Computer Networks Overview
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Importance of Computer Networks (4)
Resource sharing
Social impact
easy access to knowledge and education
economic impact
OSI Model Layers (7)
Application (APDU)
Presentation (PPDU)
Session (SPDU)
Transport (Segment)
Network (Packet)
Data Link (Frame)
Physical (Bit)
Define Computer Network
A collection of computers / nodes connected by communication links (wired / wireless)
Links can be point-to-point or broadcast
Define Broadcast
shared link where unique address of individual nodes is used in message headers, more scalable
Bus topology
Reliability issue as if bus breaks whole network goes down
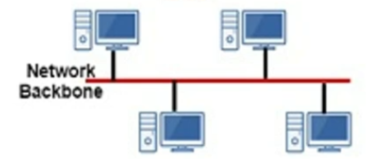
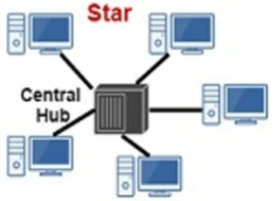
Star topology
point-to-point link but more flexible as easier to add nodes
reliability issue as if central hub breaks whole network goes down
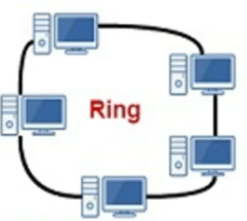
Ring topology
goes all the way around the ring
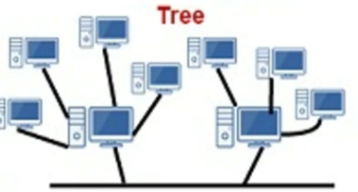
Tree topology
bus network of star networks
don’t need to go to the main bus if you want to send a message within a star network
Full mesh topology
Every node is connected
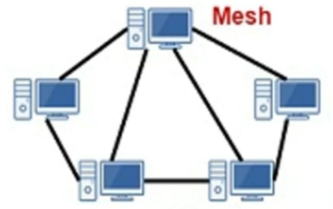
Partial mesh topology
nodes are connected to those they communicate with the most
Personal Area Network
Interprocessor Distance - 1m
Processors located in same square meter
local area network (interprocessor distance / processors located in same)
10m / room
100m / building
1km / campus
metropolitan area network (interprocessor distance / processors located in same)
10km / campus
wide area network (interprocessor distance / processors located in same)
100km / country
1000km / continent
the internet (interprocessor distance / processors located in same)
10,000km / planet
Define Pervasive Computing
Integration of computer capabilities and communication technologies into everyday objects and environments, making them interconnected and responsive to human needs without requiring conscious interaction
Mobile Ad-hoc NETwork (MANET)
node dynamically self-organizes without using any pre-established infrastructure
network of nodes where each node communicates wirelessly and acts as both a host and a router
topology not fixed - another router can be added to the network if another fails and easily take over
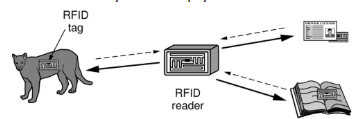
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) network
Tags (stickers with not even a battery when passive) are placed on objects
Readers send signals that the tags reflect to communicate
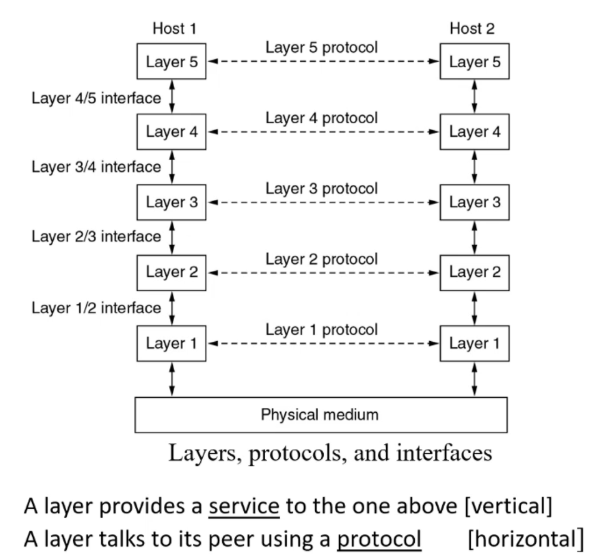
Protocol / Service Hierarchies
Networks are organised as a series of layers, each has a set of protocols that offers services to the upper layers, shielding them from the details of how services are implemented
Define circuit switch
dedicated physical path established between sender and receiver for the entire duration of the exchange (exclusive resources)
Define packet switch
virtual circuit - behaves like a circuit switch but operates on a packet-switch network (pre-determined path) less robust if node fails then entire circuit breaks
Datagram - each packet is treated completely independently containing full destination address so can take different routes / be re-routed dynamically
OSI Model layer traversal
Source host - moves down the layers Application → Physical
Destination host - moves up the layers Physical → Application
Routers / Switches / Hubs
Routers 3 / Switches 2 / Hubs 1; the more layers a device operates on, the more information it can use to make forwarding decisions (smarter and more efficient)
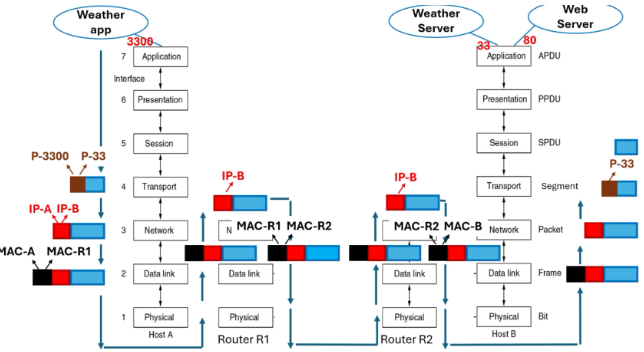
Type of data: x (unit exchanged)
P-3300
P-33
IP-A
IP-B
method of transmission
Source port number: P-3300 (segment)
Destination port number: P-33 (segment) distinguishes between Host B’s two offered services
Source IP Address: IP-A (packet)
Destination IP Address: IP-B (packet)
Source MAC address: changes depending place in chain of nodes as transmission is between adjacent nodes (frame)
frame translated into bits → signal transmitted between routers until destination host
Define socket
a combination of a port-number and IP address - uniquely identifies a certain application on a certain host in the Internet
Kilo storage vs networks
storage 2^10 = 1024
networks 10^3 = 1000
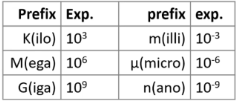
TCP/IP protocols
narrow waist architecture
ubiquitous (everywhere at the same time) by keeping the IP layer everyone has to agree to minimal
which layers of the OSI model are host-to-host layers?
Transport, Session, Presentation, Application
Error control is the responsibility of what layers?
Data link and Transport
IP Packet routing step 1
check if destination is on local network (compare own IP address and subnet mask to destination address)
local → packet sent directly to destination device using layer 2 protocols
remote → packet sent to default gateway
IP Packet Routing step 2 (Router - default gateway)
default gateway almost always local router
examines destination IP address and decides which connected network is the best path to send this packet towards its final destination
IP packet routing step 3 (Routing table)
if the router doesn’t know the complete path to the destination it consults the routing table
list of rules that state ‘to get to network X, send the packet out interface Y or to next-hop router Z’
IP packet routing step 4 (Hop-by-Hop journey)
process in step 3 repeats at every router along the path until packet reaches a router on the same local network as destination node
at each hop the data link header (MAC address) is stripped and re-created for the next immediate link
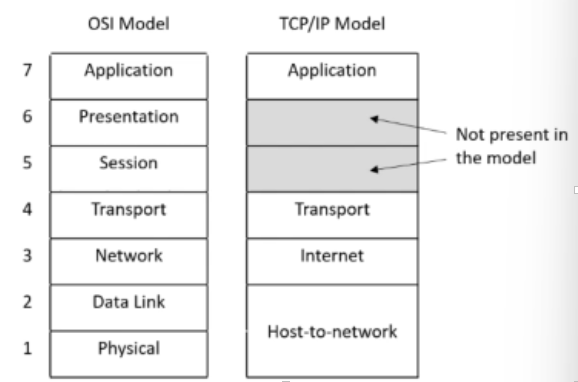
Network Access / Host-to-Network layer (= OSI physical + data link)
Catch all layer that represents the underlying network infrastructure that an IP packet uses to travel from one device to the next
Model designed to be independent of the underlying hardware

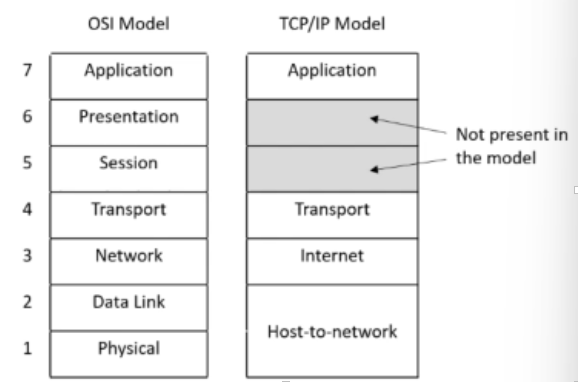
Internet layer (=OSI network layer)
packet-switching network based on a connectionless layer
official packet format and protocol (IP); unreliable (no acknowledgement message)
packet routing is major issue here
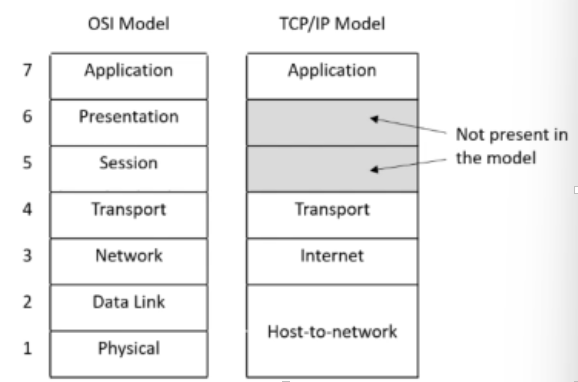
Transport Layer (= OSI transport layer)
designed to allow peer entities on the source and destination hosts to exchange data
TCP (transmissionless control protocol) is a reliable connnection-oriented protocol, used for reliable application
UDP (User datagram protocol) is an unreliable connectionless protocol, used for applications which require prompt delivery
Application layer (=OSI application, session, presentation)
contains all higher-level protocols
prompt delivery → quickly (low-latency), in sequence, consistently (without large variations in delay, called jitter)