Chapter 14- Dynamics of Labour Relations
Labour Relations Process is a
logical sequence of four events
Unions are often associated with
strikes
picketing exercises
tough negotiators
public inconvenience
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Labour Relations Process is a
logical sequence of four events
Unions are often associated with
strikes
picketing exercises
tough negotiators
public inconvenience
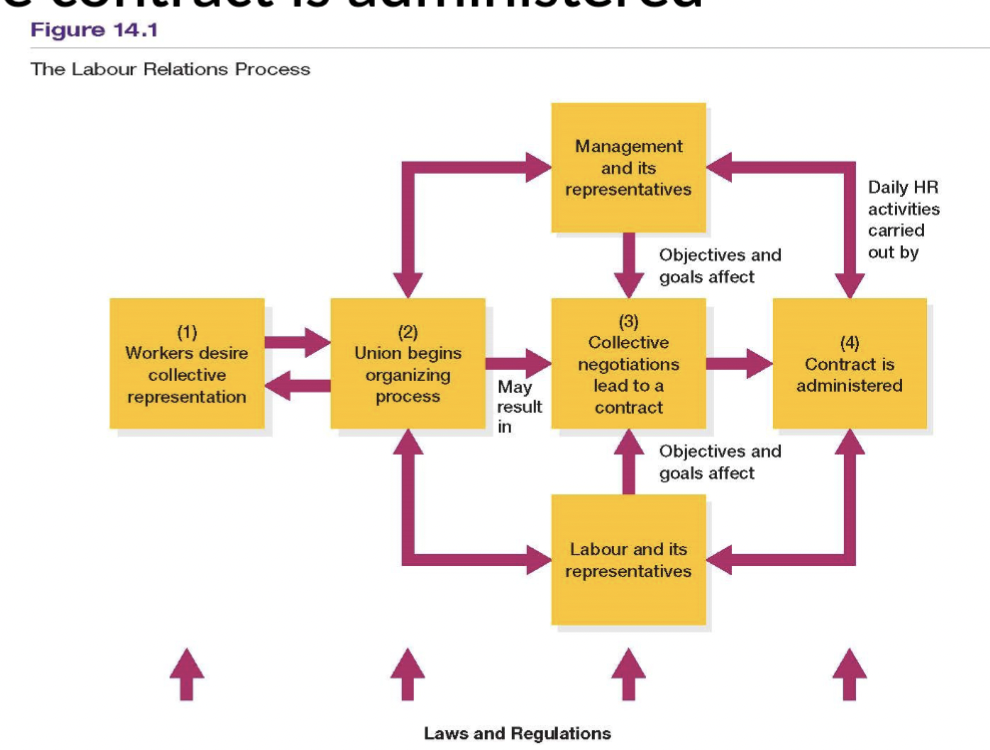
What 4 events make up Labour Relations Process:
Workers desire collective representation
Union begins its organizing campaign, which may lead to certification & recognition
Collective negotiations, lead to a contract
Contract is administered
Unions are organizations formed to
give workers more bargaining power with their employers and to improve their pay and working conditions.
Many people believe that the purpose of unions is
to create an adversarial relationship between employees and managers.
Employees see unions as
a way to achieve results they cannot achieve acting individually
Dissatisfaction with
wages, benefits, and working conditions appear to provide the strongest reason to join a union
Employees may seek unionization when
they perceive that managerial practices regarding promotion, transfer, shift assignment, or other job- related policies are administered in an unfair or biased manner
Union shop:
provision of the collective agreement that requires employees to join the union as a condition of their employment
Employees whose needs for recognition and social affiliation are being frustrated may do what?
join unions as a means of satisfying those needs
Key Legislation
The Industrial Relations Disputes and Investigation Act (1948)
Canada Labour Code
Provincial labour law statutes
The Industrial Relations Disputes and
Investigation Act (1948) involves…
The act provided for the right of workers to join unions and required management to recognize them as exclusive bargaining agents.
The organizing process normally includes the following steps:
1) Employee/union contact—to win employee support, labour organizers must build a case against the employer and for the union
2) Initial organizational meeting—to attract more supporters
3) Formation of an in-house organizing committee - authorization cards (i.e., a statement signed by an employee authorizing a union to act as their representative for the purposes of collective bargaining) → kept private
4) Application to a labour relations board (e.g., the Ontario Labour Relations Board)
5) Issuance of a certificate by a labour relations board—declare whether or not the union has been successful in its application for certification
6) Election of a bargaining committee and contract negotiations
- Employers are prohibited by law from dismissing, disciplining, or threatening employees for exercising their right to form a union
Card-check
—union is certified if the union submits to the labour board
authorization cards on behalf of a majority of workers
Mandatory ballot
the union must obtain authorization cards on behalf of a certain number of workers (in Ontario, it is 40% or more) to obtain a vote
Employers can make the case that the employees have the right to….
not to join a union and that they can deal directly with the employer on any issue steps
Unions also have a duty to
…act in accordance with labour legislation
(e.g., they cannot intimidate or coerce employees to become or remain members of a union, cannot strike before the expiration of the union contract)
Bargaining unit
group of two or more employees who share common
employment interests and conditions and may reasonably be grouped together for the purposes of collective bargaining
Unfair labour practices (ULPs)
specific employer and union illegal practices that deny employees their rights and benefits under federal and provincial labour law
Ex. The UFCW accused Walmart of ULPs in thwarting a union organizing drive in British Columbia.
Voluntary recognition is a process
in which the employer simply agrees
to recognize the union as the representative of the employees
What happens IF the majority of employees indicate they do not want to be represented by the union or they want to be represented by another union, or if the union has failed to bargain
an application for decertification can be made to the labour relations board
If a collective agreement has been reached with the employer, then the decertification application….
application can be made only at specified times, such as a few months before the agreement expires
Unions can have
a significant effect on the rights exercised by management in making decisions about employees
Management rights
decisions regarding organizational operations over which
management claims exclusive rights
Management’s authority
is supreme in all matters except those it has expressly
conceded in the collective agreement, or in those areas where its authority is restricted by law
Specific contract language
can reduce the supervisor’s ability to manage in areas such as scheduling, training, transfers, performance evaluation, promotions
Under the provisions of the collective agreement, supervisors
may have to promote employees by seniority
Craft Unions
Represent skilled craft workers
Example: United Brotherhood of Carpenters
Industrial unions:
Represent all workers—skilled, semiskilled, unskilled—employed along industry lines
Example: Unifor
Employee associations:
Represent various groups of professional and white-collar employees in labour-management relations
Example: Alberta Teachers’ Association.
Union (shop) steward:
employee who as a nonpaid union official represents the interests of members in their relations with management
Business agent
normally a paid labour official responsible for negotiating and administering the collective agreement and working to resolve union members’ problems
Being a business Agent entails
Resolving grievances that cannot be settled by union stewards
Administering the daily affairs of the local union
What does CUPE stand for?
Canadian Union of Public Employees
How many public employees are unionized?
More than 70% of public employees are unionized
The Canadian Union of Public Employees (CUPE) is
the largest union in Canada
Whats the difference between labour relations in private vrs public sector?
Labour relations in the private sector have an economic foundation, whereas in government, the foundation tends to be political
The right to strike is limited to
specific groups of employees—those performing nonessential services—and the strike cannot endanger the public’s health, safety, or welfare (rotating strikes)
To avoid potentially critical situations,
various arbitration methods are used for resolving collective bargaining deadlocks in the public sector
Compulsory binding arbitration:
binding method of resolving collective bargaining deadlocks by a neutral third party
Final offer arbitration
method of resolving collective bargaining deadlocks whereby the arbitrator has no power to compromise but must select one or another of the final offers submitted by the two parties
The government can also
enact back-to-work legislation
Collective bargaining process
process of negotiating a collective agreement, including the
use of economic pressures by both parties
What does the bargaining process entail?
Strikes and boycotts by a union & Lockouts and strike
replacements by an employer
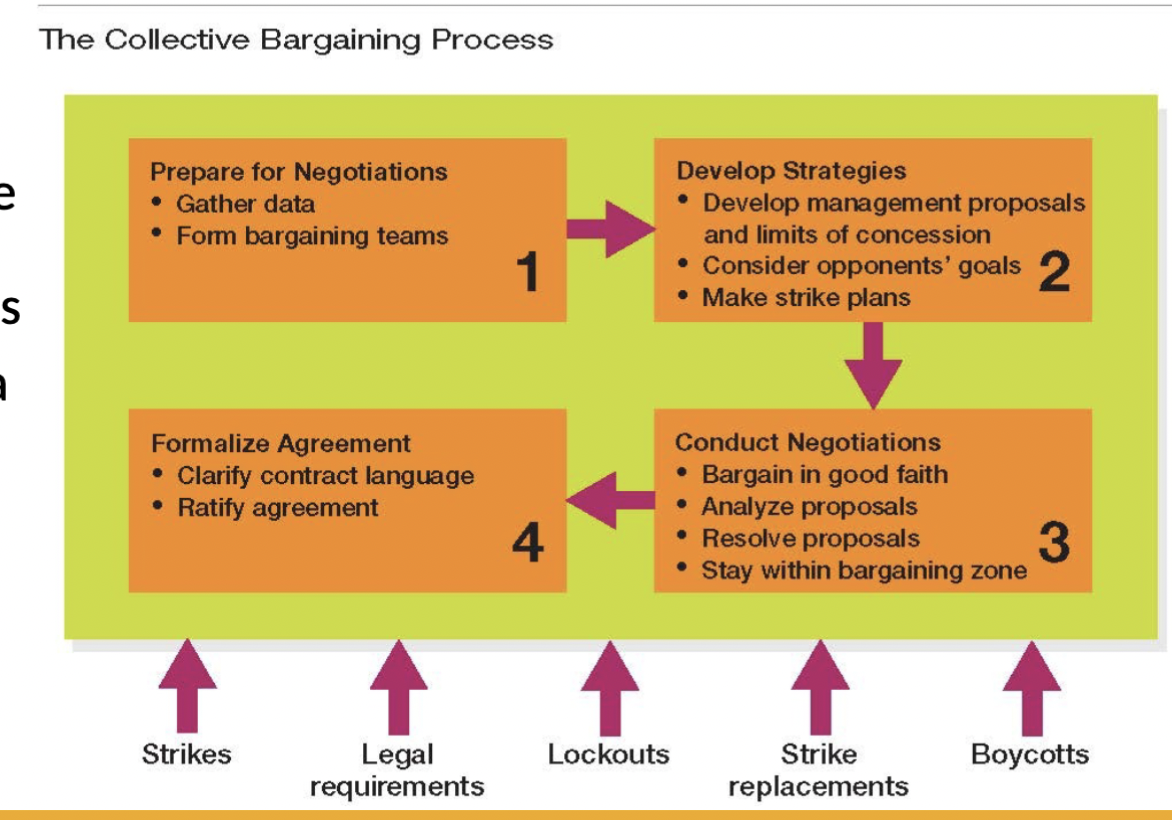
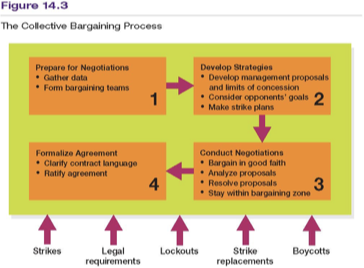
Preparing for negotiations includes doing what
assembling data to support bargaining proposals and forming the bargaining team
The initial demands presented in a bargaining zone…
by each side are greater than those it may hope to achieve
Typically, each side in a bargaining strategy focuses on
one issue or several related issues until agreement is reached
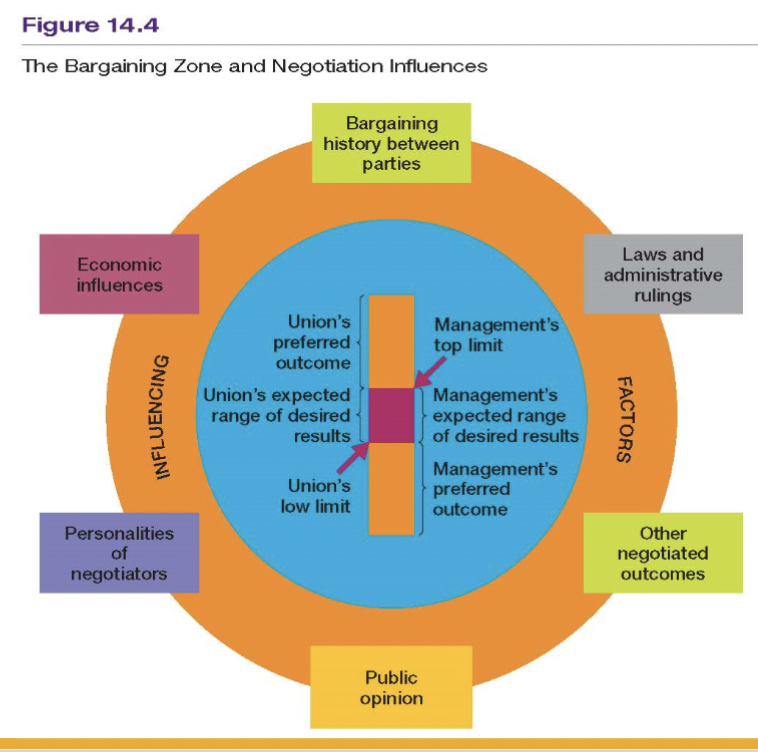
Bargaining zone
area within which the union and the employer are willing to
concede when bargaining
Good faith requires
meetings to be held at reasonable times and places
to discuss employment conditions; also requires that the proposals submitted by each party be realistic
With adversarial bargaining, negotiators
start with defined positions, and, through deferral, persuasion, trade, or power, the parties work toward the resolution of individual bargaining demands
Interest-based bargaining (IBB):
problem-solving bargaining based on a win–win philosophy and the development of a positive long-term relationship
Bargaining power
the power of labour and management to achieve their
goals through economic, social, or political influence
The bargaining power of the union may be
exercised by striking, picketing, or boycotting the employer’s products or services
- It is a legal requirement that unions hold and win a strike vote as a condition of striking lawfully
The employer’s bargaining power
largely rests on being able to continue operations in the face of a strike or to shut down operations entirely (lock out)
Another prevalent bargaining strategy is for
the employer to continue operations by using managers and supervisors to staff employee jobs
Mediation is
a voluntary process that relies on the communication and
persuasive skills of a mediator to help the parties resolve their
differences
In all Canadian jurisdictions,
conciliation is compulsory before a legal strike or lockout
Interest arbitrator
third-party neutral who resolves a labour dispute by
issuing a final decision in the disagreement
The grievance process is normally initiated by
the union
an individual employee
when it feels management has violated some article of the collective agreement
Grievance procedure
formal procedure that provides for the union to
represent members and nonmembers in processing a grievance
When a grievance cannot be resolved…
most agreements provide for the grievance to be submitted to a third party—usually an arbitrator—whose decision is final
The function of rights arbitration is to
provide the solution to a grievance that a union and an employer have been unable to resolve by themselves
Rights arbitration
arbitration over interpretation of the meaning of
contract terms or employee work grievances
In arbitrating a dispute,
it is the responsibility of the arbitrator to ensure
that each side receives a fair hearing during which it may present all the facts it considers pertinent to the case
Arbitration award
final and binding award issued by an arbitrator in a
labour–management dispute
Labour relations legislation in Canada
recognizes the right of employees to form and join unions and prohibits both unions and employers from engaging in ULPs
Employee unionization is
largely caused by dissatisfaction with managerial practices and procedures
When negotiations become deadlocked
bargaining becomes a power struggle to force from either side the concessions needed to break the deadlock
When differences arise between labour and management
they are normally resolved through the grievance procedure
What is important for unions vrs. What is important to Millennials
Increases in pay are important for union members
millennials care about EQUALITY & TRANSPARENCY
At what rate do millennials approve of unions?
66%, higher than previous generations
Union shop
Provision of the collective agreement that requires employees to join as a condition of employment.
Why employees unionize? (3)
Economic needs
Dissatisfaction w management
Social & Leadership concerns
Employer Tactics: “Do’s” and “Don'ts”
−Can emphasize current advantages in wages, benefits, or working conditions the employees may enjoy, but cannot promise better conditions
−Cannot interfere with the labour relations process or certification
−Cannot threaten to close the business
−Cannot dismiss, discipline, or threaten employees who wish to join the union
**Must bargain in good faith
•Union Tactics: “Do’s and Don’ts”
−Cannot interfere with the formation of an employer association
−Cannot intimidate or coerce employees to become members of a union
*Must provide fair representation for all in the
bargaining unit
How are union certifications across Canadian jurisdictions?
The procedures for union certification vary across Canadian jurisdictions.
Common practice for unions to do what?
Common practice is for unions to present documentation to the appropriate labour relations board for certification.
The labour relations board must do what before it can act as a bargaining unit?
The labour relations board must certify a union before it can act as a bargaining unit for a group of employees.
How long are collective agreement terms valid for?
A collective agreement's terms are valid for a minimum of one year and a maximum of three years, though there is no legally mandated maximum.
Whats an important difference between collective agreement & individual employment contracts?
Enforcement Methods
Enforcement Methods
−A nonunion employee must sue the employer in a court for breach of the employment contract.
−A unionized employee must file a grievance alleging that the collective agreement has been violated and that grievance, if not settled or resolved, may be referred to a labour arbitrator instead of a court.
Labour arbitrator
A person assigned to interpret and decide disputes (“grievances”) about the meaning, interpretation, and application of a collective agreement governing employees in a unionized workplace
What is an important rule of contract law?
Mutual Consideration
*Both parties to the contract must receive some benefit in the exchange
Constructive dismissal
occurs when an employer commits a fundamental breach of the contract, such as by unilaterally changing a key term of the contract, the employee can treat the breach as a termination.
Common practice for unions is to
present documentation to the appropriate labour relations board for certification
The labour relations board must
certify a union before it can act as a bargaining unit for a group of employees.
A collective agreement's terms
are valid for a minimum of one year and a maximum of three years, though there is no legally mandated maximum
What happens if contract expiry date approaches?
party must notify the other of its intention to negotiate a new collective agreement
Decertification under certain conditions…
all legislation allows for the decertification of unions
Decertification means that If the majority of employees indicate that they do not want to be represented by the union or want to be represented by another union, or if the union has failed to bargain…
If the majority of employees indicate that they do not want to be represented by the union or want to be represented by another union, or if the union has failed to bargain, an application for decertification can be made to the labour relations board.
Challenges to Management Decisions
May involve such issues as the subcontracting of work, productivity standards, and job content
Employers seek to claim many of these decisions as their exclusive management rights
Loss of Supervisory Authority
Contract language can limit a supervisor's ability to manage in areas such as scheduling, training, transfers, and performance evaluations.
Labour organizations are diverse organizations and can be divided into three levels:
(1) central labour congresses,
(2) international and national unions, and
(3) local unions belonging to a parent national or international union.
Each level has its own reason for existence and its own operating policies and procedures.
The Canadian Labour Congress (CLC)
was founded in 1956 and represents more than two-thirds of all unionized workers in Canada.
How many unions in Canada?
40 international
196 national unions
We examine the differences in two contexts:
1.the political nature of the labor–management relationship; and
2.strikes in the public sector.
What is the difference in labour relations in private and political?
Labour relations
private sector → an economic foundation
government sector → a political foundation.
Compulsory binding arbitration
Binding method of resolving collective bargaining deadlocks by a neutral third party
final offer arbitration
Method of resolving collective bargaining deadlocks, whereby the arbitrator has no power to compromise but must select one or another of the final offers submitted by the two parties
Collective bargaining process
Process of negotiating a collective agreement, including the use of economic pressures by both parties
Required: Long hours of preparation, diplomatic maneuvering, and the development of bargaining strategies