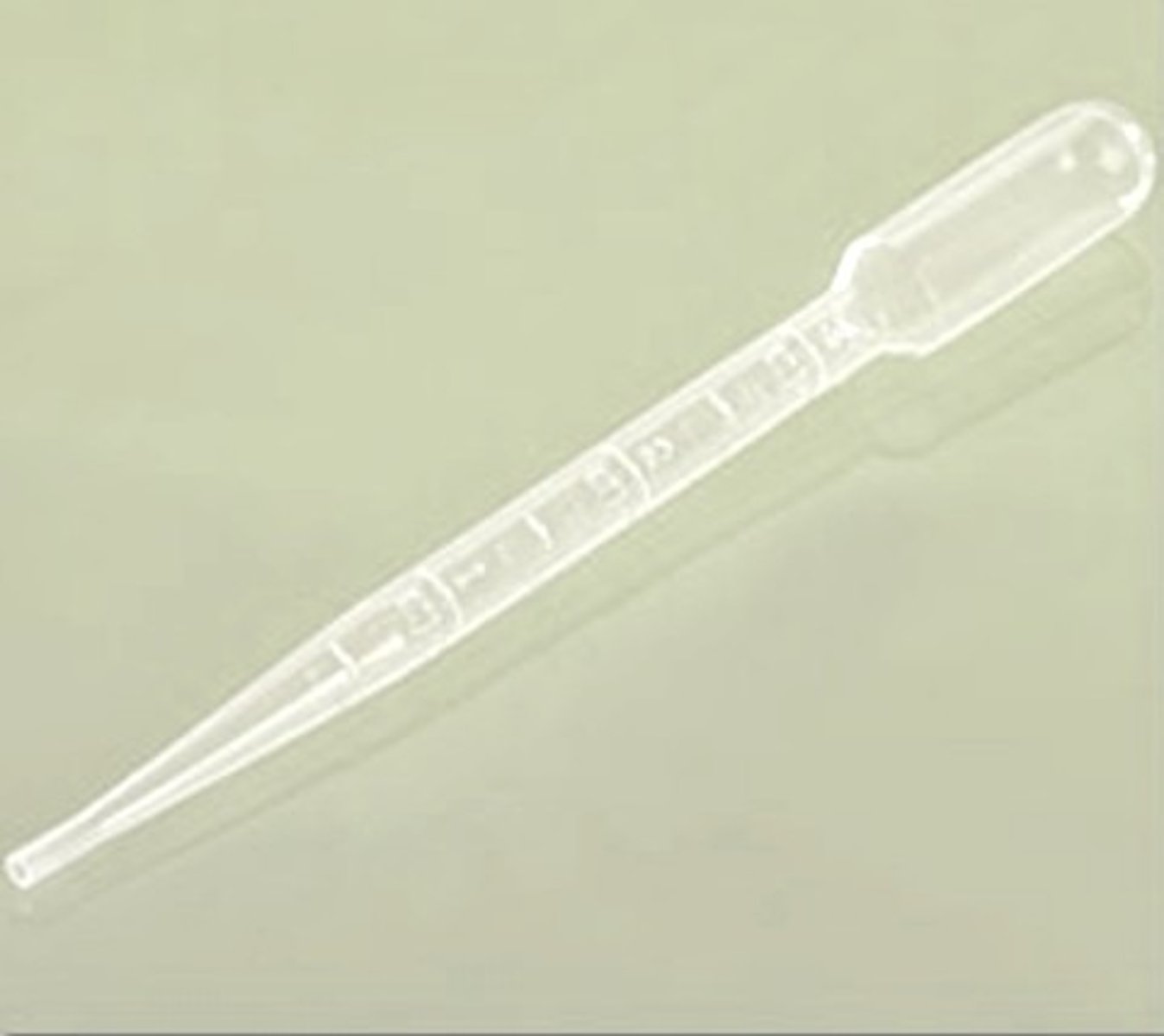
Pipet
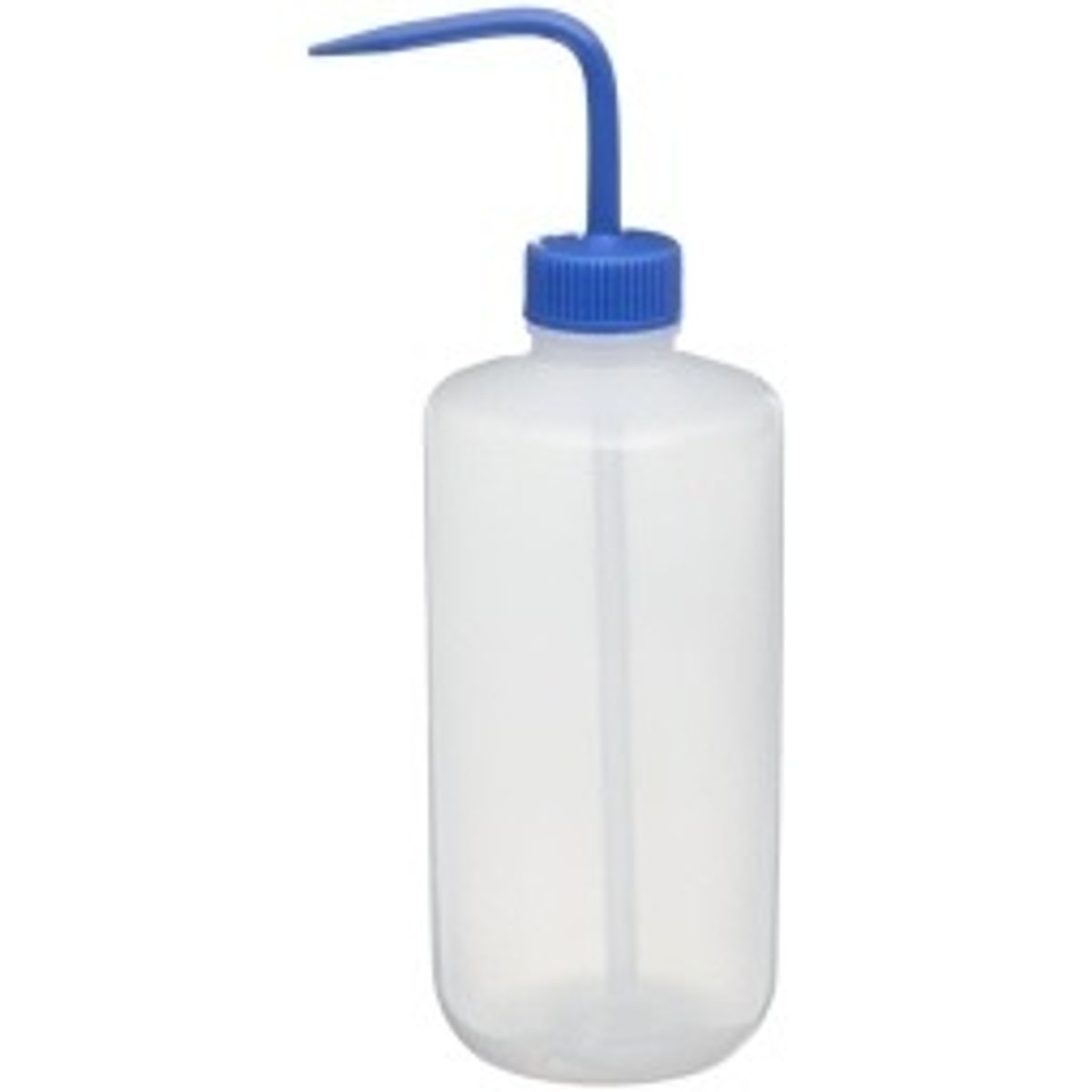
Wash bottle

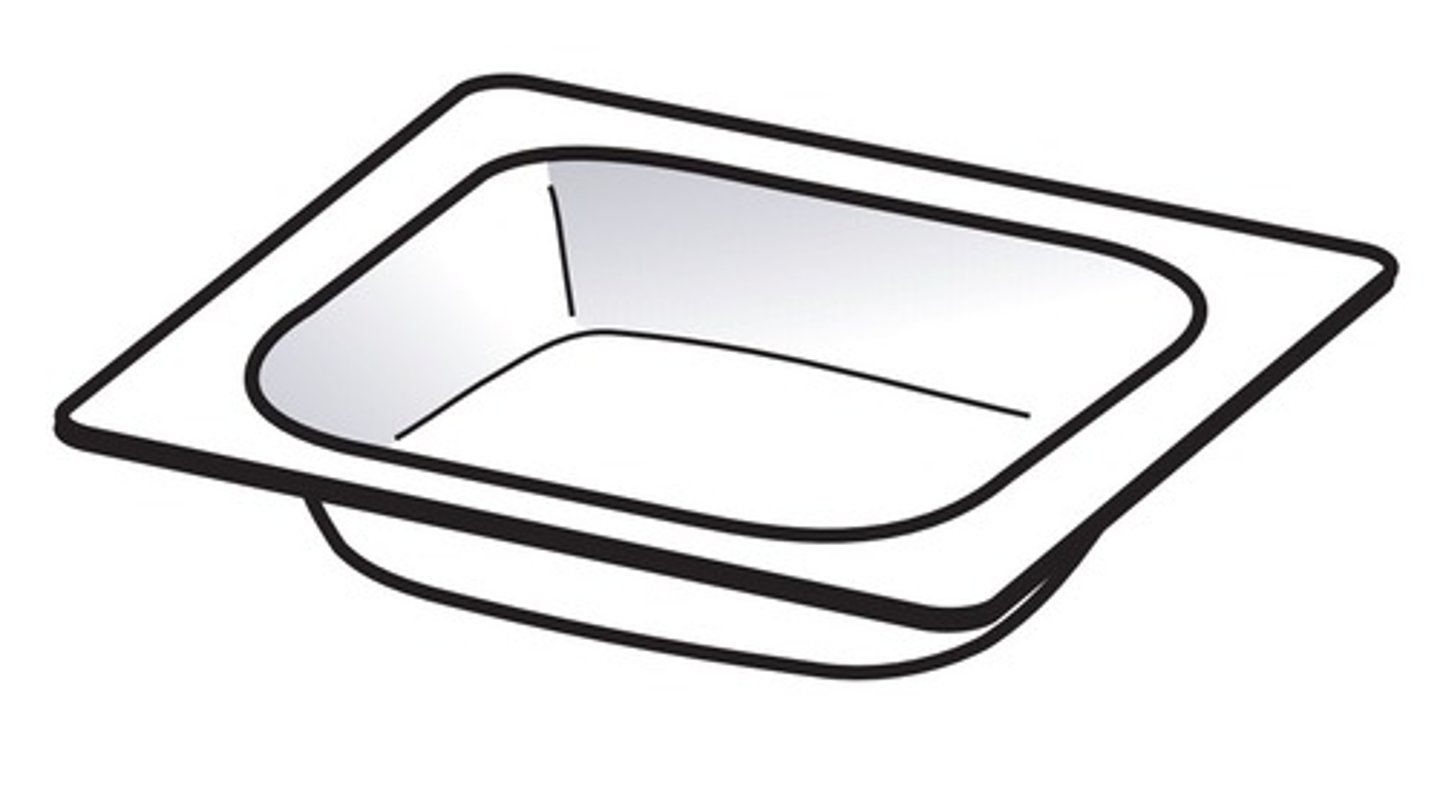
Weighing dish

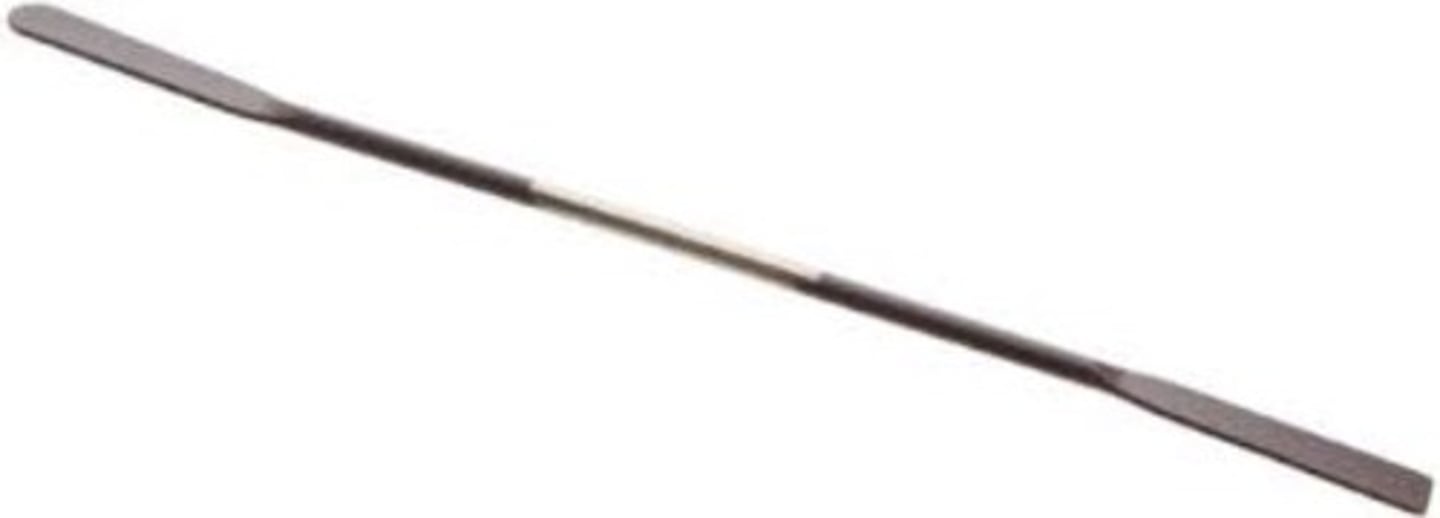
Spatula / Microspatula

Beaker tongs

Bunsen burner

Medicine Dropper

Crucible

Clay triangle

Crucible tongs

Glass Plate

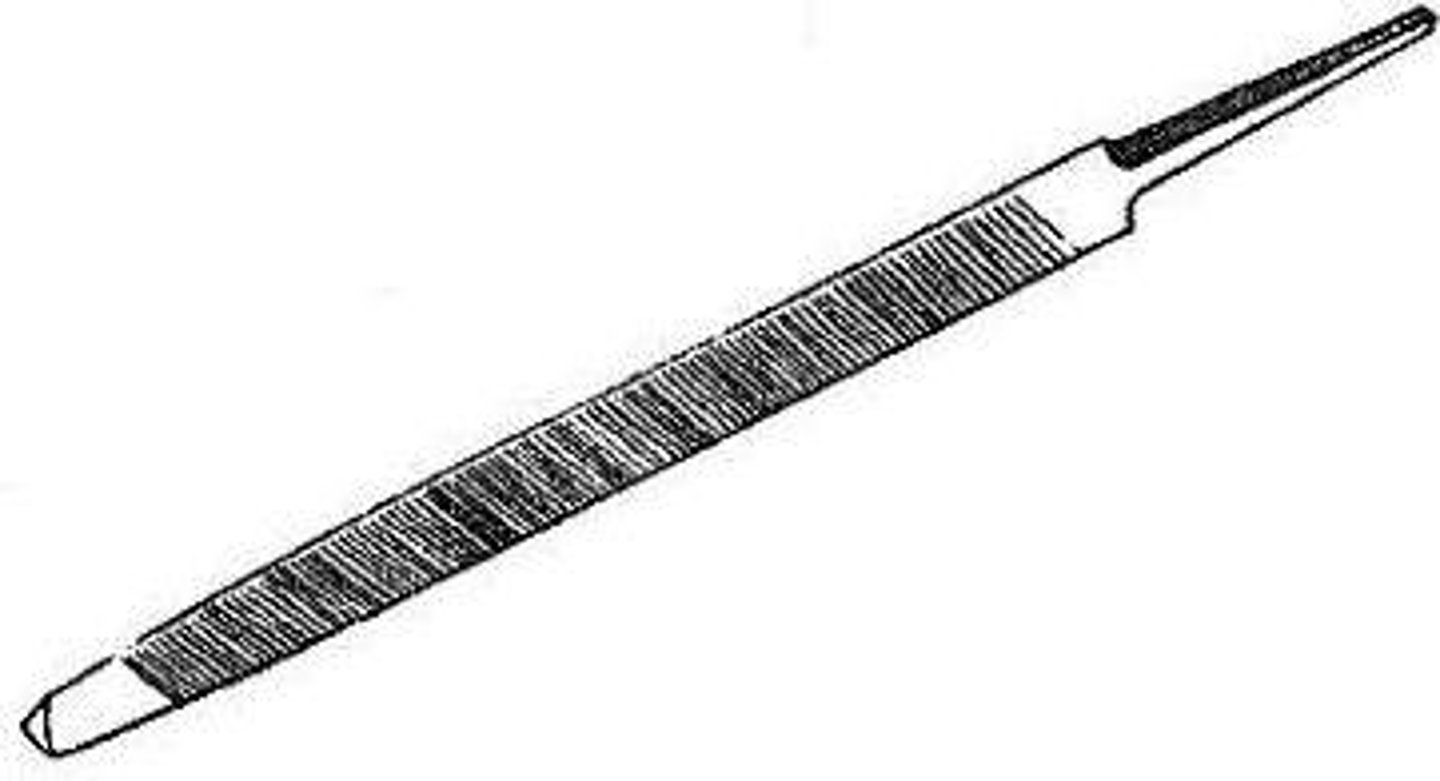
Triangular File
Ring stand

Iron Ring
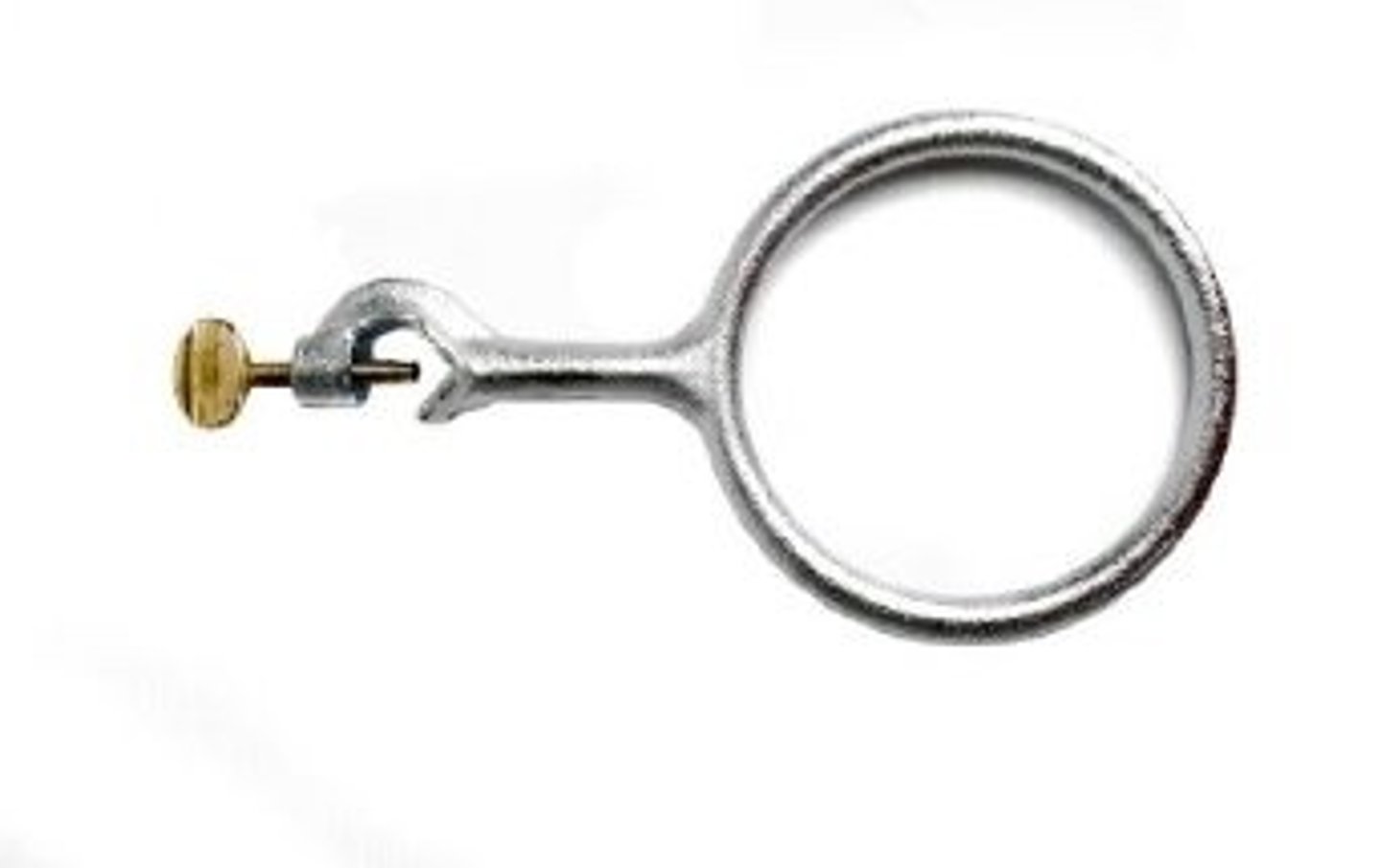

Utility clamp
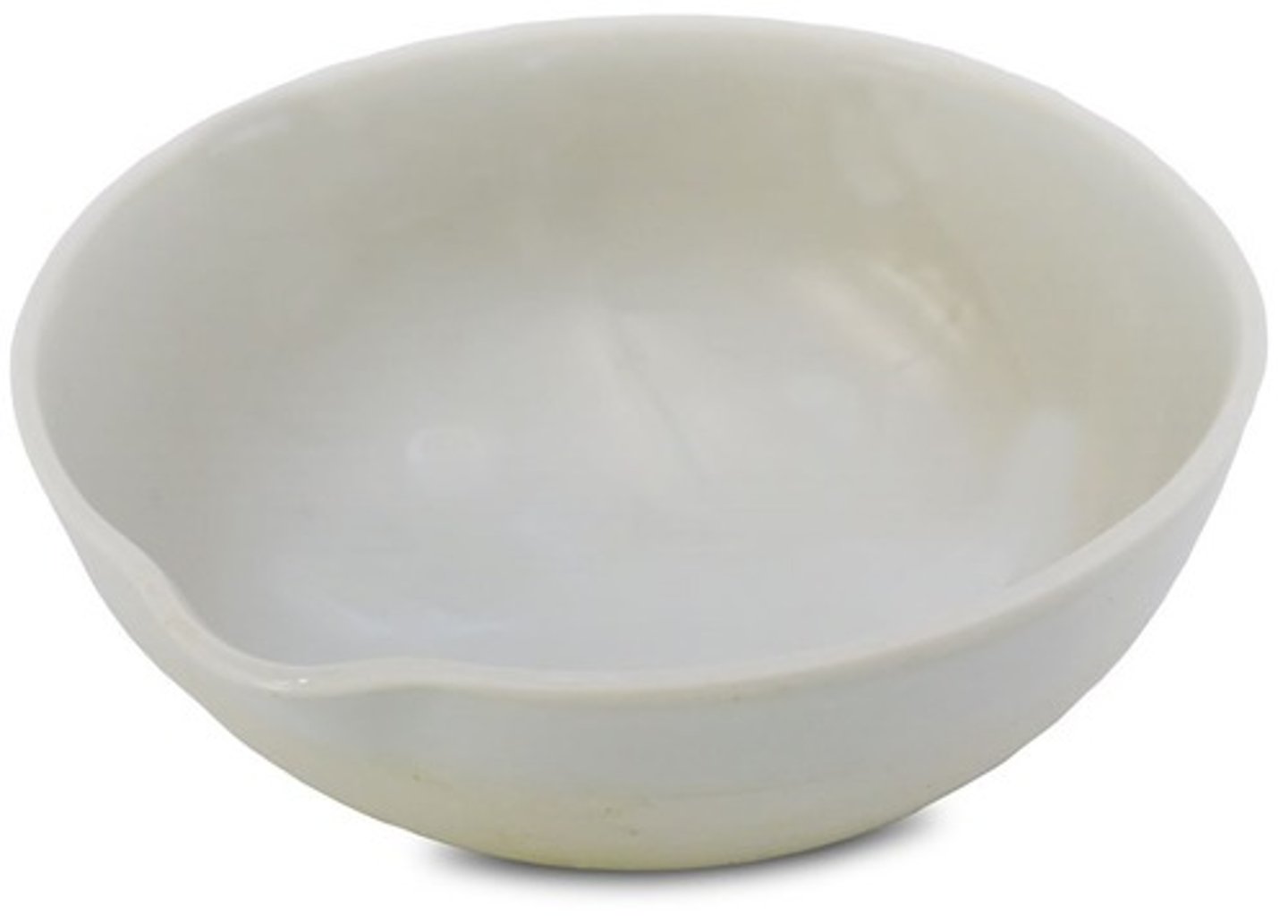
Evaporating dish

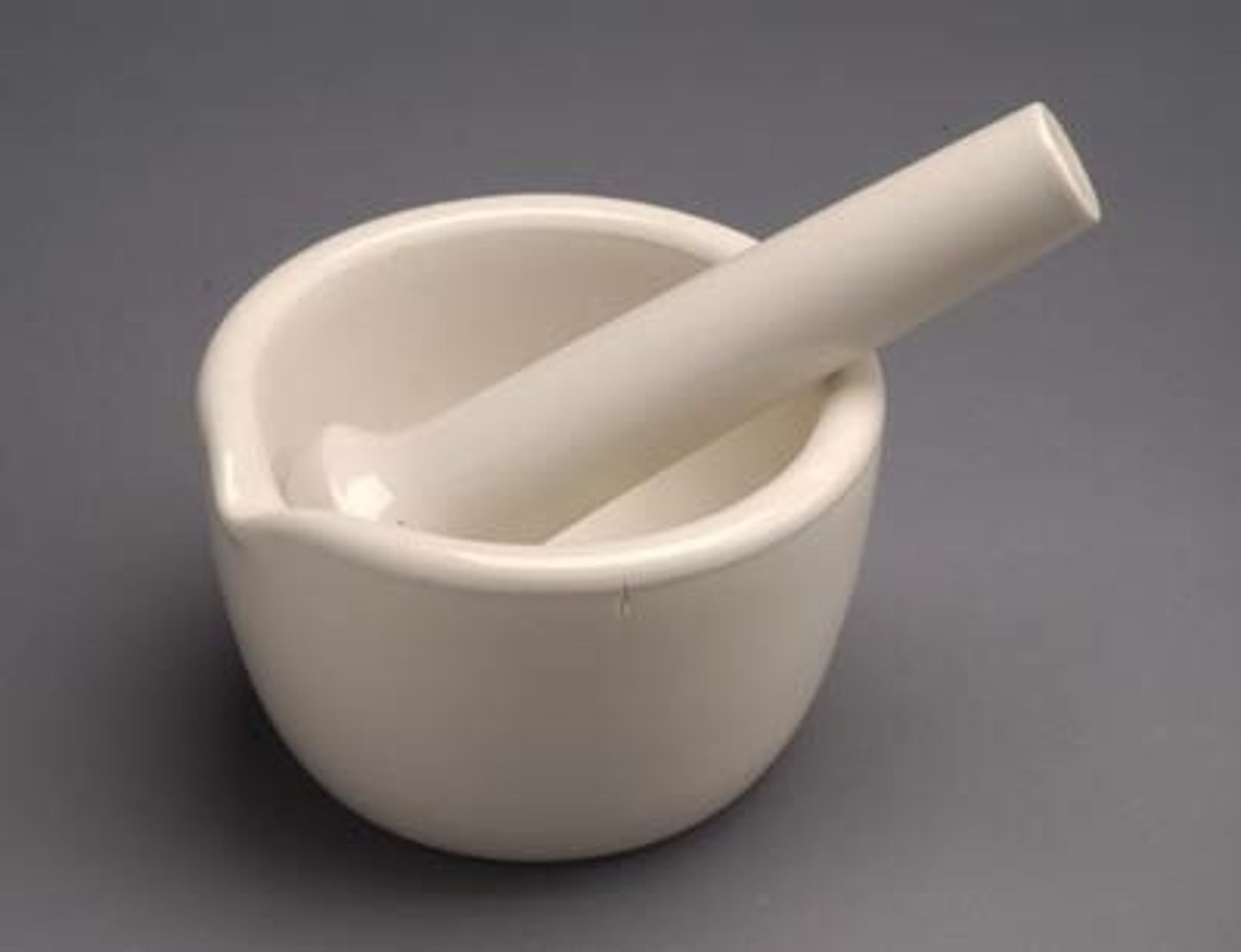
Mortar and pestle

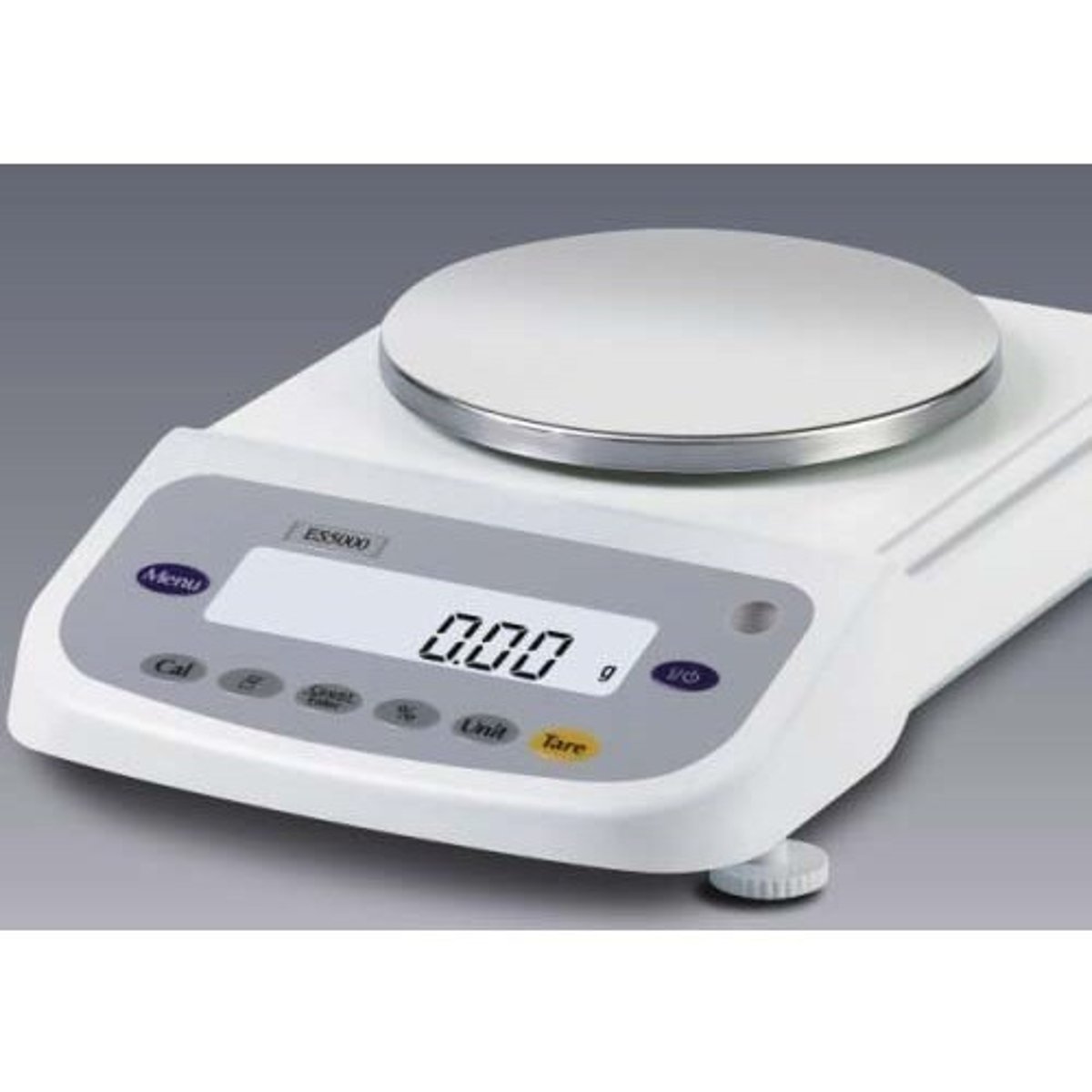
Electronic balance

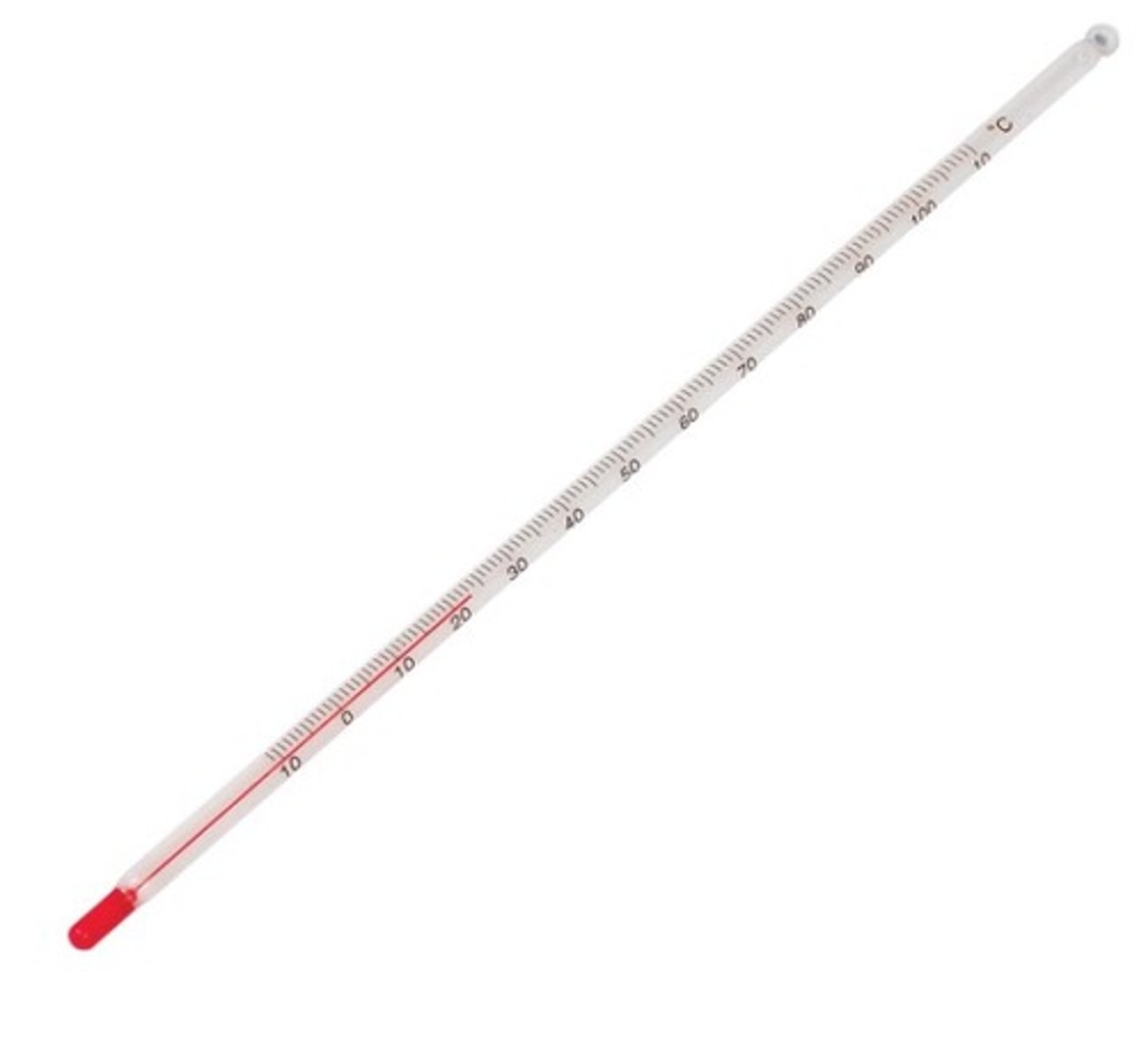
Thermometer

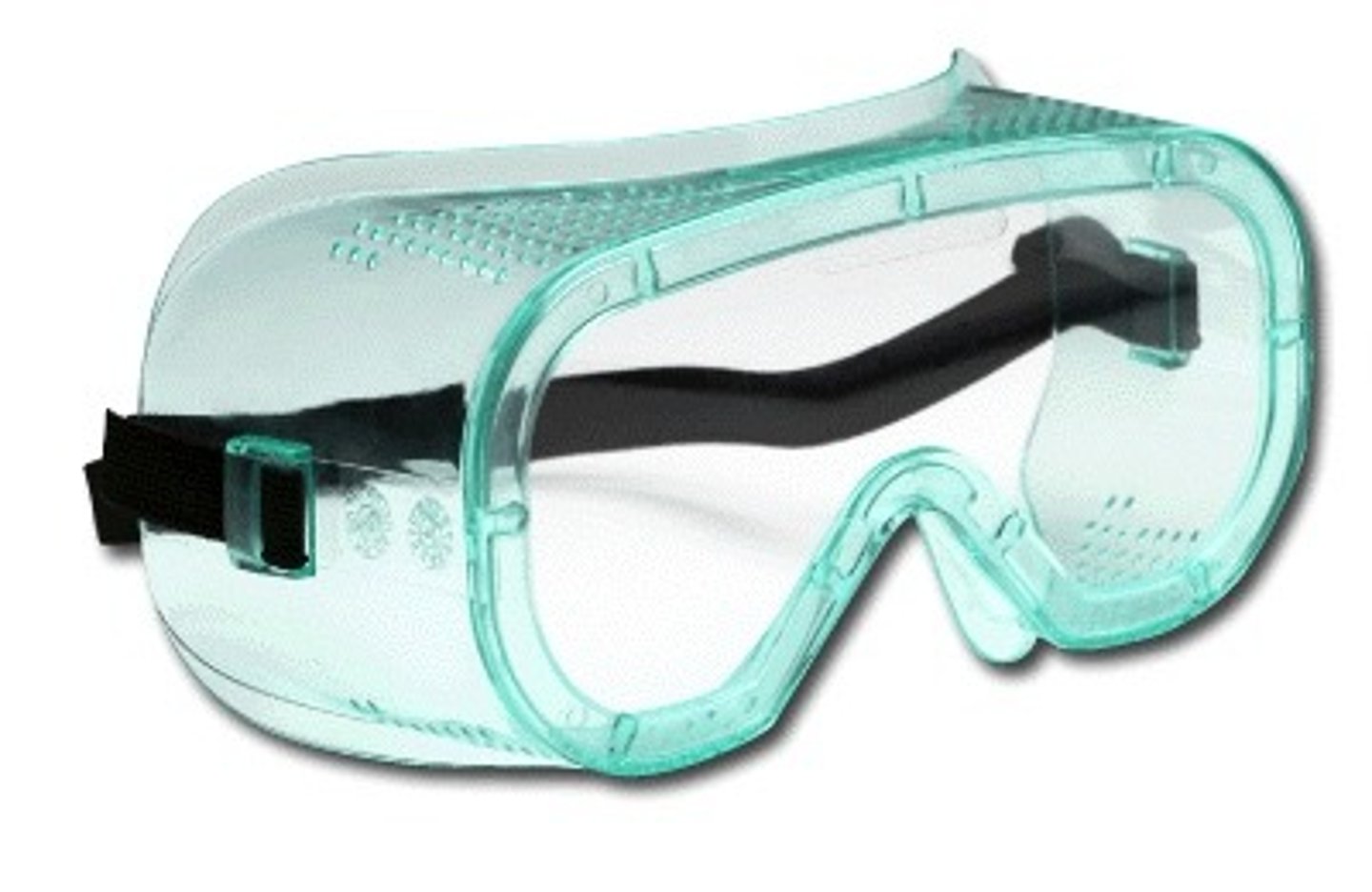
Safety goggles

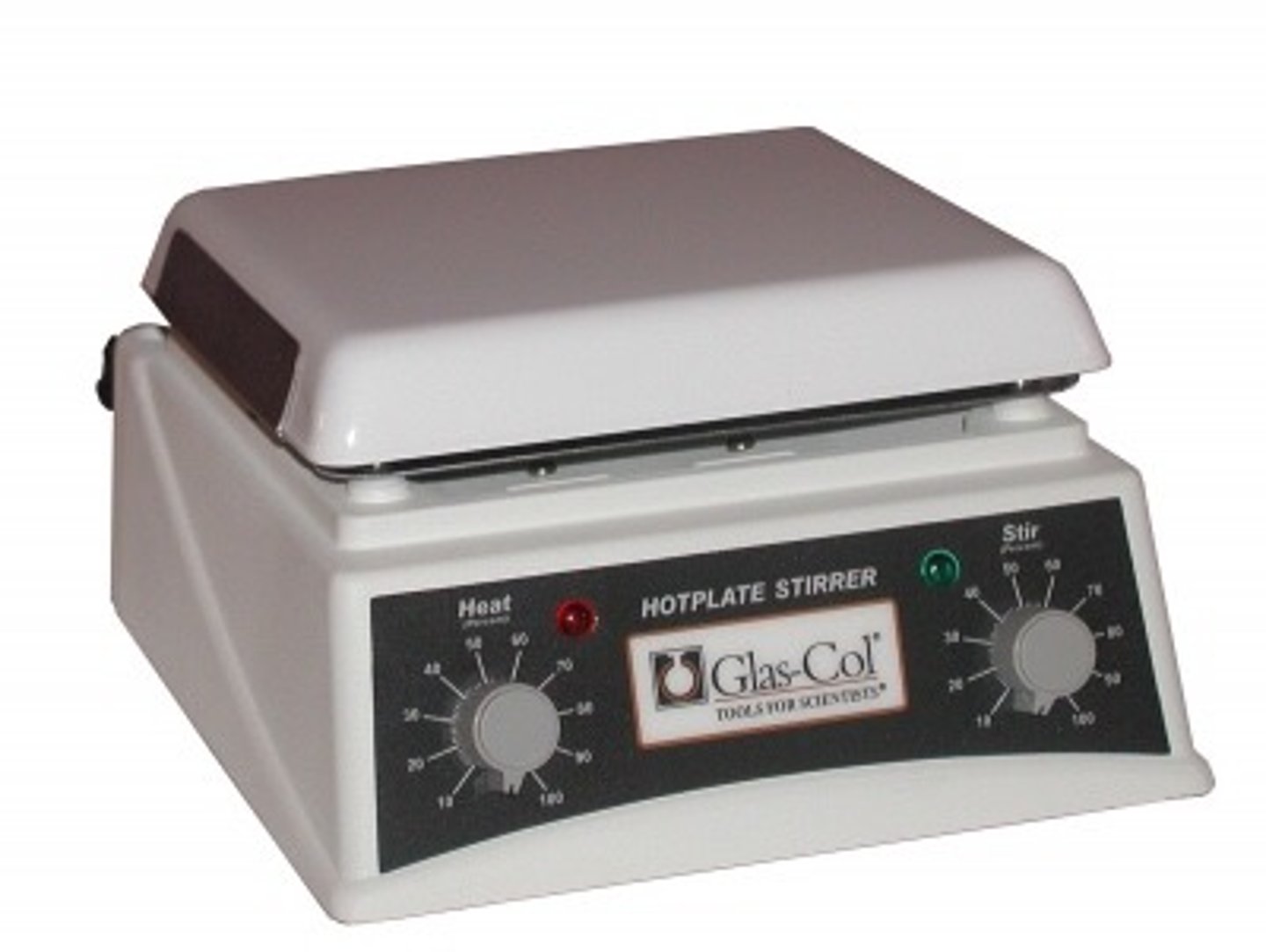
Hot plate

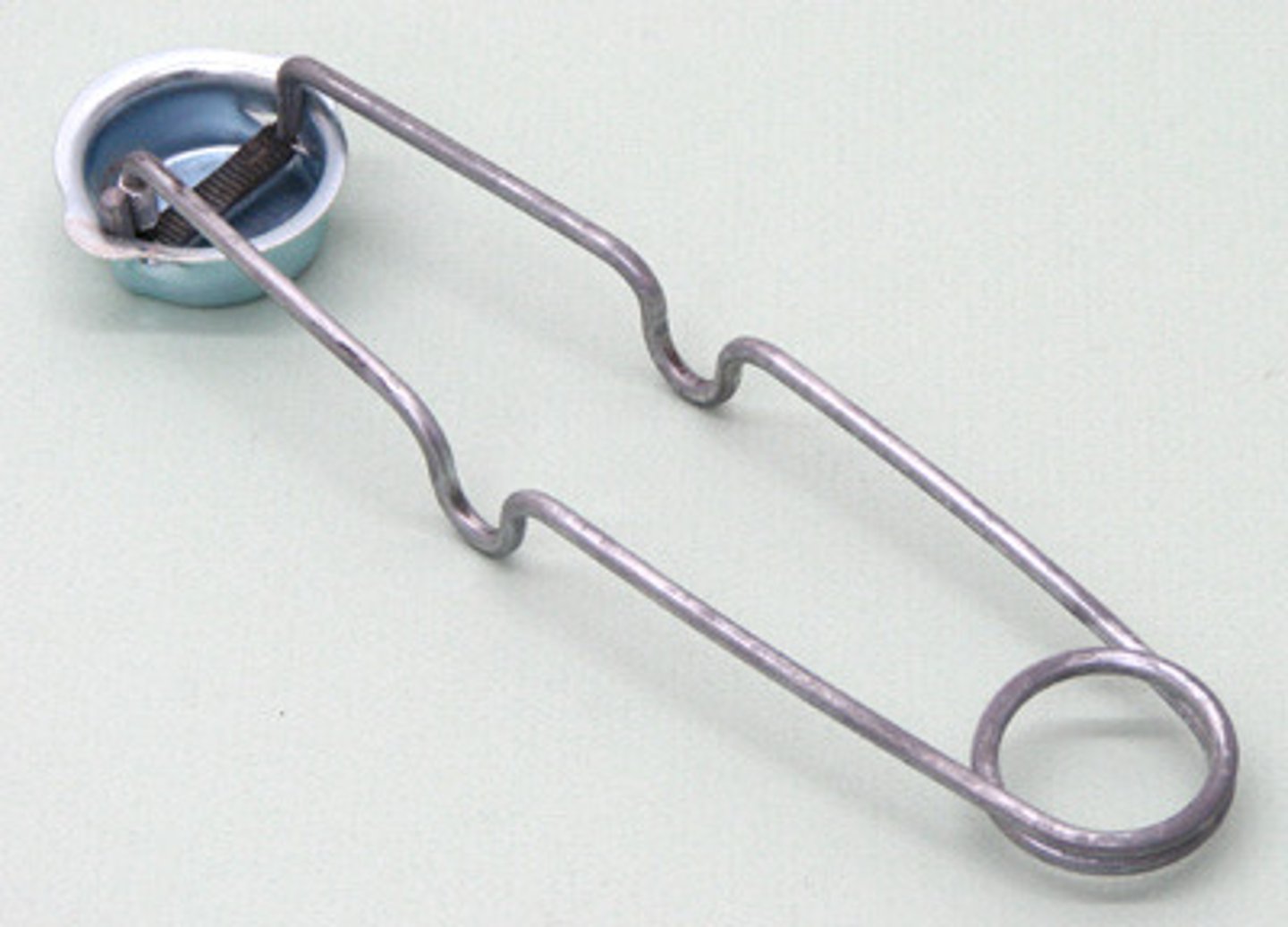
Striker

Meniscus
the curve at a liquid's surface by which one measures the volume of the liquid
water displacement
A technique for determining the volume of a solid placed into a liquid. You look at how much the liquid rises.
cm^2 to m^2
divided by 100^2 or (10,000)
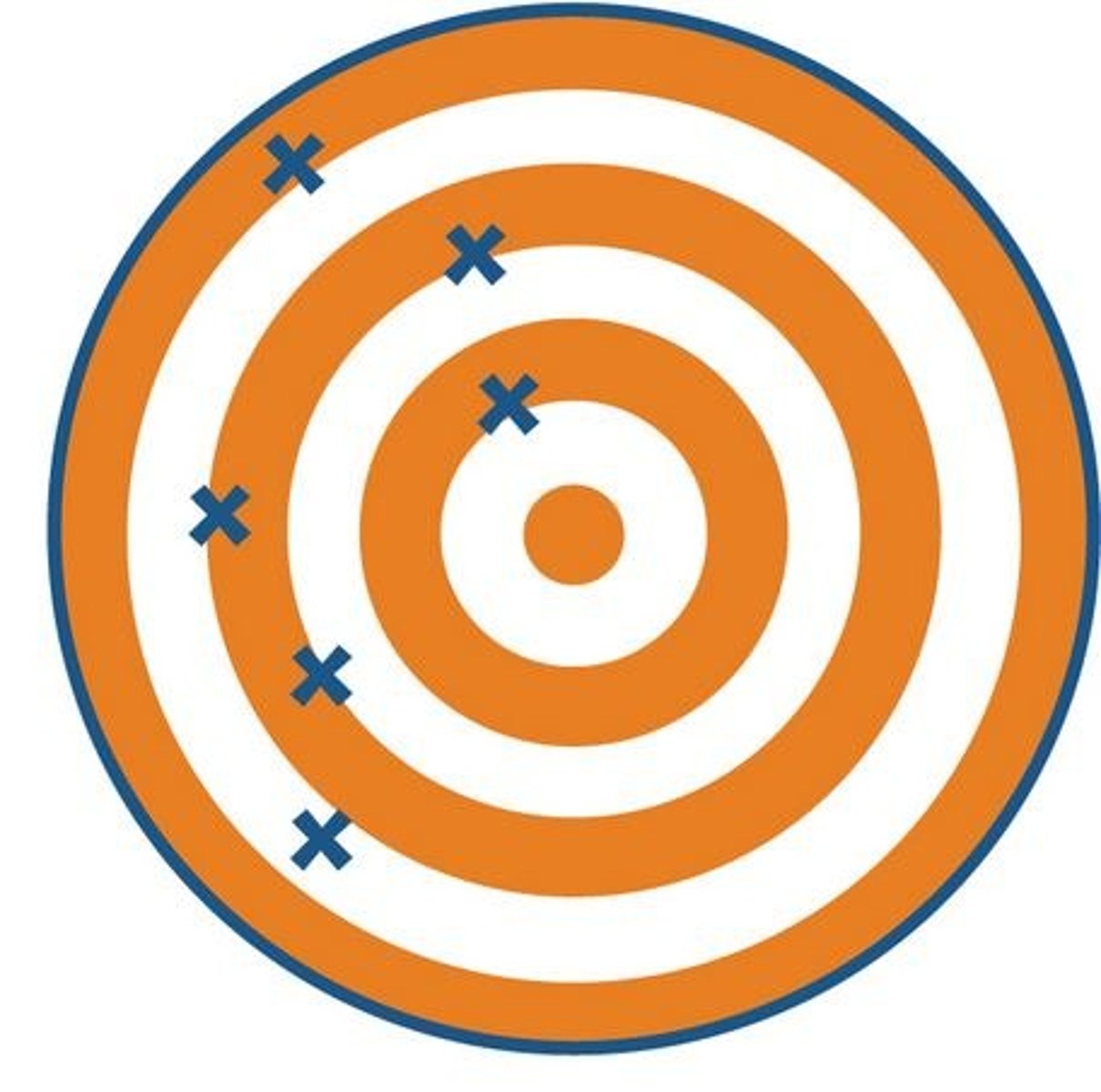
systematic error
Error that shifts all measurements in a standardized way. Decreases accuracy.
random error
Error that is due to chance and is not standardized. Decreases precision.
significant figures (sig figs)
communicate how precise measurements are
how many sig figs in 100
1 sig fig
how many sig figs in 0.050
2 sig figs
how many sig figs in 0.500
3 sig figs
how many sig figs in 3.040 x 10^4
4 sig figs
2.0 x 3.00 to the correct sig figs
6.0
2 x 3.0 to the correct sig figs
6
2.00 x 3.000 to the correct sig figs
6.00
4.0 + 1 to the correct sig figs
5
4.00 + 1.0 to the correct sig figs
5.0