Lecture 29 - Chemiosmosis + ATP Synthase
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Chemiosmosis
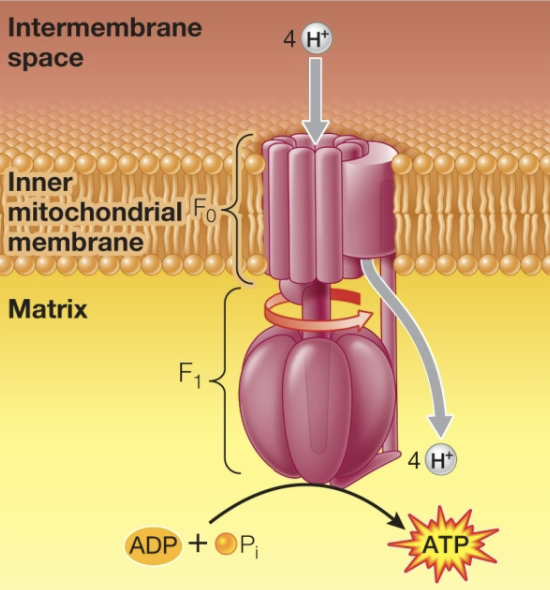
as protons flow back across the membrane through ATP synthase, ATP is generated
ATP synthase units
F0 Unit - protons enter through here and it begins to rotate, which causes central shaft to rotate
protons energize the shifting of the shaft due to kinetic energy of movement
Central Shaft - rotates and causes conformational change to occur in F1 unit
F1 Unit - ATP is produced here due to conformational changes
3 States of F1 Subunit
Open - free, low affinity for ADP + Pi, no catalysis occurring
Loose - Low affinity for ADP + Pi, it binds and is preparing for catalytic activity
Tight - High affinity for ATP + Pi catalysis, ATP formed
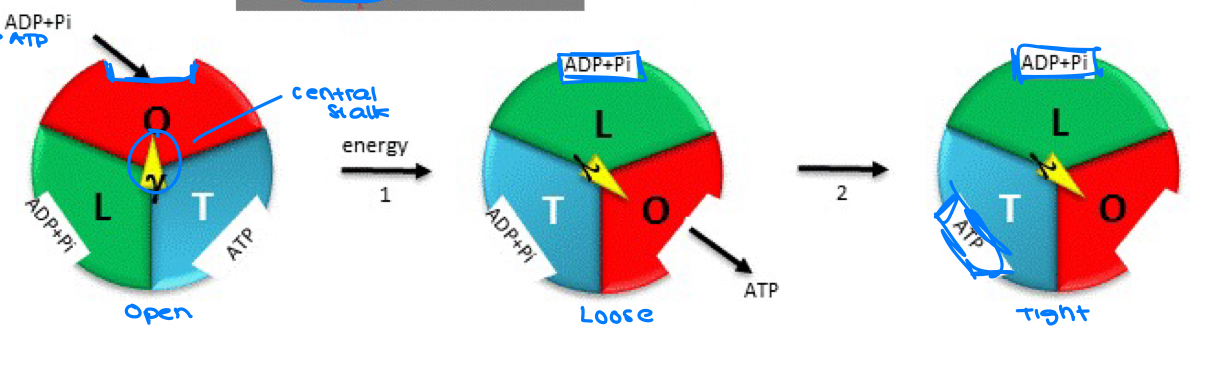
How is the ATP formed
ADP is forced to accept the phosphate (tight)
12 protons = 1 full rotation of central shaft
4 protons for each ATP
3 ATP formed in 1 full rotation
Each site willl always be in one comformation
Only one will be in tight conformation at a time
making ATP
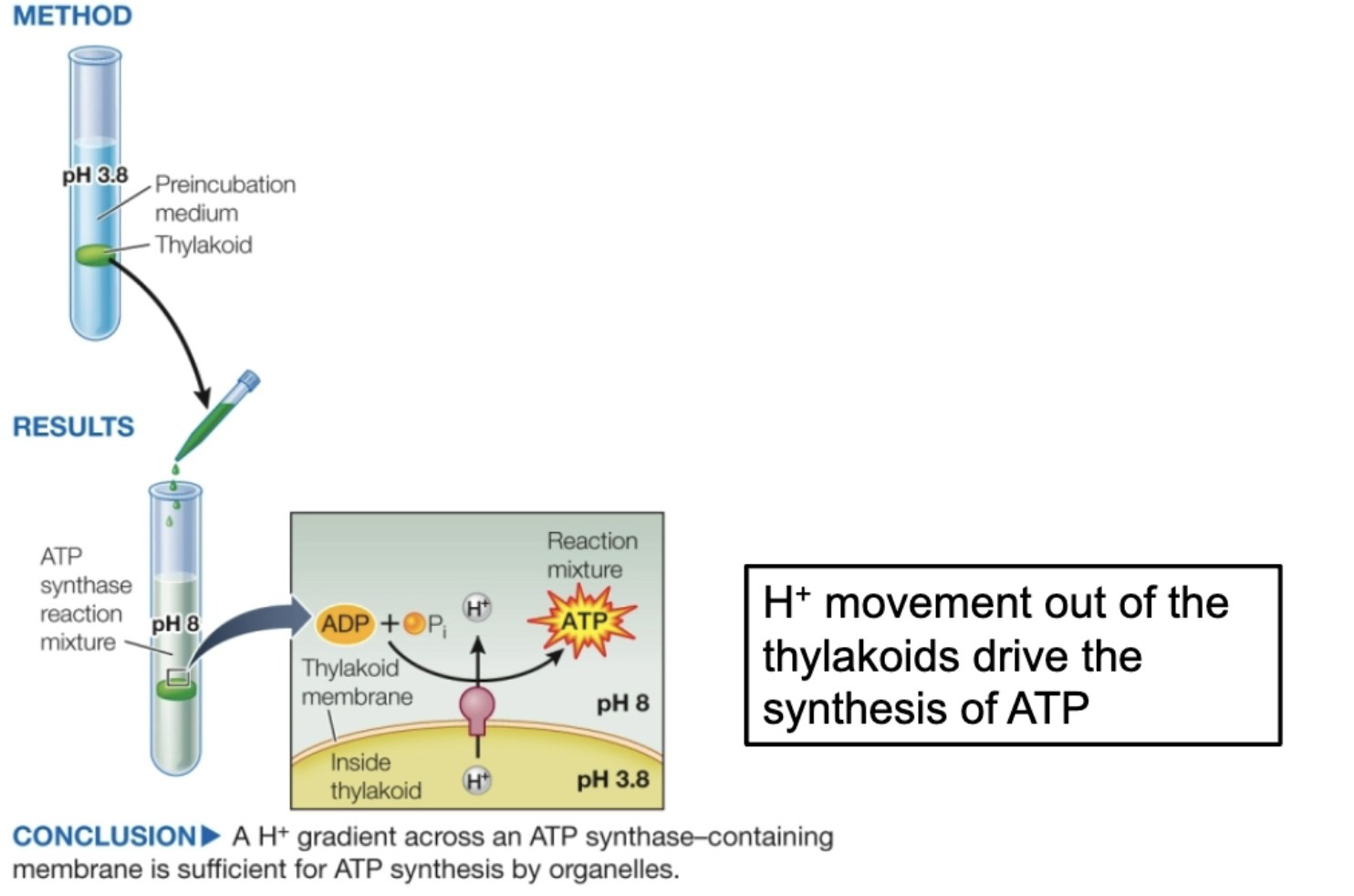
H+ gradient across ATP-synthase containing membrane is sufficient for ATP synthesis by organelles