IB Economics: Microeconomics
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 3-15 of Hodder IB Economics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Demand
a.k.a effective demand. the quantity of a good or service that customers are willing and able to buy at given prices in a particular period of time.
Law of Demand
states that the quantity demanded of a product will fall if the price increases, and vice versa.
The Income Effect
as the price of a product falls, the real income of consumers increase so they are able to buy more goods & services at lower prices.
The Substitution Effect
as the price of a product falls, more people can buy the product, so they choose this over rival products. It causes consumers to replace higher priced products with lower priced ones.
Market
any place where transactions take place between buyers and sellers
Market Demand Curve
refers to the sum of all individual demand of a product at each price level
Non-Price Determinants of Demand
are the various factors other than the price of the good or service that affect the demand for the product. Include Related products, Income, Preferences, Expectations of future prices, and Number of consumers (R-I-P-E-N).
Normal Goods
products that customers tend to buy more of as their real income level increases. This includes both necessities and luxury goods and services.
Inferior Goods
products of which the demand decreases when the consumers real incomes rise.
Complements/ Complementary Goods
products that are jointly demanded. Ex: torches and batteries.
Substitutes
are products that are in competitive demand because they can be used in place of each other. Ex: Pepsi & Coco-Cola
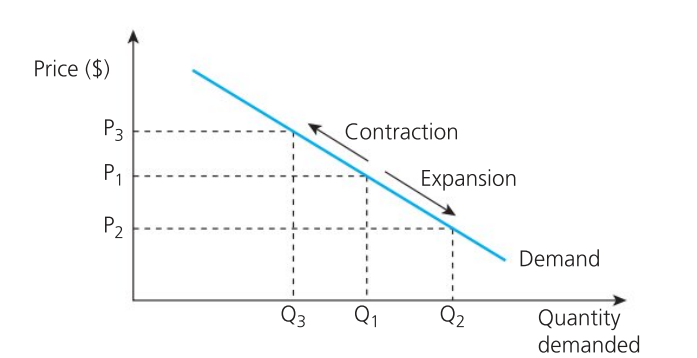
Movement Along Demand Curve
caused by the price changes only. A fall in price causes quantity demanded to expand while an increase in price causes quantity demanded to contract
Contraction in Demand
occurs when there is a fall in the quantity demanded for a product following an increase in it’s price
Expansion in Demand
occurs when there is an increase in the quantity demanded for a product following a fall in its price.
Increase in Demand
refers to a rightwards shift of the entire demand curve for a product, caused by favorable changes in non-price factors that affect demand.
Decrease in Demand
refers to a leftwards shift of the entire demand curve for a product caused by unfavorable changes in non-price factors that affect demand.
Demand Curve Shift
occurs when the is a change in any non-price factor that affects the demand for a product.
Supply
the amount of a good or service that firms are willing and able to provide at any particular price, per time period
Law of Supply
states that there is a direct (or positive) relationship between quantity supplied and price, ceteris paribus
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
explains what happens to the output of products when a firm uses more variable inputs while keeping at least one factor of production fixed in the short run. Employing additional variable factors of production will eventually decline the marginal returns.
Short Run
a period of time when at least one factor of production is fixed (usually land, capital, enterprise) , whereas other factor inputs are variable (usually labor)
Long Run
a period of time when no factors of production are fixed; all factor inputs are variable.
Marginal Cost
refers to the cost of producing an additional unit of output.
Market Supply
the sum of all individual supply of producers at each price level for a given product
Non-Price Determinants of Supply
the various factors other than the price of a good or service that affect the supply of the product. Includes Costs of production of factors of production, Indirect taxes, subsidies, Technological change, Expectation of future prices, prices of related products, number of firms in the industry. Can be remembered through C-I-S-T-E-R-N.
Competitive Supply
means the output of one product prevents or limits the production of alternative products, due to competing resources.
Joint Supply
refers to the supply of a product that results in the output of at least one by-product
Indirect Taxes
government levies on expenditure rather than on incomes. Essentially, these taxes add to the producer’s costs of production
Expansion in Supply
caused by a higher price for the product, thus causing an upward movement along the supply curve.
Contraction in Supply
caused by a lower price for the product, thus causing a downward movement along the supply curve.
Supply Curve Shifts
occur when there is a change in non-price factors that affect supply, resulting in changes in supply. This is represented by a shift of the entire supply curve of the product.
Market Equilibrium
occurs when the quantity demanded for a product is equal to the quantity supplied of the product, so there are no shortages or surpluses
Equilibrium
the condition that holds when a market is cleared of any shortages of surplus. Hence, it occurs at the price where the quantity demanded for a product is equal to the quantity supplied.
Market Disequilibrium
occurs when the quantity demanded for a product is either higher or lower than the quantity supplied in the market, i.e. there is either a shortage (excess demand) or surplus (excess surplus).
Excess Supply
refers to a disequilibrium situation where the price of product is set above the equilibrium price, thus creating a surplus in the market.
Surplus
created when the supply of a product exceeds its demand because the price is set higher than the market equilibrium price.
Excess Demand
occurs when the price is set below the equilibrium, i.e. a shortage exists.
Price Mechanism
refers to the interaction between buyers and sellers (forces of demand and supply) in the free market in order to allocate resources, thereby determining production and consumption choices.
Signaling Function
an aspect of the price mechanism in allocating resources by providing information to producers and consumers on where resources are required (markets with price increases) and where they are not (markets with price falls).
Incentive Function
an aspect of the price mechanism in allocating resources as a price changes provide an incentive (motivation) for producers and consumers to change their behavior in order to maximize their benefits.
Rationing Function
aspect of the price mechanism that deters some consumers from buying a product or resource owing to higher prices, thereby rationing (preserving) it. It serves to ration scarce resources when the demand for a product exceeds its supply.
Consumer Surplus
refers to the gain or benefit to buyers who can purchase a product at a price lower than that which they are willing and able to pay.
Producer Surplus
refers to the gain or benefit to firms that receive a price higher than the price they are willing and able to supply at.
Community Surplus
a.k.a social surplus. the sum of consumer and producer surplus at a given market price and output, thereby maximizing economic welfare.
Allocative Efficiency
socially optimal situation that occurs when resources are distributed in such a way that consumers and producers get the maximum possible benefit.
Market Failure
any situation when the price mechanism (the free market forces of demand and supply) allocates scarce resources in a inefficient way.
Equilibrium Price
a.k.a market clearing price. the price where the quantity demanded for a product matches the quantity supplied in the market at a given time.
ADD CHAPTER 6
ADD CHAPTER 6
Elasticity of Demand
a measure of how the quantity demanded of a product changes owing to a change in a factor that affects demand (price, real disposable income, etc)
Price Elastic Demand
describes demand for a product that is relatively responsive to changes in the product’s price, usually due to close substitutes being widely available. In this case, the value of PED > 1.
Price Inelastic Demand
describes demand for a product that is relatively unresponsive to changes in the product’s price, mainly due to the lack of close substitutes being available. In this case, the value of PED < 1.
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
measures the degree of responsiveness of quantity demanded for a product following a change in it’s own price.
Change in Quantity Demanded
refers to a movement along a demand curve, that is, a change in quantity demanded when price changes.
Unitary Price Elastic Demand
occurs when a given price change of a product leads to the same percentage change in the quantity demanded. Hence, the PED value = 1.
Change in Demand
refers to a shift in the demand curve for a product due to a change in non-price factors affecting demand.
Real Disposable Income
the money available after the impact of inflation, or higher prices, and taxes have been accounted for.
Income Elasticity Of Demand (YED)
measures the degree of responsiveness of quantities demanded following a change in the real income of consumers.
Income Elastic Demand
occurs when the % change in the QD of a product is greater than the % change in consumers’ real income. Applies to demand for services and luxury products.
Services
intangible (non-physical) products.
Ex: haircuts, bus rides, internet access.
Luxury Products
products with income elastic demand, i.e. goods & services with a value of YED > 1.
Income Inelastic Demand
occurs when % change in the QD of a product is less than the % change in consumers’ real income. Applies to the demand for necessities
Necessities
essential products that consumers buy in order to meet their needs. They are income inelastic.
Normal Goods
products customers tend to buy more of as their real income level increases.
Luxuries
superior goods and services with a YED > 1, i.e. demand is highly income elastic. increase in real incomes lead to a proportionally greater increase in demand for luxuries.
Engel Curve
used to demonstrate the relationship between income and QD. Normal goods have positive slopes, Inferior goods have negative slopes along this curve.
Inferior Goods
products with a negative income elasticity of demand. The demand for such products fall when real incomes rise.
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
measures the degree of responsiveness of quantity supplied of a product due to a change in it’s price
Unitary Price Elastic Supply
refers to a theoretical situation when the value of PES = 1, that is, the percentage change in quantity supplied is equal to the percentage change in the price of the product
Mobility of Factors of Production
refers to the level of ease and cost of factor substitution in the production process. The easier it is to substitute factors of production, the more price elastic supply tends to be
Public Goods