Clinical correlations
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
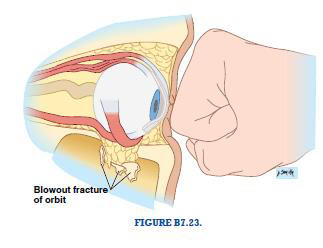
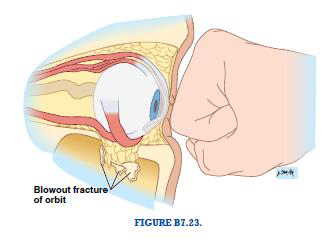
“Blowout” fracture
Fracture to the floor of the orbit that results in prolapse of the orbital contents in the maxillary sinus
Floor of orbit is relatively thin
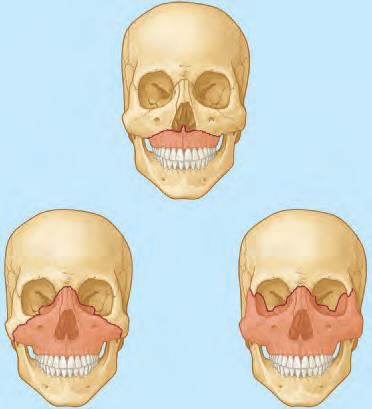
Le Fort Fractures
Traumatic fractures that cause a separation of a portion of the midface from the basicranium
• Typically involves the maxillae, sphenoid, nasals, zygomatics
Le Fort Fractures
Traumatic fractures that cause a separation of a portion of the midface from the basicranium
Typically involves the maxillae, sphenoid, nasals, zygomatics
Trans-sphenoidal Hypophysectomy
Surgical procedure for resecting tumors of the pituitary gland
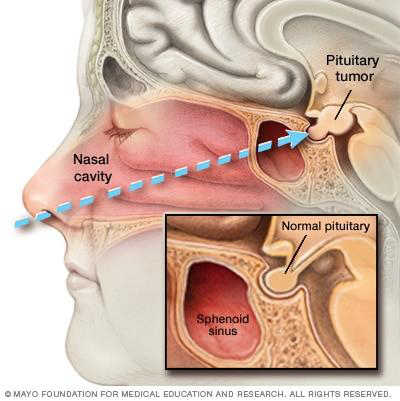
Pterion Fracture
Pterion is a weak point in the skull
Pterion overlies the middle meningeal artery
Pterion fractures can rupture this vessel (or its branches) and cause epidural hematoma
Cranial Modification
Fontanelles (“Soft Spots”) are stretched from a baby laying on its back
Craniosynostosis
Fontanelles (“Soft Spots”) are stretched from a baby laying on its back
Eagle Syndrome
Calcification of the stylohyoid ligament
Elongation of the styloid process of the temporal bone
AKA styloid syndrome, stylohyoid syndrome, styloid-carotid syndrome
Can cause throat/neck or ear pain, dysphagia
Can compress the internal carotid artery
•~4% of population has an elongated styloid process~4% of those are symptomatic (overall incidence ~0.16%)
Tx -styloidectomy
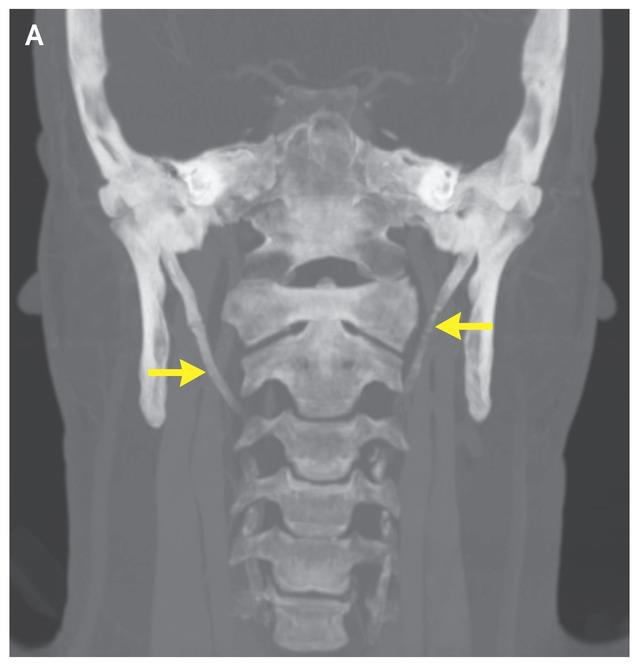
TMJ Dislocation
Extreme opening of mouth (yawning, eating, etc.), sideways impact to the chin
Anterior dislocation much more common
Mandible will fracture before posterior dislocation due to strength of the lateral ligament
Tx: manual reduction
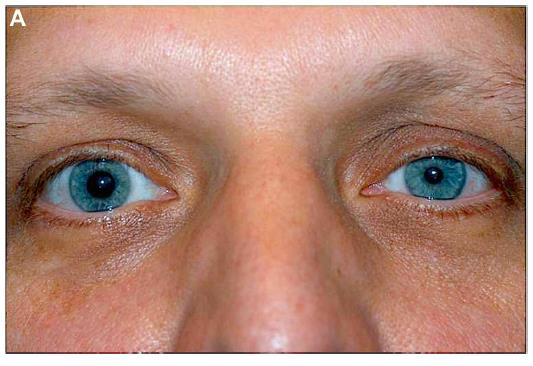
Horner’s Syndrome
Damage to sympathetic structures in the upper thorax or neck T1-T2 spinal cord, ascending cervical sympathetic chain, cervical ganglia
Symptoms (unilateral)
Partial ptosis (drooping eyelid)→ paralysis of the superior tarsal m.
Miosis (pupil constriction)→ paralysis of the dilator pupillae m.
Anhidrosis→ loss of stimulation to sweat glands
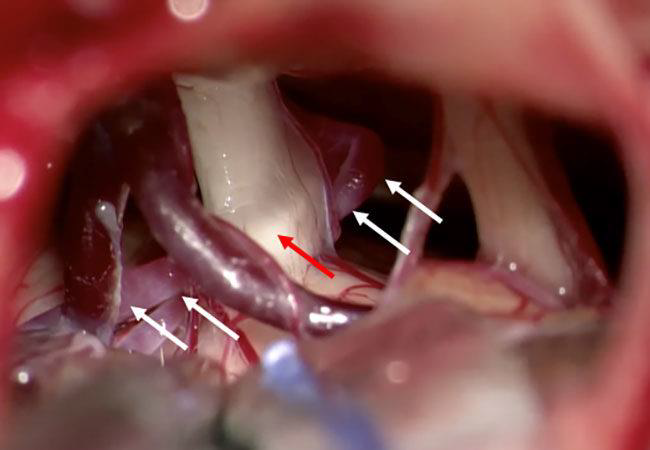
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Neuropathic pain to one side of the face
May cover regions supplied by one or more of the main branches of the trigeminal nerve
“Tic douloreux”
Typically caused by compression of the
trigeminal ganglion inside of the cranial
cavity
Usually caused by an aberrant artery
Causes demyelination of sensory axons
Excruciating, episodic pain
Can be set off by touching the face, brushing teeth, chewing
Gustatory Sweating (Frey’s Syndrome)
Localized hyperhidrosis (sweating) and
erythema (redness) in response to gustatory
stimuli
Commonly caused by surgical damage to the auriculotemporal n.
Parasympathetic stimulation of the parotid gland (production of saliva) improperly stimulates sweat glands (normally stimulated by sympathetic)
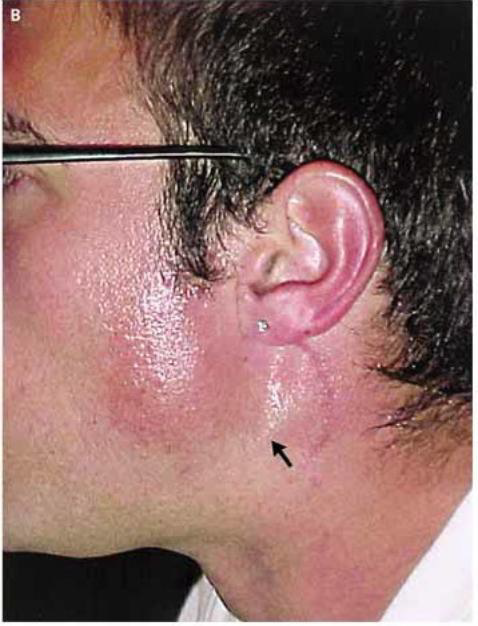
Retropharyngeal Abscesses
Infection w/in retropharyngeal space
Infections in the true retropharyngeal space may result from spread of infections of the middle ear, nasopharynx, and posterior oral cavity
Inferior boundary of the true retropharyngeal space is ~T4
Infections in the danger/alar space may spread inferiorly to the mediastinum (central compartment of the thorax) and cause very dangerous infections
Inferior boundary of the danger/alar space is the diaphragm and includes the area around the heart
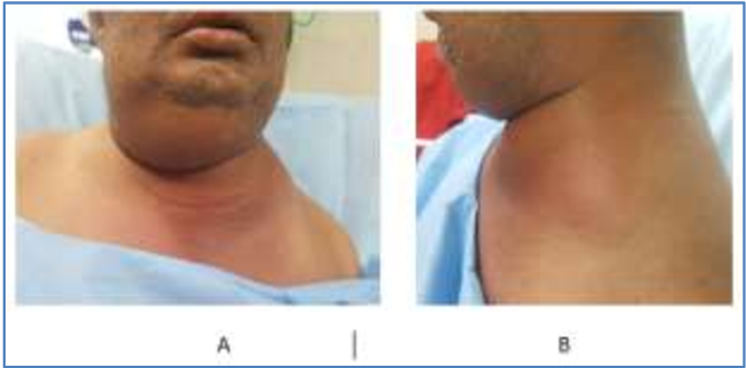
Congenital torticollis
Fibrous tissue tumor in SCM, injury to SCM at birth
Contraction/shortening of the SCM
Causes head tilt & neck twist = head will tilt towards the affected side, chin points away from the affected side

Spasmodic torticollis (AKA cervical dystonia): usually begins in adulthood
•May involve any bilateral combination of neck muscles, especially SCM and trapezius
•Results in sustained turning, tilting, flexing, or extending of the neck
Swollen Glands
“Swollen glands” felt in the neck due to upper respiratory infections, strep throat, etc. are not actually glands
Usually swollen submandibular lymph nodes surrounding the gland
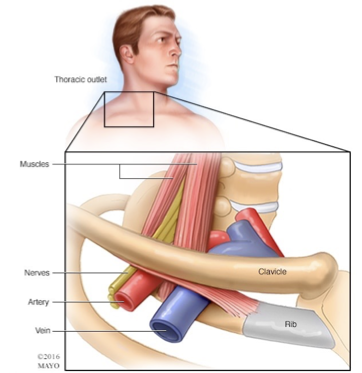
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Compression of the neurovascular structures at the superior thoracic outlet by:
Scalene muscle spasms or tension
Clavicle fracture or congenital defects
Cervical ribs (long cervical transverse process)
Apical lung tumor
Repetitive strain injury
Symptoms:
Numbness, pain (nerve compression)
Discoloration, temperature abnormalities (vasculature compression)
Why are ear infections more common in children
•Pharyngotympanic tube is shorter and more horizontal in children
•Ear infections are more common in children
•Movement of air and fluid is more difficult
•When tubes become swollen from a cold, upper respiratory infection, or allergies, bacteria can become trapped
•Ear tubes – tiny, hollow cylinders placed in the tympanic membrane to allow air circulation between the outer and middle ear
Epistaxis
Epistaxis = nosebleed
Very rich blood supply to the nasal mucosa
Most commonly from trauma to the anterior third of the nose
Kiesselbach’s area –
Common nose bleed area: anastomotic plexus involve branches of the ophthalmic, maxillary, and facial arteries
Adenoidectomy
Surgical removal of pharyngeal tonsils due to impaired breathing through the nose, chronic infections, or recurrent earaches
Caused by tonsilitis
Tonsillectomy
Surgical removal of palatine tonsils due to recurrent tonsillitis, throat infections, or sleep apnea
Danger Triangle of the Face
Infections on the face can through the angular vein into the superior/inferior ophthalmic veins and into the cavernous sinus (w/in the cranial cavity)
•Often affects movements of the eye
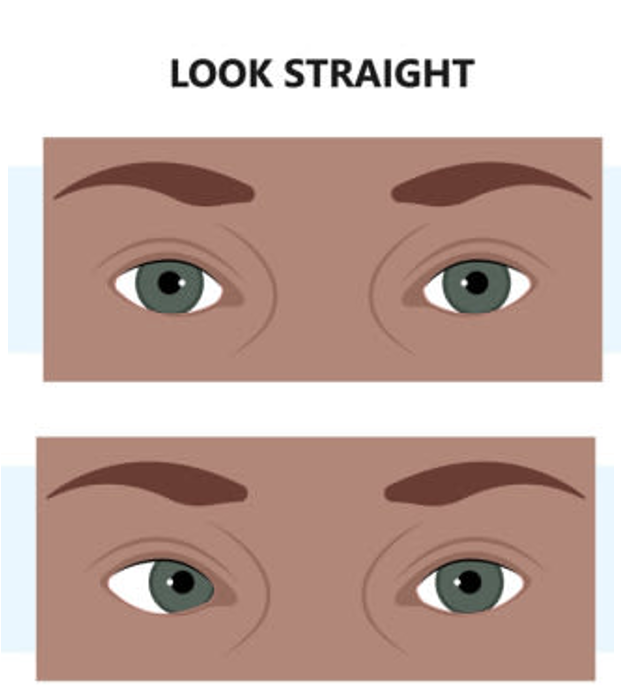
CN III Palsy
Symptoms
Affected eye is directed “down and out”
Lateral rectus & superior oblique are unopposed
Partial ptosis (eyelid drooping)
Pupil is abnormally dilated
Mydriasis
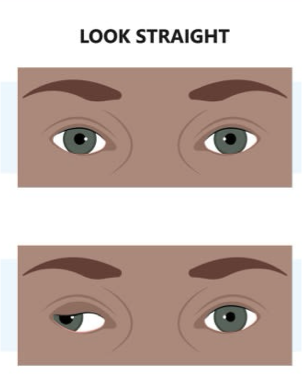
CN IV Palsy
Symptoms
Affected eye is directed “up and in”
Loss of only the superior oblique m.
All other muscles unopposed
Diplopia (double-vision)
Often have a compensatory head tilt
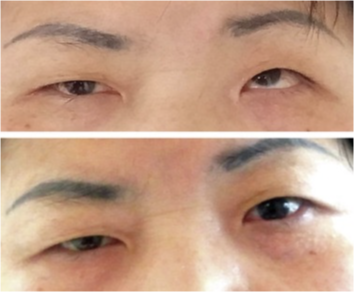
CN VI Palsy
Symptoms
Affected eye is directed medially
Loss of lateral rectus
Medial rectus is unopposed
Affected eye cannot be abducted to look laterally
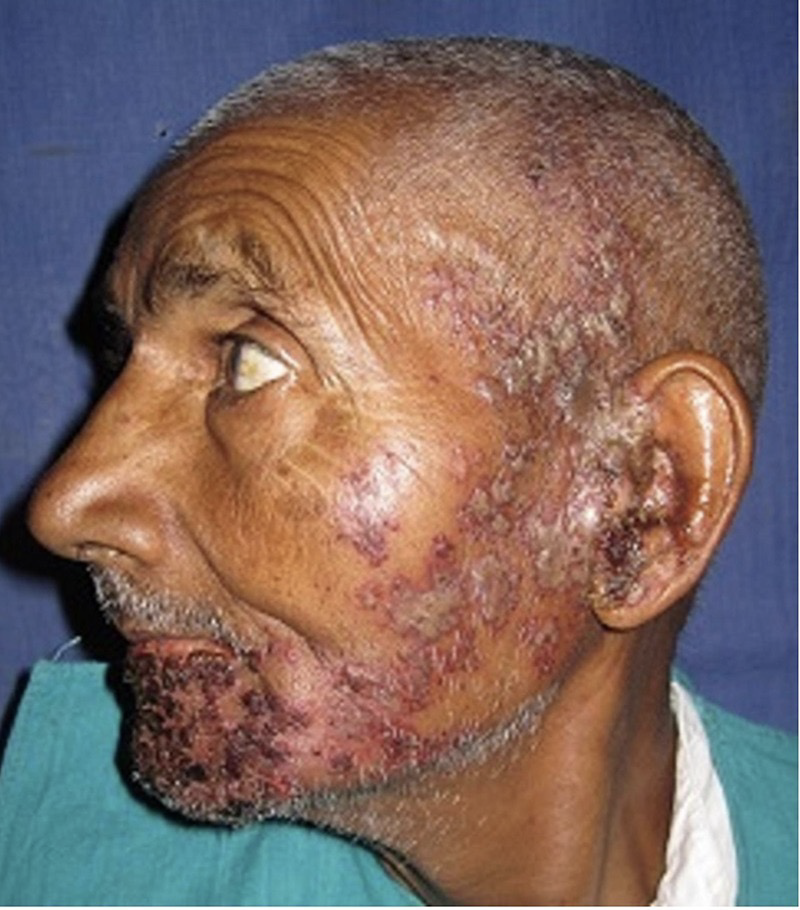
Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
Reactivation of the chickenpox virus
After initial infection, virus stays dormant in sensory ganglia
Development of painful blisters along a
dermatome
Trigeminal involvement ~10-20% of cases
May involve one or multiple branches
V1 involvement can severely impact the eye