Principles of Business Management Midterm Study Guide
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Using computers to design products and prepare engineering documentation
Shorter development cycles, improved accuracy, and lower cost
Info and designs can be deployed worldwide
Benefits of CAD/CAM
Product quality
Shorter Design Time
Production cost reductions
Database availability
New range of capabilities
Virtual Reality Technology
A visual form of communication in which images substitute for reality and typically allow the user to respond interactively
Allows people to ‘see’ the finished design before a physical model is built
Very effective in large-scale designs such as plant layout
Product Decision
Develop and implement a product strategy that meets the demands of the marketplace with a competitive advantage
Product Strategy Options
Differentiate
Shouldice Hospital
Low Cost
Taco Bell
Rapid Response
Toyota
Product decisions have major implications throughout the operations function
GM’s steering columns
Tesla Model 3 vs Model Y
Product Life Cycle- Growth Phase
Product design begins to stablize
Effective forecasting of capacity becomes necessary
adding or enhancing capacity may be necessary
Product Life Cycle- Decline Phase
unless the product makes a special contribution to the organization, management must plan to terminate the offering
Social Entrepreneurship
Found its roots in the 1980s when businesses began to realize that their customers care about specific social issues
Social entrepreneurs measure success by the positive impact they have made in the community in the long run
Why entrepreneurial ventures fail
lack of effective planning
insufficient capital
poor management
lack of customer interest
obtaining financing
personal funding
family and friends
bank loans
venture capital
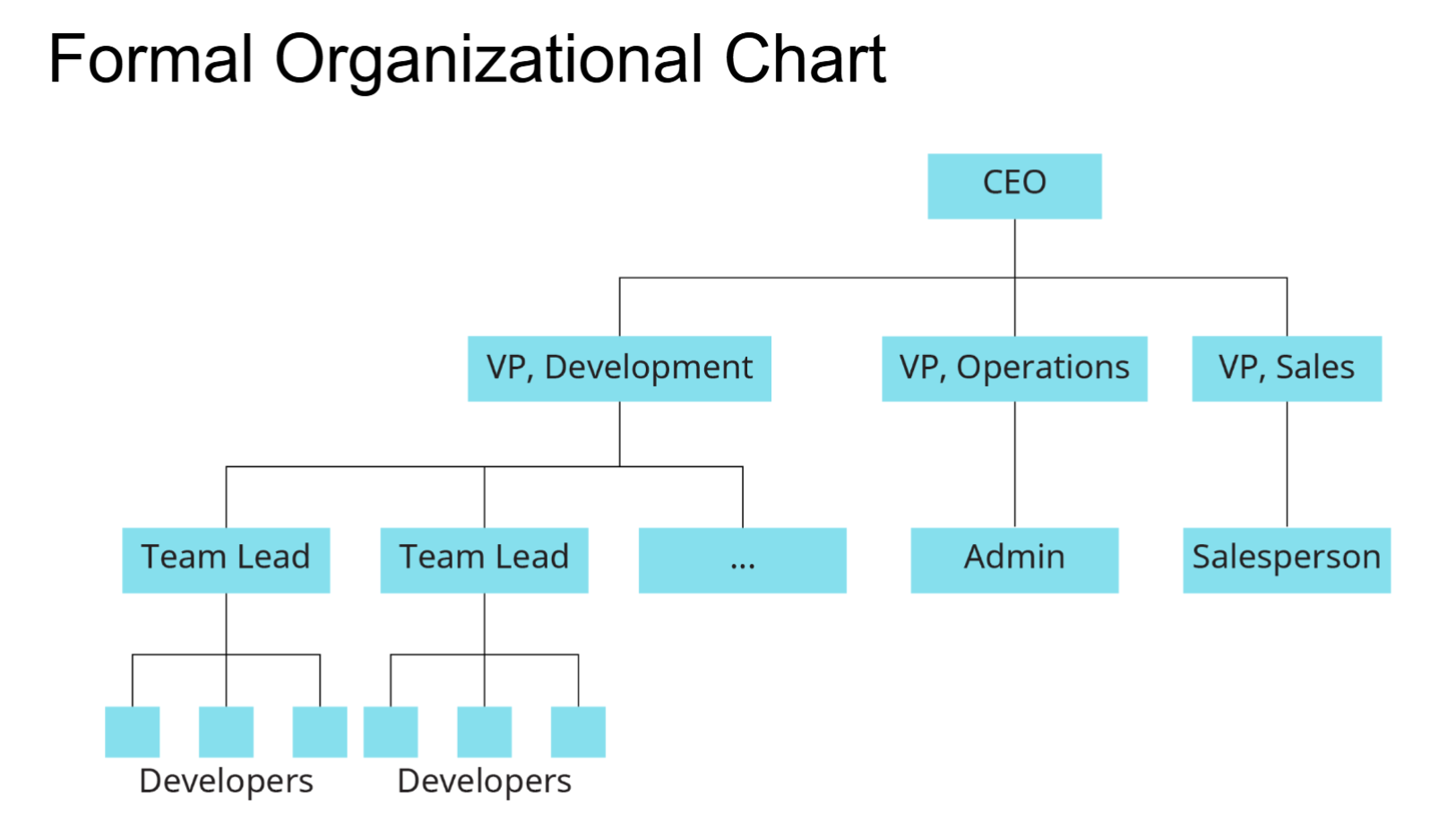
Formal Organizational Chart
How an organization’s culture, structure, and HR practices Support strategic implementation
Organizational Culture
shared assumptions that affect how work gets done
who reports to whom and who does what
HR Practices
How the organization manages its talent
Leadership creates alignment among culture, structure, and HR practices
Business Acumen
The skill to understand and manage business situations for positive outcomes and success
Business Acumen for Students
Helps student interpret data, forsee market trends, and engage in strategic decisions. Increases your potential value to employers if you show an understanding the elements of bus. acumen
Elements of Business Acumen
Strategic thinking, decision making, financial literacy, adaptability, market awareness, leadership, communication skills, problem solving, customer focus, operational understanding
What is Forecasting?
the art and science of predicting future events
underlying basis of all business decisions
production, inventory, personnel, and facilities
Forecasting Time Horizons- Short Range
Up to 1 year
purchasing, job scheduling, workforce levels, job assignments, production levels
Forecasting Time- Medium Range
3 months to 3 years
Sales planning, production planning and budgeting, cash budgeting, and analysis of various operating plans
Forecasting Time- Long range
3+ years
new product planning, facility location or expansion, capital expenditures, research and development
Forecasting Approach- Qualitative methods
used when a situation is vague
new products and technology
involves intuition, emotions, personal experiences, and value systems
Forecasting Approach- Quantitative Methods
Used when the situation is ‘stable’ and historical data exists
Existing products, current tech
involves mathematical techniques
Random Component
“Blips” in data caused by chance and unusual situations
follow no discernible pattern
cannot be predicted
Naive Approach
Assumes demand in next period is the same as demand in most recent period
phone sales in January will be the same in February
Sometimes cost effective and effecient
Can be a good starting point for comparison w/ more sophisticated models
Process Strategy
an organization’s approach to transforming resources into goods and services
The objective is to create a process to produce offerings that meet customer requirements within cost and other managerial constraints
repetitive focus
facilities often organized as assembly lines
characterized by modules with parts and assemblies made previously
modules may be combined for many output options
less flexibility than process-focused facilities but more effecient
product focus
facilities organized by product
high volume but low variety products
long, continuous production runs enable efficient processes
typically high fixed cost but low variable cost
generally skilled labor
benefits of VMI
•Reduced stockouts and overstocking.Improved inventory turnover and cash flow.
•Stronger vendor-customer relationships through collaboration.
•Lower administrative costs for the customer (less need to place frequent orders).
•Common Industries Using VMI:
•Retail (e.g., Walmart pioneered VMI with suppliers like Procter & Gamble).
•Manufacturing, Healthcare, Automotive.
Centralized Purchasing
One department at Corporate purchases for all locations
leverage volume
develop specialized stuff
develop supplier relationships
maintain professional control
maintain professional control
devote resources to selection and negotiation
reduce duplication of tasks
promote standardization
logistics managements
•Objective is to obtain efficient operations through the integration of all material acquisition, movement, and storage activities
•Is a frequent candidate for outsourcing
•Allows competitive advantage to be gained through reduced costs and improved customer service
airfreight
fast and flexible for light loads
may be expensive
uses passenger aircraft
cost and speed of shipments
Faster shipping is generally more expensive than slower shipping
Faster methods tend to involve smaller shipment sizes, while slower methods involve very large shipment sizes
third-party logistics 3PL
•Outsourcing logistics can reduce inventory, costs, and improve delivery reliability and speed
•Coordinate supplier inventory with delivery services
•May provide warehousing, assembly, testing, shipping, customs
establishing sustainability in supply chains
return or reverse logistics
sending returned products back up the supply chain for resale, repair, reuse, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal
closed-loop supply chain
proactive design of a supply chain that tries to optimize all forward and reverse flows
prepares for returns prior to product introductions
sales and operations planning
elements of an aggregate plans
• Coordination of demand forecasts with functional areas and the supply chain
• Typically done by cross-functional teams
• Determine which plans are feasible
• Limitations must be reflected
• Provides warning when resources do not match expectations
the objective of aggregate planning is usually to meet forecast demand while minimizing cost over the planning period
capacity options: changing inventory levels
–Increase inventory in low demand periods to meet high demand in the future
–Increase costs associated with storage, insurance, handling, obsolescence, pilferage, and capital investment
–Shortages may mean lost sales due to long lead times and poor customer service
capactiy options: varying workforce size by hiring or layoffs
Match production rate to demand
Training and separation costs for hiring and laying off workers
New workers may have lower productivity
Laying off workers may lower morale and productivity
capacity options: varying production rates through overtime or idle time
–Allows constant workforce
–May be difficult to meet large increases in demand
–Overtime can be costly and may drive down productivity
–Absorbing idle time may be difficult
capacity options: subcontracting
Temporary measure during periods of peak demand
May be costly
Assuring quality and timely delivery may be difficult
Exposes your customers to a possible competitor
demand options
backordering during high-demand periods
requires customers to wait for an order without the loss of goodwill or the order
backordering during high-demand periods
requires customers to wait for an order without loss of goodwill or the order
most effective when there are few, if any, substitutes for the product or service
Often results in lost sales
revenue management
allocating resources to customers at prices that will maximize revenue or yield
service or product can be sold in advance of consumption, demand fluctuates
relativity fixed resource (capacity)
segmentable demand
low variable costs; high fixed costs
defining quality
build a total quality management system that identifies and satisfies customer needs
costs of quality
prevention costs- reducing the potential for defects
apprasial costs- evaluating products, parts or service before delivery
external failiure costs- defects discovered after delivery
total quality management
•Encompasses entire organization from supplier to customer
•Stresses a commitment by management to have a continuing companywide drive toward excellence in all aspects of products and services that are important to the customer
continuous improvement
•Never-ending process of continuous improvement
•Covers people, equipment, suppliers, materials, procedures
•Every operation can be improved
•End goal is perfection, which is never achieved but always sought.
•Kaizen describes the ongoing process of unending improvement
•T Q M and zero defects also used to describe continuous improvement
six sigma
two meanings
–In a statistical sense, it describes a process, product, or service with an extremely high capability
–A program designed to reduce defects, lower costs, save time, and improve customer satisfaction
•A comprehensive system for achieving and sustaining business success
•Originally developed by Motorola, adopted and enhanced by Honeywell and G E
•Highly structured approach to process improvement
•A strategy
•A discipline – D M A I C
•A set of 7 tools
six sigma 2
•Defines the project’s purpose, scope, and outputs, then identifies the required process information keeping in mind the customer’s definition of quality
•Measures the process and collects data
•Analyzes the data, ensuring repeatability and reproducibility
•Improves, by modifying or redesigning, existing processes and procedures
•Controls the new process to make sure performance levels are maintained
benchmarking
selecting best practices to use as a standard for performance
1.Determine what to benchmark
2.Form a benchmark team
3.Identify benchmarking partners
4.Collect and analyze benchmarking information
5.Take action to match or exceed the benchmark
Just-in-Time (JIT)
•’Pull’ system of production scheduling including supply management
–Production only when signaled
•Allows reduced inventory levels
–Inventory costs money and hides process and material problems
•Encourages improved process and product quality
TQM tools
•Tools for Generating Ideas
Check Sheet
Scatter Diagram
Cause-and-Effect Diagram
Tools to Organize the Data
Pareto Chart
Flowchart (Process Diagram)
Tools for Identifying Problems
Histogram
Statistical Process Control Chart
source inspection
Poka-yoke is the concept of foolproof devices or techniques designed to pass only acceptable products