Speed + Distance, Displacement, Velocity + Acceleration + Velocity time graphs
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Speed equation
Speed = distance/ time
V=s/t
Units for acceleration
deceleration
(m/s²)
how fast the velocity is changing when an object slows down.
Typical speed (m/s) for:
Sound, walking, jogging, bike
Sound - 300-360 m/s
Walking - 1.5 m/s
Jogging - 3 m/s
Bike - 6 m/s
Instantaneous speed
The speed of an object at a particular moment in time.
Average speed
The total distance the object travels divided by the total amount of time taken.
Distance time graphs:
What is on the y axis?
distance
Distance time graphs:
What is on the x axis?
time
Distance time graphs:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
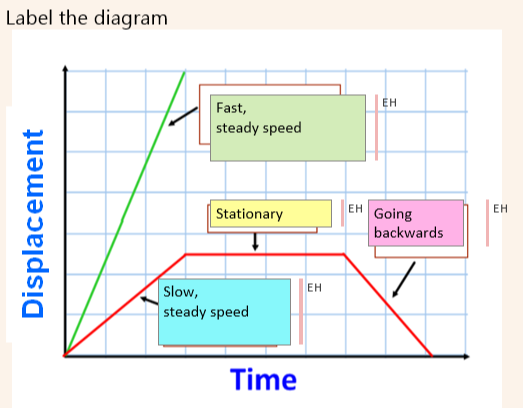
Distance time graphs
Scalar meaning
having only magnitude, not direction.
Vector meaning
a quantity having direction as well as magnitude, especially as determining the position of one point in space relative to another.
Distance def
Displacement def
Distance | How far the object has travelled in metres - scalar |
Displacement | distance in a given direction - vector. |
How do you calculate the speed in a displacement-time graph?
To calculate the speed you need to divide the distance by the time taken. This is the gradient of the straight line.
Reminder of how to calculate the gradient
gradient = rise/run
Therefore speed is:
speed = distance traveled/ time taken
Speed just tells us how fast something is moving.
Velocity tells us how fast something is moving AND what direction it is moving in.
Speed just tells us how fast something is moving.
Velocity tells us how fast something is moving AND what direction it is moving in.
Def of these key words:
Magnitude
Scalar
Vector
Another word for size
Just magnitude
Direction and magnitude
Acceleration def
is a measure of how quickly an object changes velocity or 'the rate of change of velocity'.
word equation for acceleration:
acceleration = change in velocity/ time taken
symbol equation for acceleration:
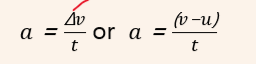
Velocity time graphs:
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 possible meanings of negative acceleration
slow down - deceleration
Going backwards
How Velocity time graphs work:
acceleration
displacement
describing the motion using words
Calculate the acceleration (this is the gradient of the line),
The displacement (the area under the line(triangles and rectangles)),
Describe the motion using words.
How do you find out how far an object has traveled using the velocity-time graph?
Finding the area under the line.