Business GCSE topic 2.3 - Making operational decisions
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Purposes for business operations
To provide services
To produce goods
Types of production processes
Job
Flow
Batch
Job Production
Single product is made at a time
Products made for specific client and is high quality
Higher prices can be charged
Advantages of Job Production
Unique → Tailored to customers measurements and specifications
Less absenteeism → More motivated workers who are more productive
Higher prices charged
Disadvantages of Job Production
High labour costs → Skilled labour are expensive
Expensive to buy necessary equipment → Increase cost of products
No economies of scale → One person making that product
Economies of scale
Cost advantages that a business can exploit by expanding their scale of production
Batch Production
Small quantities of identical products are made
Used when business wants to make more than one item (ie → Bread factory makes crumpets and tortillas)
Advantages of Batch Production
Flexible → Production can change to meet customer needs or fluctuation in demand
Less labour involved → Due to the standard production of items through machines
Specialisation → Employees specialise in their areas to become good at their job
Disadvantages of Batch Production
Repetitive → Monotonous work so workers may be demotivated leading to inefficient productivity
If one batch takes too long, other batches will all be held up
Idle time between batches need to be managed as this is wastage as work stops while machines are changed to make the next product
Flow Production
Continuous movement of items through the production process.
Large numbers of the same goods are produced continuously in this production process.
Often an opportunity for a high level of automation on a flow production assembly line.
Advantages of flow production
Economies of scale can be achieved as cost per unit will be low
Automated assembly lines save time and money
Quality systems can be built into the production at each stage
Disadvantages of flow production
Standardised product produced
High initial set-up costs of automated assembly lines
Workers find work repetitive and boring
Logistics
Commercial activity of transporting goods to customers
Stocks
A share in the ownership of a company
Bar gate stock graph
Graph which gives a business a plan to make sure they do not run out of stock to sell
Diagram helps business to plan when to order more stock
High stock holding
Massive storage space and huge insurance along with a larger amount of manpower and warehouse maintenance cost.
Problems with high stock holding
Expensive and adds cost to business reducing profits
Business can be left with unwanted stock making it hard to compete on price due to stock holding costs
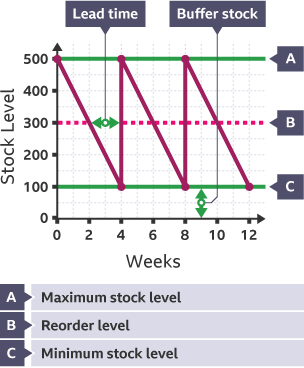
Parts of a bar gate stock graph
Max Stock Level
Re order Level
Min Stock Level
Lead time
Max Stock Level
Most a business can store in a shop or warehouse and business can’t share more stock as they don’t have space and will go out of date
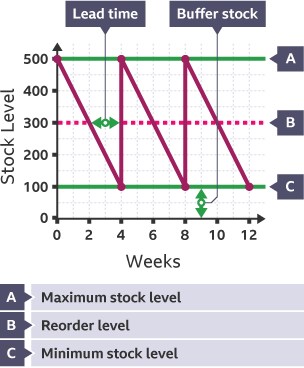
Reorder Level
Level of stock in a business that should signal when it is time to reorder
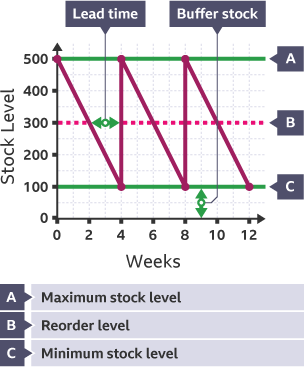
Min Stock Level (Buffer Stock)
Least a business should store, any less and they will run out and won’t keep up with demand
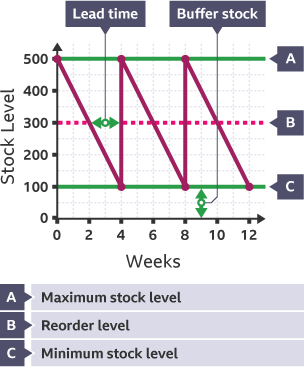
Lead time (Delivery time)
How long it takes from ordering stock for it to arrive
Just in time stock control
Business doesn’t keep stocks of parts in a warehouse but instead they order the parts and get them delivered the same day from the supplier
How to make JIT to work
Manufacturer needs to have great relationships with their smaller parts supplier
Times when JIT doesn’t work
Quality issues
Delivery issues
Advantages of JIT
Parts are ordered when needed so no wastage
Parts aren’t warehoused so costs are saved
Stocks less likely to be out of date
Business cash flow will improve
Disadvantages of JIT
Unable to meet unpredicted surges in demand
Unable to replace damaged parts quickly
Late delivery stops whole production line
Procurement
Where business buys raw materials, components, products, services from suppliers to make their own products/services
Relationships with suppliers on quality
Business wants its suppliers to sell them the best possible quality products for the price
Relationships with suppliers on delivery
Some businesses may wish to enter into JIT agreement with a supplier involving number of deliveries being made a day
Relationships with suppliers on availability
There’ll be problems if the stock isn’t available which may stop production entirely and if products are still out of stock, customers will shop elsewhere
Relationships with suppliers on cost
Both sides want deal to last a long time to reduce costs of having to find another supplier or customer or renegotiate another deal
There’ll be initial costs in setting up agreements such as administration
Relationships with suppliers on trust
Important for joint problem solving and open communication between the businesses which is what makes a great relationship.
Trust is built through reliable deliveries and quality products/services
Quality
Measure of excellence or a state of being free from defects, deficiencies and significant variations
Ways to preserve quality
Quality Control
Quality Assurance
Quality Control
Inspectors check standards have been met at end of production process:
Standards consistent ensuring quality standards are met
Customer doesn’t receive a sub-standard product
Advantages of Quality Control
Controlling quality means less wastage
Less wastage means lower cost of production
Disadvantages of Quality Control
Faulty goods means costly wasted resources/materials
Could be a lot of waste as the fault is only identified at end of production process
Quality Assurance
Building quality into every stage of production process and isn’t left until the end
When product is sold, business can assure customer it’s a quality product
Each worker is responsible for making sure that the work they do meets quality standards
Advantages of high quality products
Differentiate products from competition increasing product range → Bring more customers → Increase brand awareness → Brand loyalty → Charge premium price for product → Increase sales revenue
Disadvantages of high quality products
Extra quality control checks → Employee specialisation training needed → Cost per unit increases → Reducing profits
Steps of the sales process
Product knowledge
Speed and efficiency of service
Customer engagement
Response to customer feedback
Providing good customer service
Product knowledge
Understanding features allows sales person to present their benefits accurately and persuasively
Customers respond to enthusiastic sales staff who’re passionate about their products and eager to share the benefits with them
Speed and efficiency of service
Customers expect a fast service with the correct order
Customer engagement
An effect, reaction, response, experience of customers with one another, with a company or brand
The initiative for engagement can be either consumer or company led and the medium of engagement can be on or offline