Environmental chemistry 9
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 1-6
Last updated 5:51 PM on 2/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Aerobic
Has or requires oxygen
2
New cards
Anaerobic
Doesn’t have or require oxygen
3
New cards
LD50
The amount of toxin needed to kill 50% of the population
4
New cards
Point source
A small defined point of pollution
5
New cards
Non point source
And undefined, usally large area creating pollution
6
New cards
What units is PPM in
Mg/kg or mg/L or ml/kl
7
New cards
Enzymes
Run the chemical reactions that take place in the body
8
New cards
Organic Nutrients
Contain carbon and hydrogen
9
New cards
Inorganic substances
made of elements other than carbon and hydrogen
10
New cards
What are the 3 treatments for Wastewater treatment
● Primary Treatment – physical separation of large solids and sediments
● Secondary Treatment – BACTERIA decompose organic matter and, once removed (BIOSOLIDS), the remaining water is treated with chlorine, ozone or UV light
● Tertiary Treatment – percolation of water through plant bed to remove PHOSPHATES or NITRATES
● Secondary Treatment – BACTERIA decompose organic matter and, once removed (BIOSOLIDS), the remaining water is treated with chlorine, ozone or UV light
● Tertiary Treatment – percolation of water through plant bed to remove PHOSPHATES or NITRATES
11
New cards
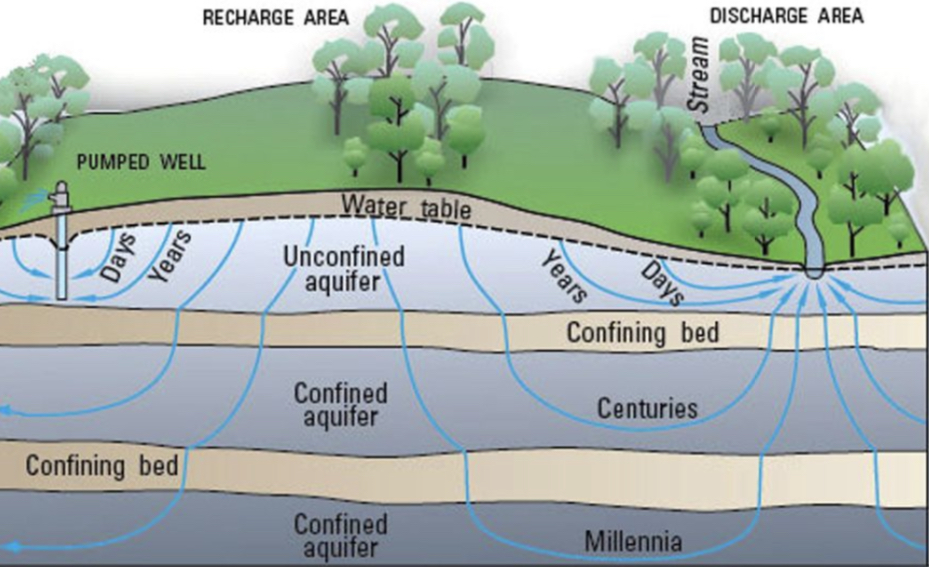
Groundwater pollution aquifers
Areas where wells will produce useful amounts of water. The water is naturally filtered and is usually free of bacteria
12
New cards
Waste management landfills
Landfills need water, oxygen, and microorganisms for proper decomposition of materials
13
New cards
Leachate
Hazardous waste
14
New cards
Biodegradability
If something is biodegradable, it is an organic substance that can be broken down by bacteria, fungi, etc into CO2 and H2O
15
New cards
Solvent
Used to dissolve another substance
16
New cards
Sanitary landfills
Used for normal household and industrial waste. Garbage is compacted and covered daily with earth and sometimes clay.
Clay liner at bottom prevents toxic leachate from reaching groundwater supplies.
Clay liner at bottom prevents toxic leachate from reaching groundwater supplies.
17
New cards
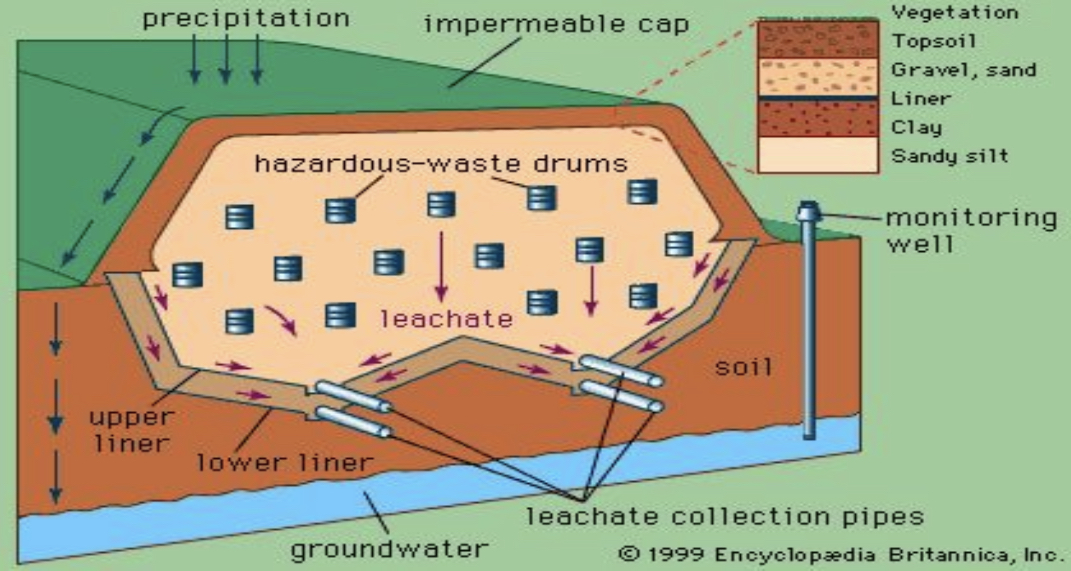
Secure landfills
where hazardous waste is placed in or on land and that is designed, constructed and operated to prevent any pollution from being caused by the facility outside the area of the facility.
18
New cards
Bioremediation
A way of using living things to solve a problem
19
New cards
The 4 Rs
Reuse, reduce, recycle, recover
20
New cards
CFC’s
human-made pollutants that react in Earth’s stratosphere and cause ozone (O3(g))to breakdown. This has caused holes to form Earth’s ozone layer that protects ultraviolet radiation from reaching and harming biological organisms. Even though CFC’s are no longer used, they are very stable so will remain in the atmosphere for a long time.
21
New cards
How can surface water pollution be controlled?
treating sewage, chlorinating wastewater, and using high-intensity ultraviolet light to destroy bacteria and viruses.
22
New cards
Persistent toxin
Cannot be broken down easily in the enviroment
23
New cards
Non-persistent toxin
Can be broken down by naturally occurring processes
24
New cards
Macroinvertebrates
organisms that tell us about the quality of the environment by their presence or absence in water
25
New cards
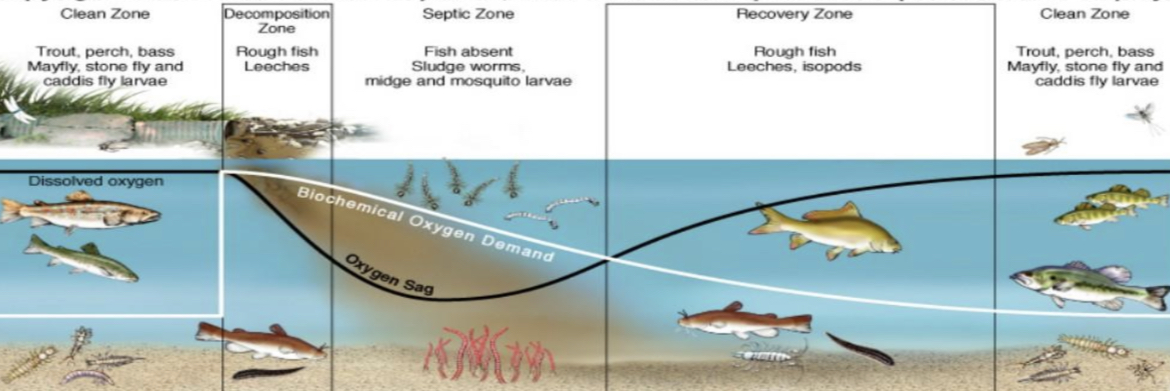
Oxygen sag graph zones
Clean zone, decomposition zone, septic zone, recovery zone
26
New cards
Accute toxicity
Fatal in 1 exposure to toxin
27
New cards
Chronic toxicity
Take time and mutiple exposures for the toxin to become fatal
28
New cards
Chemicals and nutrients are used for:
Energy, growth, bodybuilding, and cell repair
29
New cards
How do plants absorb minerals
Root hairs specially designed to uptake and concentrate these minerals
\- They are then transported to other parts of the plant where they are used to create organic compounds such as proteins, lipids and vitamins.
\- They are then transported to other parts of the plant where they are used to create organic compounds such as proteins, lipids and vitamins.
30
New cards
Substrate
A material on which an organism moves or lives
31
New cards
What number for fertilizer is what nutrient? 5-10-5
5-nitrogen 10-phosphate 5-potash