Module 3 communications
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terminology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Aphasia
a neurological condition that affects a person’s ability to communicate

Body language
the nonverbal signals, such as movements, expressions, and postures, that a person, whether patient or healthcare provider, uses to communicate thoughts, feelings, and physical or emotional states without words

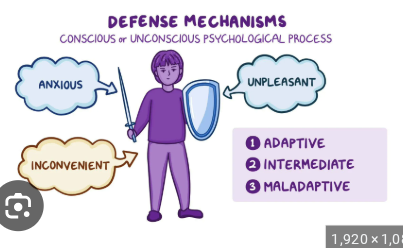
Defense mechanisms
means to protect oneself when feeling upset or anxious; common mechanisms are denial, projection, and repression
Denial
Refusing to accept or experience a situation

Displacement
the movement of an object or structure from its original position
Dyslexia
a learning disorder that involves difficulty reading due to problems identifying speech sounds and learning how they relate to letters and words

Dysphasia
a disorder affecting language abilities

Interpersonal
the relationships and interactions between people, most notably the patient, their family, friends, and the healthcare team

Myth
false or unproven beliefs, practices, or theories that have become widely accepted within the medical profession or public, despite lacking scientific evidence

Physiological
the normal functioning of the body's systems and processes
Psychosocial
the interaction between psychological (mental) and social factors that influence a person's health and well-being

Rationalization
explaining an action, decision, or belief with seemingly logical reasons that mask or deny the true, often less flattering, motivation or cause

Regression
when a patient temporarily or permanently reverts to an earlier, less mature stage of development

Repression
when the subconscious brain ignores thoughts or situations to protect oneself

Sublimation
process of channeling unacceptable or difficult impulses and emotions into a positive, socially acceptable outlet.

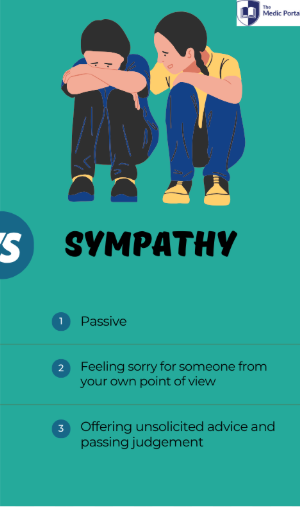
Sympathy
an emotional response of pity or sorrow for another person's misfortune, a feeling of care for someone else's trouble or grief
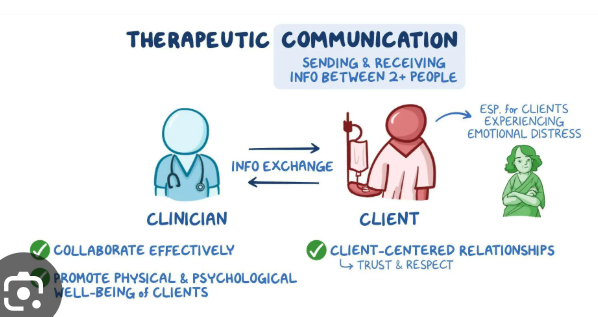
Therapeutic Communication
A way of combining active listening skills and acknowledging the feelings of the sender before responding to the sender