Science Physics Revision 🧪
1/53
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is a force?
A push, pull or twist that is measured in Newtons (N).
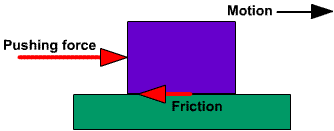
What is friction?
Friction is a force that acts in a direction opposite to motion.
Are force and work measurable?
Yes.
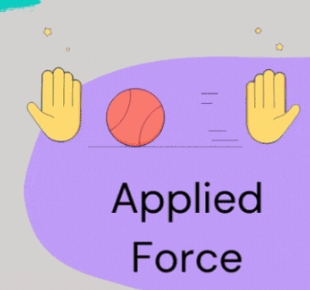
What is Applied Force? (Fapp, Contact)
A force applied to an object by another person or object. Eg. Kicking a soccer ball
What is Frictional Force? (Ffric, Contact)
The force a surface makes as an object makes an effort to move. Acts in the opposite direction that it’s going. Eg. Pen rolling on a table.

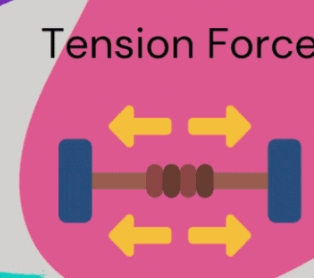
What is Tensional Force? (Ftens, Contact)
The force transmitted through a string, rope or wire when it’s pulled tight. Eg. Dog pulling it’s leash.
What is Normal Force/Supporting Force? (Fnorm, Contact)
The opposite of gravity, support force exerted upon an object. Eg. Pushing against someone’s hand, you require force not be pushed over.

What is Air Resistance? (Fair, Contact)
Acts upon an object when it moves through the air. Opposes the motion of the object. Eg. If there was no air resistance, a rock & a feather would fall at the same rate.

What is Spring Force? (Fspr, Contact)
Exerts a force when stretched/compressed. Eg. Springs on a trampoline.

What is Gravity Force/Weight Force? (Fgrav, Non-Contact)
It causes things to fall and makes things attract towards others. It is a force that pulls objects together. Eg. Apple falling.

What is Electrical Force? (Felect, Non-Contact)
When charged objects interact with other objects. Eg. Getting a spark when you go down a slide.
What is weight?
The force down.
What is a bouyant force?
The force up on an object in water.
(T/F) All objects have a gravitational force if they have matter.
True
What is Magnetic Force? (Fmag, Non-contact)
Caused by the motion of charges. Eg. A magnet picking up paperclips.

What is the definition of Contact?
Two objects that are in contact/touching.
What is the definition of Non-Contact?
Two objects that aren’t touching but create force.
Does your mass ever change?
No
How do you calculate Weight?
Weight = mass x gravity
What are forces measured in?
Newtons (N)
What is the pull of gravity?
10m/s²
Is a force a vector quantity?
Yes
What is a vector quantity?
Something that has both magnitude/size, and direction. Eg. 10 N left.
What is a free body diagram?
Used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces.
What is the Net Force/Resultant Force?
Overall force acting on an object.
What can an unbalanced force do?
Move, stop, or change the speed of an object. (Can also change to size/shape)
What can a balanced force do?
Nothing, the object will stay the same.
What does accelerate mean?
Go faster/Speed up.
What is the formula for Work?
Work = Force x distance
What does decelerate mean?
Slow down
What is a simple machine?
A basic device that changes the size/direction of a force.
How many simple machines are there?
6
What are all the simple machine types?
Pulley, Lever, Wedge, Wheel and Exle, Inclined plane and Screw.
Is energy needed to create a force?
Yes
What is a lever?
A stiff bar that moves around a fixed point.
What are the 3 parts of a lever?
Fulcrum, Load and Effort
What is the fulcrum?
The support of the turning point.
What is the load?
The object to be moved.
What is the Effort?
The applied force on the lever.
What are the 3 types of levers?
1st, 2nd, and 3rd class.
What is a 1st class lever?
When the fulcrum between the load and the effort.
What is a 2nd class lever?
When the load is between the fulcrum and the effort.
What is a 3rd class lever?
When the effort is between the fulcrum and the load.
What is a wedge?
Variations of the inclined plane that changes the size or direction of a force.
What can wedges be used for?
To cut, split, tighten/hold back, hold together, scrape.
What is the mechanical advantage formula?
Mechanical Advantage = Load ÷ Effort
Is an effort equal to 1 or less applicable?
No
If something is flexible, will the load go faster?
Yes
In an inclined plane, what is the formula for mechanical advantage?
MA = length of slope ÷ height of slope.
What is friction?
A force that acts against motion when two surfaces touch.
Which way does friction move?
The opposing way to the applied force.
What is static friction?
When the applied force isn’t big enough to overcome the frictional force.
What is kinetic friction?
The friction between two MOVING surfaces. Sliding/rolling.