Ancient and Medieval Art History Exam 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
acropolis
Greek, "high city". In ancient Greece, usually the site of the city's most important temples
canon
a rule of proportion. The ancient Greeks considered beauty to be a matter of "correct" proportion and sought a _____ of proportion
contrapposto
Disposition of the human figure in which one part is turned in opposition to another part, creating a counter-positioning of the body about its central axis
cult statue
statue of the deity that stood in the cella of an ancient temple
lost-wax process
a bronze-casting method in which a figure is modeled in wax and covered in clay; the whole is fired, melting away the wax and hardening the clay, which then becomes a mold for molten metal
Pinakotheke
Greek, "picture gallery". An ancient building for the display of paintings on wood panels
white-ground painting
An ancient Greek vase-painting technique in which the pot was first covered with a slip of very fine white clay, over which black glaze was used to outline figures, and diluted brown, purple, red, and white were used to color them.
black-figure painting
in early Greek pottery, the silhouetting of dark figures against a light background of natural, reddish clay, with linear details incised through the silhouettes
caryatid
a female figure that functions as a supporting column
cella
the chamber at the center of an ancient temple; in a classical temple, the room in which the cult statue usually stood
gigantomachy
in ancient Greek mythology, the battle between gods and giants
Doric
one of the two systems invented in ancient Greece for articulating the three units of the elevation of a classical building. This order is characterized by, among other features, capitals with funnel-shaped echinuses, columns without bases, and a frieze of triglyphs and metopes
Ionic
one of the two systems invented in ancient Greece for articulating the three units of the elevation of a classical building. This order is characterized by, among other features, volutes, capitals, columns with bases, and an uninterrupted frieze
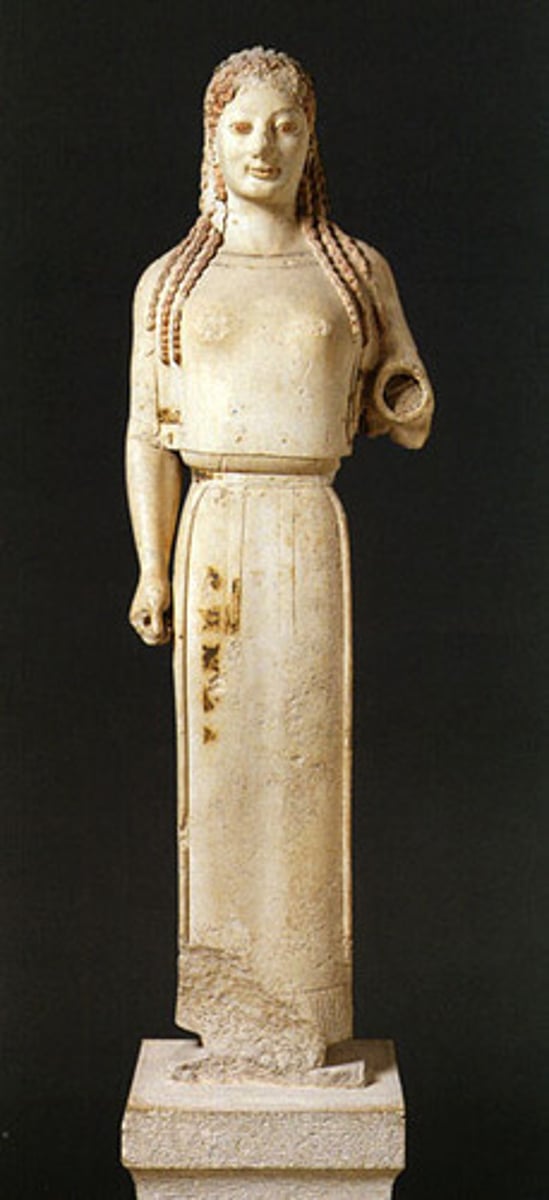
kore
Greek, "young woman". An Archaic Greek statue of a young woman
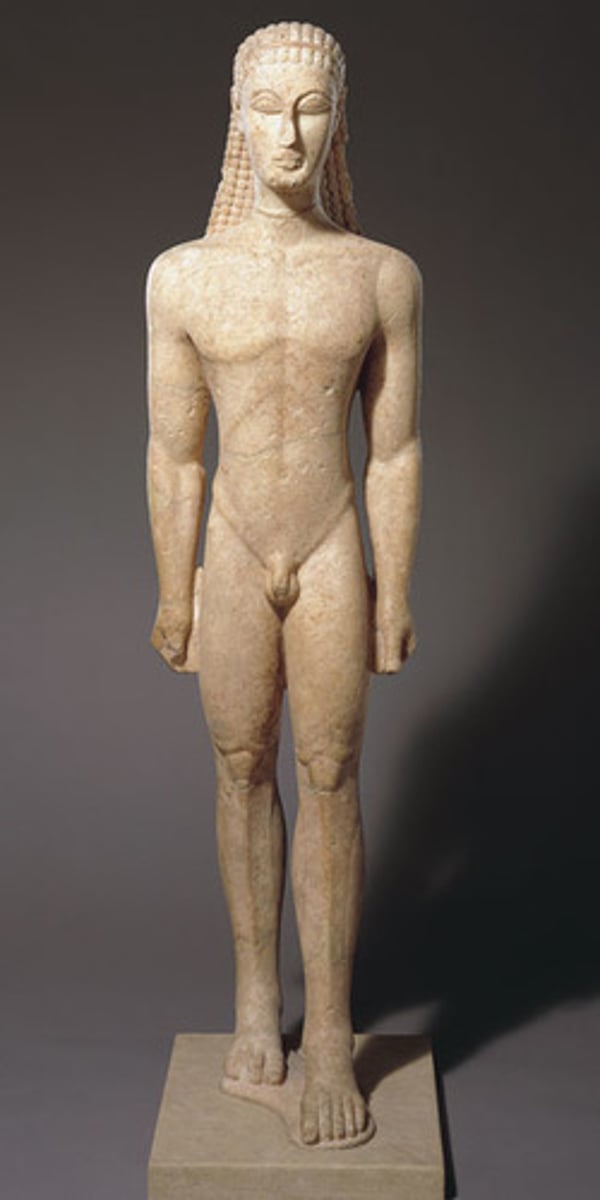
kouros
Greek, "young man". An Archaic Greek statue of a young man
meander
an ornament, usually in bands but also covering broad surfaces, consisting of interlocking geometric motifs
peristyle
in classical architecture, a colonnade all around the cella and its porch(es). A peripteral colonnade consists of a single row of columns on all sides
red-figure painting
in later Greek pottery, the silhouetting of red figures against a black background, with painted linear details; the reverse of black-figure painting
stylobate
the uppermost course of the platform of a classical temple, which supports the columns
agora
an open square or space used for public meetings or business in ancient Greek cities
Corinthian capital
a more ornate form than Doric or Ionic; it consists of a double row of acanthus leaves from which tendrils and flowers grow, wrapped around a bell-shaped echinus
Hippodamian plan
a city plan devised by Hippodamos of Miletos, in which a strict grid was imposed on a site, regardless of the terrain, so that all streets would meet in right angles
mosaic
patterns or pictures made by embedding small pieces of stone or glass in cement on walls or floors
tesserae
Greek, "cube". Tiny stones or pieces of glass cut to the desired shape and size for use in forming a mosaic
portico
a roofed colonnade; also an entrance porch
chimera
a monster of Greek invention with the head and body of a lion and the tail of a serpent. A second head, that of a goat, grows out of one side of the body
concrete
a building material invented by the Romans and consisting of various proportions of lime mortar, volcanic sand, water, and small stones
fibula
a decorative pin, used to fasten garments
granulation
a decorative technique in which tiny metal balls (granules) are fused to a metal surface
tumulus
burial mound; in Etruscan architecture, these cover one or more subterranean multi-chambered tombs cut out of local tufa (limestone)
Tuscan column
the standard type of Etruscan column. Resembles ancient Greek Doric columns, but is made of wood, unfluted, and has a base
Veristic
true to natural appearance; superrealistic
amphitheater
Greek, "double theater". A Roman building type resembling two Greek theaters put together. The Roman version of this featured a continuous elliptical cave around a central arena
atrium
the central reception room of a Roman house that is partly open to the sky. Also the open, colonnaded court in front of and attached to a Christian basilica
basilica
in Roman architecture, a civic building for legal and other civic proceedings, rectangular in plan with an entrance usually on a long side
forum
public square of an ancient Roman city
linear perspective
a method of presenting an illusion of the 3D world on a 2D surface
skenographia
Greek, "scene painting"; the Greek term for perspective painting
Triclinium
dining room of a Roman house
First Style Mural
aim of the artist in this mural style was to imitate, using painted stucco relief, the appearance of costly marble panels
Second Style Mural
a style of Roman mural painting in which the aim was to dissolve the confining walls of a room and replace them with the illusion of a 3D world constructed in the artist's imagination
Third Style Mural
in this style of Roman mural painting, the style in which delicate linear fantasies were sketched on predominantly monochromatic backgrounds
Fourth Style Mural
A style of Roman mural painting that marked a return to architectural illusionism, but the architectural vistas of this style are irrational fantasies
barrel vault
a masonry roof or ceiling constructed on the arch principle. This is semi-cylindrical in cross-section, is in effect a deep arch or an uninterrupted series of arches, one behind the other, over an oblong space
coffer
a sunken panel, often ornamental, in a vault or ceiling
encaustic
wax based paint kept molten on a heated palette; after application to an absorbent surface, it is reheated to fuse the paint
engaged column
a non-structural partial column projecting from a wall
oculus
Latin, "eye". The round central opening of a dome. also, a small round window in a Gothic cathedral
pilaster
a flat, rectangular, vertical member projecting from a wall of which it forms a part. Usually has a base and a capital, often fluted
tempera
a technique of painting using pigment mixed with egg yolk, glue, or casein; also the medium itself
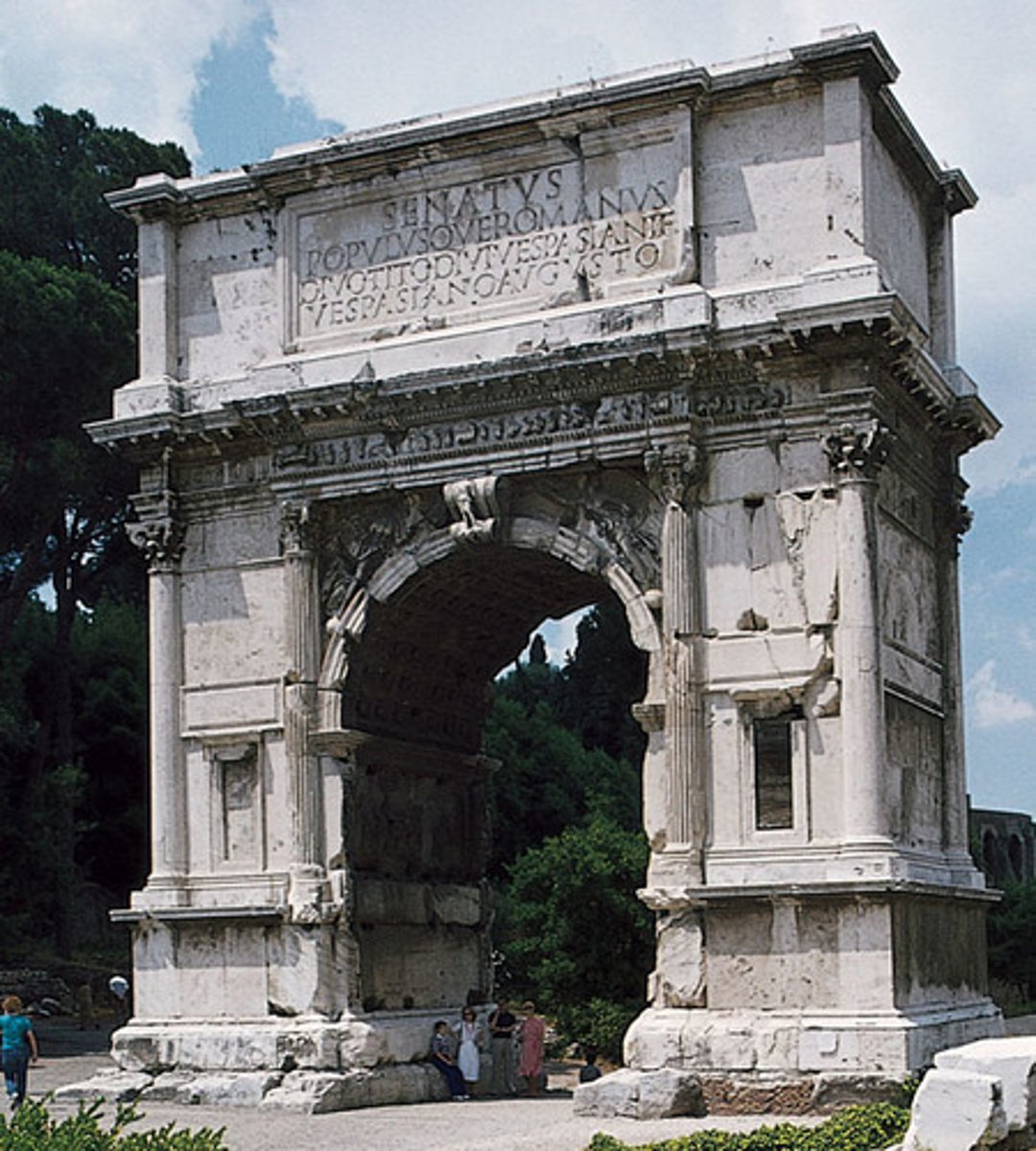
triumphal arch
in Roman architecture, a freestanding arch commemorating an important event
baptistery
in Christian architecture, the building used for baptism, usually situated next to a church
catacombs
subterranean networks of rock-cut galleries and chambers designed as cemeteries for the burial of the dead
central plan
parts of the structure are of equal or almost equal dimensions around the center
codex
separate pages of vellum or parchment bound together at one side; the predecessor of the modern book
illuminated manuscript
a luxurious handmade book with painted illustrations and decorations
mausoleum
lie in the grass next to a monumental tomb
mithraem
an underground rock cave for a male cult dedicated to the Roman god Mithras
nimbus
a halo or aureole appearing around the head of a holy figure to signify divinity
orant
in early Christian art, a figure with both arms raised in the ancient gesture of prayer
parchment
lambskin prepared as a surface for painting or writing
typology
in Christian theology, the recognition of concordances between events, especially between episodes in the Old and New Testaments
vellum
calfskin prepared as a surface for writing or painting
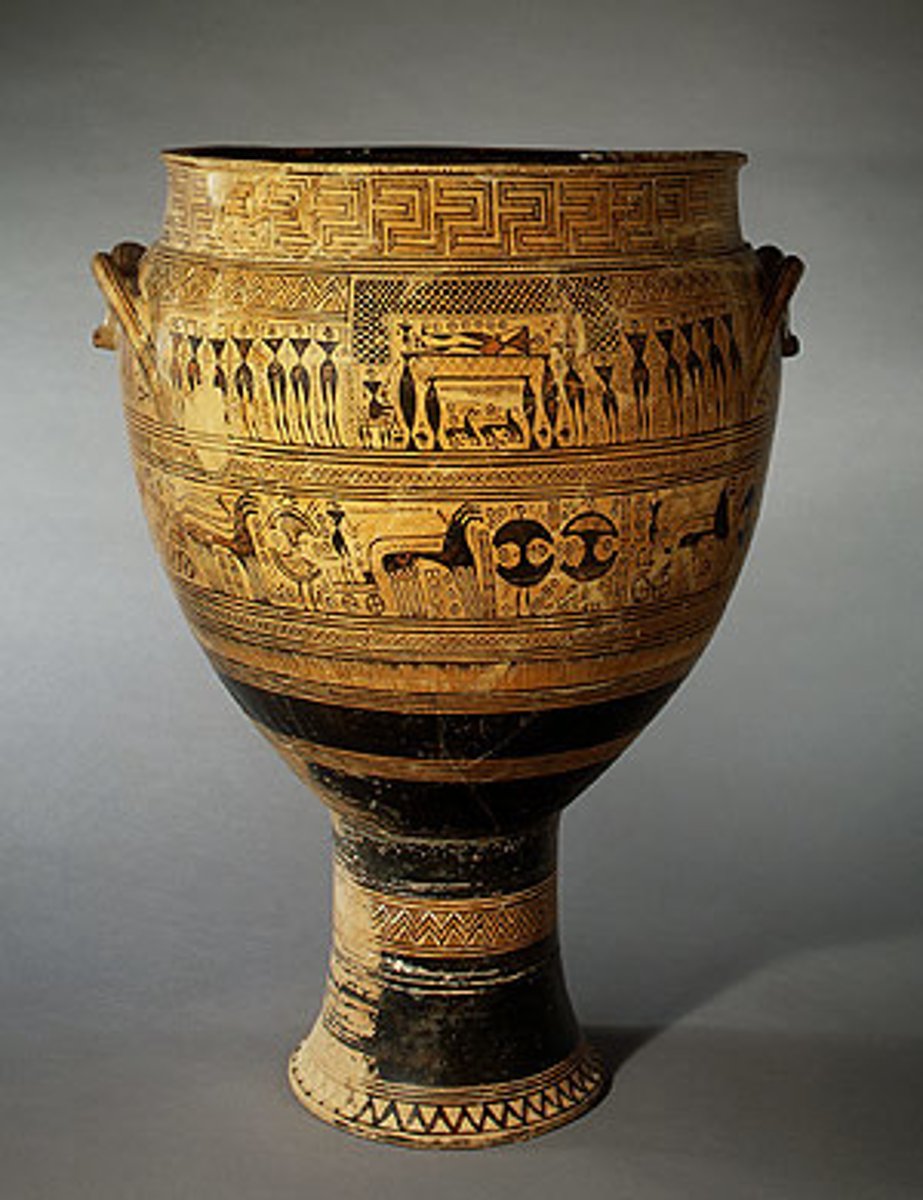
geometric krater, Greece. Geometricizing

Kouros, Greece. Marble. Archaic

Kore, Greece. Marble. Archaic

EXEKIAS, Achilles and Ajax playing a dice game, Italy. Archaic

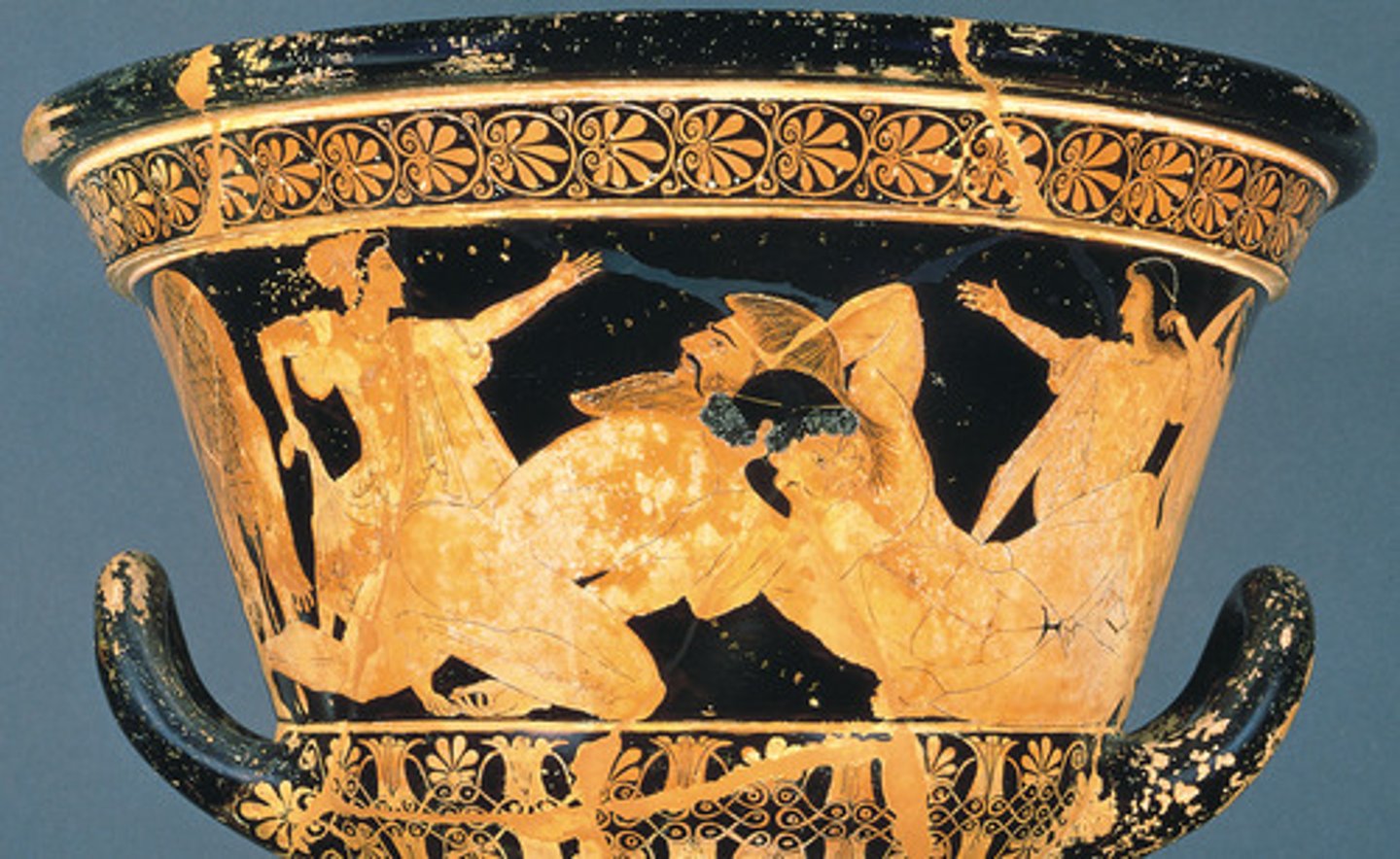
EUPHRONIOS, Herakles wrestling Antaios, Italy. Archaic

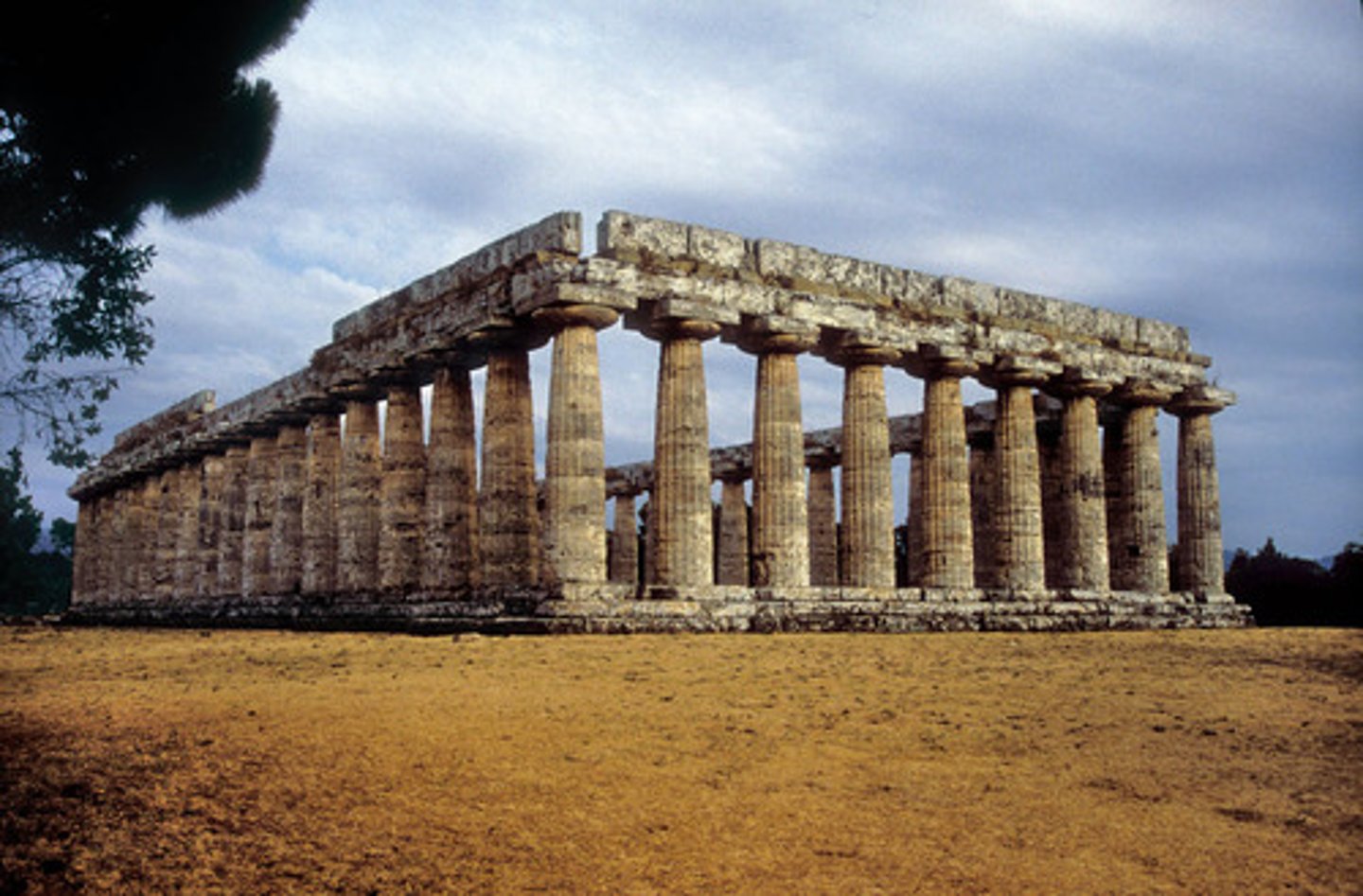
Temple of Hera, Italy. Archaic

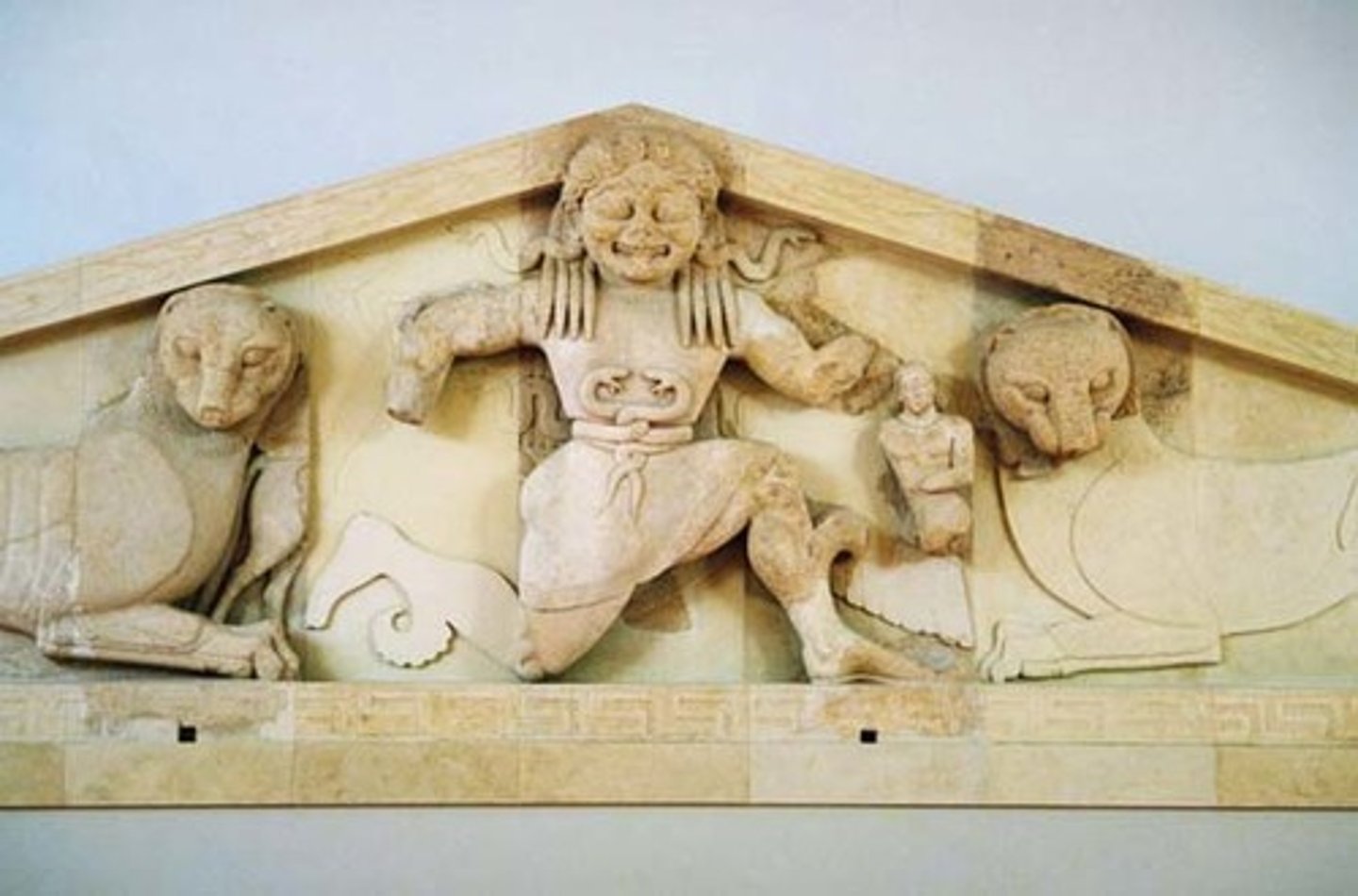
West pediment of Temple of Artemis, Greece. Limestone. Archaic

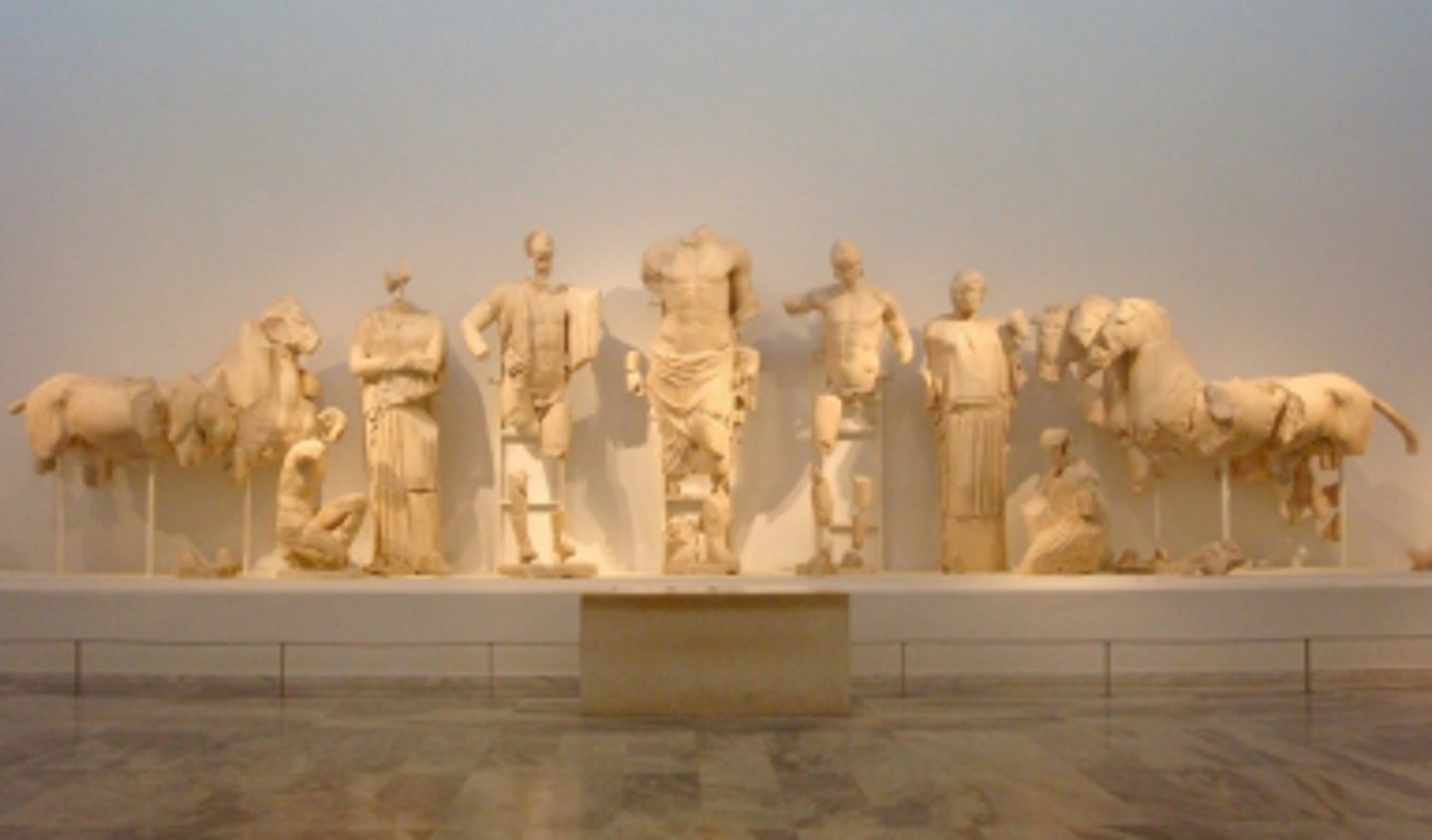
East pediment from the Temple of Zeus, Greece. Marble. Classical.

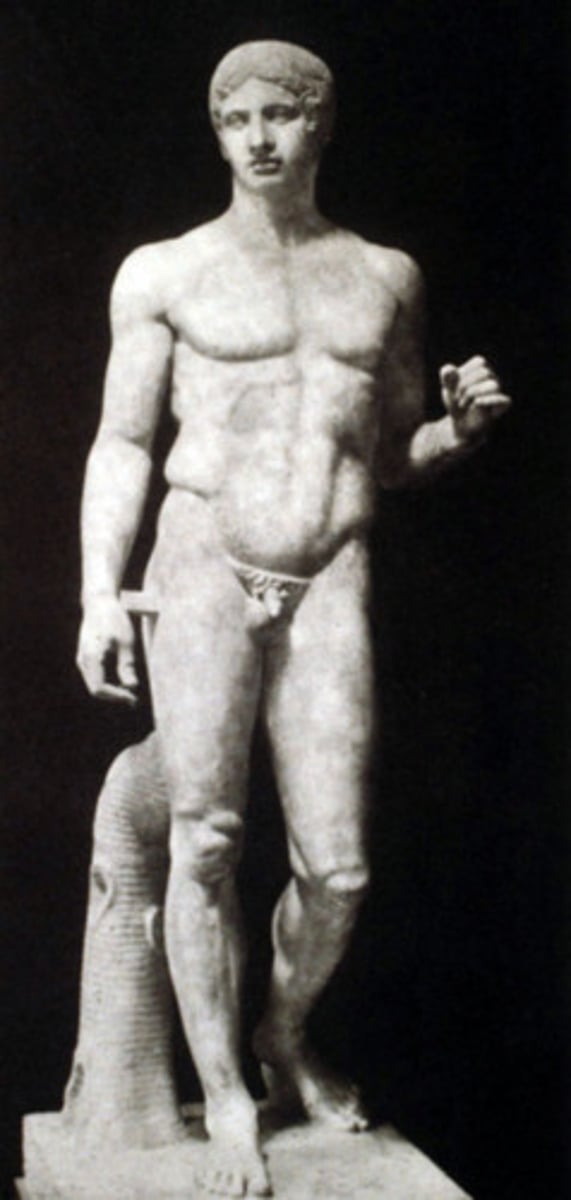
POLYKLEITOS, Doryphoros, Italy. Marble copy. Classical.

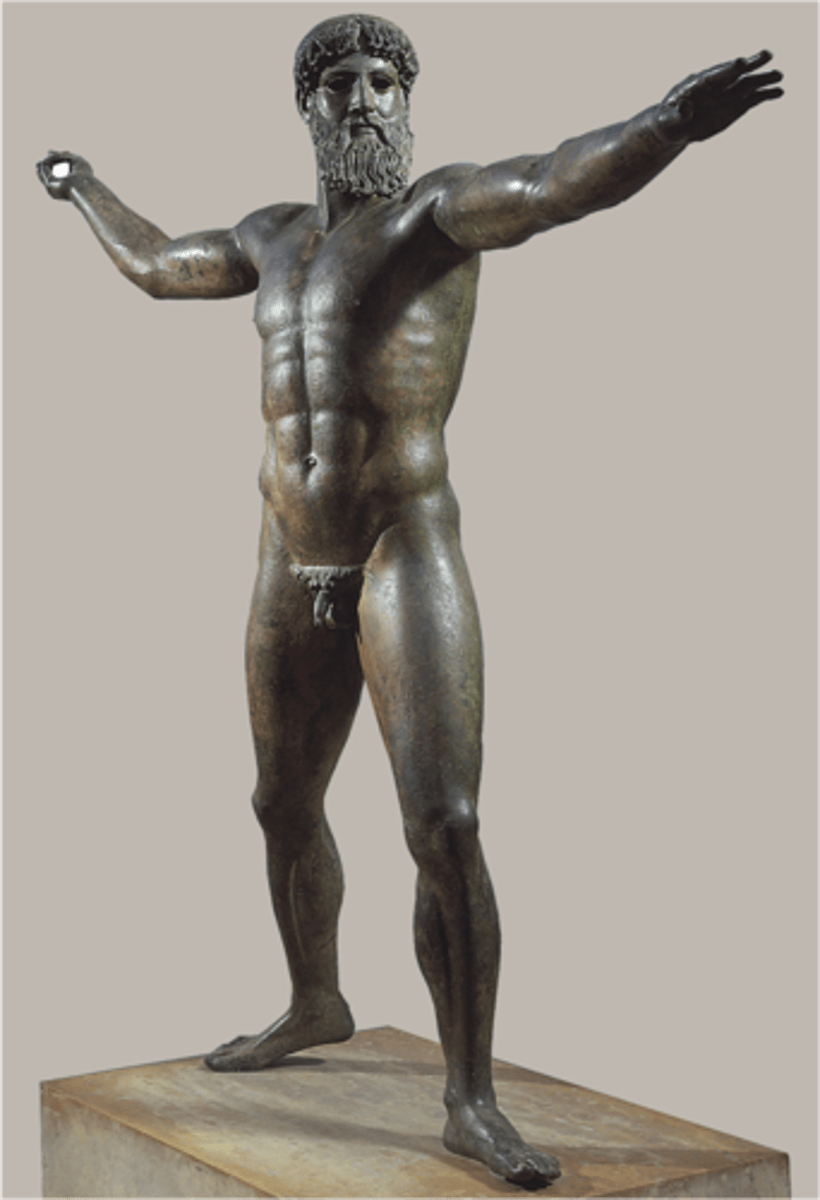
Zeus, Greece. Bronze. Classical

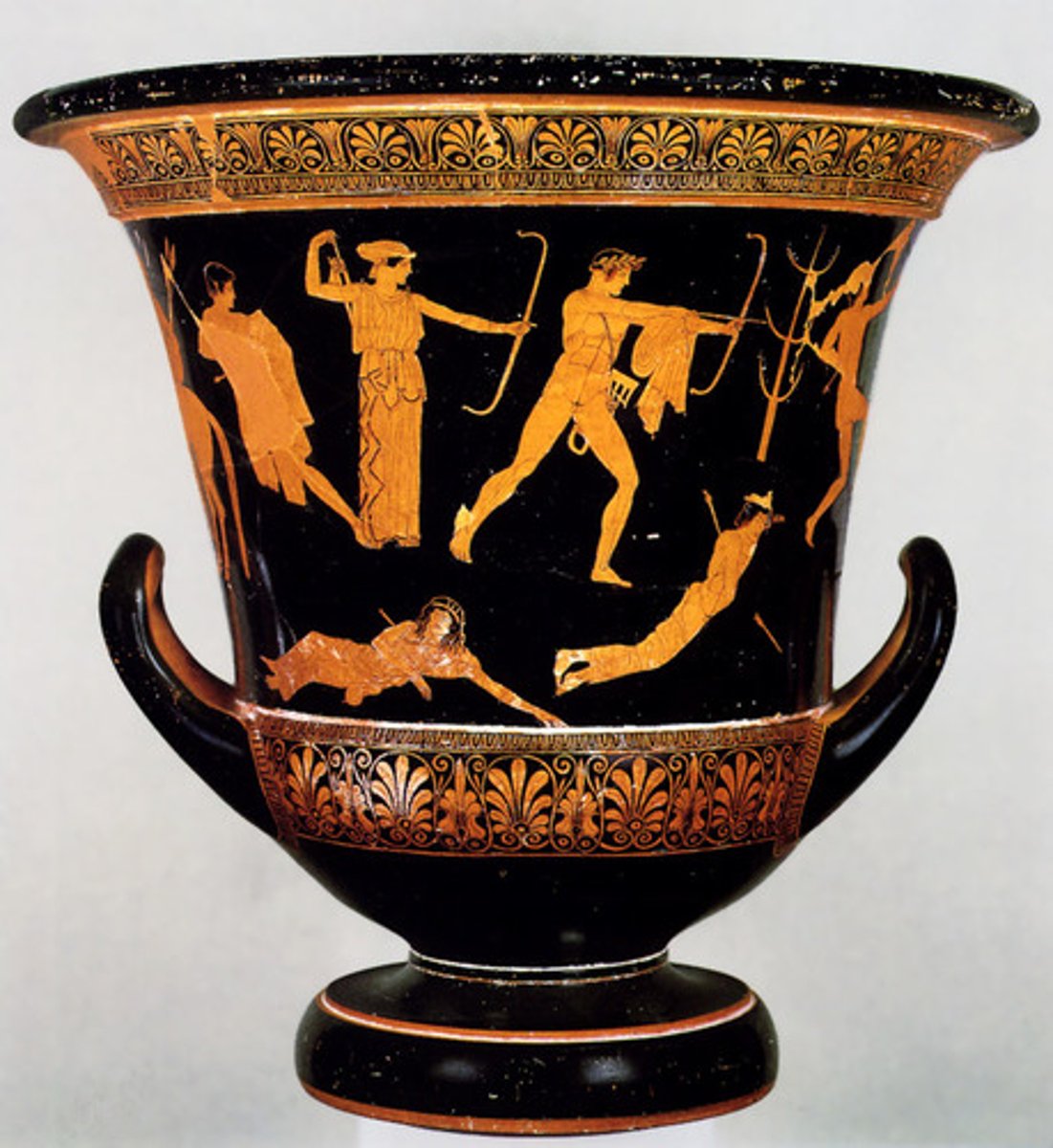
NIOBID PAINTER, Artemis and Apollo slaying the children of Niobe, Italy. Classical

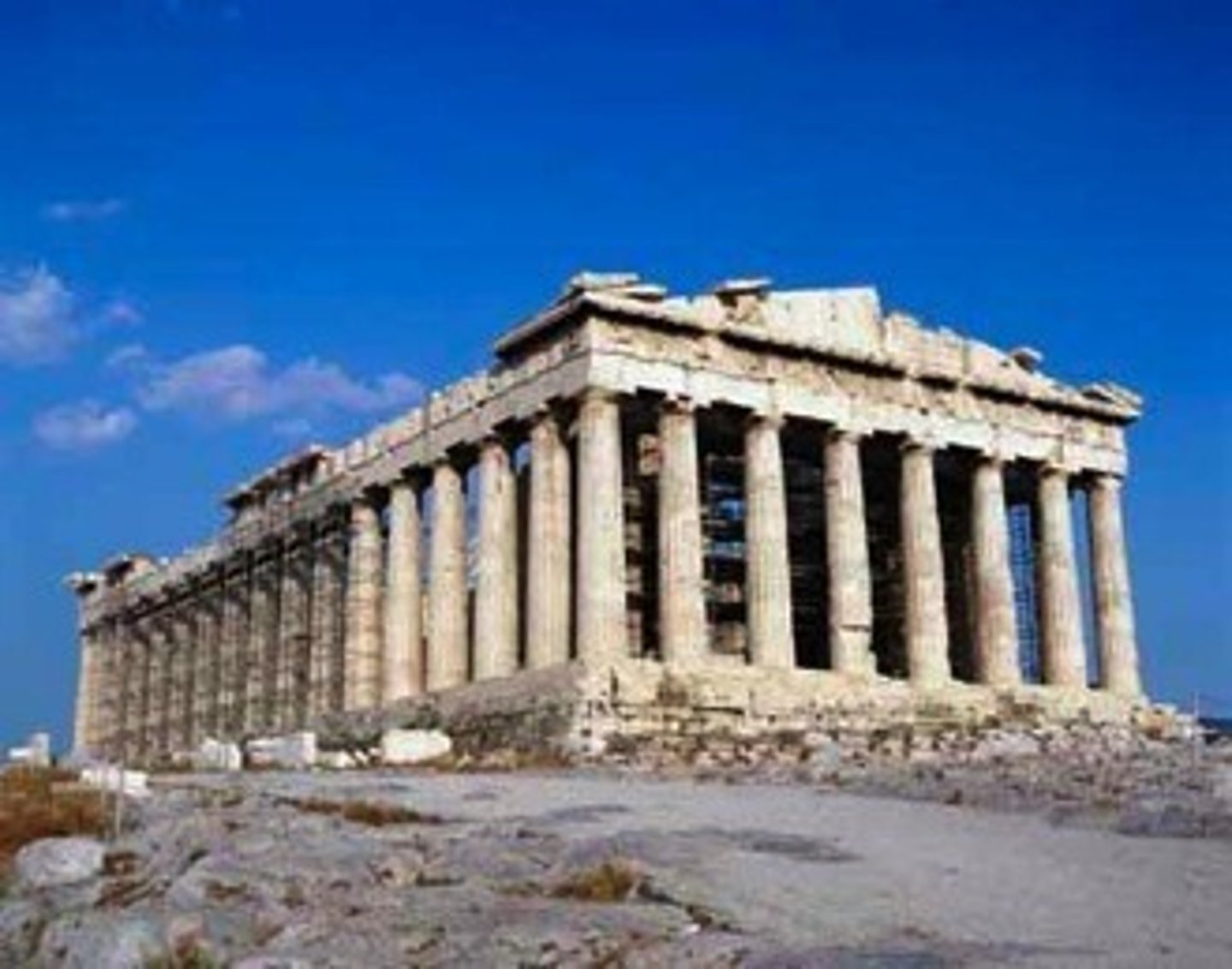
Parthenon, Greece. Classical

Three Goddesses, Greece. Marble. Classical
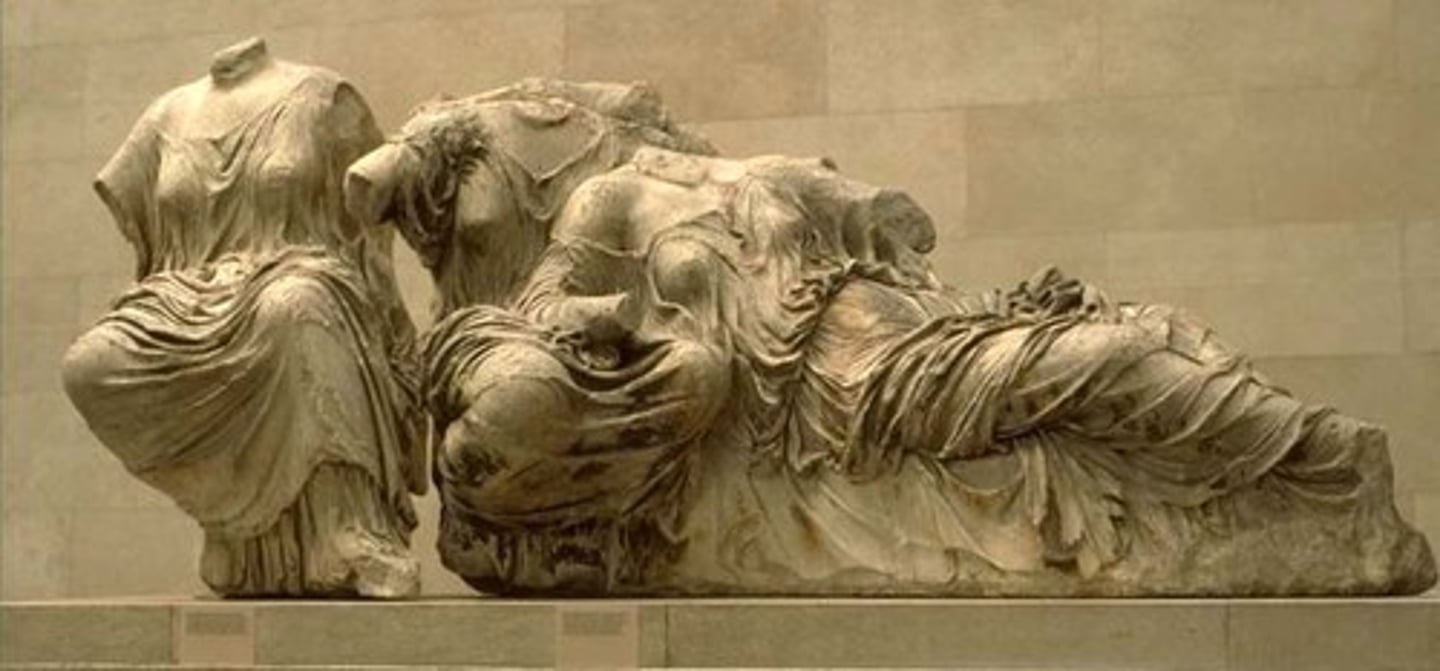

Procession frieze, Greece. Marble. Classical
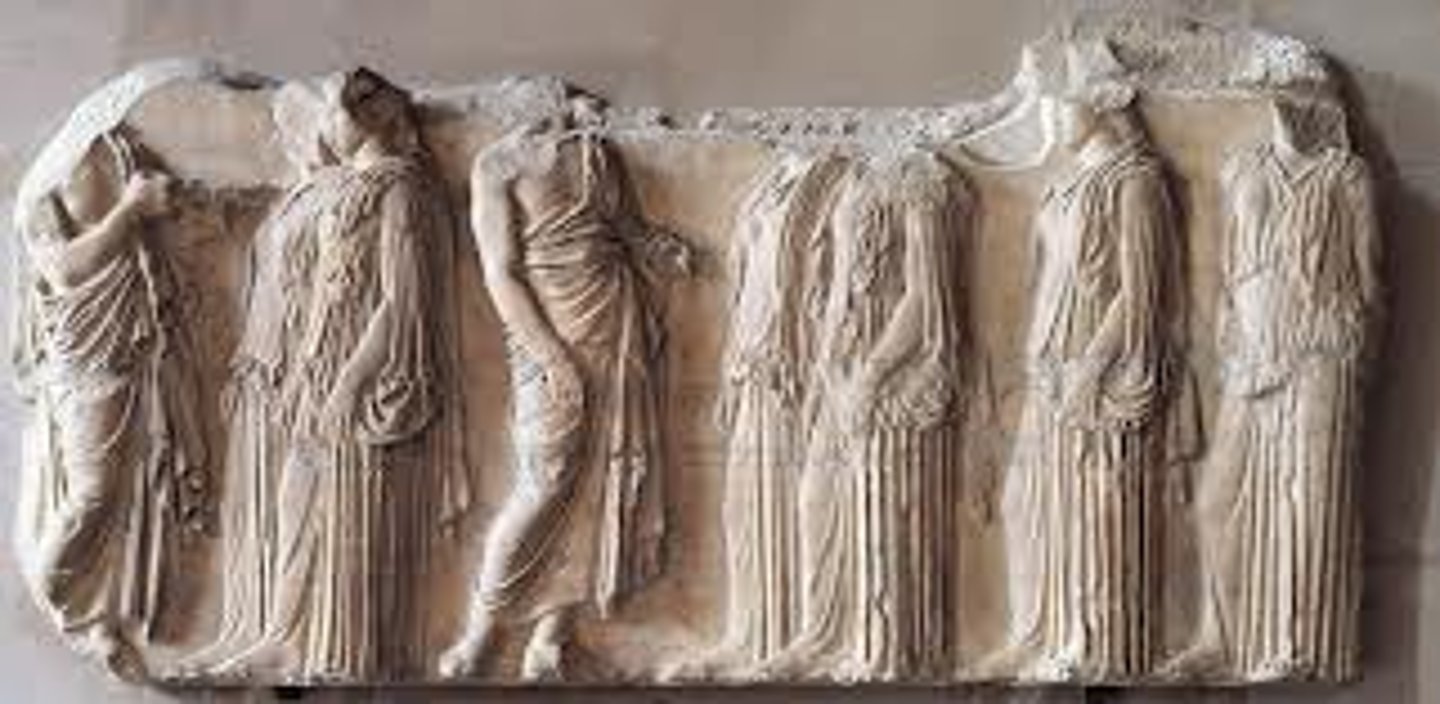

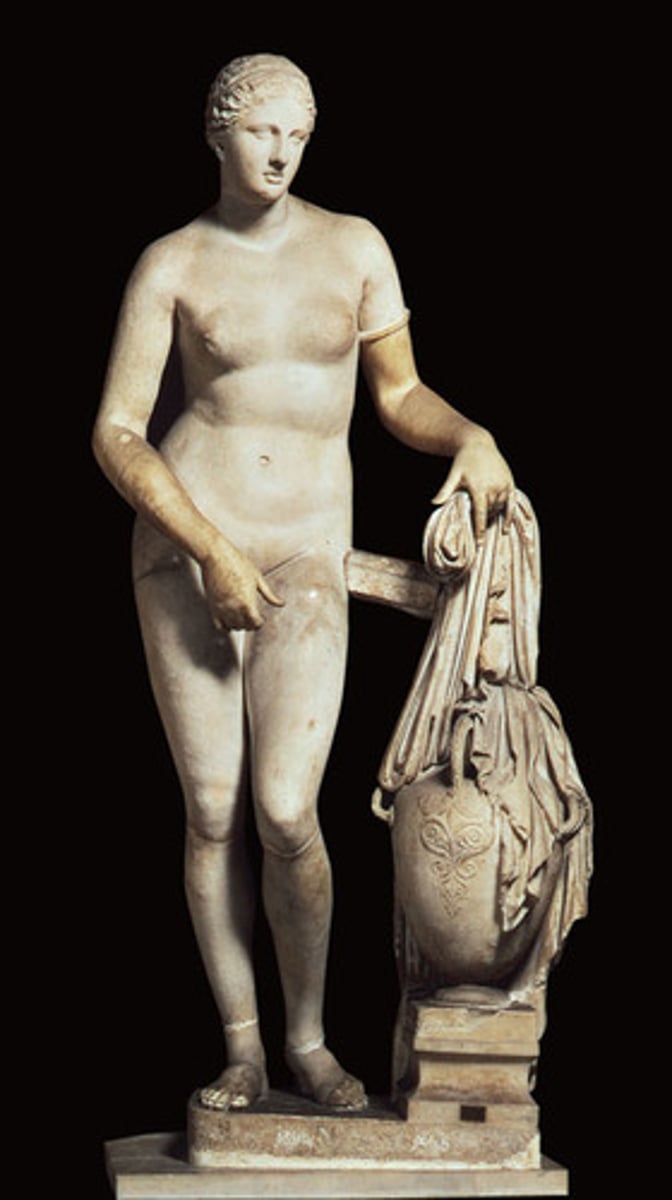
PRAXITELES, Aphrodite. Marble copy. Late Classical

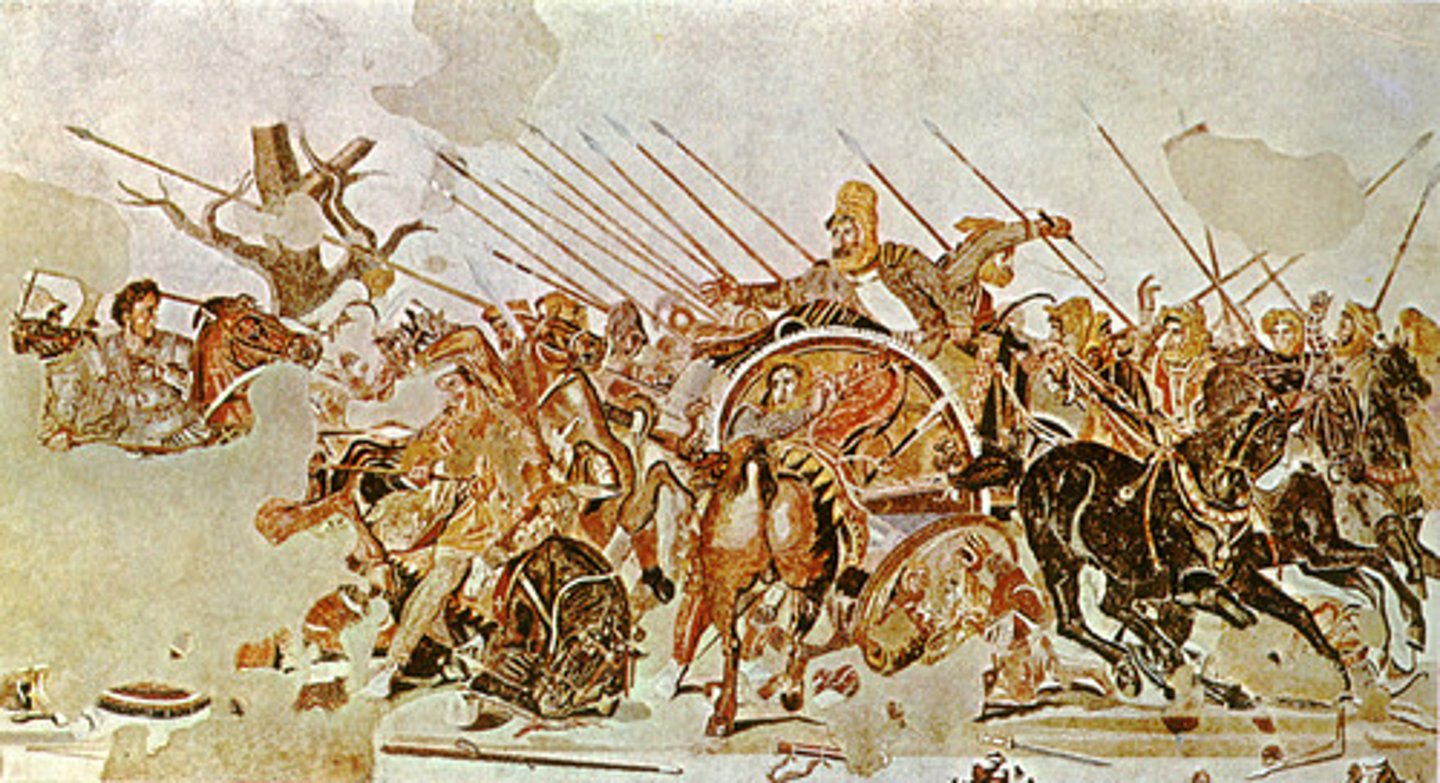
PHILOXENOS OF ERETRIA, Battle of Issus, Italy. Tessera mosaic. Hellenistic

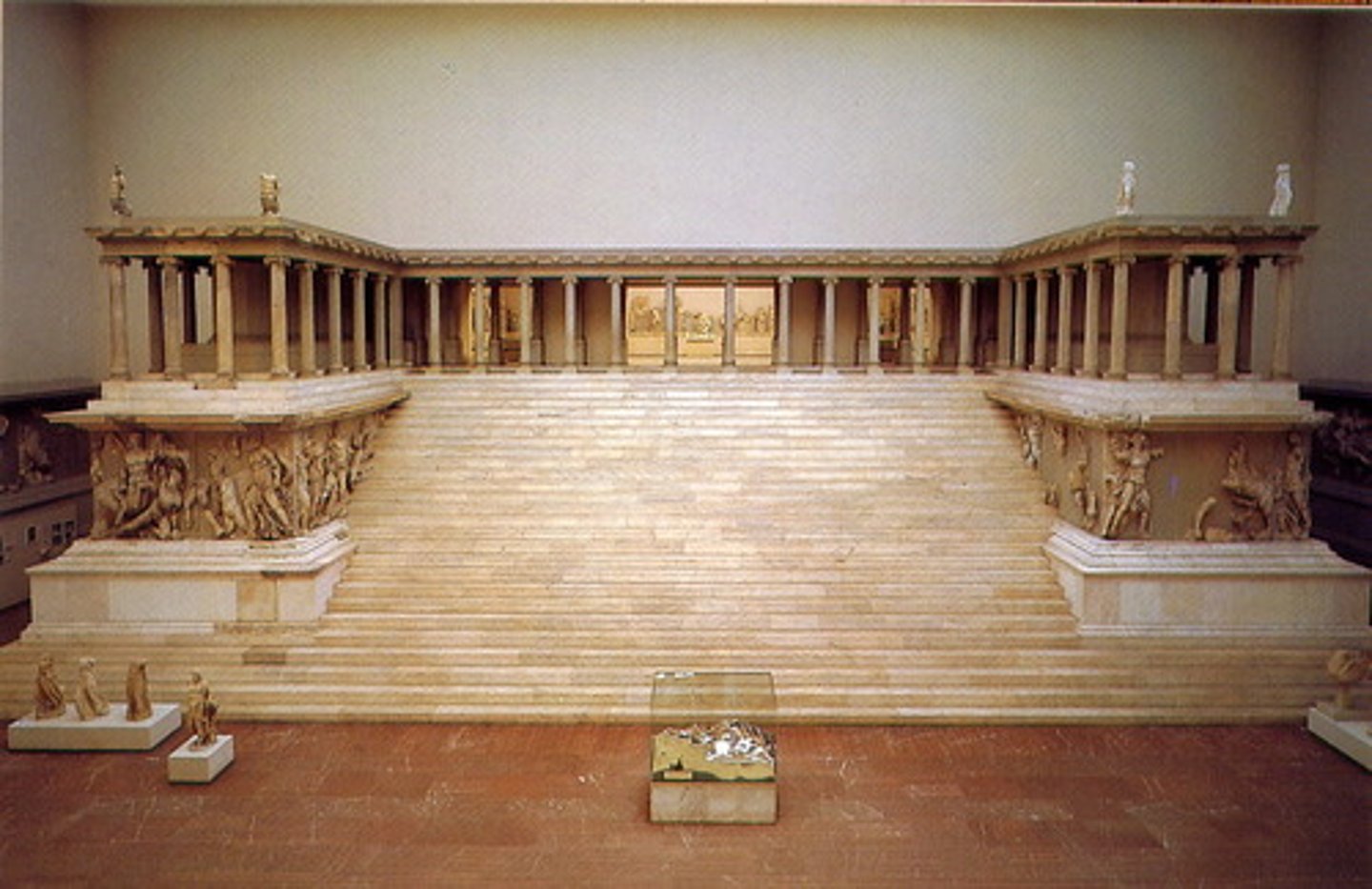
Altar of Zeus, Turkey. Hellenistic

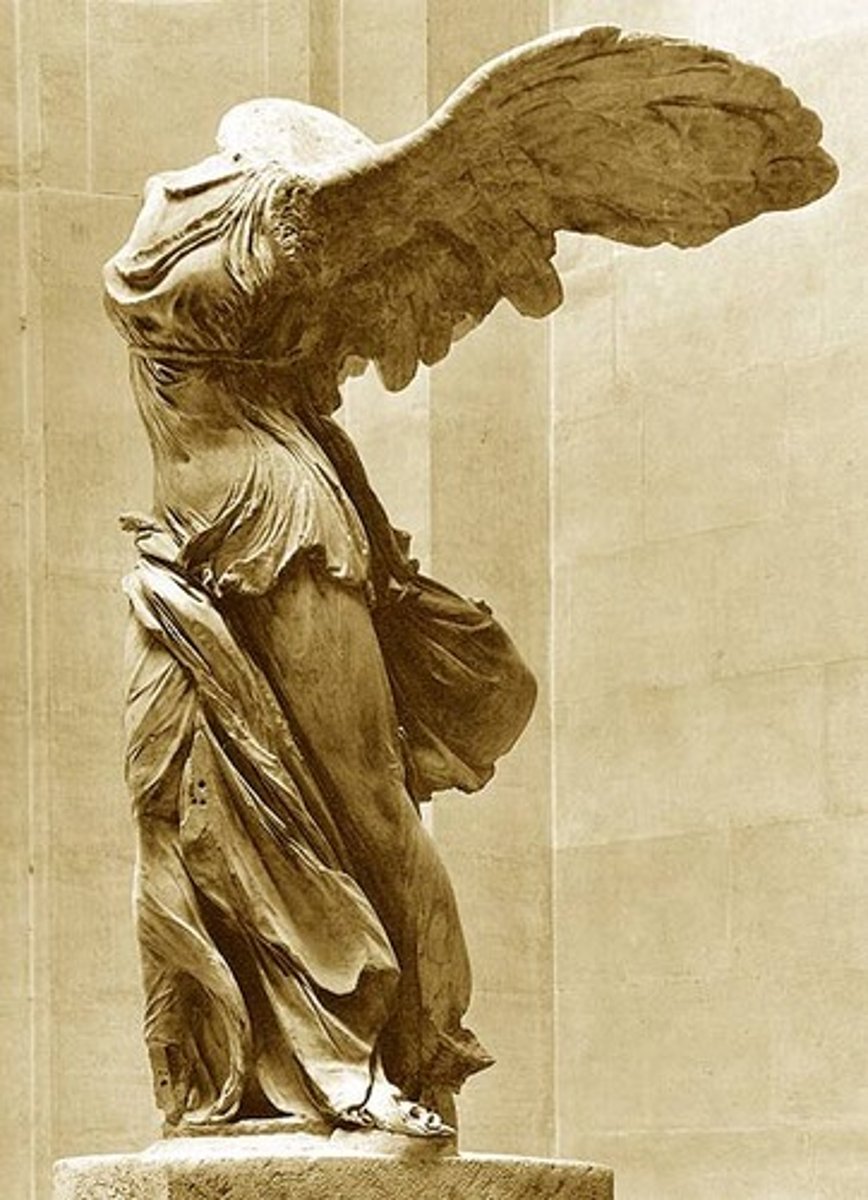
Nike alighting on a warship, Greece. Marble. Hellenistic

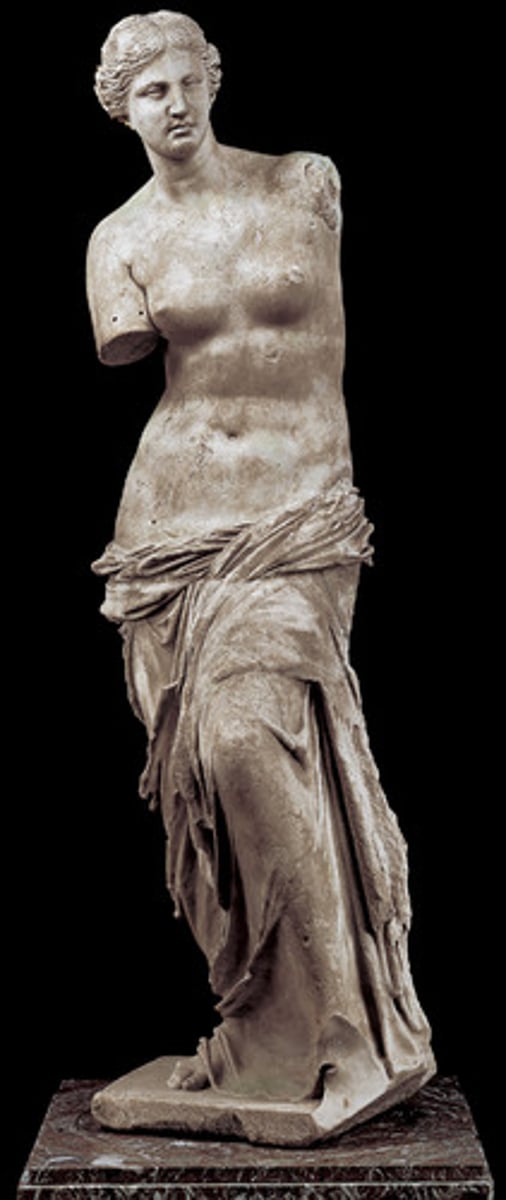
ALEXANDROS OF ANTIOCH-ON-THE-MEANDER, Aphrodite. Marble. Hellenistic

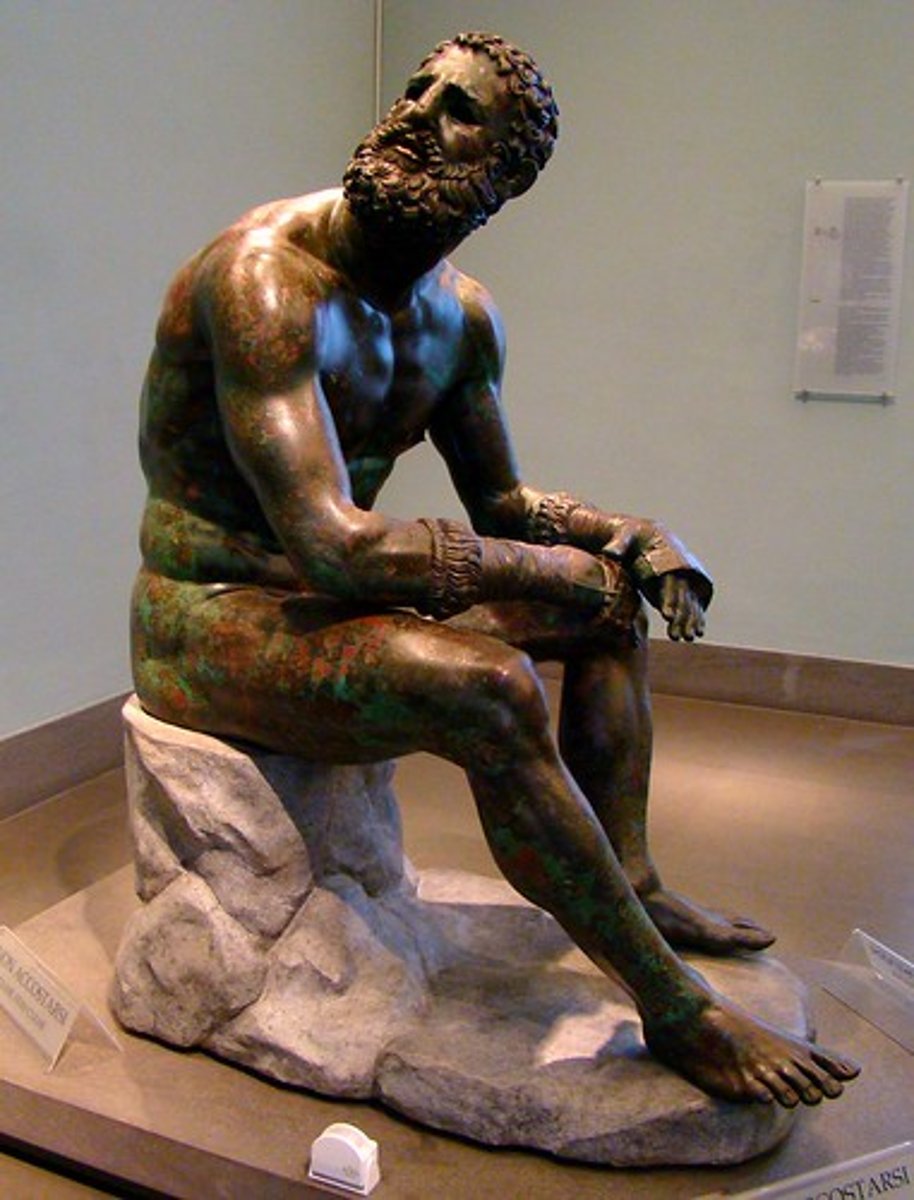
Seated Boxer, Italy. Bronze. Hellenistic

Laocoon and his sons, Italy. Marble. Hellenistic
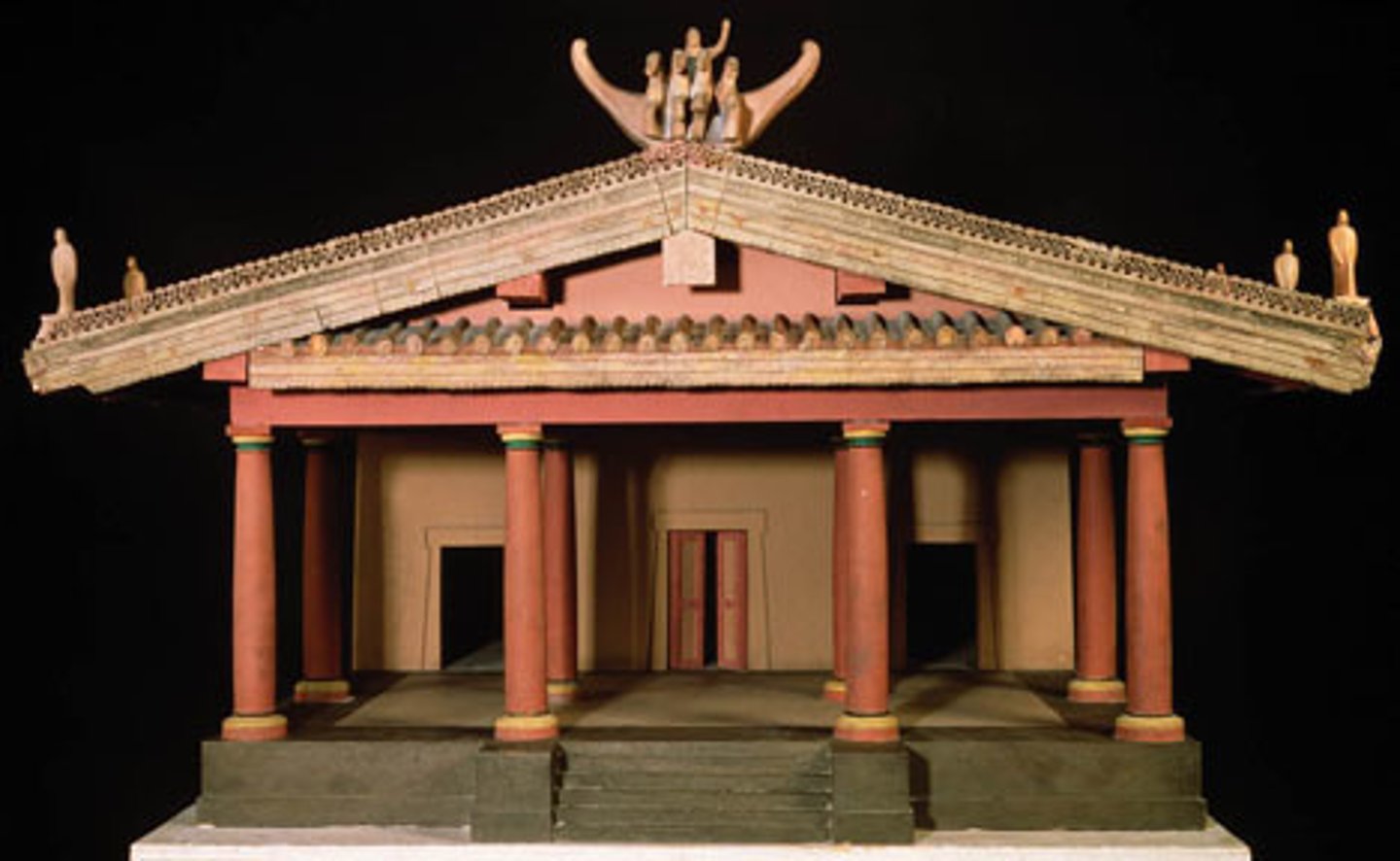
Model of a typical sixth-century Etruscan temple

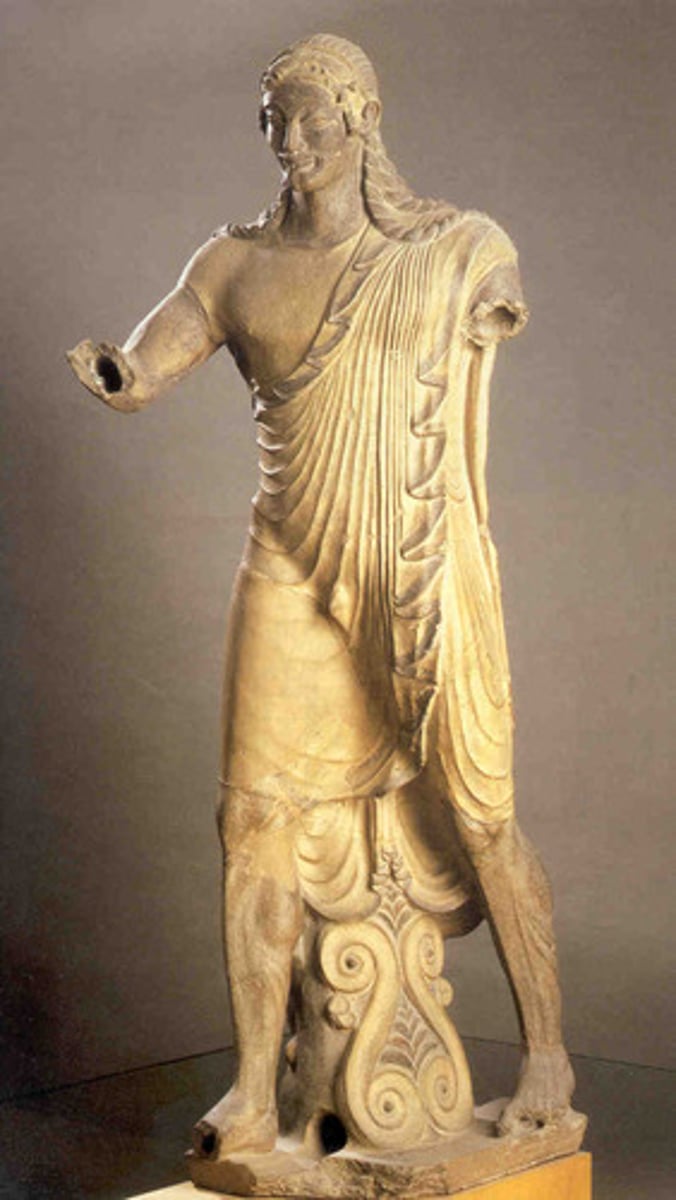
Apollo, Italy. Painted terracotta. Republic

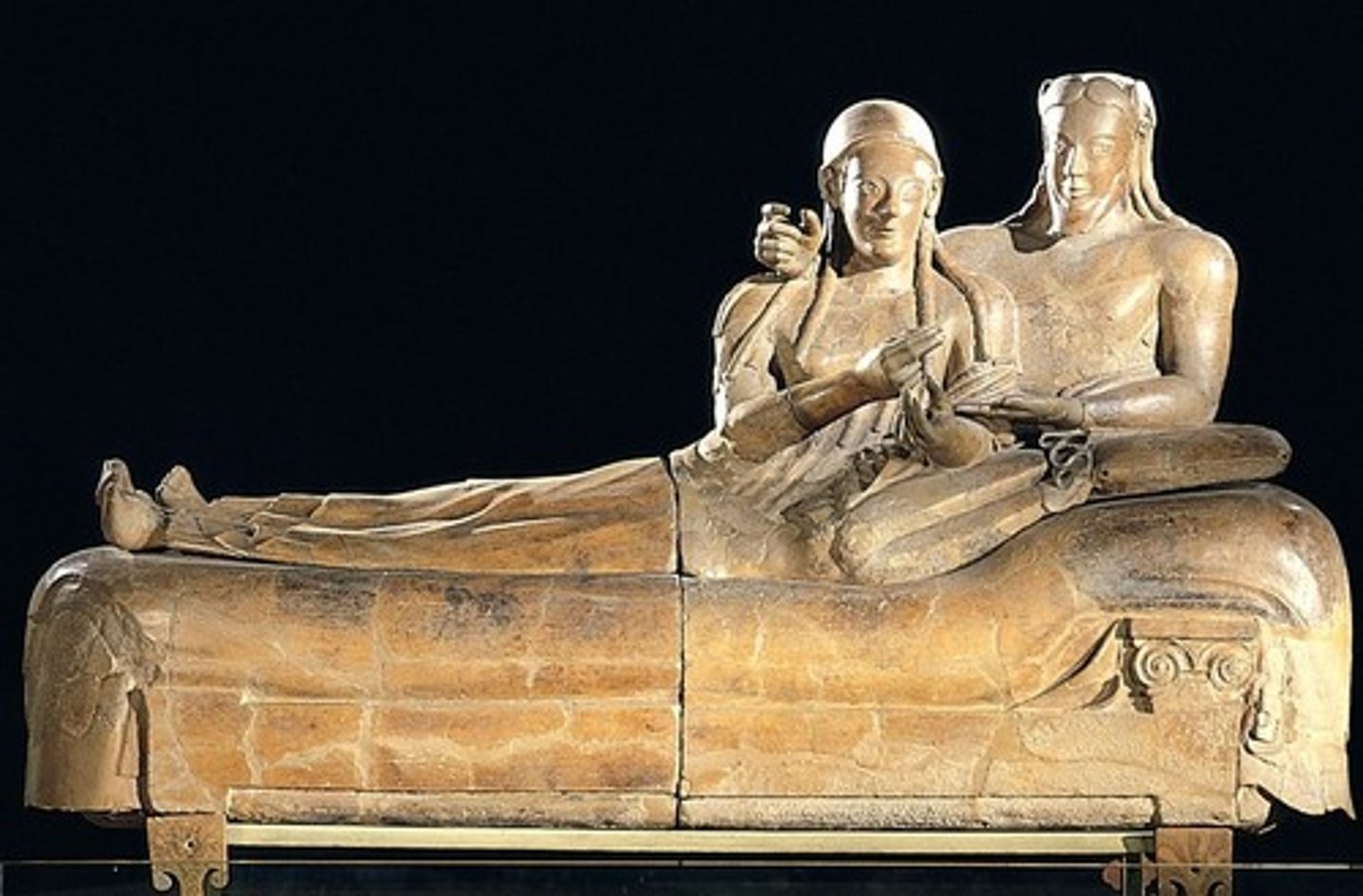
Sarcophagus with kneeling couple, Italy. Painted terracotta. Republic

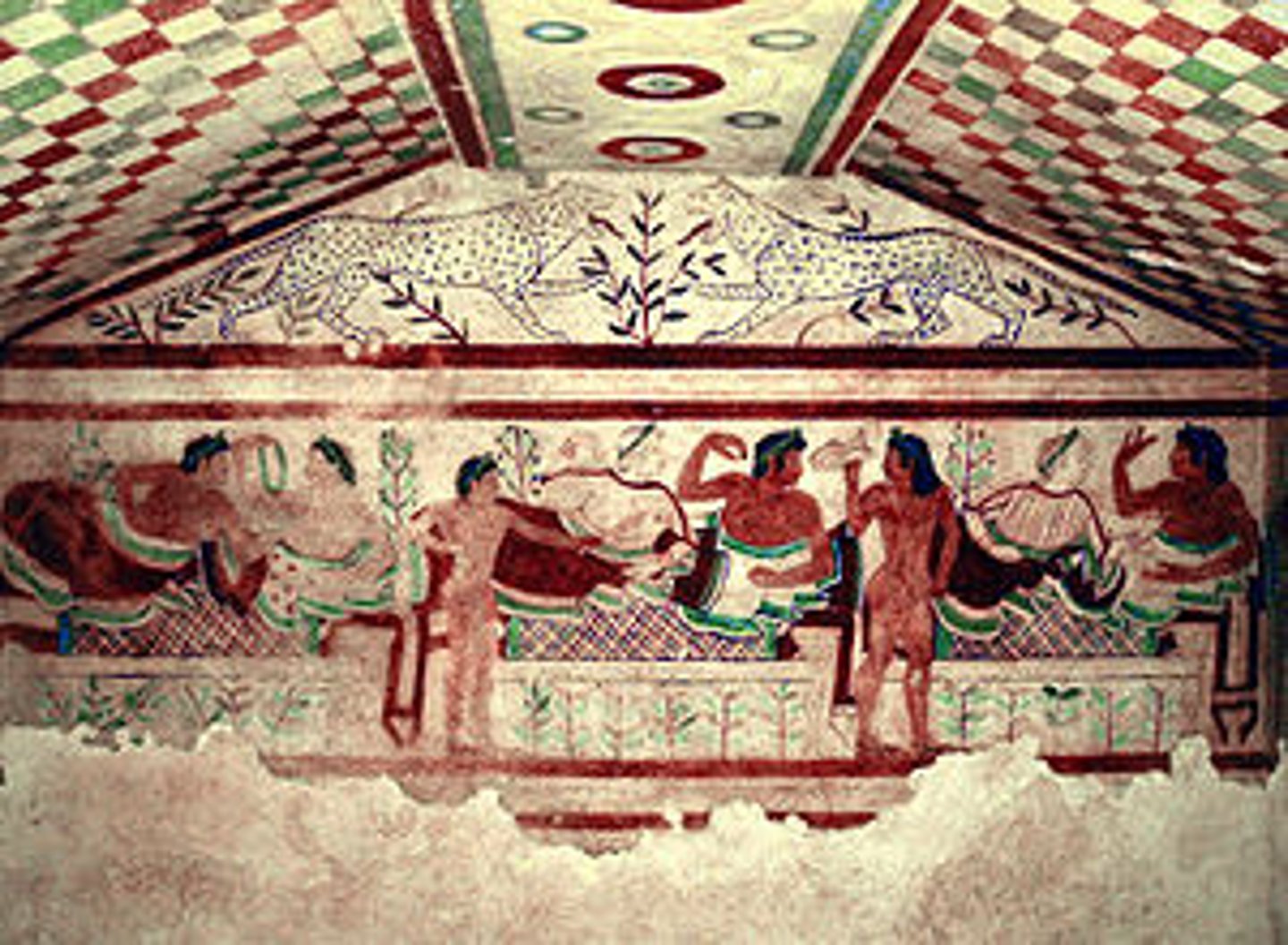
Interior of the Tomb of the Leopards, Italy. Republic

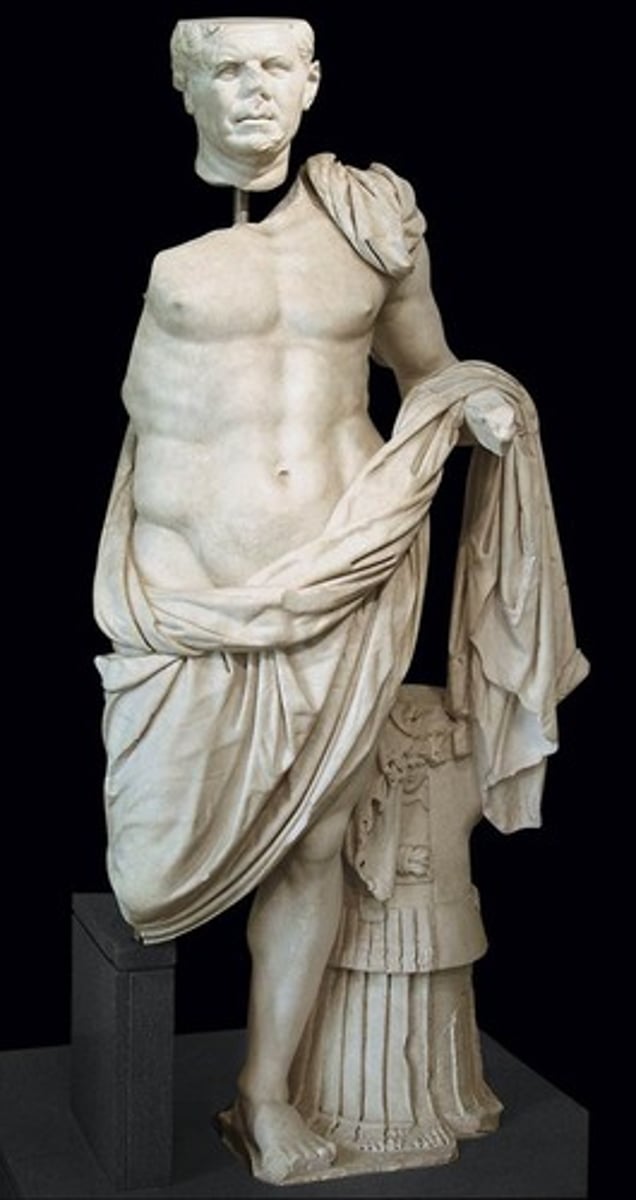
Aule Metele, Italy. Bronze. Early first century BCE

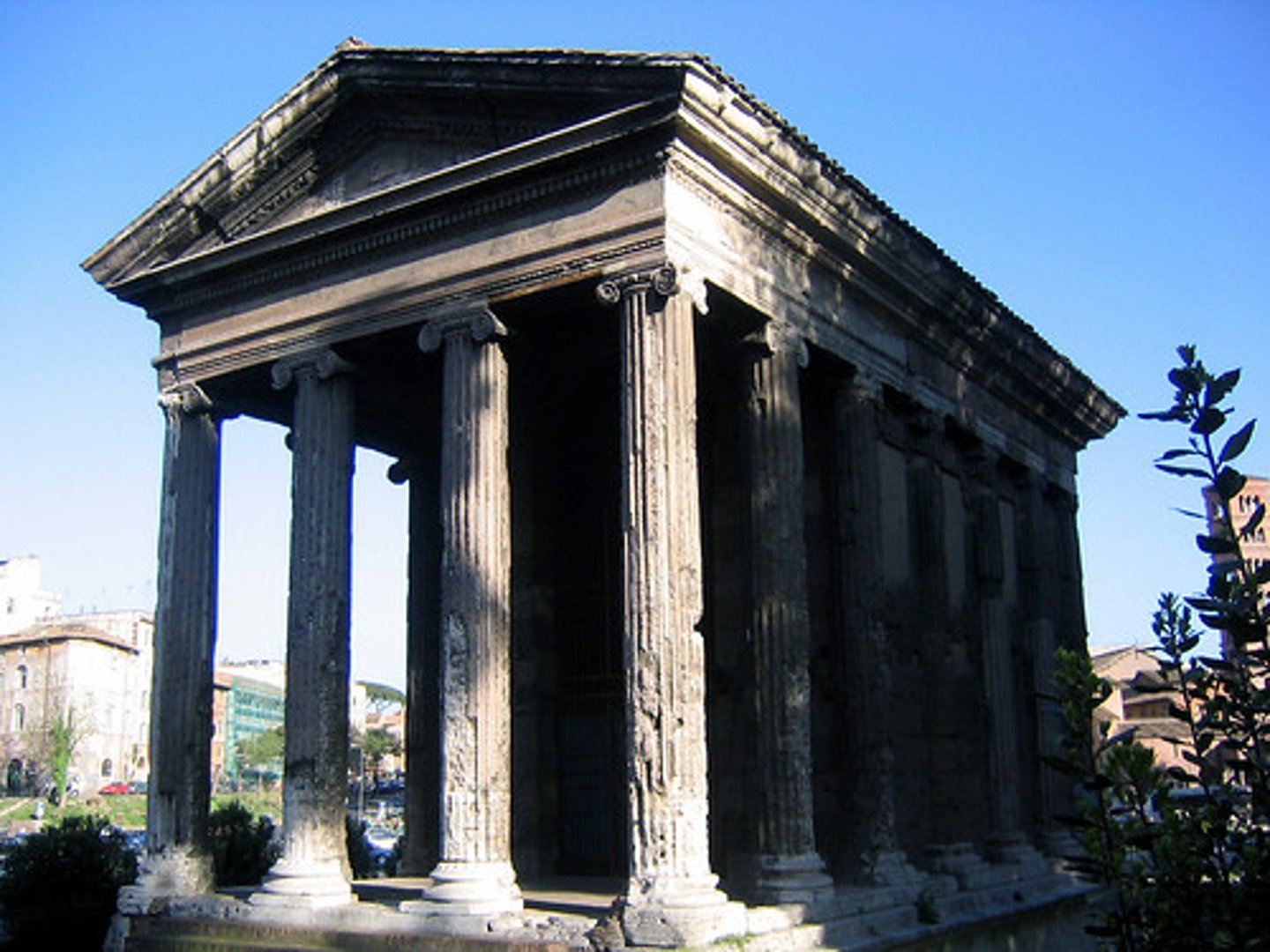
Temple of Portunus, Italy. Republic.

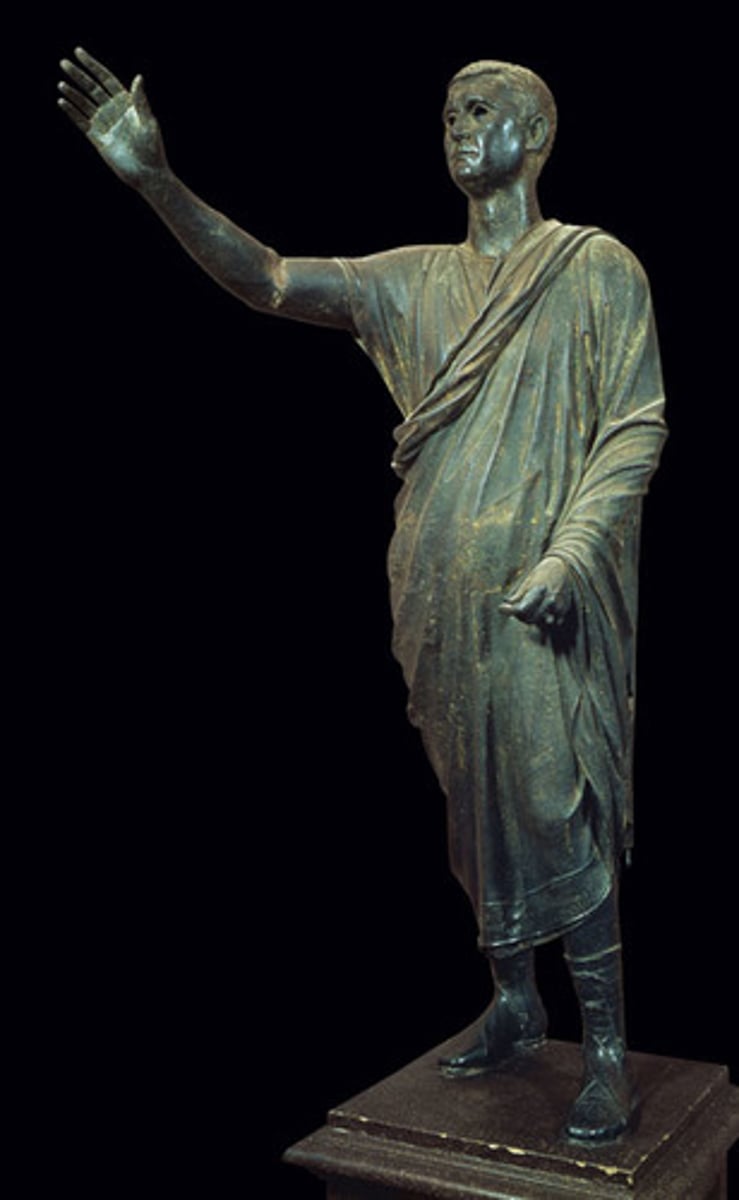
Portrait of a Roman general, Italy. Marble. Republic

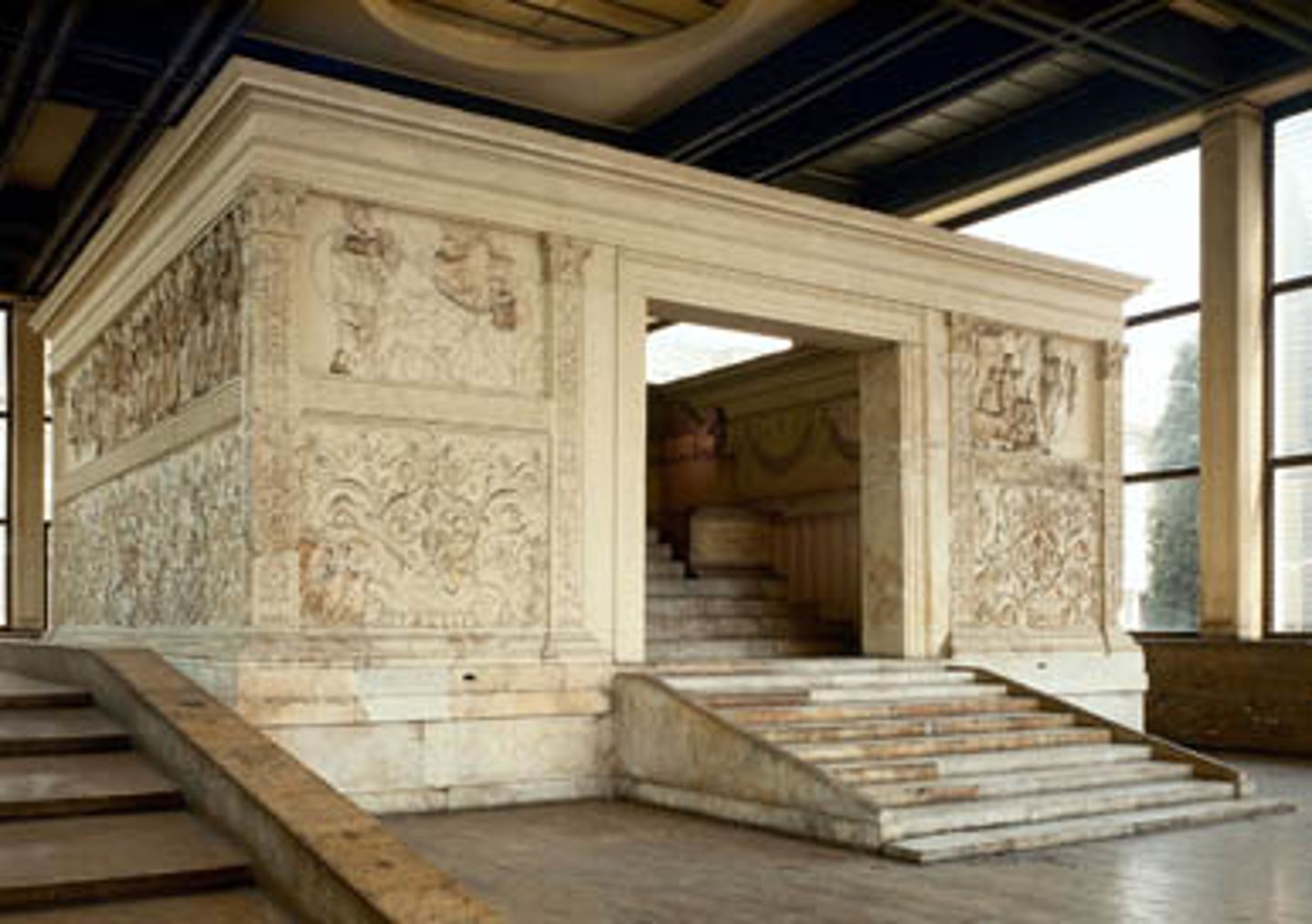
Ara Pacis Augustae, Italy. Early Empire

SEVERUS and CELER, Domus Aurea, Italy. Early Empire
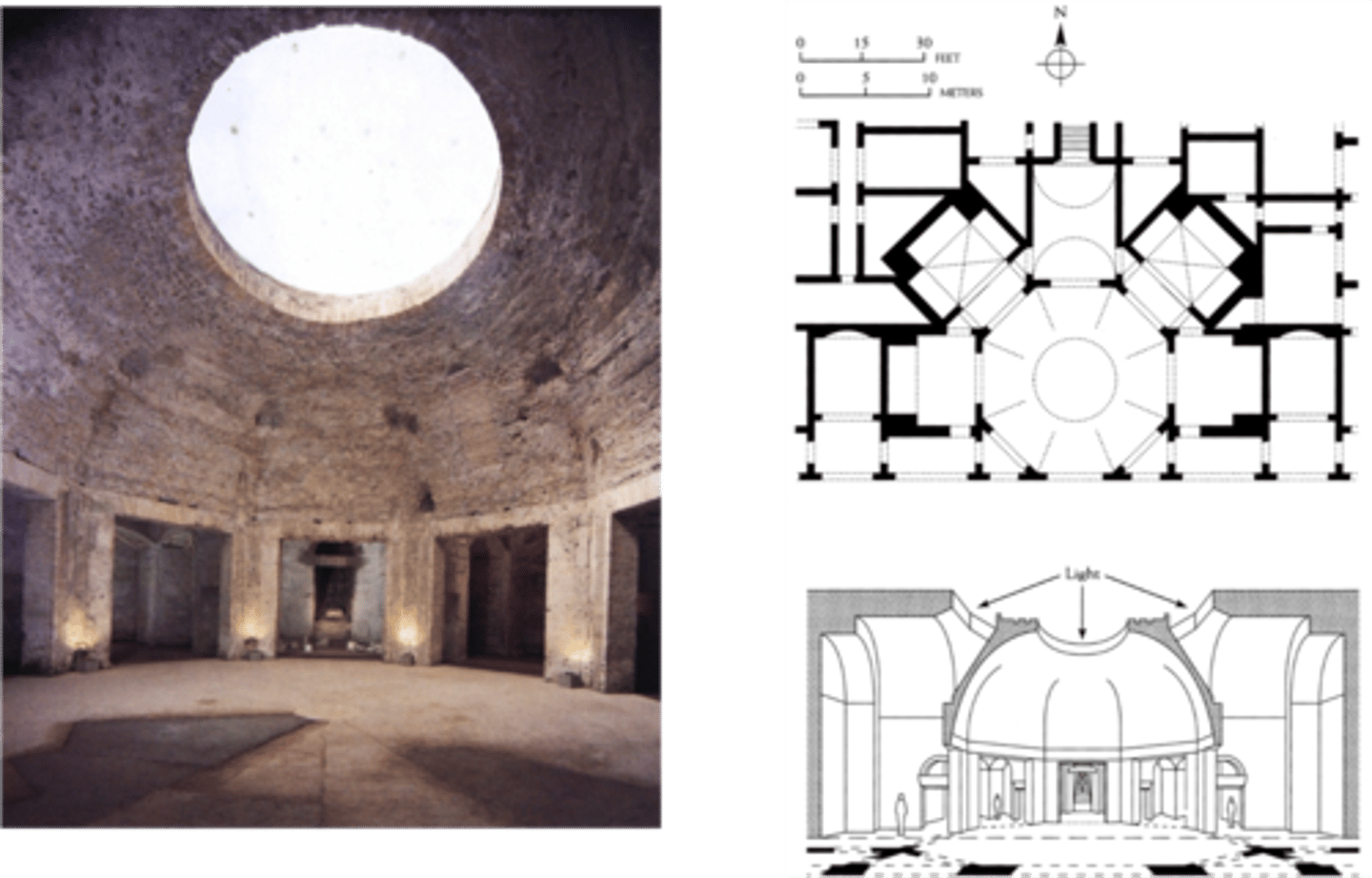
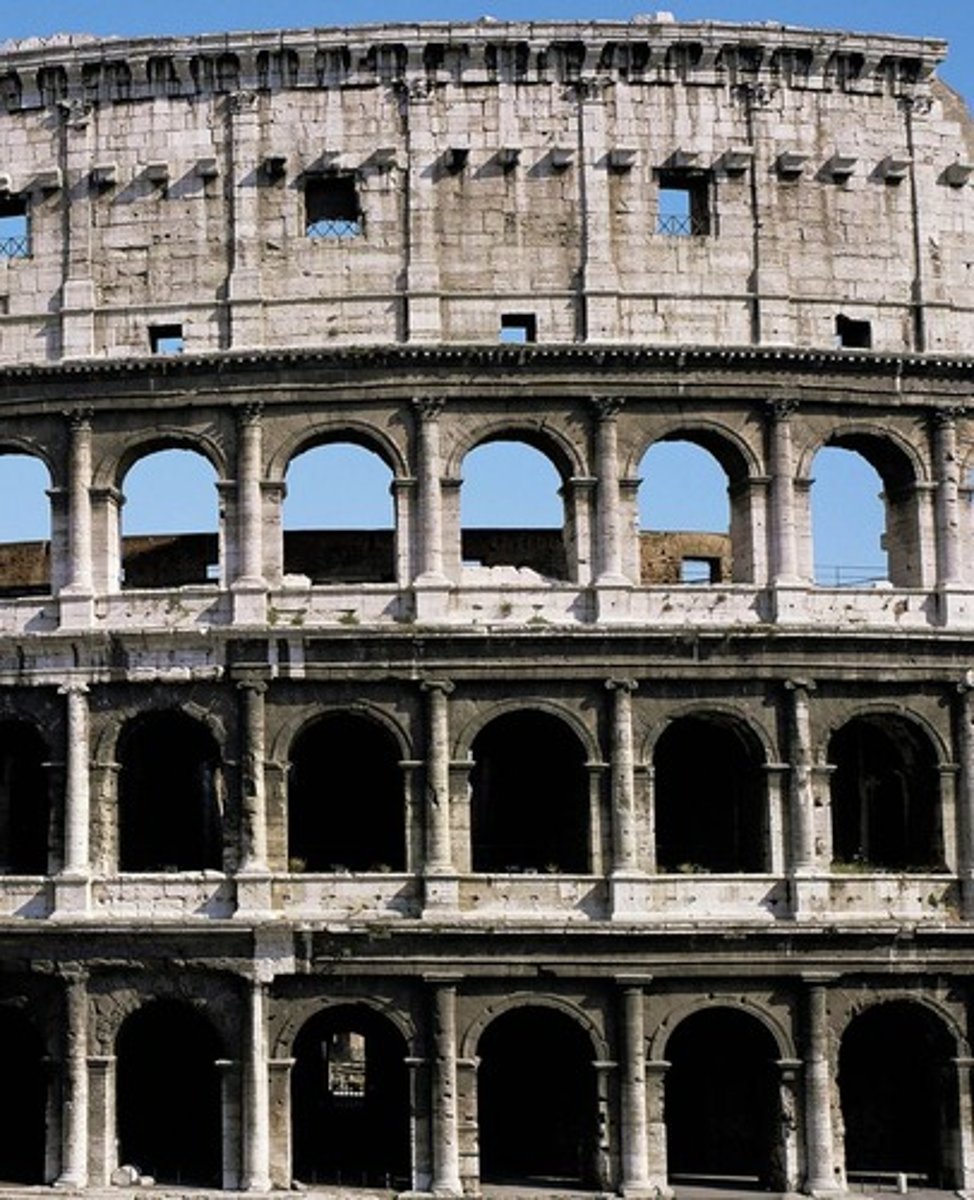
facade of the Colosseum, Italy. Early Empire

Arch of Titus, Italy. Early Empire

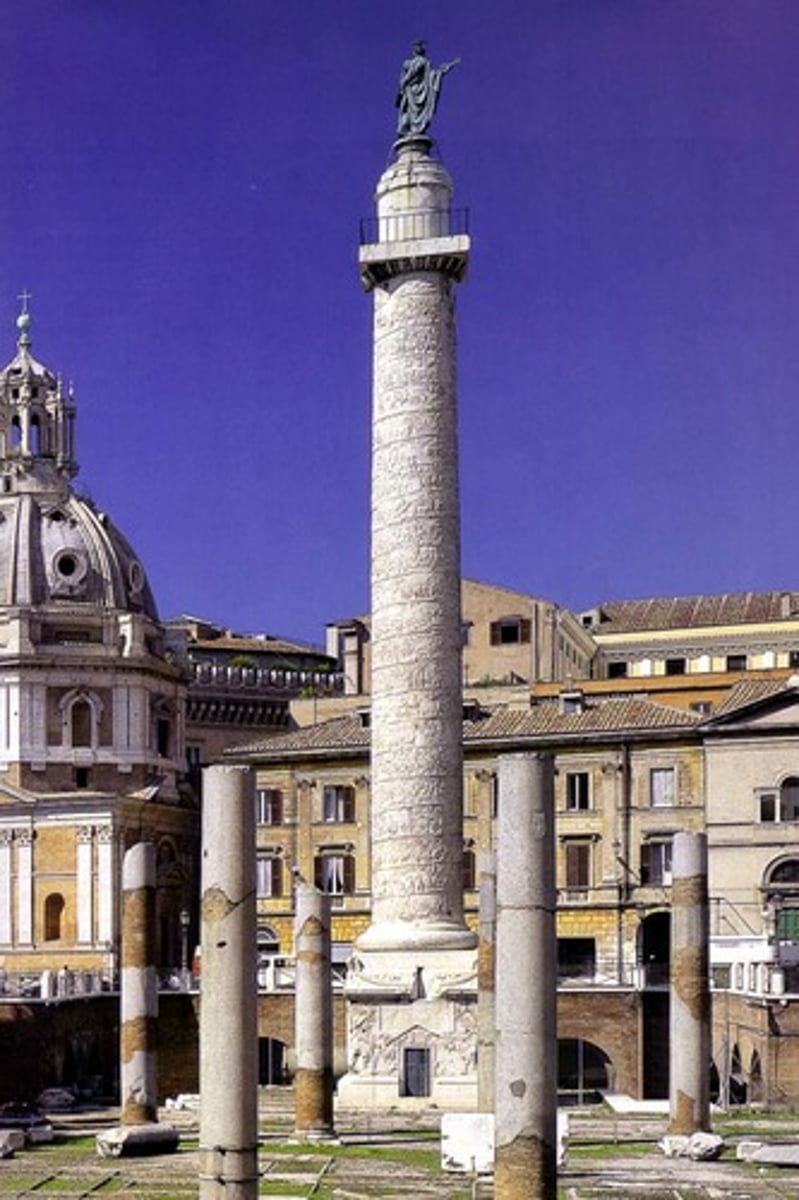
Column of Trajan, Italy. High Empire

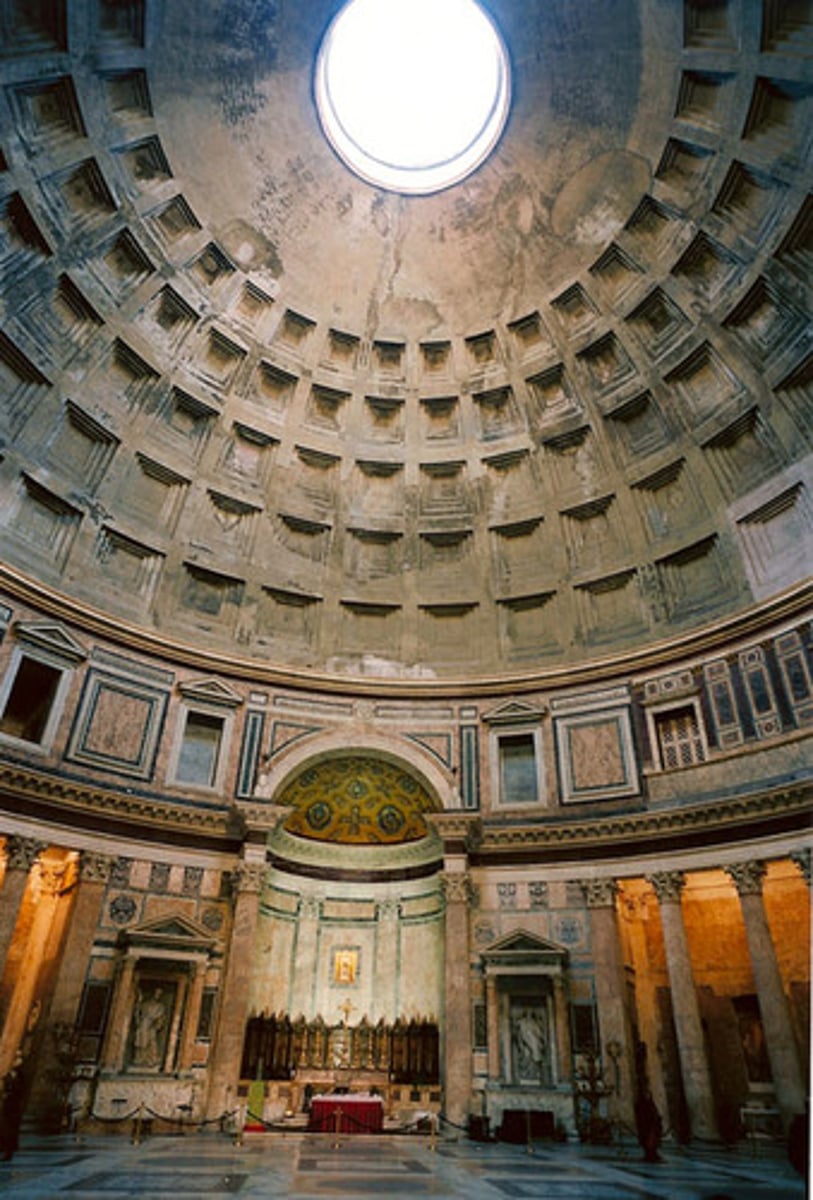
Interior of the Pantheon, Italy. High Empire

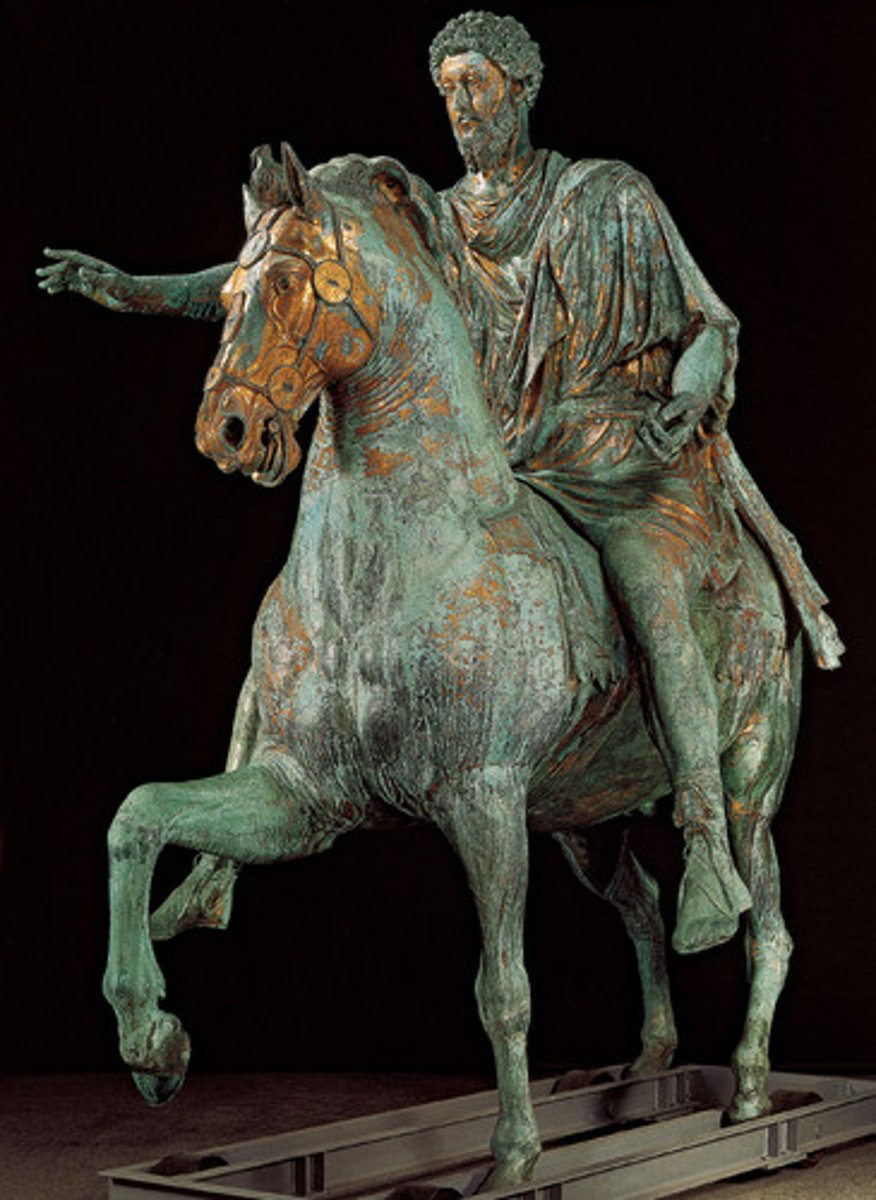
Equestrian statue of Marcus Aurelius, Italy. Bronze. High Empire

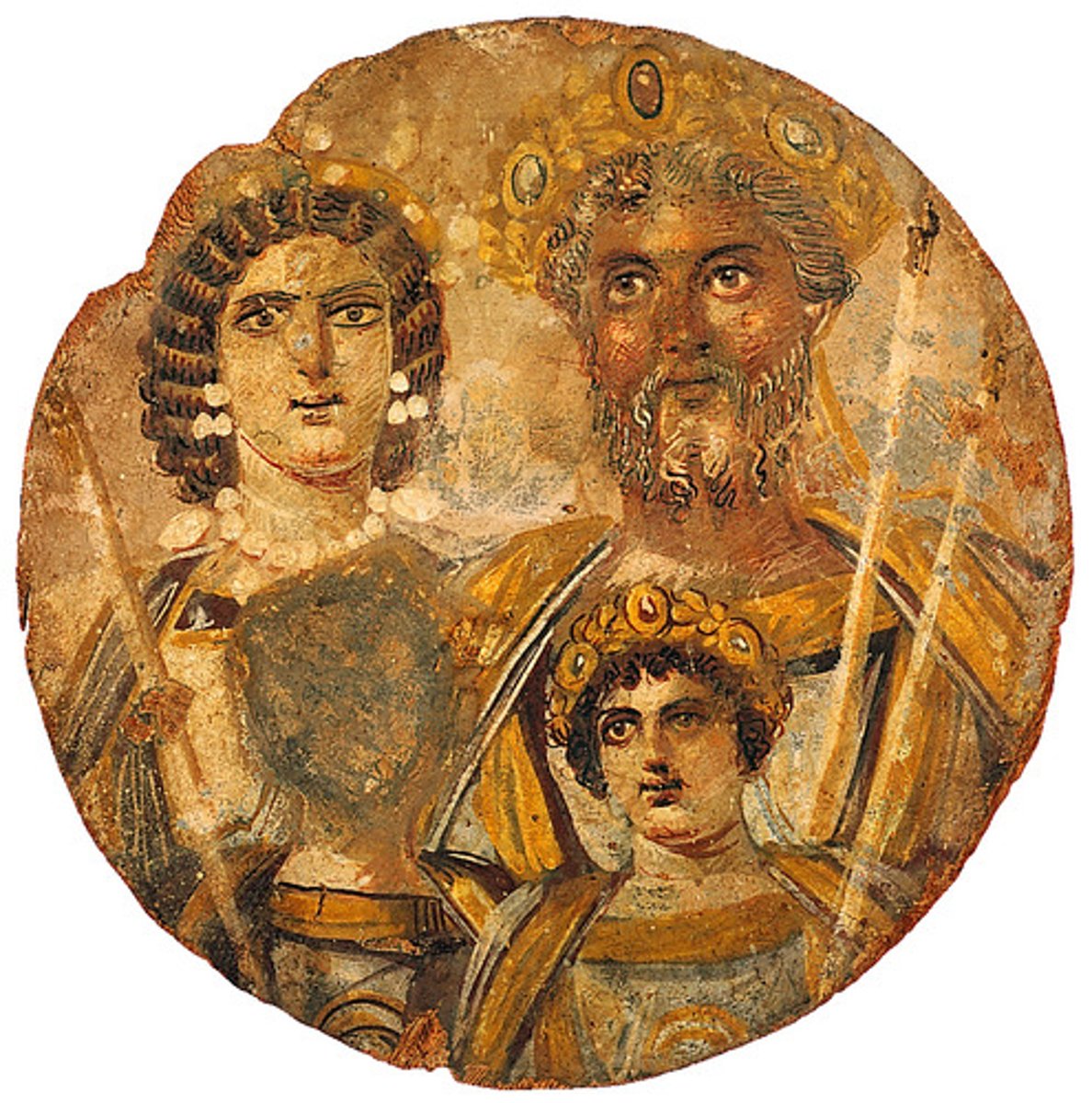
Painted portrait of Severus and family, Egypt. Tempera on wood. Late Empire

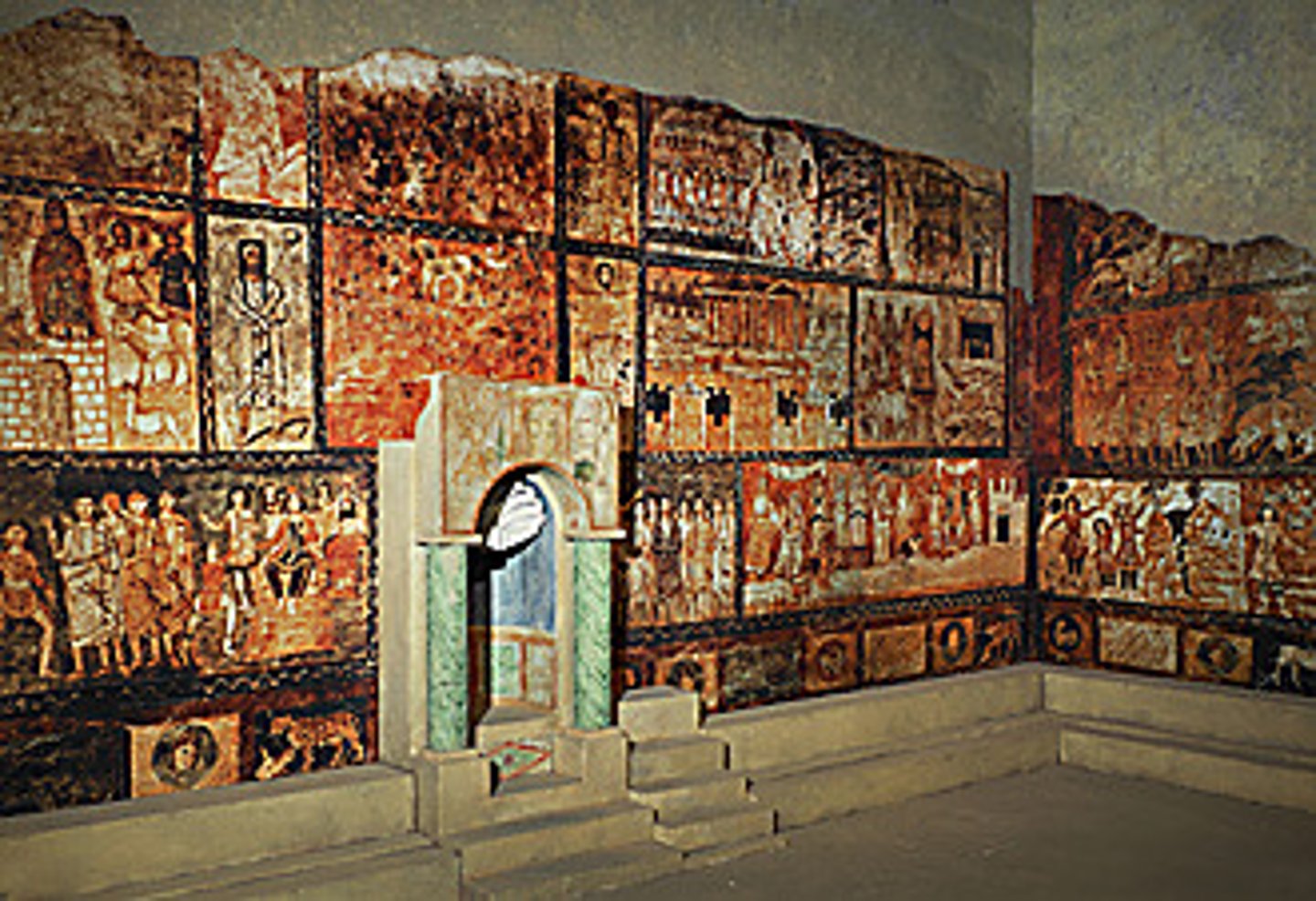
Interior of the synagogue, Syria. Tempera on plaster. Pre-Constantinian
