3.4.5 - monopoly
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
characteristics of a monopoly market:
how many firms
barriers to entry
products
price maker/taker
single seller
high barriers to entry
unique products (no substitutes)
price maker (total market control)
what kind of monopoly are we referring to here
pure monopoly (100% market share)
how is a legal/working monopoly determined by the UK Competition and Markets Authority (CMA)?
more than 25% market share
how is a dominant firm defined
a firm with 40% or more market share
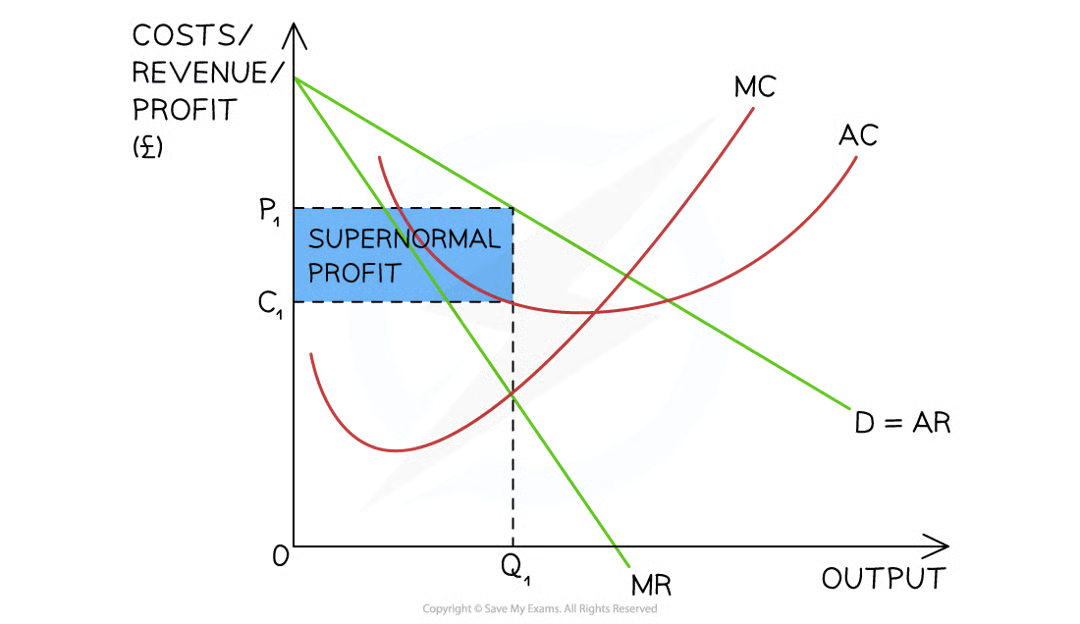
monopoly diagram
same in both long and short run
what is PRICE DISCRIMINATION
when a firm charges a different price for the same g/s in order to maximise its revenue
what is THIRD DEGREE price discrimination
when a firm charges different prices to different consumers for the same g/s
3 conditions to be met for third degree price discrimination to occur:
market power
varying consumer PED
ability to prevent resale
market power
has the ability to change prices (works best when there are no substitutes)
varying consumer PED
different groups (eg based on income) of consumers must be willing to pay more
ability to prevent resale
consumers shouldn’t be able to buy for cheap and sell for more
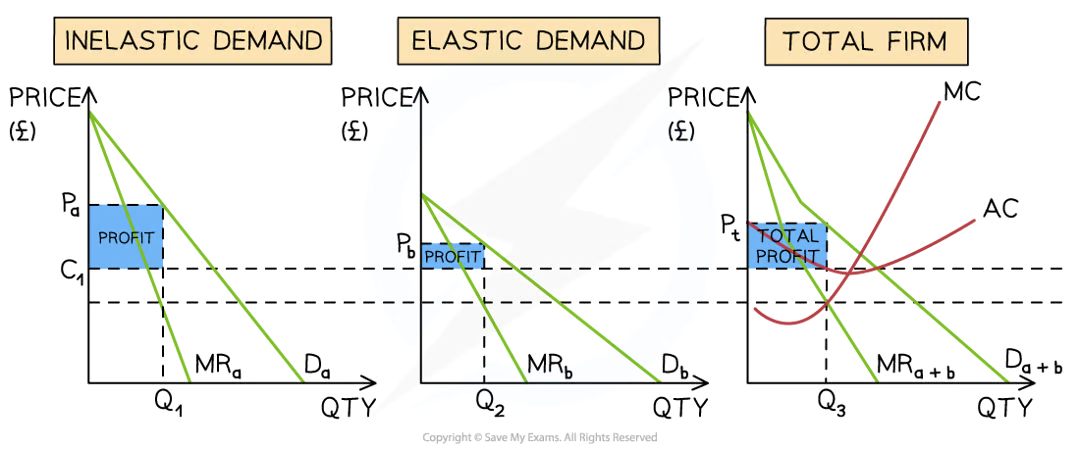
third degree price discrimination in a diagram
EXAMPLE: rail market
inelastic = peak travel
elastic = off-peak
more profit from inelastic obvs bc its priced higher
good and bad about third degree price discrimination - consumers
↑ consumer surplus - lower prices for some
↑ prices = ↓ demand = ↑ utility (eg. train less crowded)
↓ consumer surplus - higher prices for some
good and bad about third degree price discrimination - producers
higher profits
↑ producer surplus
setting up price discrimination = ↑ average costs
good and bad about monopoly - the firm
more supernormal profits
therefore more investment
market power = ↑ global competitiveness
↑ economies of scale
↑ producer surplus
price discrimination = ↑ revenue
no competition = no efficiency incentive
no competition = no innovation incentive
cross subsidisation can lead to inefficiencies
not allocatively efficient (P > MC)
what might incentivise a monopoly to innovate
‘patent box’ - a government tax incentive that allows firms to pay a LOWER rate of corporation tax on profits earned from patented inventions
what is cross subsidisation
using the profit generated by one product to lower the price of another
eg. airlines use first class air tickets to subsidise economy ones (first class more expensive than it should be, economy cheaper than it should be)
good and bad about monopoly - employees
↑ wages
↑ job security
one supplier in the industry = limited opportunity to change employers
good and bad about monopoly - consumers
supernormal profit = investment = ↑ product quality
cross subsidisation will lower prices on some products
economies of scale = lower prices
economies of scale = higher prices
no innovation = worsening product quality
no competition = bad customer service
cross subsidisation will increase prices on some products
↓ consumer surplus
good and bad about monopoly - suppliers
secure contract = ↑ sales volume
monopsony power —> the firm will dictate what price they will pay to the suppliers
this may not be profitable in the long run
what is a natural monopoly
when the optimum number of firms in the industry is one
natural monopoly diagram
.

4 reasons why a natural monopoly could occur
infrastructure —> makes sense to have one company delivering water rather than multiple pipelines
cost of entry/exit in the industry (eg. sunk costs)
economies of scale —> lower average costs by having one firm doing something than many smaller firms (provide for all the demand in the market)
productive efficiency —> if even one firm can’t achieve production at the lowest point on the AC, having more competition would only increase costs + therefore prices
where do natural monopolies usually occur
utility industries
how are natural monopolies dealt with
regulated by the government —> ensure fair prices for consumers
(usually a maximum price)
what advantage might a company have related to how they started
first mover advantage - first firm in a new market