Unit 3 - Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Use in Function: Dynamic sitting
Weight Shifting
Turning
Reaching for an object
Completing ADLs
Sitting on an Unstable Surface or Unstable BOS
Lifting or Carrying
Use in Function: Sitting transfers
Asymmetrical Scooting
Symmetrical Scooting
Pivot from Bed to Chair or W/C
Pivot from W/C to Toilet
Pivot from W/C to Car
Body Structure and Function Impairments
Aerobic capacity/endurance
Arousal, attention, and cognition
Cranial and peripheral nerve integrity
Joint mobility § Motor function
Pain
Range of motion
Reflex integrity
Sensory integrity
Part to Whole Task
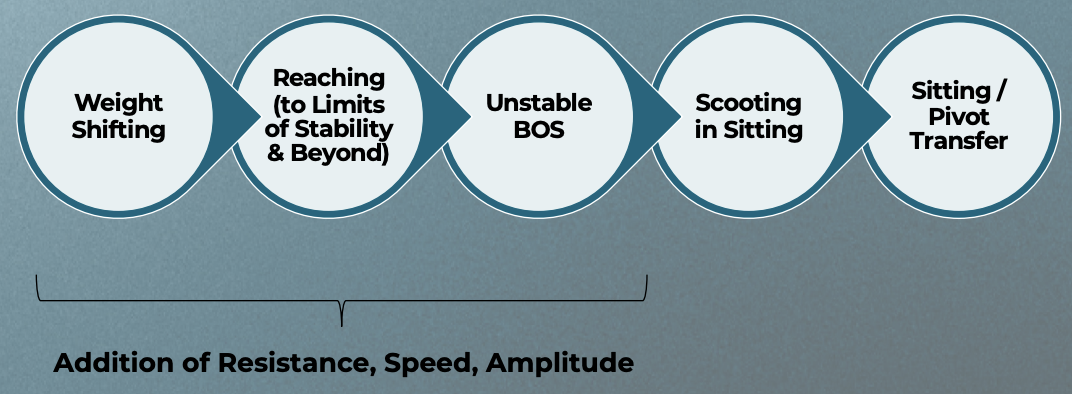
Dynamic sitting
Occurs when sitting and moving the limbs or when changing posture
Requires anticipatory postural adjustments
Initially requires attention, later becomes automatic
Impairment management: Strength Dynamic sitting and transfers
Initially, the patient's attention is directed toward the critical tasks that require efficient movement and postural adjustments.
With more repetition, posture modifications will become automatic
Proper alignment must be accomplished first before starting with dynamic sitting balance exercises
The cervical, thoracic, lumbar and pelvis must be in neutral position
Sitting Muscles
Erector Spinae Muscles
Abdominals muscles
Hip flexors muscles
Gluteal muscles
Trunk rotators
Arm and shoulder muscles
Sitting Balance: Starting Point
Patient is seated on a rigid platform with hip-width between LEs and 90º angles at the knee and hip.
Start with easier tasks that slightly challenge the pt then progress to more challenging tasks
Patients initially require more concentration to perform tasks
Sitting balance: Interventions
Sitting-weight shifting with upper extremity support
Active Weight Shifts Against Resistance
Voluntary Movements and Task-Oriented Practice
Resisted Limb Movements
Dynamic Sitting Interventions
Seated Leg Lifts
Seated Marching
Seated Twists
Reaching activities
Balancing on a Stability Ball
Resistance Band Rows
Ball Pass
Pulleys
Scooting
a seated movement where the body shifts forward or backward
Requires shifting weight to the stable side and lifting the dynamic side to move the pelvis
Upper extremities are not used for pushing or assisting
prepares for independent bed mobility and sit-to-stand transfers
Scooting: Interventions
Scooting in the Short-Sitting Position
Scooting in the Long-Sitting Position
Scooting Off a High Table Into Supported Unilateral Standing
Rocker Board or Inflated Disc
Computerized Platform/Feedback Training
Ball Activities
Dynamic Ball Activities
Seated Integrative Medicine Exercises
Seated Tai Chi
An ancient Chinese martial art involving slow, deliberate movements emphasizing body awareness, flexibility, strength, and balance.
Studies highlight improvements in balance, functional mobility, and walking endurance
Seated Integrative Medicine Exercises
Seated Yoga
originated in India to integrate the physical, mental, and spiritual aspects of the body. It includes various styles, typically combining physical postures (asanas) and controlled breathing (pranayama)
Dynamic Sitting with Increased Tone
Common presentation
Flexor synergy UE (elbow flexion, shoulder adduction)
LE extension synergy (hip/knee extension, PF)
Impairment Management: Tone (UE/LE) Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
Dynamic Sitting with Increased Tone: Common Presentation
Flexor synergy UE (elbow flexion, shoulder adduction)
LE extension synergy (hip/knee extension, PF)
Impairment Management: Tone (UE/LE) Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
Dynamic Sitting with Decreased Tone: Common Presentation
UE and LE flaccidity
Poor postural control
Head forward, trunk slumped
Impairment Management: Tone (UE/LE) Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
UE Positioning – Increased Tone
Elbow, wrist, finger flexion
Shoulder adduction/internal rotation
Management:
WB, positioning aids, splints, slow stretching, modalities
Impairment Management: Tone (UE/LE) Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
UE Positioning – Decreased Tone
Arm drop, shoulder subluxation
Poor scapular stability
Management:
Arm troughs, taping, facilitation of proximal control, modalities
Impairment Management: Tone (UE/LE) Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
LE Positioning – Increased Tone
Hip adduction, knee extension, PF
Difficulty with WB and foot placement
Management:
WB, wedges, slow transitions
Impairment Management: Tone (UE/LE) Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
LE Positioning – Decreased Tone
LE abduction, hip/knee buckling
Foot instability
Management:
Ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs), supported WB, compression
Transfer Challenges with Increased Tone
Extensor thrust
Scissoring of legs
UE flexor patterns blocking push-off
Postural Tone
Transfer Challenges with Decreased Tone
Trunk collapse
Inability to engage UE/LE for support
High risk of slipping or falling
Pre-Transfer Tone Management
Normalize tone before task:
ROM/stretching
WB activities
Environmental control (light, noise, cold)
Abnormal Tone-transfers
Transfer Strategies for Increased Tone
Slow, rhythmical movements
Break down task into steps
Facilitation techniques: tapping, guided movement
Equipment: sliding boards, grab bars
Abnormal Tone-transfers
Transfer Strategies for Decreased Tone
Maximize stability: block knees, support trunk
Engage trunk with facilitation
Use of transfer belts, AFOs, and surface height optimization
Common Positioning Aids
Lap trays
Arm troughs
Foot blocks
Cushions and wedges
Dynamic splints
UE Intervention Techniques
WB through UE
Rhythmic stabilization
Bilateral movement tasks
Use of therapy balls, mirror therapy
LE Intervention Techniques
Sit-to-stand training
Supported standing
Weight shifts and reach in seated
Supported hip/knee control work
Ataxia: Impairments Overview
Impaired timing of movements
Impaired coordination
Impaired posture at rest and with movements
Intention tremor impacting movements
Dysmetria impacting accuracy of movements
Impaired overall control of movements
Impaired hand-eye and/or eye-foot coordination
Ataxia
Interventions: General Approach
Safety and fall prevention
Improve postural control at rest and during activities
Compensation and adaptation strategies
Start with simple tasks and then progress to more complex tasks
Modulate speed: start with self-selected speeds to fast movements while maintain accuracy
External cues: visual and tactile
Environmental modifications to facilitate completion of functional tasks
Ataxia
Interventions: Dynamic Sitting
Start with sitting with full support and then progress to less support and then no support
Static sitting on stable surface > static sitting on unstable surface
Functional weight shift and reaching in various directions: stable surface > unstable surface
Functional training while sitting: grooming and feeding
These exercises can help with ADLS
Ataxia
Interventions: Dynamic Sitting Progression
Eyes open > Eyes Closed
Sitting on hard surface > sitting on foam pad > sitting on a physio ball
Perform dual-task activities: cognitive and mechanical
Perturbations in sitting: static at first, progress to dynamic sitting activities
Dynamic sitting activities while sitting on an unstable surface: physio ball
Ataxia
Interventions: Transfers
Postural alignment before performing transfers
External cues to improve movement timing and coordination
Break down to the task to be performed: scooting forward, forward trunk lean (nose over toes), trunk extension to come to standing
Manual cues to guide the movements
Start with full support: chair with back rest, feet on floor
Ataxia
Interventions: Transfers Progression
High intensity with repetitions
Focus on proper biomechanics
Performance of sit to stand transfers during functional tasks: stand by kitchen sink to wash face, shave etc
Use surface of various heights: sit to stand from a higher surface > sit to stand from a lower surface
Transfers to/from different surfaces
Ataxia
Interventions: Home Exercises
Safety education
Patient and caregiver education
Involve caregivers in providing assistance with activities
Evaluate the need for assistive devices to promote independence with daily living activities
Perform HEP to maintain improvements with therapy
Somatosensation in Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
Somatosensation includes proprioception, kinesthesia, and vibration
These are key to maintaining posture, alignment, and adaptive movement
Deficits affect trunk stability, orientation, and reactive balance
Somatosensation
Ex; Key Clinical Findings
Impaired static and dynamic sitting balance
Delayed protective and reactive responses
Relies on visual input
Impaired proprioception in the left upper and lower extremities
Requires verbal/tactile cueing
High fall risk
Somatosensation
Treatment Considerations
Prioritize safety and modify the environment
Simplify tasks and enhance multisensory feedback
Emphasize task-specific, repetitive training
Improve weight bearing through the left upper and lower extremities
Stimulate proprioception with touch, pressure, and visual inputs
Somatosensation
Ex: Compensatory Interventions
Use mirror for midline orientation and visual feedback
Provide tactile/verbal cues to promote weight shift to the left side
Incorporate bright-colored floor tape to guide reaching and foot placement
Somatosensation
Ex: Restorative Interventions
Use joint compression and rhythmic stabilization
Incorporate textured mats and vibration for re-education
Task specific training
Vision in Dynamic Sitting and Transfers
Visual Input for Postural Control and Balance
Spatial Orientation and Navigation
Compensatory Transfer Strategies Due to Visual Deficits
Increased Fall Risk and Safety Concerns
Vision
Ex: Key Clinical Findings
Visual Deficit: Left homonymous hemianopia (visual cut in the left field of vision in both eyes)
Motor Deficits: Mild left-sided trunk weakness and delayed trunk righting reactions
Functional Impact:
Misses objects on her left side
Slightly loses balance when reaching to the left
Requires contact guard assistance with pivot transfers due to poor spatial awareness and delayed protective reactions
Vision
Ex: Treatment Considerations
Improve safety and independence during transfers through visual compensation and retraining
Promote dynamic sitting balance through graded, task- oriented interventions
Increase spatial awareness of the left visual field
Vision
Ex: Compensatory Strategy — Environmental Setup
Arrangement
bed and toilet angled slightly to the right
high-contrast tape
decluttered path
Lighting
ensured even and adequate
Consistent Setup
predictable positions
mirror feedback
Vision
Ex: Compensatory Interventions
Transfer rehearsals with cuing
use of landmarks and visual anchors
Vision
Ex: Restorative Interventions
Visual Scanning Training During Transfers
Reaching and Scooting Tasks with Leftward Bias
Graded Transfer Practice
Evaluation Considerations — Seated position requires:
Upright trunk posture
Support surface through ischial tuberosities and posterior thighs
Various combinations of head, trunk, UE and LE motions
Evaluation Considerations — Transfers requires:
Dynamic trunk postural control
Ability to control the center of mass over the base of support
Various combinations of head, trunk, UE and LE motions
Evaluation Considerations — Consider impairments that are contributing to poor balance contro
Standardized tests specific to sitting include:
Reach Test
Sit-and-reach Test
Sitting Arm Raise Test
Trunk Impairment Scale
Trunk Control test
Scale for Contraversive Pushing
Lateropulsion Scale
Goals of Balance intervention
Safety and fall prevention education
To improve balance
To teach compensation strategies when needed
To return the patient to previous activity levels
Safety (balance)
Determine the amount of assistance needed
Proper guarding technique to prevent falls
Gait belt and/harness
Non-slip shoes
Wide base of support
Proper lighting
Remove environmental hazards/obstacles
Balance
Interventions: General approach
Do not leave the patient unsupported
Plan ahead for necessary equipment needed
Gait belt to protect against falls
Never “pull” on a weak or impaired upper extremity
Therapist positioning for required tasks
Consider position of the patient’s UE to avoid injury
Consider patient’s goals, current sitting ability, prognosis
Determine if focus is
Compensation (orthotics, use of upper extremities, chair back/arm rests)
Recovery: Level of motor control-mobility, stability, controlled mobility, skill
Surface considerations
Strategies to move from supine to short sit or long sit
Balance
Interventions: Dynamic Sitting Balance
Static sitting balance on stable surface
Static sitting balance on unstable surface
Dynamic sitting balance
Functional weight shift and reaching:
Seated on a stable surface
Seated on an unstable surface
Balance
Interventions: Dynamic Sitting Balance —> Short Sitting
Rolling chair, reach for desk or books on bookshelves
Edge of bed, donning socks and shoes
Balance
Interventions: Dynamic Sitting Balance —> Long Sitting
Sitting in bed, pulling slacks on hips
Sitting on floor, watching TV
Balance
Interventions: Progression to transfers —> Mobility
Symmetrical weight bearing
Perform lateral pelvic tilts
Scooting in all directions
Balance
Interventions: Progression to transfers —> Stability
Maintain sitting against Perturbations
Alter surfaces and functional tasks
Dynamic reaching and weight transfers
Balance
Interventions: Progression to transfers —> Controlled Mobility
Upright positioning during weight shifts, reaching and scooting
Dissociate upper & lower trunk movement
Combined trunk and extremity movements with functional tasks
Alter environment, speed, manipulation of objects and coordination tasks
Balance
Interventions: Progression to transfers —> Improve Skills
Upright positioning during weight shifts, reaching and scooting
Transfer to different surfaces
Move from sit to stand
Balance
Interventions: Home Exercises
Safe practice at home and with social roles
Dressing and bathing
Transfers: dining room chair, toilet seat, car seat
Lower caregiver assistance over a period of time
Patient and family education/ Home exercises
Practice transfers from and to various surfaces
Home adaptations: elevated seated surface, grab bars
Incorporate exercises with daily living tasks
Perception in Dynamic Sitting & Transfers
Deficits: Difficulty interpreting sensory input to guide safe and appropriate actions
Misjudging distance during reaching, scooting, or transferring
Missing or misjudging support surfaces
Delayed or unsafe postural adjustments
Cognition in Dynamic Sitting & Transfers
Deficits: Impaired attention, memory, organization, and executive function
Distractibility during motor tasks
Difficulty following multi-step directions
Unsafe decisions during complex movements
Communication in Dynamic Sitting & Transfers
Deficits: Impairments in speaking, understanding, reading, or writing
Misunderstanding safety instructions
Inability to express needs or concerns
Delayed or inappropriate task performance
Perception/Cognition/Communication
Ex: Key Clinical Findings
Mild left-sided neglect
Visuospatial deficits
Mild somatosensory deficits
Mild cognitive impairment
Attention impairments
Functional impact?
Perception/Cognition/Communication
Ex: Treatment Considerations
Enhance left-sided awareness
Support cognitive function
Improve alignment and weight shifting
Manage attention deficits
Use clear, step-by-step verbal cues
Gradually increase complexity
Perception/Cognition/Communication
Ex: Compensatory Interventions
Visual scanning strategies
Environmental setup
Use of tactile, verbal and visual markers
Simplified task environment
Written or pictorial cue cards
Perception/Cognition/Communication
Ex: Restorative Interventions
Visual scanning training: structured to the left
Dynamic sitting balance training
Object recognition exercises
Task specific training
Dual-task activities
Attention training
Progressive complexity
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Direct impairments
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Slowed postural reflexes
Decreased initiation of movement
Resting Tremor
Decreased motor control
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Indirect impairments
Postural impairments
Strength deficits
Decrease ROM
Festinating gait pattern
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Composite impairments
Decreased coordination
Impaired balance
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Functional Performance
Activity limitations:
Impaired bed mobility
Impaired transfers
Impaired locomotion
Difficulty with dressing
Difficulty with feeding
Increased fall risk
Participation restrictions:
Cannot help around house
Cannot drive car
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: PT Interventions — General Approach
Exercise with bracing/adaptive equipment
Auditory and visual cues
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation techniques
Mirror therapy
Constraint Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT)
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Active range of motion, motor control
Fall prevention
Home exercise program
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Interventions — Dynamic Sitting
Improve sitting posture: heat application, myofascial release, stretching, contract relax and joint mobilizations
Improve alignment in sitting
Improve endurance by working on improving breathing control
Improve chest expansion
Improve dynamic sitting: provide external cues – visual and auditory
Improve attention and motor learning
Improve active ROM of UE and LE: active weight shifts, reaching for objects at various heights
Improve ability to perform dynamic activities
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Interventions — Transfers
Preparation for activity: provide external cues: visual, auditory (including instructions – nose over toes, extend your back as you stand)
Improve attention and motor learning
Improve scooting: work on side to side scooting and scooting front and back
Improve dynamic movements, prepare for transfers
Improve UE and LE motor control: weight shifts while sitting a foam surface, leaning forward with hands on a physio ball, sit to stand from a high surface height
Practicing a part of sit of stand task before attempting the task
Improve transition from sit to stand: provide external cues – auditory and visual, progress from easy to more difficult task
Improve performance across all stages of a sit to stand transfer
Movement Disorder (BG)
Ex: Home Activities
Encourage Ed to implement the exercise to daily living tasks such as dressing himself and when eating
Teach Ed to safely perform activities around the house
Educate on fall prevention strategies
Focus on improving ADLs and IADLs
Extrinsic Feedback Strategies
Dynamic Sitting
Involves maintaining postural control in sitting while moving and shifting one’s weight.
Requires controlling a moving center of gravity over one’s base of support.
Becomes more challenging when:
Feet and/or hands are not bearing weight
Points of assistance/support are moved lower on the trunk
Activities are performed farther away from midline
Movement speed increases
Extrinsic Feedback Strategies
Common Functional Tasks in Dynamic Sitting
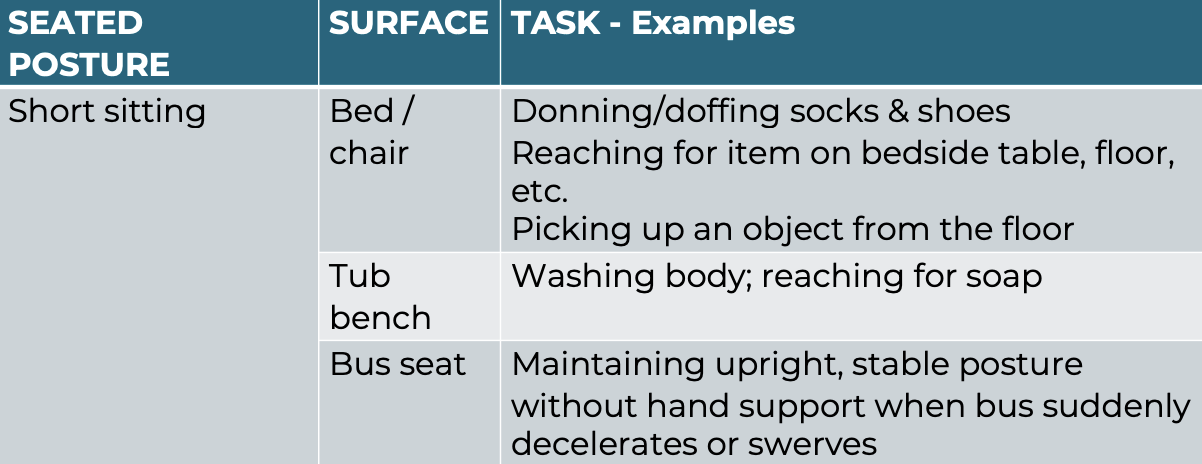
Extrinsic Feedback Strategies
Task Analysis — Stage of Learning: Initial (Cognitive)
Provide lots of visual FB
Demonstrate task
Emphasize desired outcome & critical task elements
Provide KR to reinforce successful movement outcomes
Provide KP when errors are consistent
Allow for trial-&-error learning
NOTE: Although constant FB improves performance in early learning, it is important to start incorporating variable FB to improve retention
Extrinsic Feedback Strategies
Task Analysis — Stage of Learning: Intermediate (Associative)
Less dependent on visual FB
Encourage pt. to self-assess motor performance & focus on the "feel of the movement"
Provide variable FB to improve retention: summary, faded, bandwidth
Reduce hands-on assistance
Continue to provide KR with successful movement outcomes
Continue to provide KP with consistent errors
Stress relevance of functional outcomes
Extrinsic Feedback Strategies
Task Analysis — Stage of Learning: Advanced (Autonomous)
Only occasional FB required
Focus on key errors
Extrinsic Feedback Strategies
Ex: Transfers
The functional task of transitioning between body positions body positions & surfaces
Bed <-> wheelchair
Floor < - > stand
Wheelchair < - > therapy mat / toilet / tub bench