Economics Semester 1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Price Elasticity of Demand
The responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price of a product. It is a measure of how sensitive buyers are to a change in price.
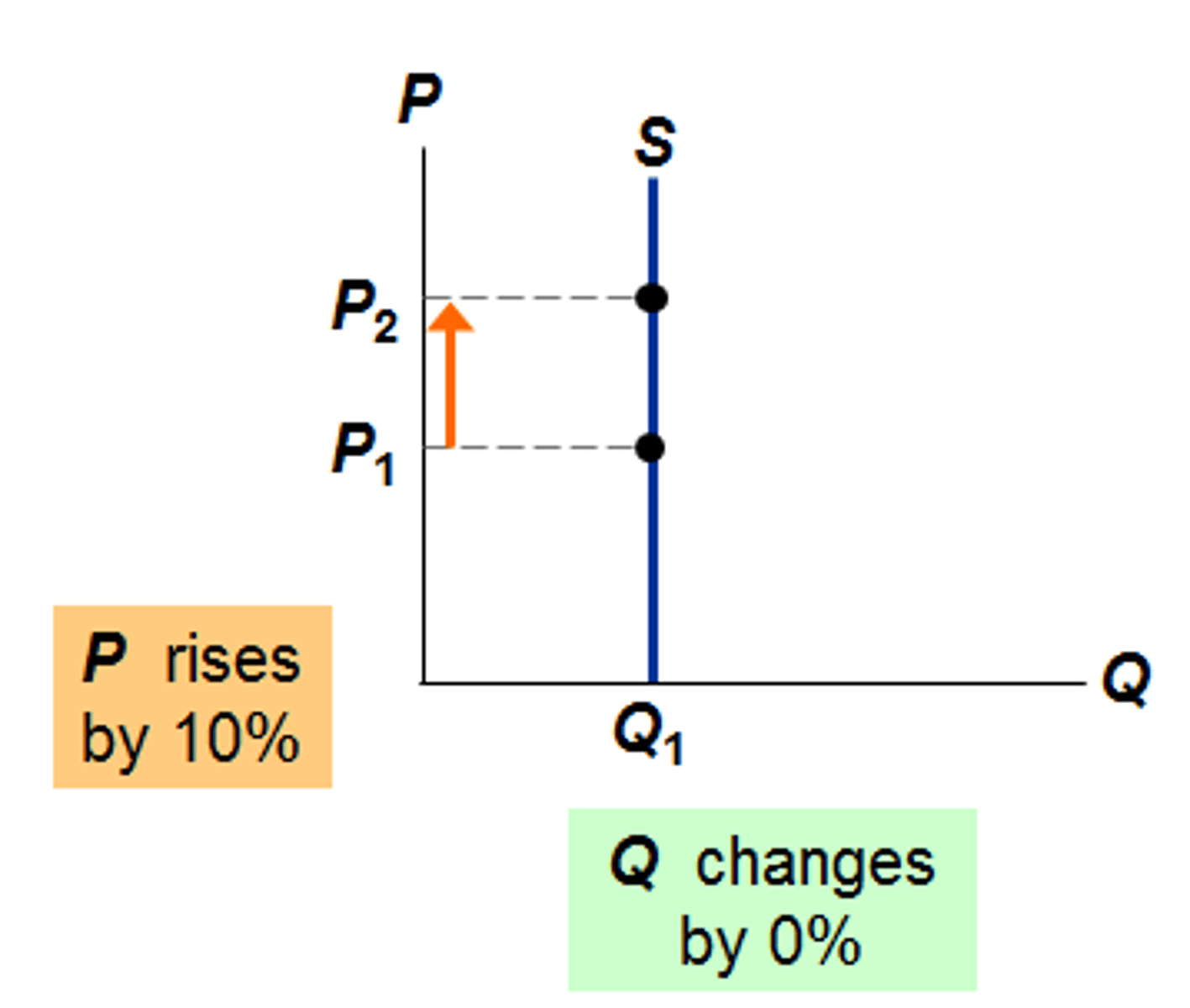
PED = 0
- Perfectly INELASTIC
- Change in P will not change Qd
- Usually necessary for survival
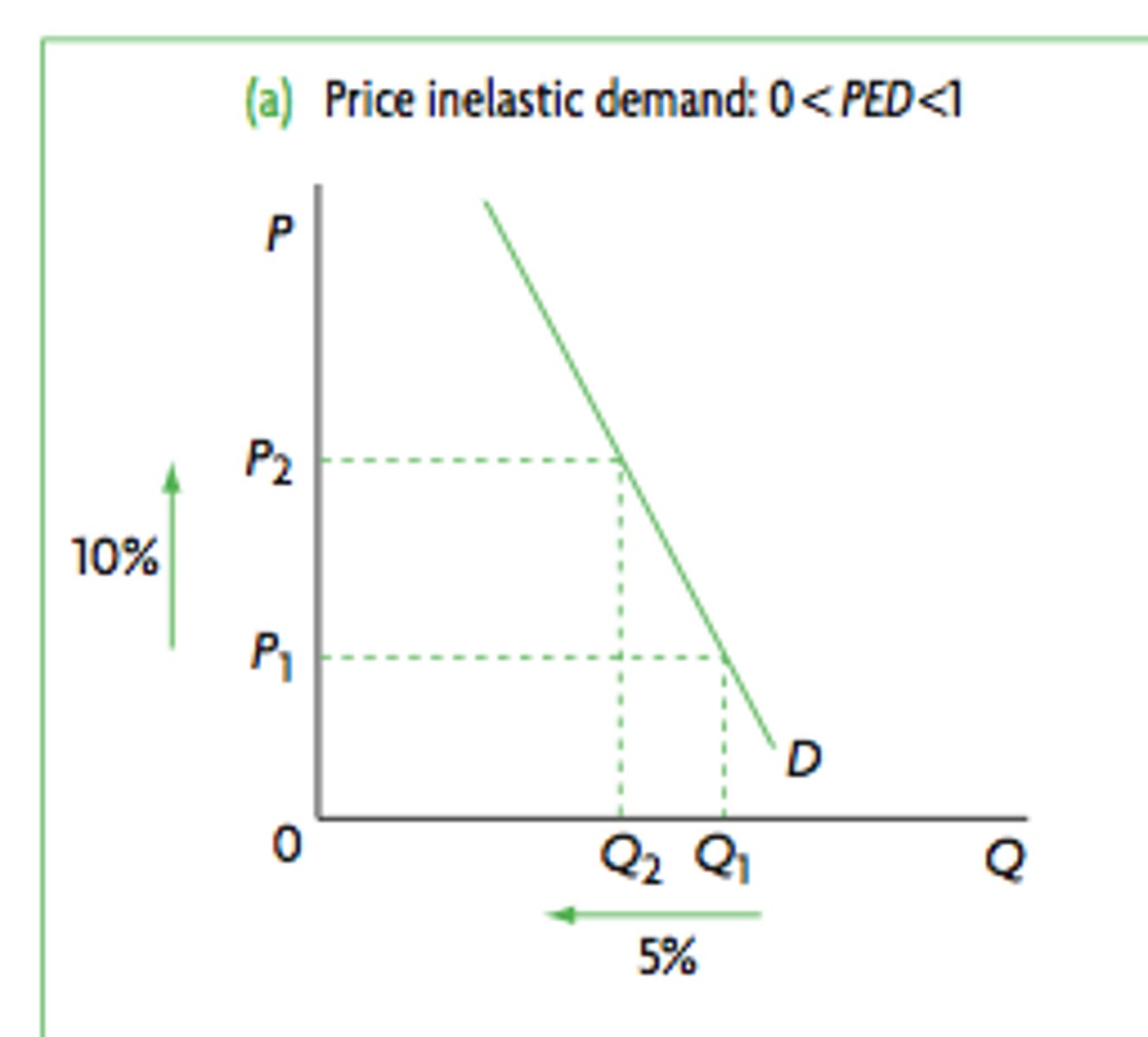
PED < 1
- Relatively INELASTIC
- If P⬆️ by 1% Qd will ⬇️ by <1%
- Less sensitive to change in P
PED = 1
- Unitary ELASTIC
- The same change will occur on both axis
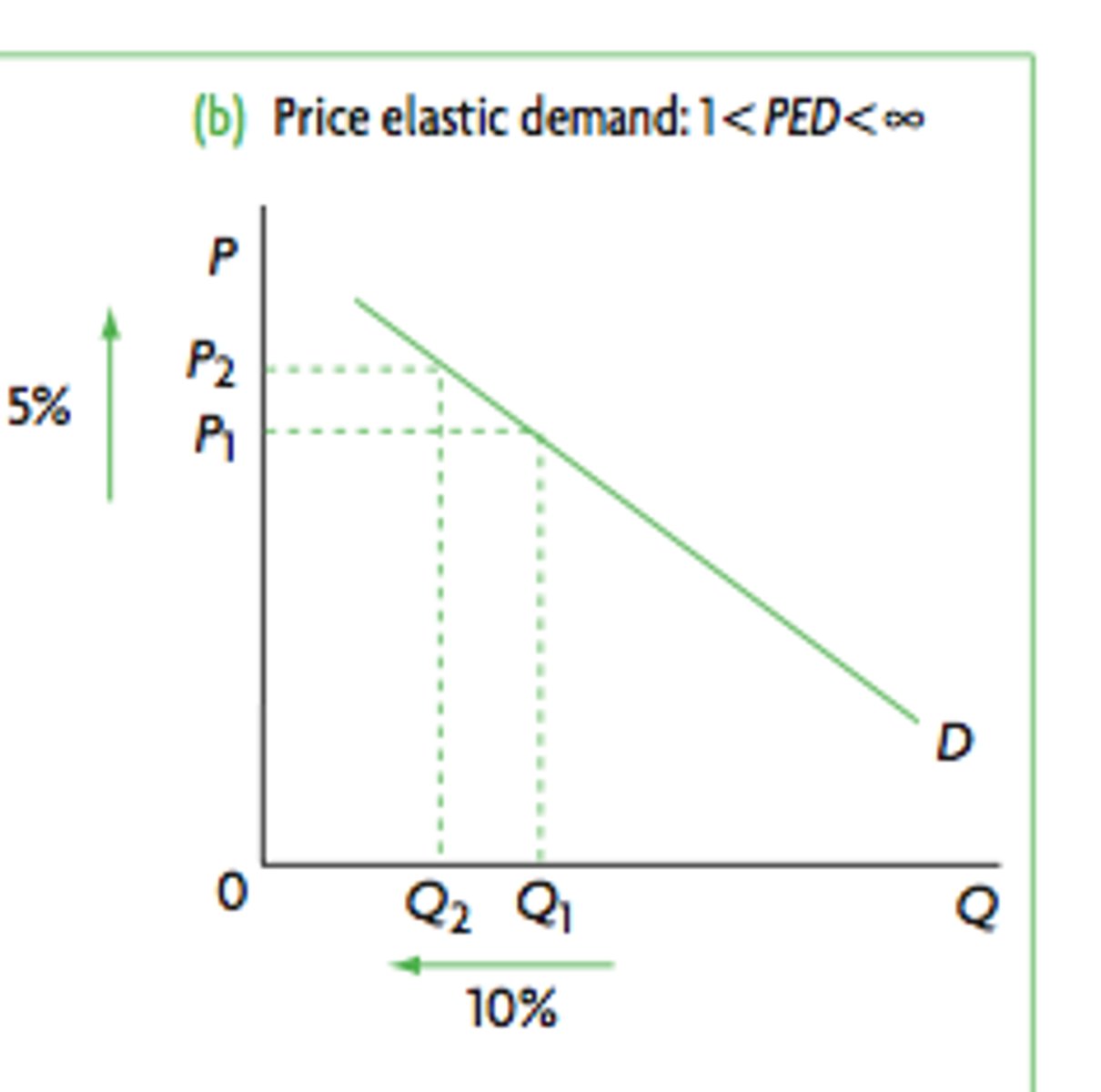
PED > 1
- Relatively ELASTIC
- If ⬆️ in P by 1% Qd will ⬇️ by > 1%
- More sensitive to ⬆️ in P
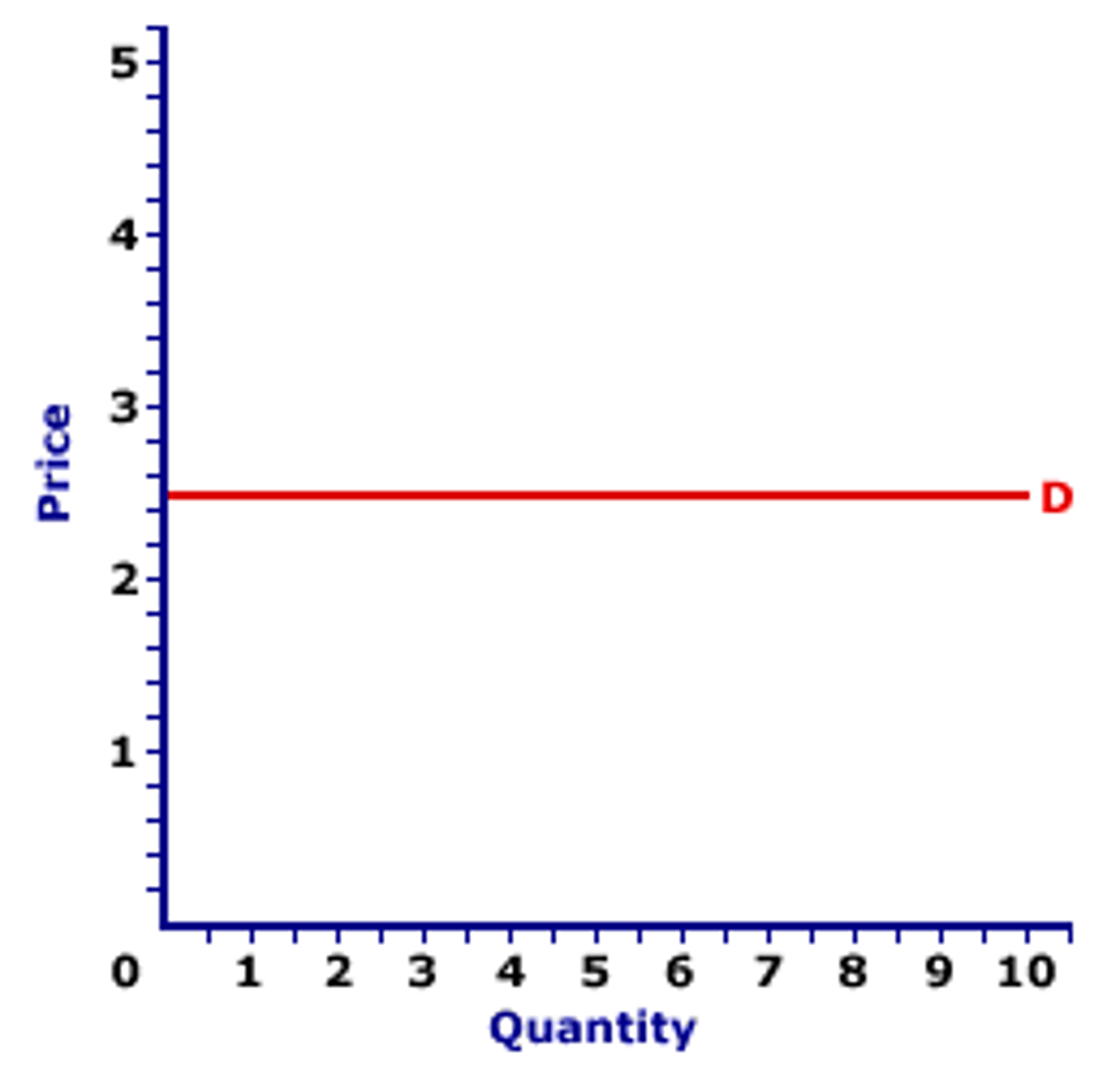
PED = Infinity
- Perfectly ELASTIC
- Any ⬆️ in P consumers will stop buying
- Usually goods with perfect substitues
Determinants of PED
- Availability of substitutes
- Proportion of income spent
- Necessity or luxury?
- Time
- Definition of a market
PED Determinant - Availability of Substitutes
- The greater the substitute the more elastic
- Demand for good that have few substitutes are inelastic
- More sensitive to change in price (can switch to other products)
PED Determinant - Proportion of income spent
- Little of our income = more inelastic
- Lots of income = more elastic
PED Determinant - Necessity or Luxury?
- If necessity = inelastic
- If luxury = more elastic
PED Determinant - Time
- How long consumers have to shop around / delay purchase
- More time = more elastic
PED Determinant - Definition of a Market
- Broadly defined market = more inelastic
- Narrowly defined market = more elastic
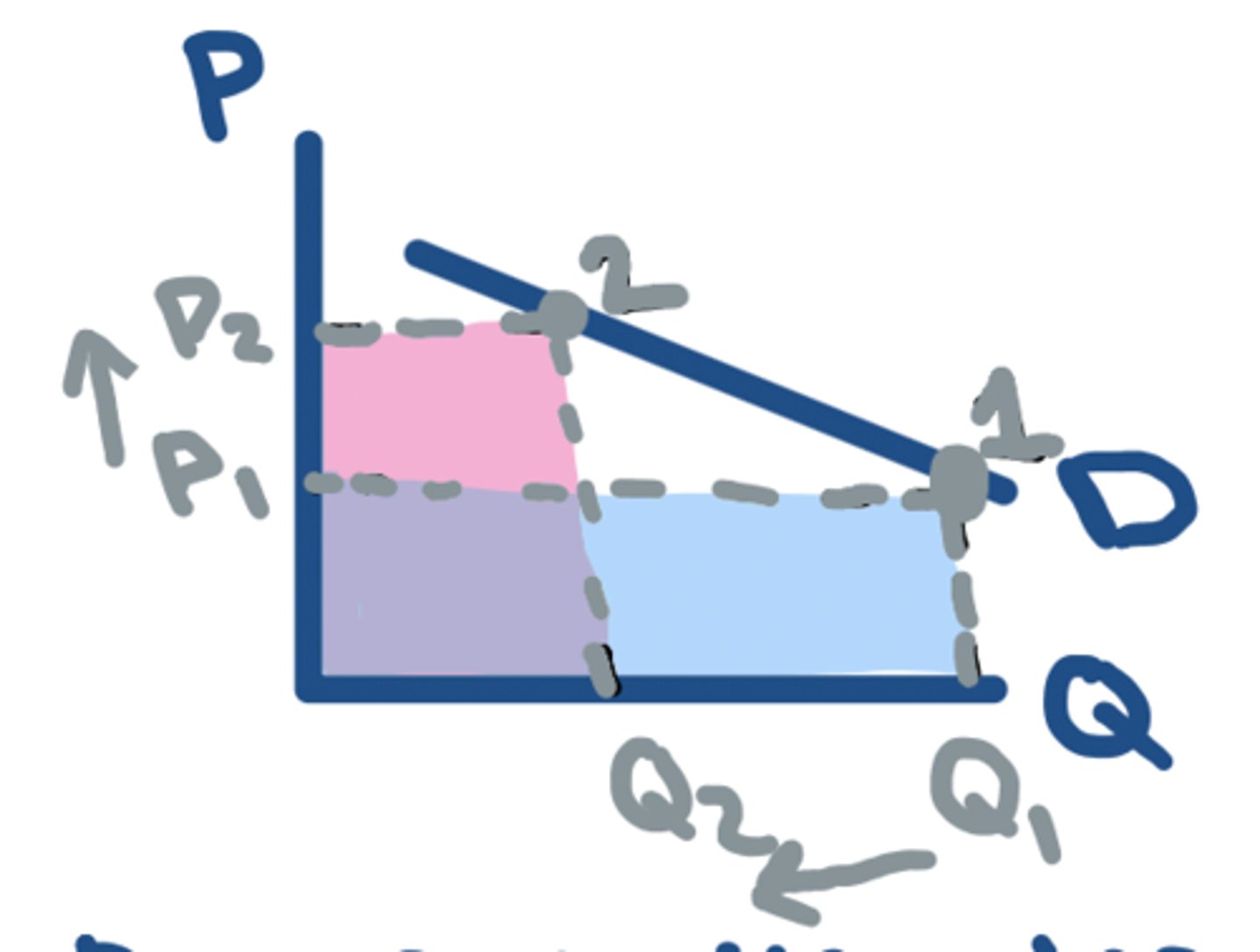
TR: P⬆️ - ELASTIC
⬆️ in P = ⬇️ in TR
- P and TR move in opposite directions
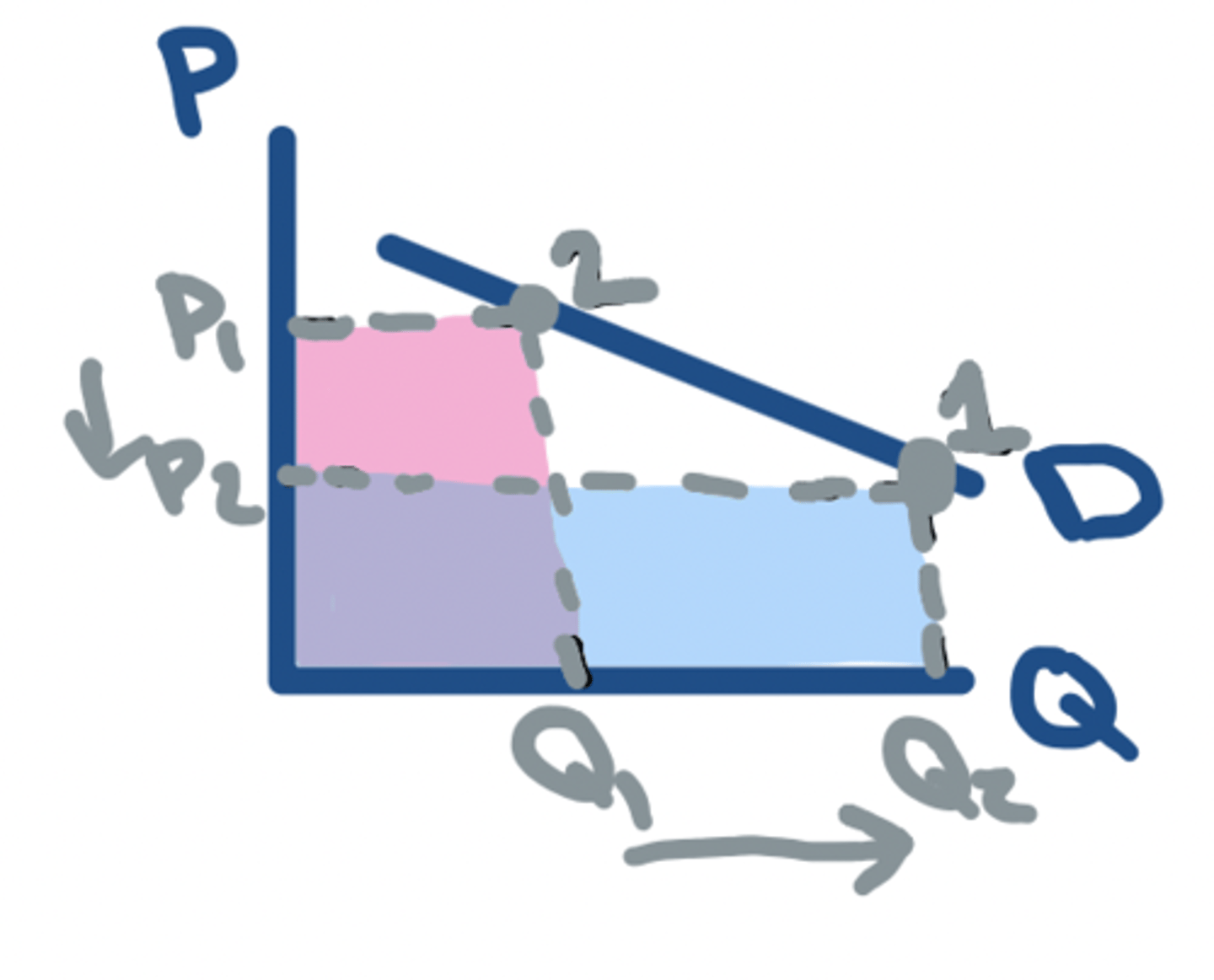
TR: P⬇️ - ELASTIC
⬇️ in P = ⬆️ in TR
TR: P⬆️ - INELASTIC
⬆️ in P = ⬆️ in TR
TR: P⬇️ - INELASTIC
⬇️ in P = ⬇️ in TR
Price Elasticity of Supply
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity supplied of a good to a change in the price of that good.
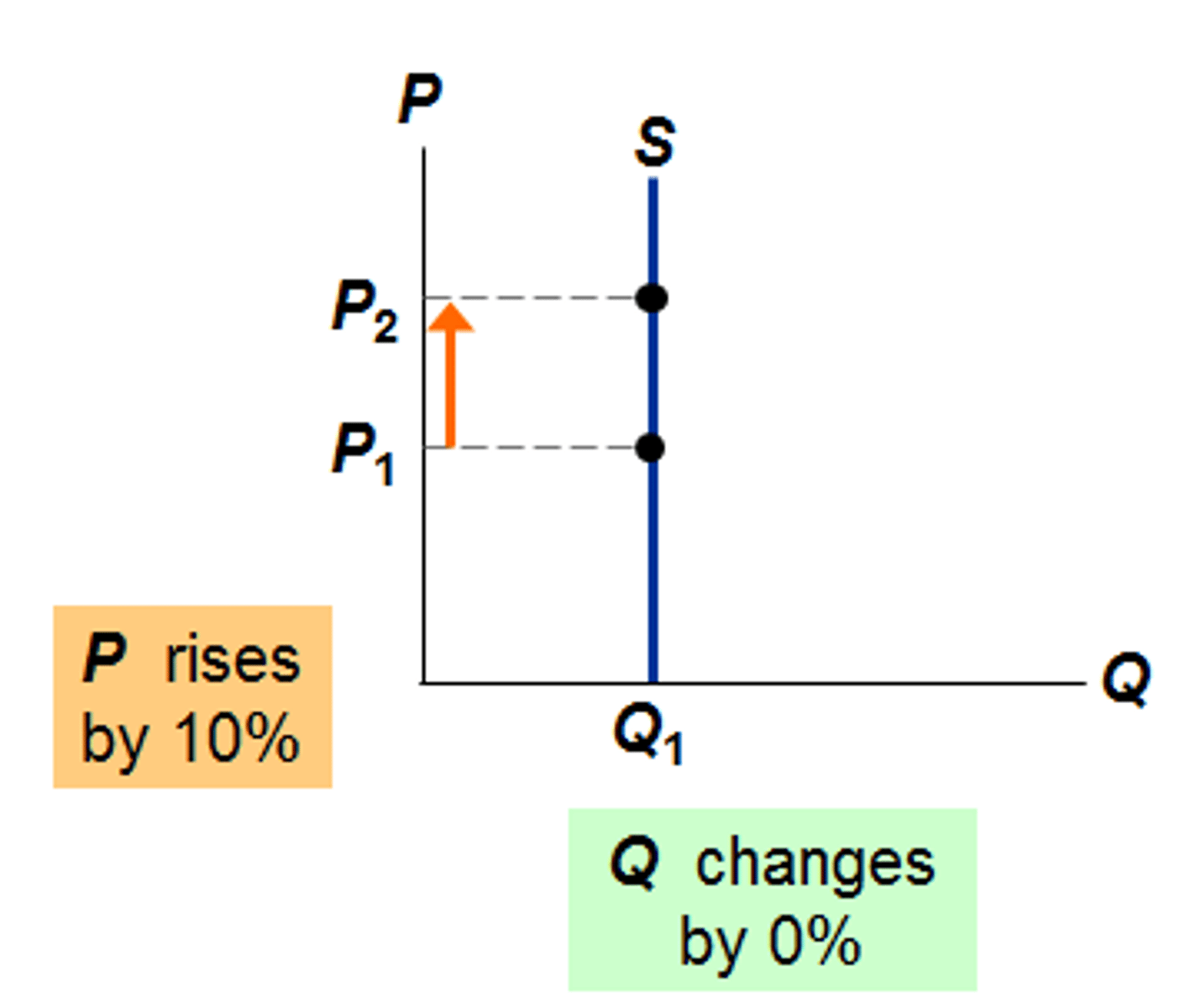
PES = 0
- Perfectly INELASTIC
- A change in P will not change Qs
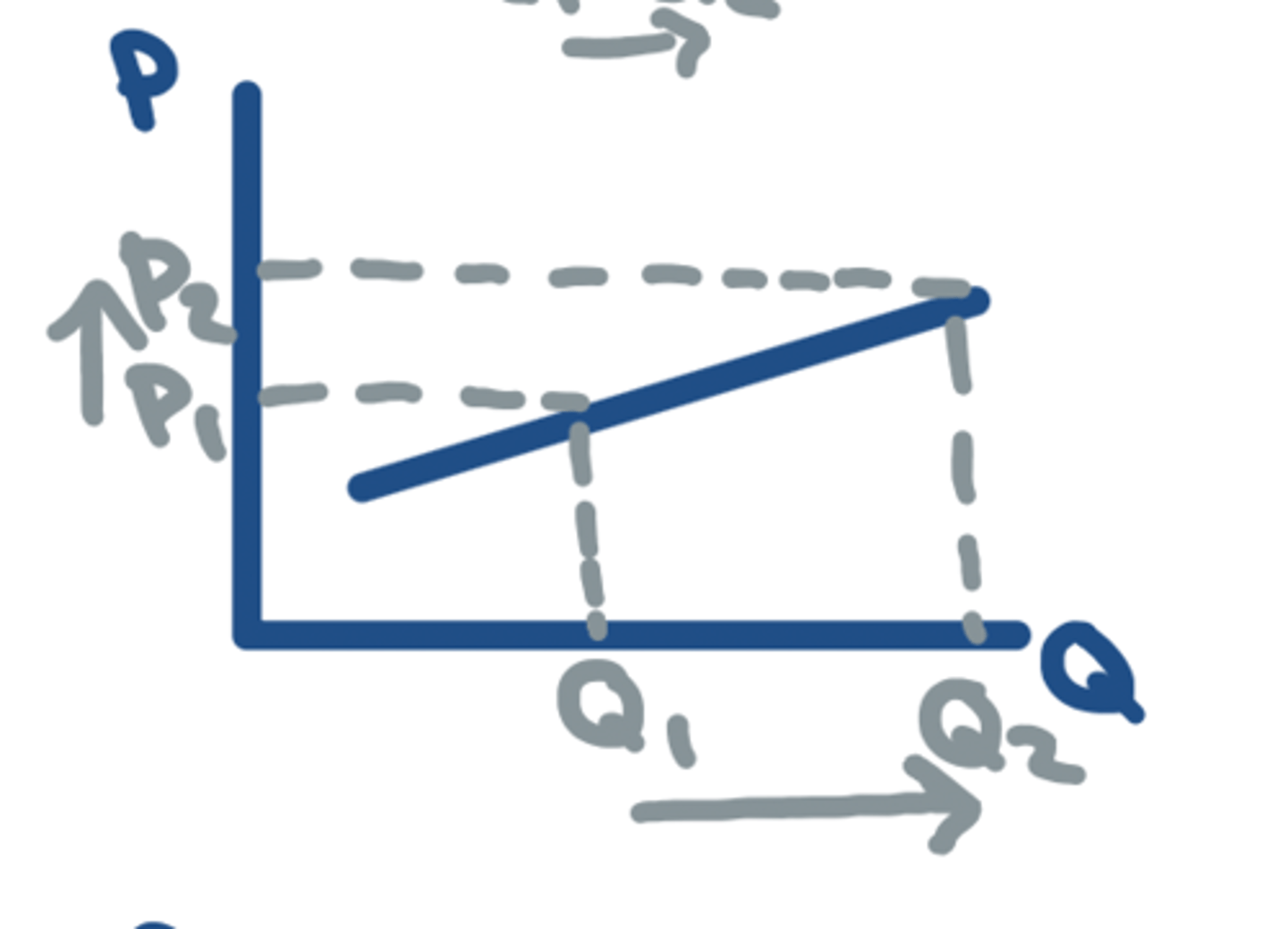
PES < 1
- Relatively INELASTIC
- A ⬆️ in P of 1% will result in < 1% ⬆️ in Qs
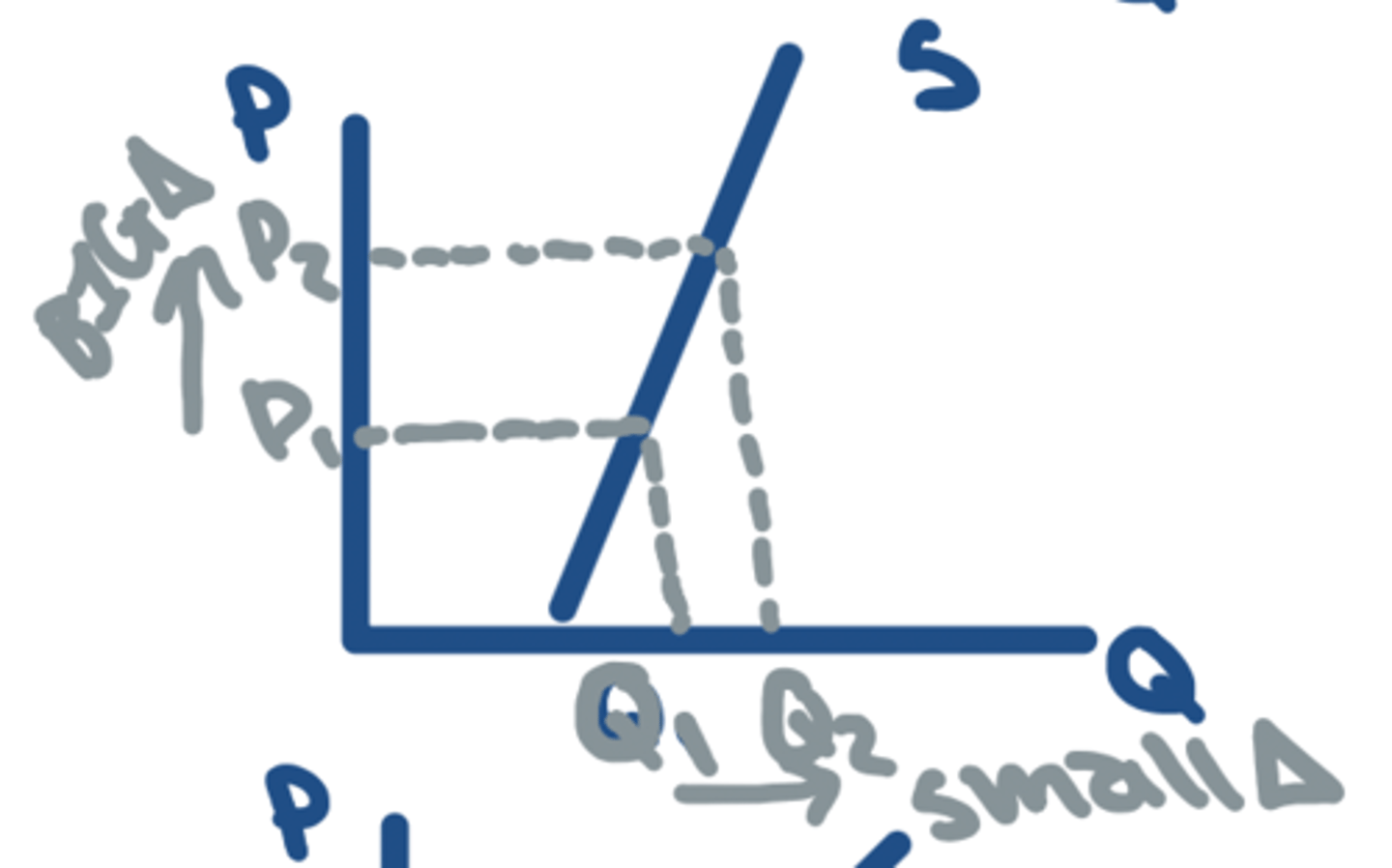
PES = 1
- Unitary ELASTIC
- P change = Qs change
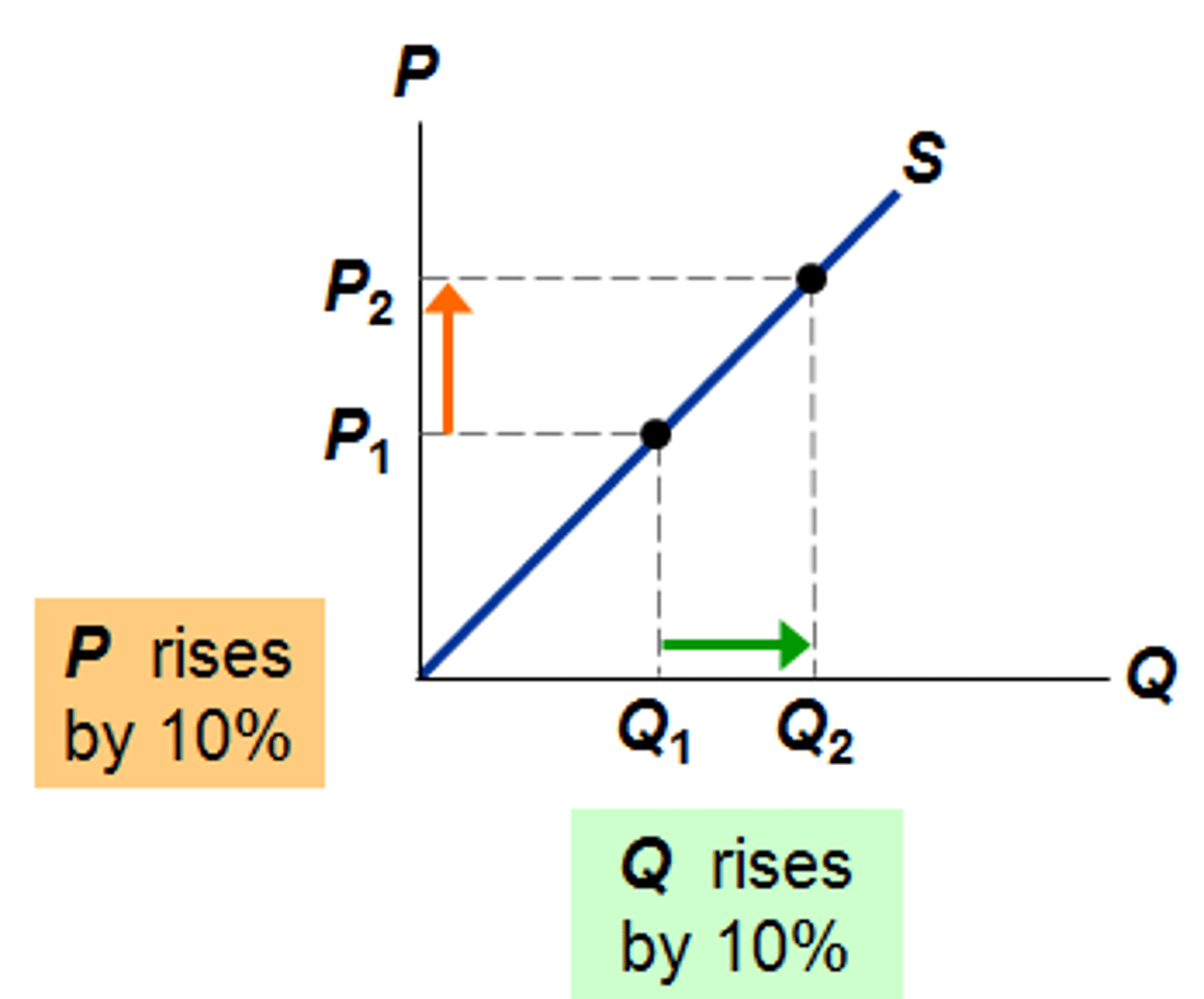
PES > 1
- Relatively ELASTIC
- a ⬆️ in P of 1% will result in > 1% change is Qs
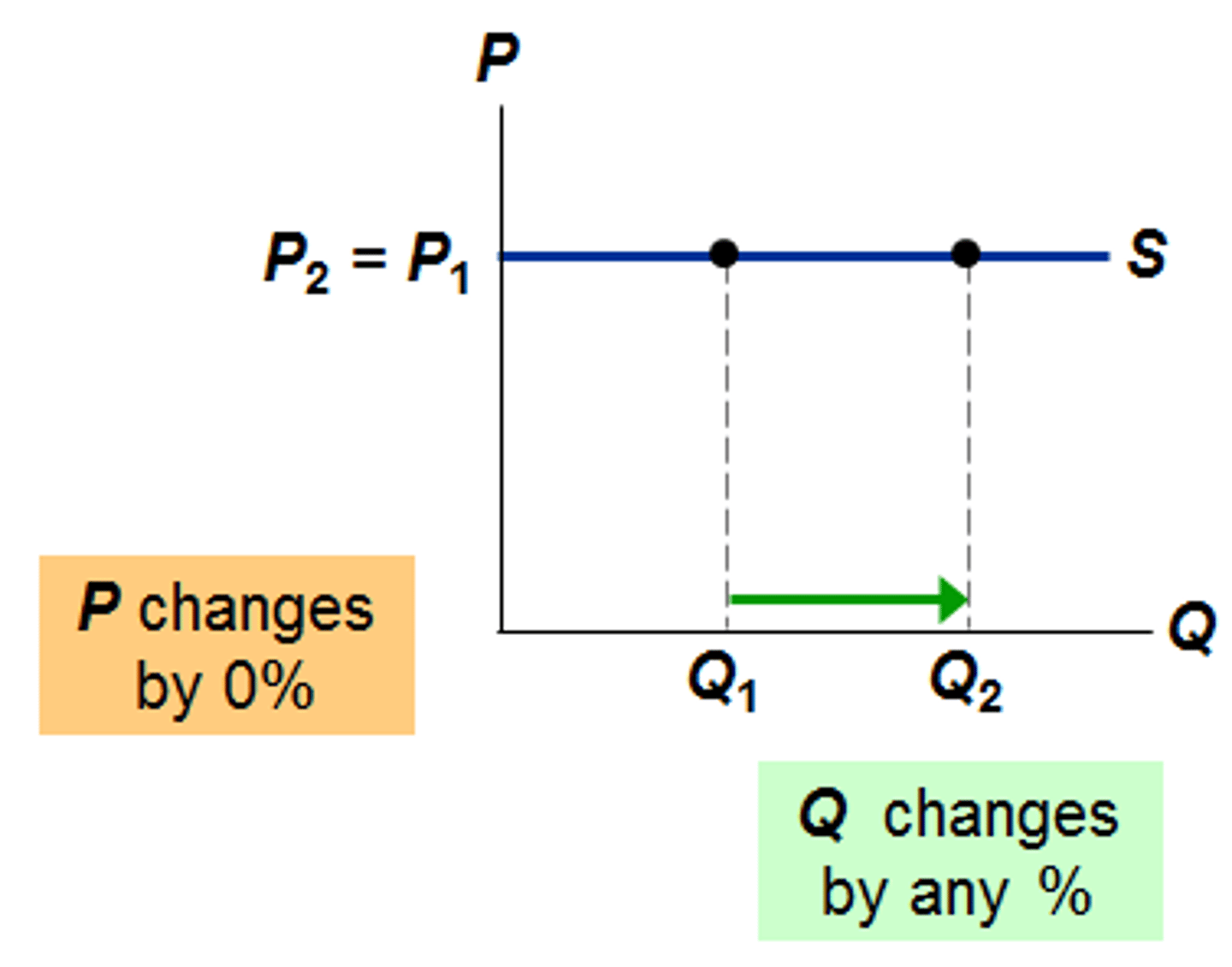
PES = Infinity
- Perfectly ELASTIC
- Eg. minimum wage
Price ELASTIC goods in SUPPLY
Sellers can easily and quickly expand supply in response to a change in P. Eg. manufactured goods
Price INELASTIC goods in SUPPLY
Sellers can not quickly and easily expand supply. Eg. Agricultural goods
Determinants of PES
- Time
- Ability to store inventory
- Nature of industry
PES Determinant - Time
- If producers can respond quickly to change in P, elastic
- If goods take a long time to produce, inelastic
PES Determinant - Ability to store inventory
- Goods that can be stored are more elastic than perishable goods
- Producers of storable goods can be flexible with their supply
PES Determinant - Nature of industry
- Agricultural goods are inelastic, manufactured is elastic
- Farmers need to wait until next growing season, manufactured goods supply can be easily adjusted depending on the market
Consumer surplus
The difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay and the actual price payed
Marginal benefit
Additional benefit gained through consuming and extra good or service
Producer surplus
the difference between the lowest price a firm would be willing to accept for a good and the price it actually receives
Total surplus
A measure of net benefits to society for the production and consumption of a good
DWL
An avoidable decrease in total surplus
Price ceiling
Legislated maximum price producers are allowed to charge
Price floor
Legislated minimum price producers are allowed to charge
Subsidy
A cash payment from governments to businesses to encourage the production of goods/services
Market failure
When resources are not allocated efficiently
Market power
The ability of a firm to raise and maintain price above market value
Causes of market power
Patent, controlling scarce resources, predatory pricing
Policy options to influence market power
1. Competition policy and regulation
2. Market deregulation
3. Legislation
Competition policy and regulation
- Strengthen competition laws
- Empowers Aus copetition & consumer commision to investigate and stop anticompetitive behaviour
- Encourages competition by promoting market entry
Market deregulation
- Deregulate certain sectors to encourage new entrants
- Promotes privatisation (selling government owned businesses to private sectors)
Legislation
- Required to address market concentration
- Required to prevent companies from engaging in anticompetitive behaviour
Externality
An unintended community consequence / side effect that causes a DWL
Policy options to correct externalities
1. Taxes
2. Subsidies
Taxes
- A fee that is charged by the government on a product
- Market will respond by ⬆️P and ⬇️Q, DWL is removed
Subsidies
- Cash payments from the government to encourage production of goods / services
- Market responds by ⬇️P and ⬆️Q, DWL is removed