AP Bio Unit 3 Test
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Cellular Respiration
the metabolic processes whereby certain organisms obtain energy from organic moelcules
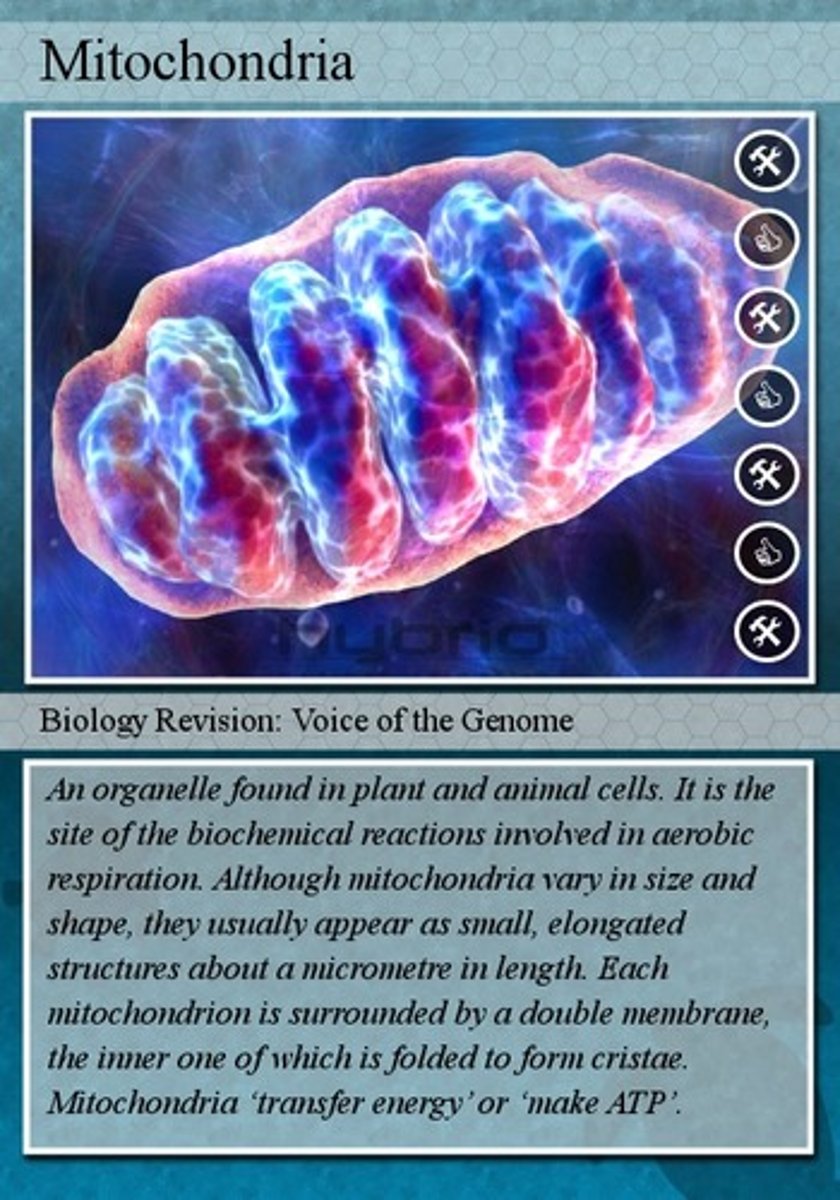
Kilocalories
the unit in which energy is measured
Redox Reaction
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction.
Oxidation
The loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction.
Reduction
any process in which electrons are added to an atom or ion (as by removing oxygen or adding hydrogen)
NAD+
electron carrier involved in glycolysis
NADH
the reduced form of NAD+; an electron-carrying molecule that functions in cellular respiration
Electron Transport Chain
a series of proteins in which the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle are used to convert ADP into ATP
Glycolysis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvate
Pyruvate Oxidation
2nd step in cellular respiration occurs on the way to the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is oxidized into 1 CO2, 1 NADH, 1 acetyl-COA (2 carbons attached to coenzyme A)
Citric Acid Cycle
in cellular respiration, series of chemical reactions that break down glucose and produce ATP; energizes electron carriers that pass the energized electrons on to the electron transport chain
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain.
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
The formation of ATP by directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism.
Intermediates
the compounds that form between the initial reactant, glucose, and the final product, pyruvic acid
Acetyl CoA
The entry compound for the Krebs cycle in cellular respiration; formed from a fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme.
Oxaloacetate
A four-carbon molecule that binds with the two-carbon acetyl unit of acetyl-CoA to form citric acid in the first step of the Krebs cycle.
Citric Acid
6 carbon; formed in Krebs Cycle; intermediate in the metabolism of carbohydrates
ATP Synthase
large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP (+28 ATP/ cycle)
FADH2
electron carrier produced during the Krebs cycle
Lactic Acid Fermentation
series of anaerobic chemical reactions in which pyruvic acid uses NADH to form lactic acid and NAD+, which is then used in glycolysis; supplies energy when oxygen for aerobic respiration is scarce
Alcohol Fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol.
Obligate Anaerobes
Organisms that cannot live where molecular oxygen is present.
facultative Anaerobes
can live with or without oxygen
Autotrophs
organisms that make their own food
Photosynthesis
process by which plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
Heterotrophs
an organism that depends on complex organic substances for nutrition
Stomata
the small openings on the undersides of most leaves through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
Stroma
thick fluid contained in the inner membrane of a chloroplast
Thylakoids
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy to chemical energy.
grana
stacks of thylakoids
Light Reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
Calvin Cycle
cycle in photosynthesis that reduces fixed carbon to carbohydrates through the addition of electrons ("dark cycle")
Carbon Fixation
The incorporation of carbon from carbon dioxide into an organic compound by an autotrophic organism.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
All of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
Wavelength
The distance between crests of waves, such as those of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Photon
a quantum of electromagnetic radiation
Chlorophyll
green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
Photosystem II
The first protein complex in the Light-dependent reactions. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae and cyanobacteria. The enzyme uses photons of light to energize electrons .
Photosystem I
The second photosystem in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and some bacteria. It uses light to reduce molecules.
Photophosphorylation
The process of generating ATP from ADP and phosphate by means of a proton-motive force generated by the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Photorespiration
A metabolic pathway that consumes oxygen and ATP, releases carbon dioxide, and decreases photosynthetic output. Photorespiration generally occurs on hot, dry, bright days, when stomata close and the oxygen concentration in the leaf exceeds that of carbon dioxide.
C3 plants
common plants- stoma close during dry weather- get CO2 directly from air- essentially stopping sugar production
C4 Plants
A plant that prefaces the Calvin cycle with reactions that incorporate CO2 into four-carbon compounds, the end product of which supplies CO2 for the Calvin cycle.
Cam Plants
Store the organic acids made at night in vacuoles and use them for photosynthesis during the day when stomata are closed