Biochem - Macromolecules
1/56
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
lipids
aka fats, NOT A POLYMER
monomer of a lipid
glycogen and fatty acids
What are lipids made of?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
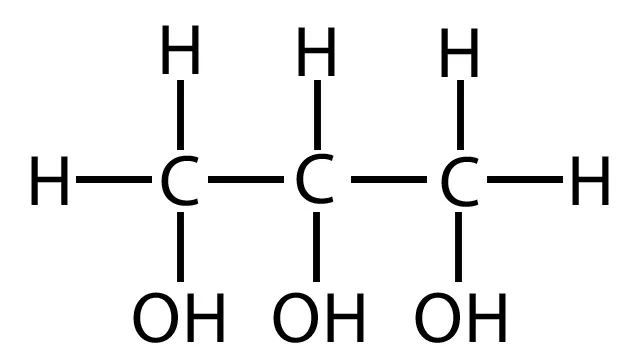
glycerol
backbone of a lipid
hydrophobic
water-fearing
hydrophilic
water-loving
What are the three types of lipids?
triglycerides, steroids, and phospholipids
triglycerides (purpose)
energy storage and insulation
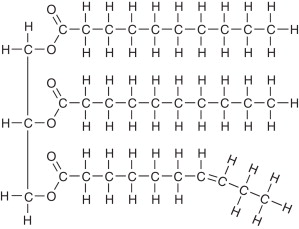
structure of a triglyceride
3 fatty acid chains and glycerol
What are the 2 types of triglycerides? (natural)
saturated fats and unsaturated fats
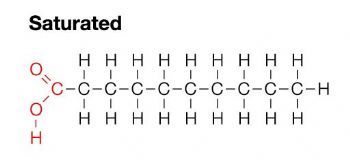
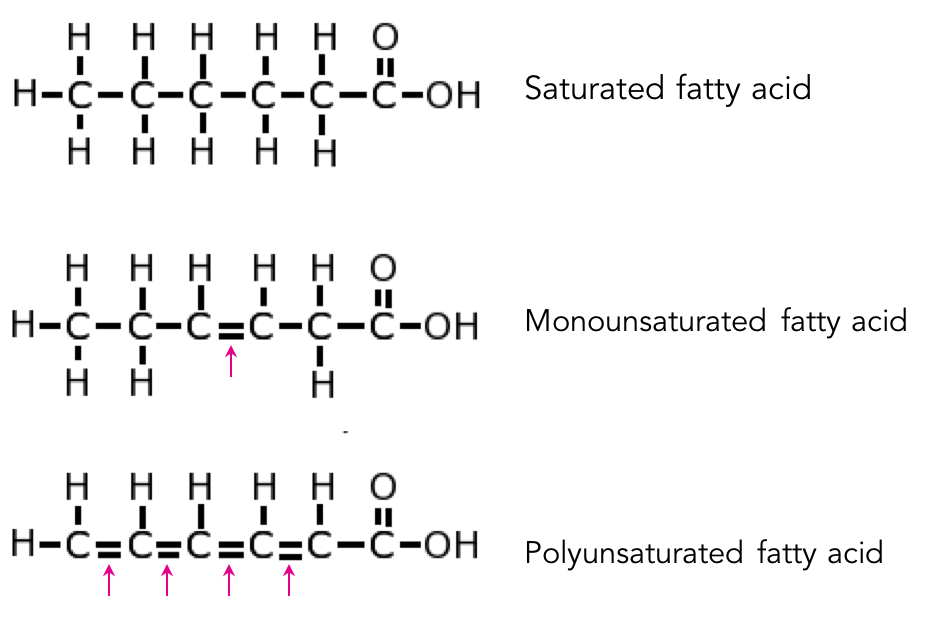
saturated fats
the unhealthy fat
single bonds between carbon atoms - makes the chain straight
solid at room temp (because the chains are able to be packed together)
comes mostly from animals
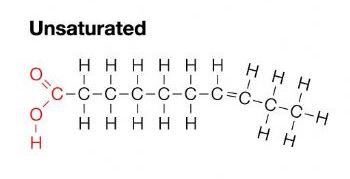
unsaturated fats
the healthy fat
has double bonds between carbons - creates kinks
liquid at room temp
mostly come from plants
the double bond fills in space that the lack of hydrogen atoms created
What are the 2 types of unsaturated fats?
monounsaturated and polyunsaturated
What’s the difference between monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats?
monounsaturated fats have one double bond, while polyunsaturated fats have multiple double bonds
trans fats
most unhealthy fat
manmade/artificial
also known as hydrogenated oils
provides better taste, texture, and longer shelf life
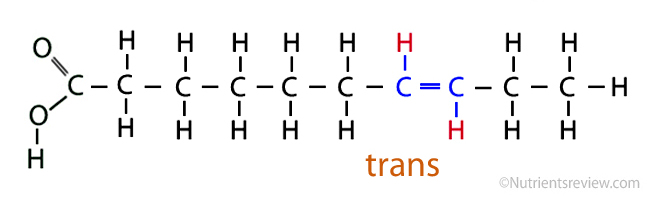
hydrogenation
adding hydrogen to unsaturated fats, turning it from a liquid to a solid (trans fats)
How do you know if a food has trans fats in them on a food label?
it will say “partially hydrogenated” on the ingredients list
cholesterol (purpose)
strengthen cell membranes
high density lipoproteins (HDL)
transports cholesterol from the body to liver for breakdown and disposal
the good type, need more of these
low density lipoproteins (LDL)
transports cholesterol from the liver to the body
the bad type, sticks to artery walls and can cause blood clots
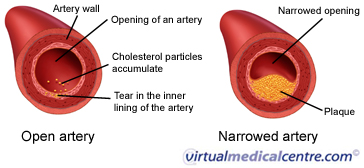
unsaturated fats (relating to cholesterol)
raises HDL, lowers LDL
saturated fats (relating to cholesterol)
raises HDL, raises LDL
trans fats (relating to cholesterol)
lowers HDL, raises LDL
phospholipids (purpose)
make up the cell membrane
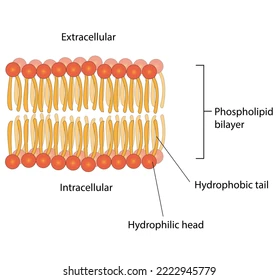
structure of a phospholipid
hydrophilic phosphate head, two hydrophobic fatty acid tails, glycerol molecule (connects head to tails)
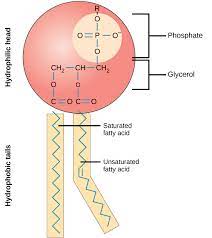
phospholipid bilayer
the arrangement of phospholipids in the cell membrane; two layers with the tails facing towards each other
nucleic acids
complex molecules that store and transmit genetic information
What are nucleic acids made up of?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous
monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
What are the 3 types of nucleic acids?
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), ribonucleic acid (RNA), adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
proteins (purpose)
involved in nearly every function of the body (structural, enzymes, transport, immunity)
What are proteins made up of?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sometimes sulfur
monomer of proteins
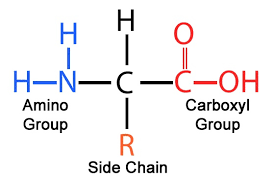
amino acids
How many (common) types of amino acids are there?
20 types (10 from the body, 10 from food)
What makes each amino acid different?
the side R chain/group
peptide bonds
a type of covalent bond, specifically connects amino acids
What’s another name for protein?
polypeptide
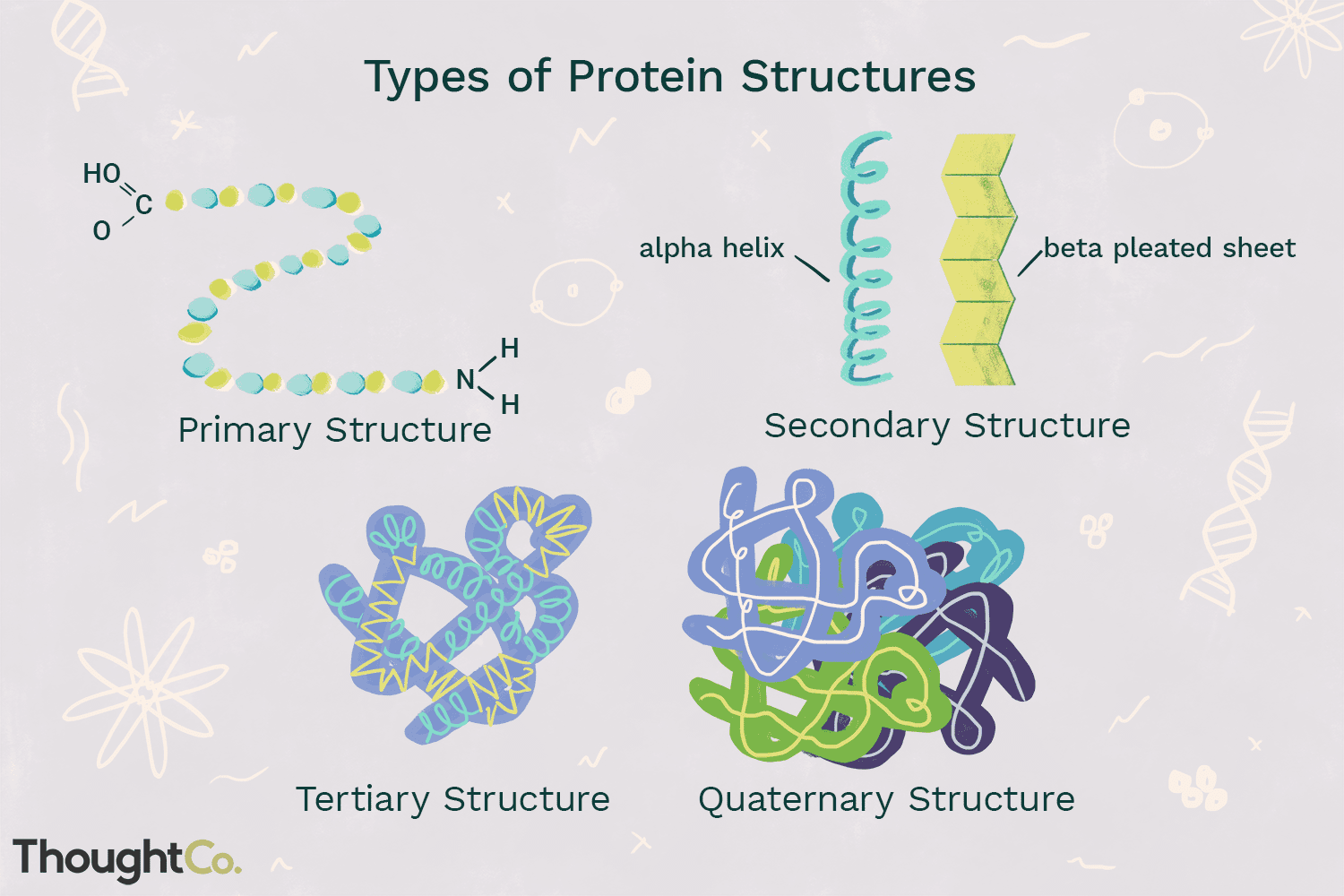
structure of protein
folded structure
denaturation
the conditions of the protein changes, unraveling it (changing structure and losing its shape), therefore becoming nonfunctional
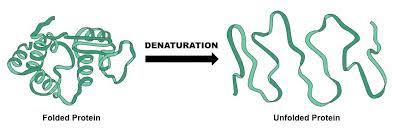
What causes denaturation?
high temperatures (NOT COLD!)
pH change
salts
enzymes (purpose)
speeds up chemical reactions in the body (catalysts) by lowering the amount of activation energy needed
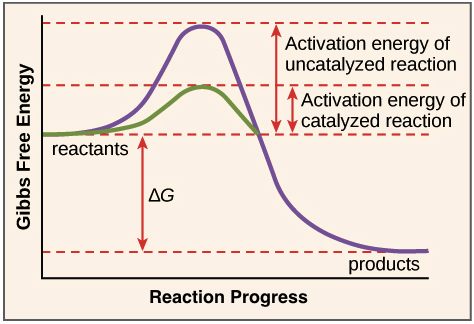
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required in order for a chemical reaction to occur
What do enzymes USUALLY end in?
-ase
Can enzymes be reused?
yes
substrate
the substance the enzyme is working with (reactants)
active site
the place on the enzyme where substrates are inserted
product
what the substrate turns into after the enzyme finishes its job
How are enzymes specific?
each enzyme’s active site is specifically shaped for one unique substrate; can either build up or break down that substrate
induced fit
when the active site changes its shape TEMPORARILY to ensure a better fit and bind the substrate to itself
cofactors and coenzymes
enzyme helpers that can help bind the substrate to the active site
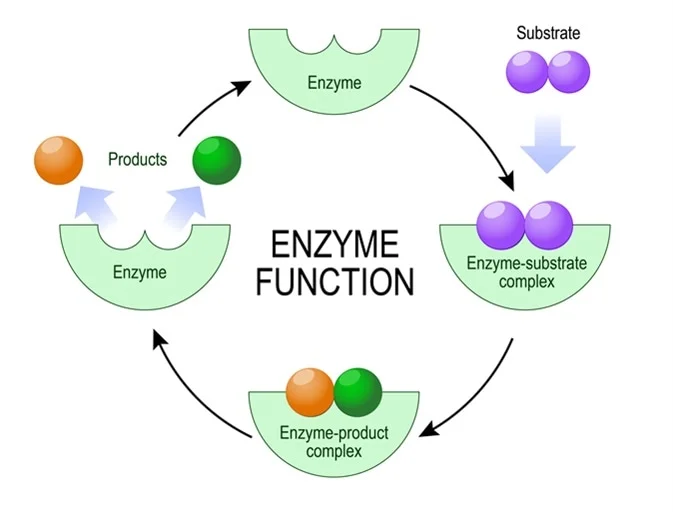
What are the steps of an enzyme at work?
substrate fits into active site of enzyme, forming enzyme-substrate complex
enzyme makes or breaks bonds to form new product
product released from enzyme
enzyme reused for the same reaction
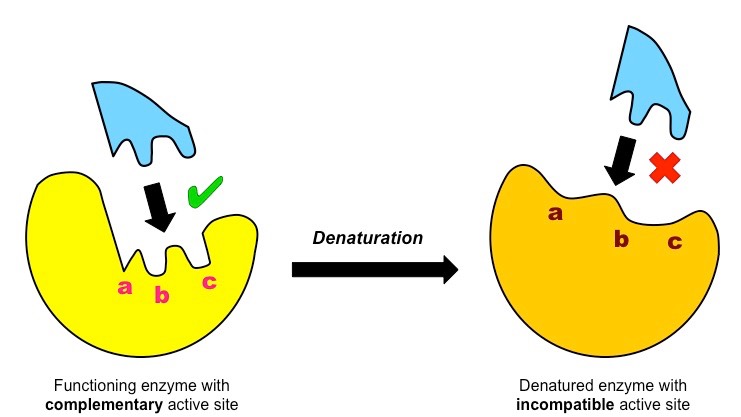
What happens to the enzyme when it becomes denatured?
the shape of the active site changes, so the substrate cannot bind to it, making the enzyme non-functional
enzyme inhibitors
molecules that reduces the rate of a reaction and/or stops the enzymes from functioning properly; can be temporary or permanent
What are the 2 types of enzyme inhibitors?
competitive inhibitors and non-competitive inhibitors
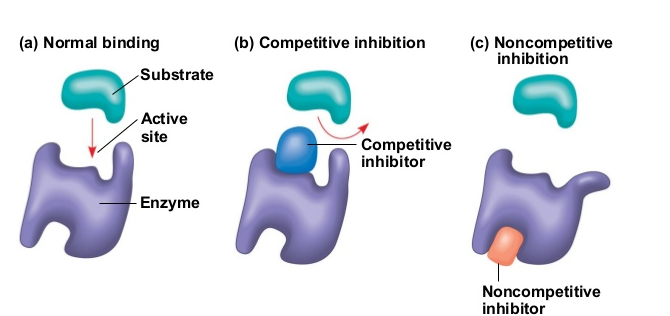
competitive inhibitors
competes with substrates by binding to the active site first, blocking it
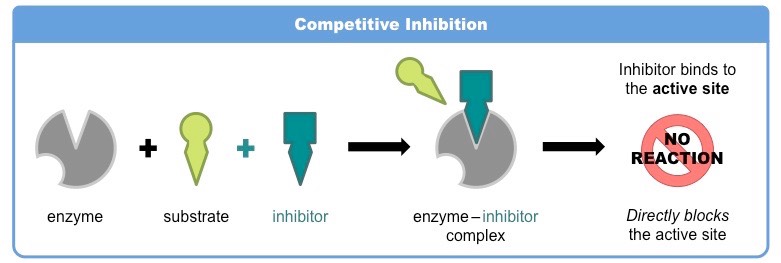
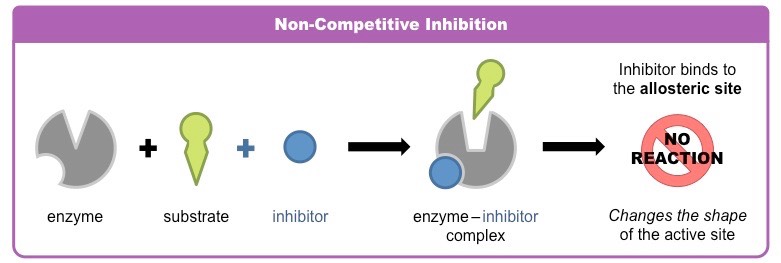
non-competitive inhibitors
binds to the enzyme at a different location (called allosteric site); this changes the shape of the active site, so the reaction can’t be catalyzed efficiently
examples of enzymes
protease, lipase, lactase, amylase, pepsin