Plant Cells
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Plasma membrane
Regulates what enters + leaves the cell
What 3 things is the plasma membrane composed of?
Lipids
Proteins
Carbs
Which microstructure has a bilayer structure?
Plasma membrane
What is the function of the plasma membrane’s bilayer structure?
To restrict other compounds from entering the cell
Cytoplasm
Protoplasm w/in cell excluding nucleus
Mitochondrion
ATP - cellular respiration
What does the mitochondrion convert?
Carbohydrates into energy (ATP)
What cell microstructure also contains DNA that codes for important traits like male sterility?
Mitochondrion
Cytoskeleton
Structural support
Movement of cell components
What 3 structures make up the cytoskeleton?
Microtubule
Intermediate filament
Actin filament
Nucleus
Stores cell hereditary material (DNA)
Coordinates cell activities
What 3 things js the nucleolus composed of?
Protein
RNA
DNA
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Ribosome synthesis
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane surrounding nucleus, protects the nucleus
Nuclear pore
Regulates movement of molecules between nucleus and cytoplasm
What is the highway in which things move/transport?
Nuclear pore
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Contains ribosomes
Protein production
What cell microstructure consists of connected, flattened sacs that synthesize proteins?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
What cell microstructure has ribsomes embedded on the outer surface of their membrane?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesis, secretion, storage of lipids
Metabolism of carbs
Golgi complex
Process + package macromolecules, proteins, + lipids
What cell microstructure consists of flattened, stacked “pouches”?
Golgi apparatus
Peroxisome
C metabolism
Abiotic stress response
Pathogen defense
Detoxifies cell by converting hydrogen peroxide to water
Cell wall
Outer layer in some organisms that provides support
Is the cell wall dead or living material?
Dead, not living
3 components of the cell wall
Polysaccharide materials
Lignin
Pectins
Polysaccharide Materials
Long-chained simple sugars
2 types of polysaccharide materials
Cellulose
Hemicellulose
Cellulose
Unbranched polymers
Hemicellulose
Branched polymers
Lignin
Polymers of phenolic acids
Lignification
Lignin will harden cellulose walls
Pectins
Acidic polysaccharides that act like cementing agents in cell wall depositions
Characteristics of cell wall composition
Cellulose chains are “braided” to form micelles which are braided into microfibrils which are braided into macrofibrils
2 types of cell wall
Primary
Secondary
Primary cell wall
Usually less than 1\mum
Found in young, growing parenchyma cells
Which cell wall is deposited following cell enlargement?
Secondary
Which cell wall contains large amounts of lignin?
Secondary
Where are secondary cell walls mostly found?
In vascular tissue
Which cell wall is thicker + stronger?
Secondary
Adjacent cell wall
Glued together by a sticky substance between their walls
Chloroplast
Organelle containing thylakoids, the sites of photosynthesis
Where is chloroplast found?
Only in plants and green algae
What 2 things does chloroplast convert?
Light energy into chemical energy
Carbon dioxide + water into sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids
Central vacuole
Storage compartment for water, sugar, ions, and pigments in plants
Tonoplast
Membrane surrounding the central vacuole
Selective of what goes in + out of the vacuole
Plasmodesmata
Openings in the cell wall that function in cell to cell communication
Allow things to move from cell to cell
Middle lamella
The pectic layer lying between the primary cell walls of adjoining cells
Where does photosynthesis happen?
Chloroplast
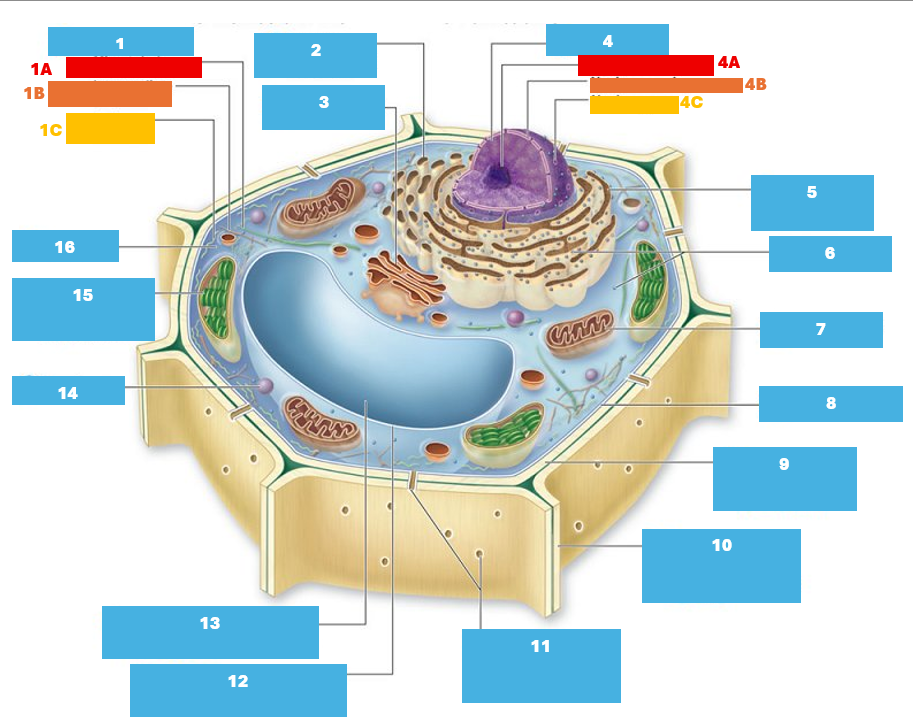
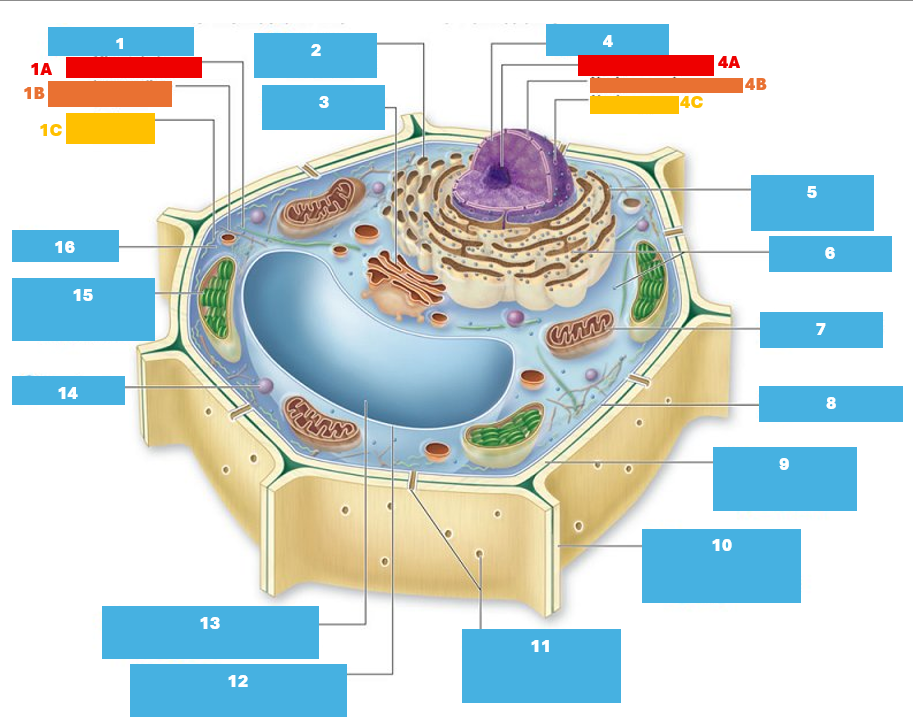
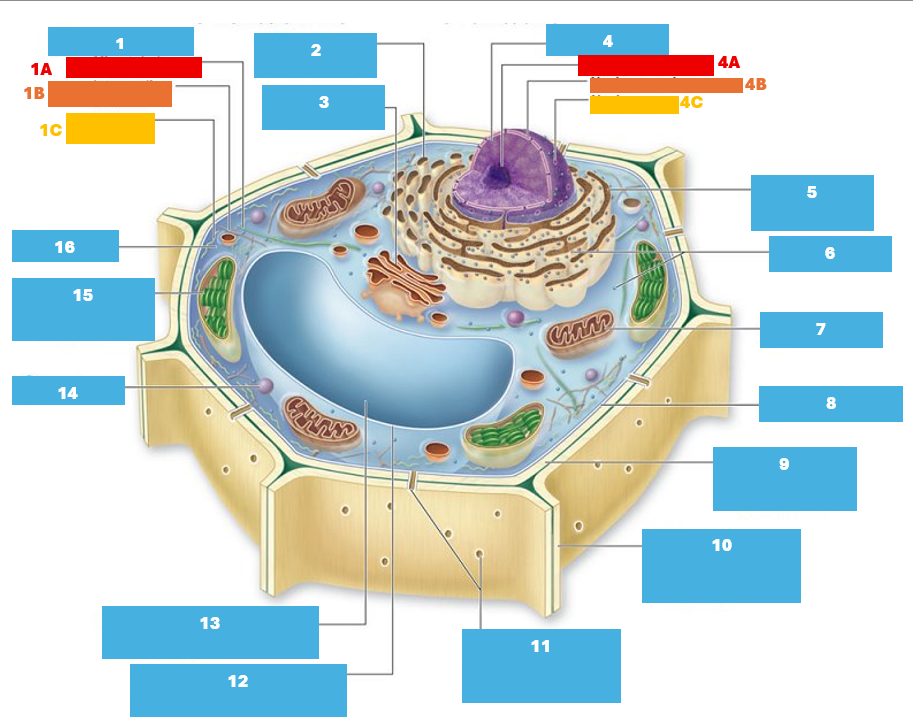
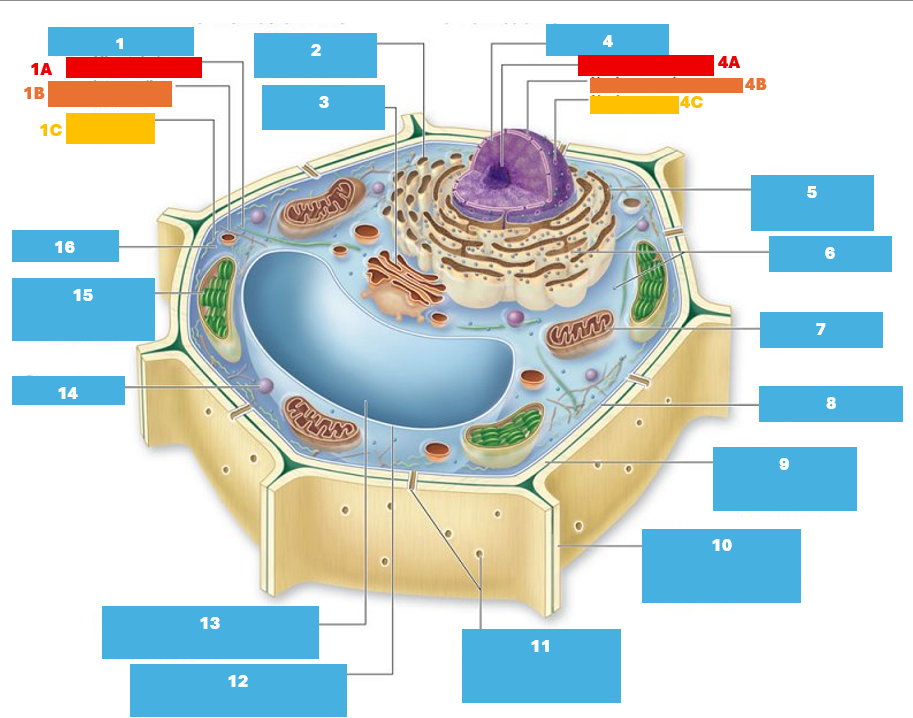
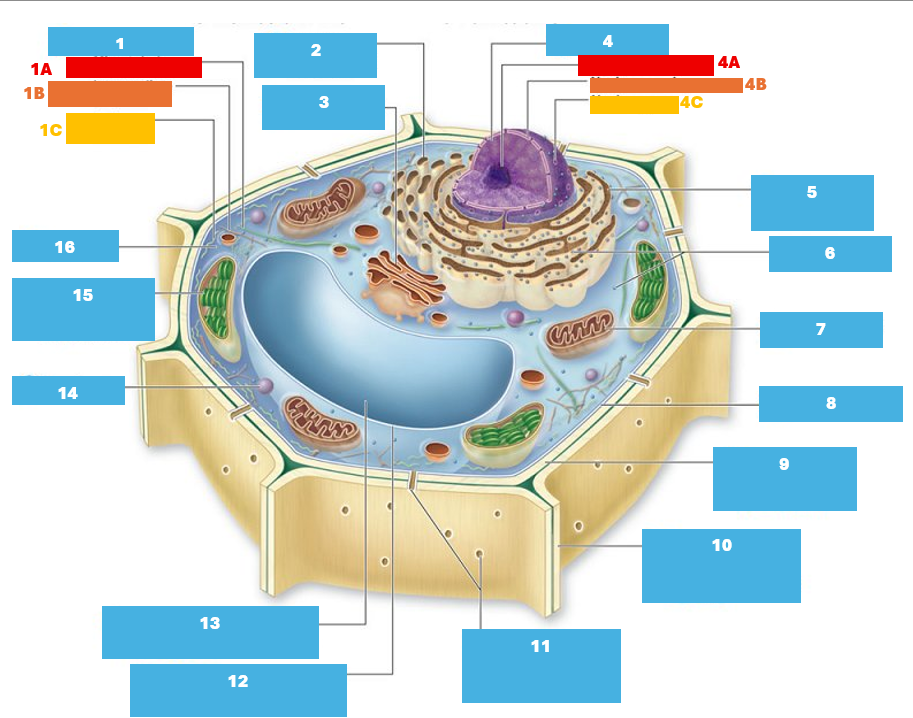
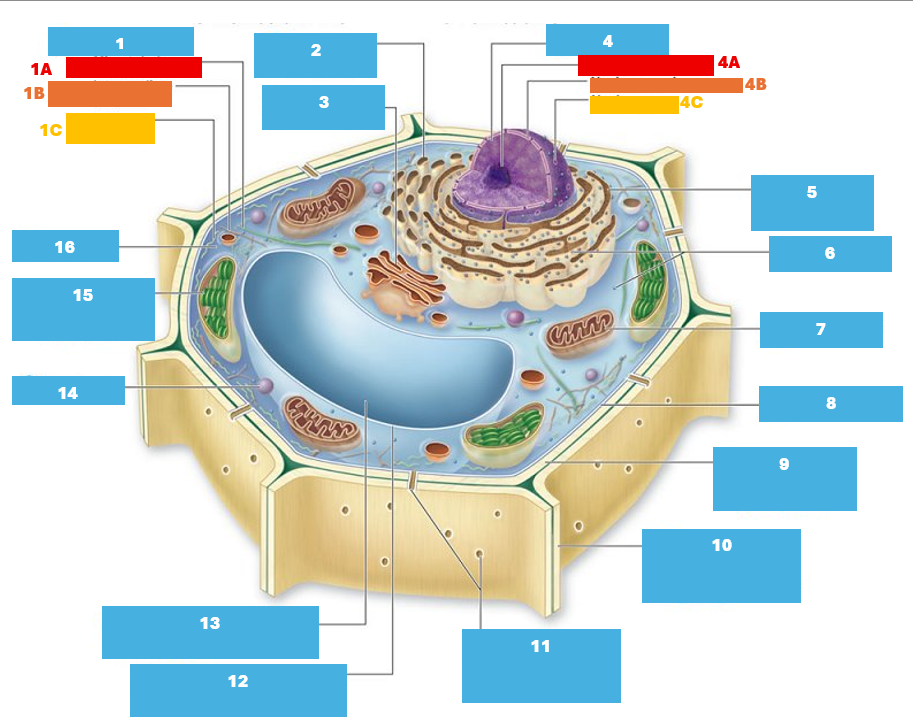
1
Cytoskeleton
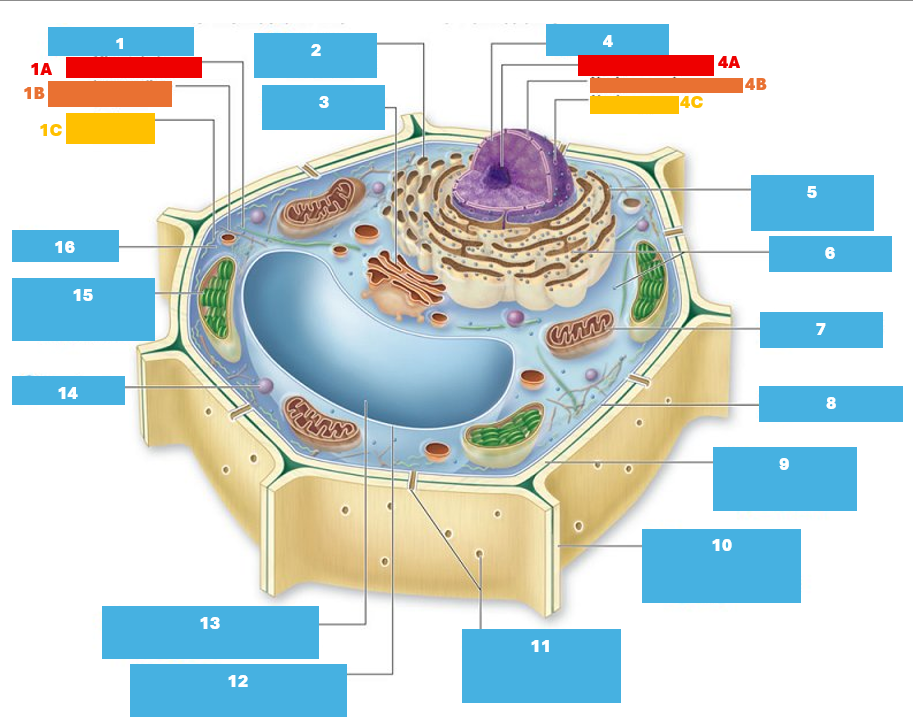
1A
Microtubule
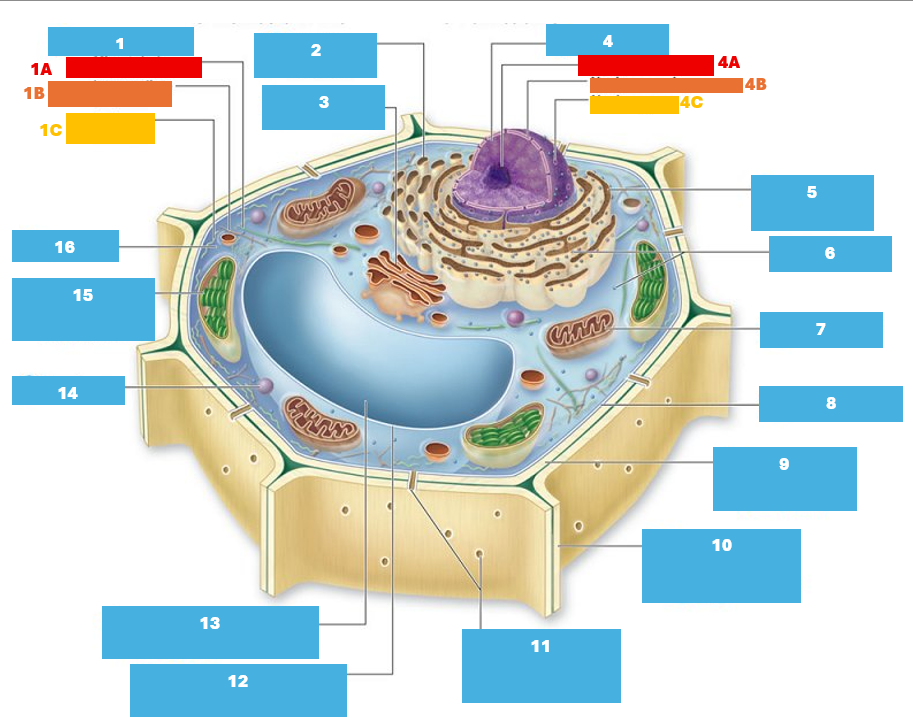
1B
Intermediate filament
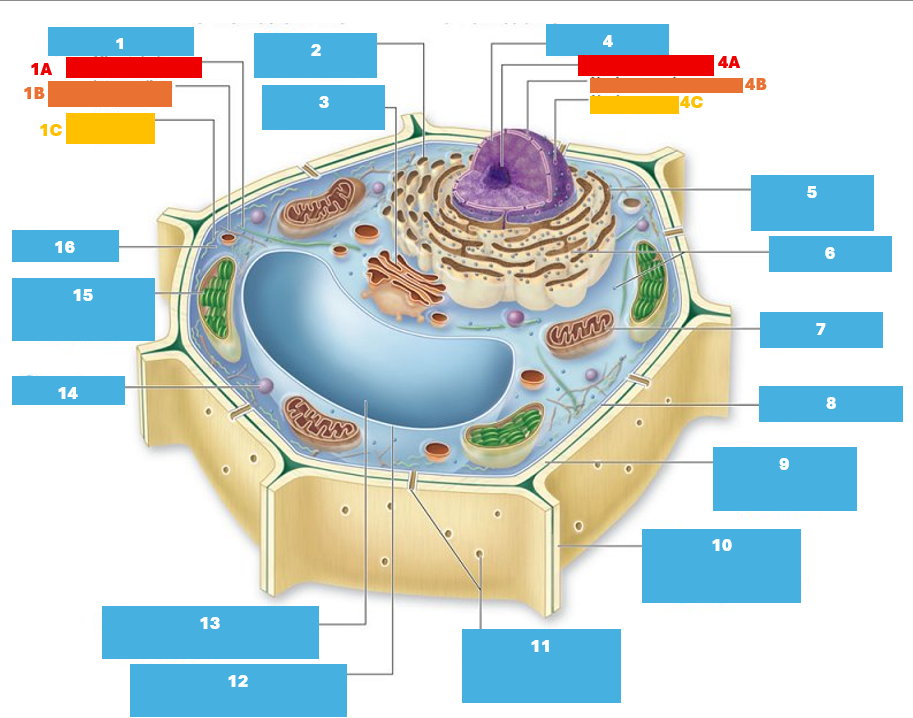
1C
Actin filament
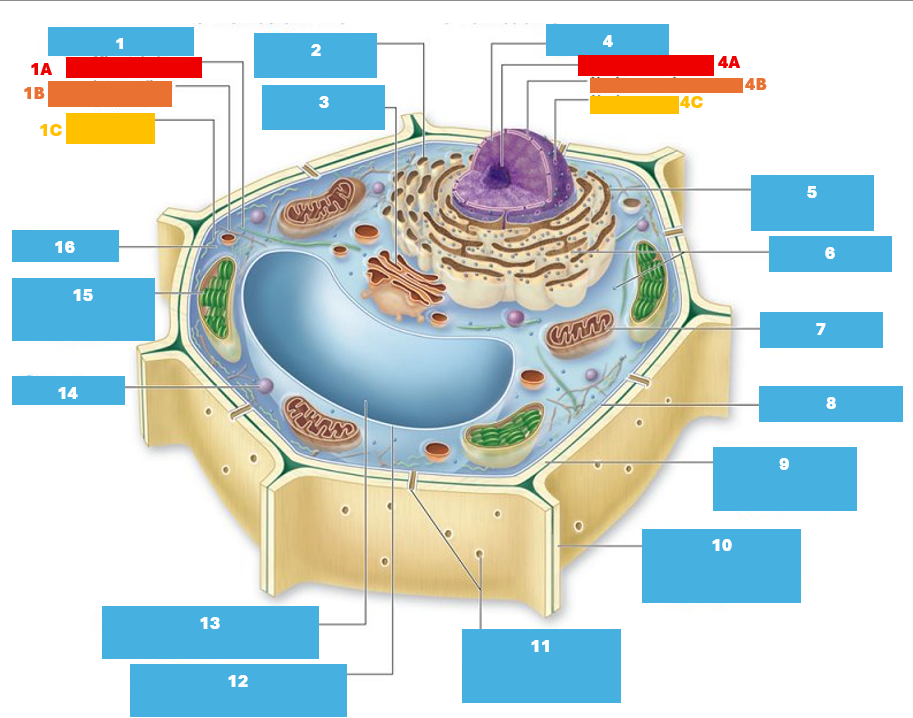
2
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
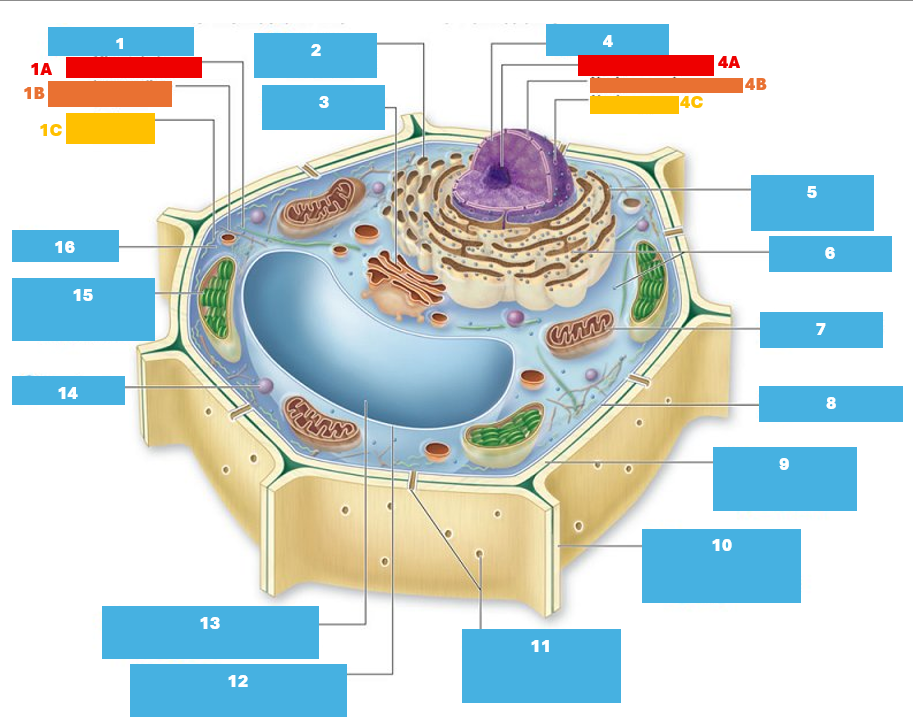
3
Golgi complex
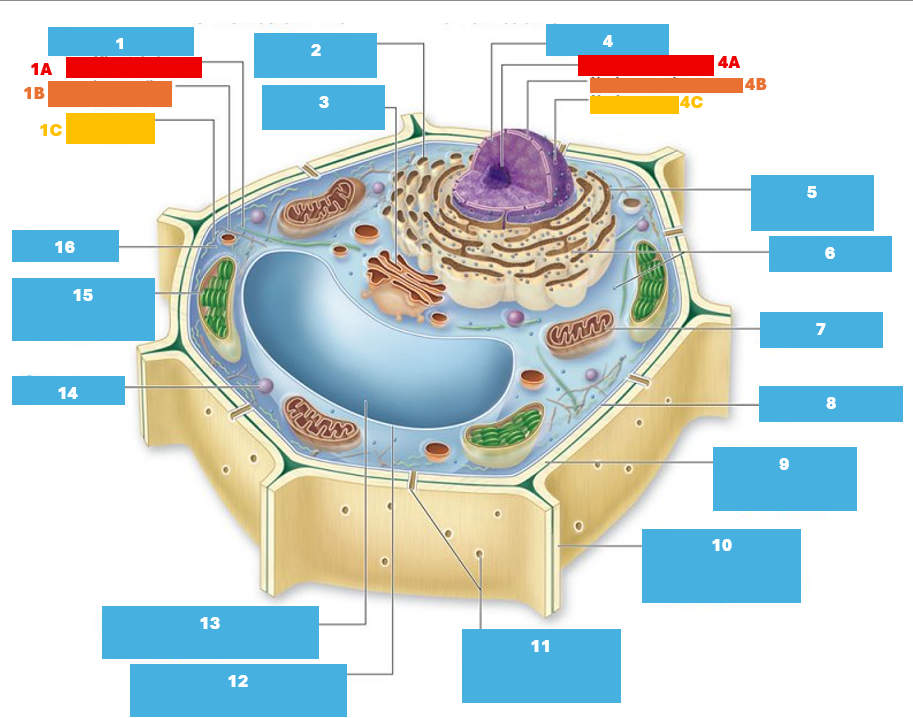
4
Nucleus
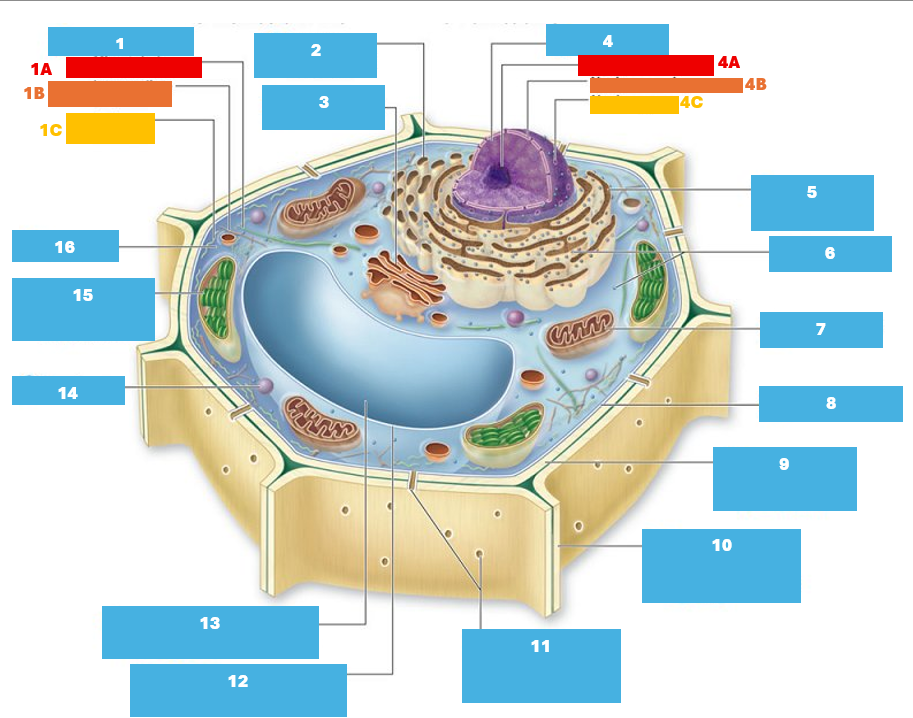
4A
Nucleolus
4B
Nuclear envelope
4C
Nuclear pore
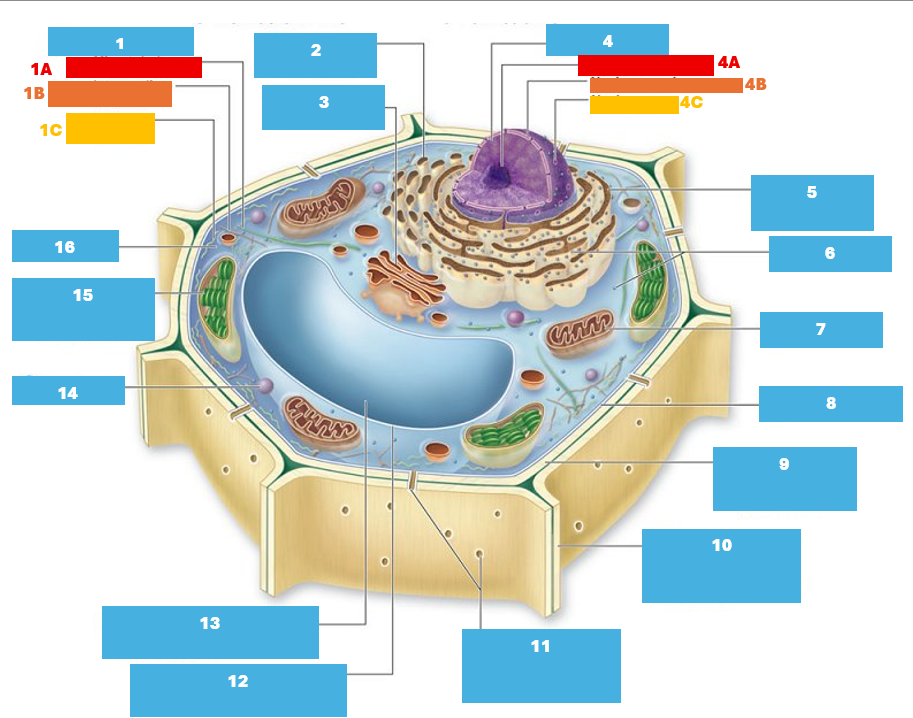
5
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
6
Ribosomes
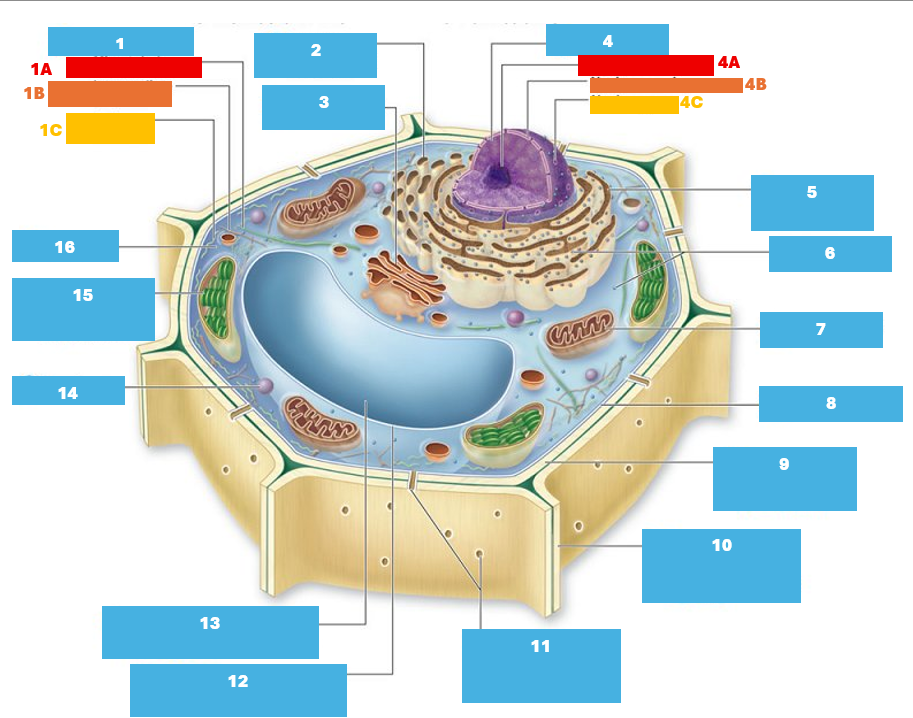
7
Mitochondrion
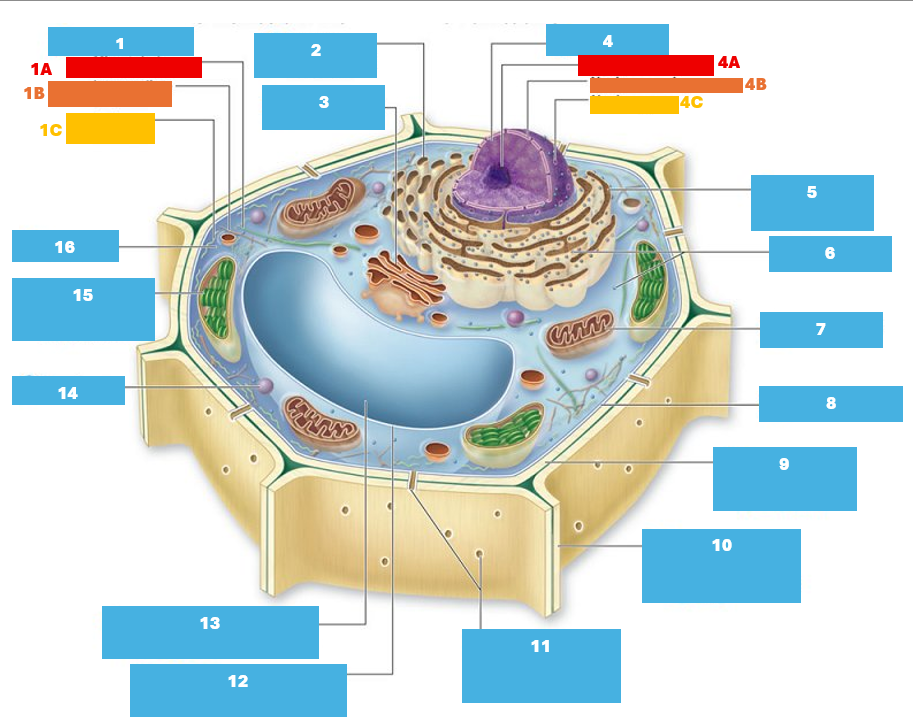
8
Plasma membrane
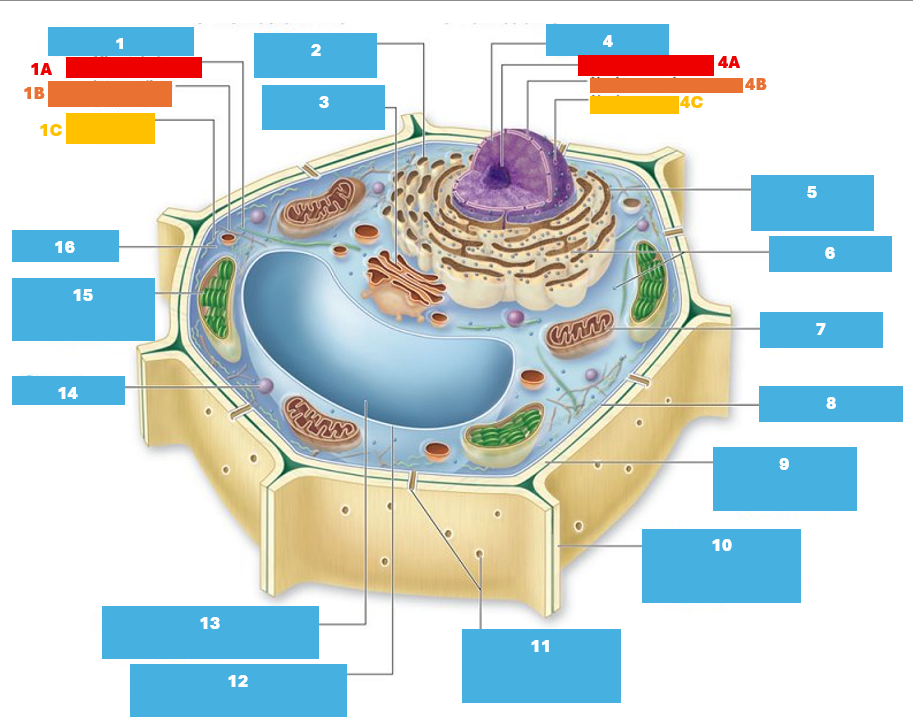
9
Cell wall
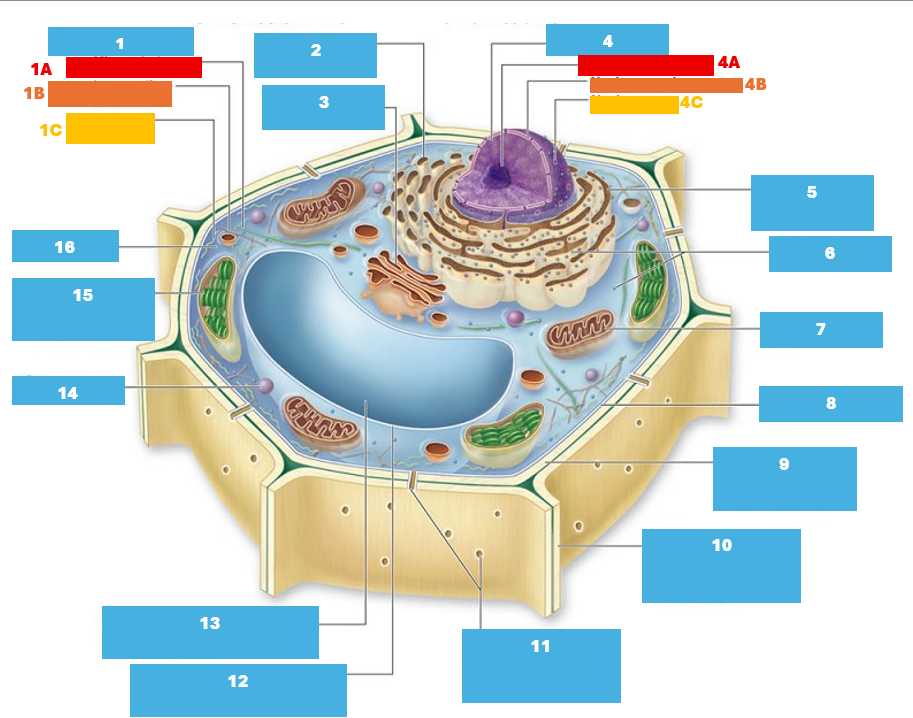
10
Adjacent cell wall
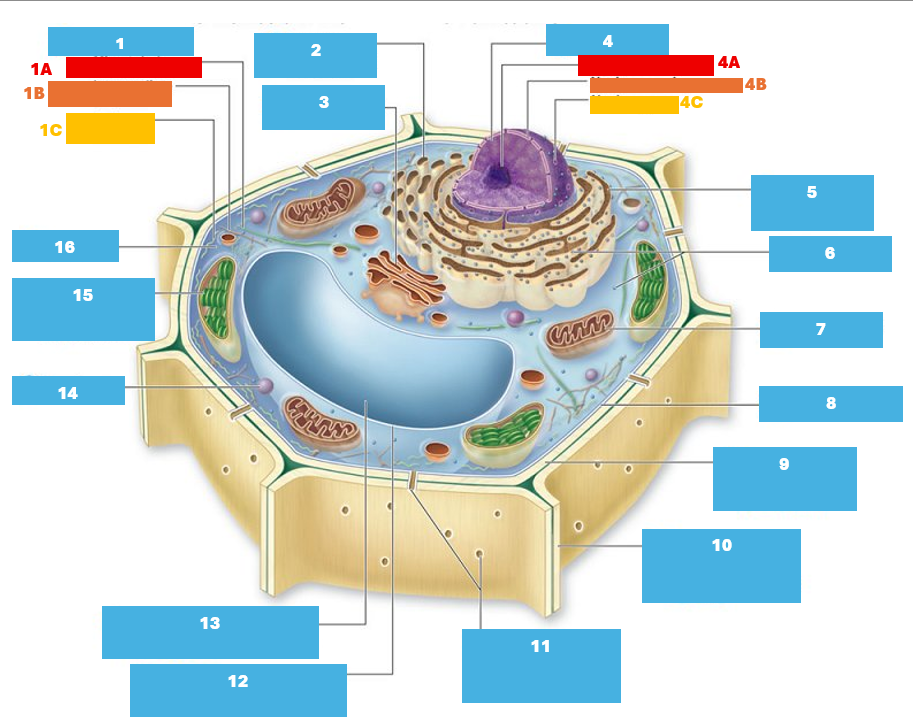
11
Plasmodesmata
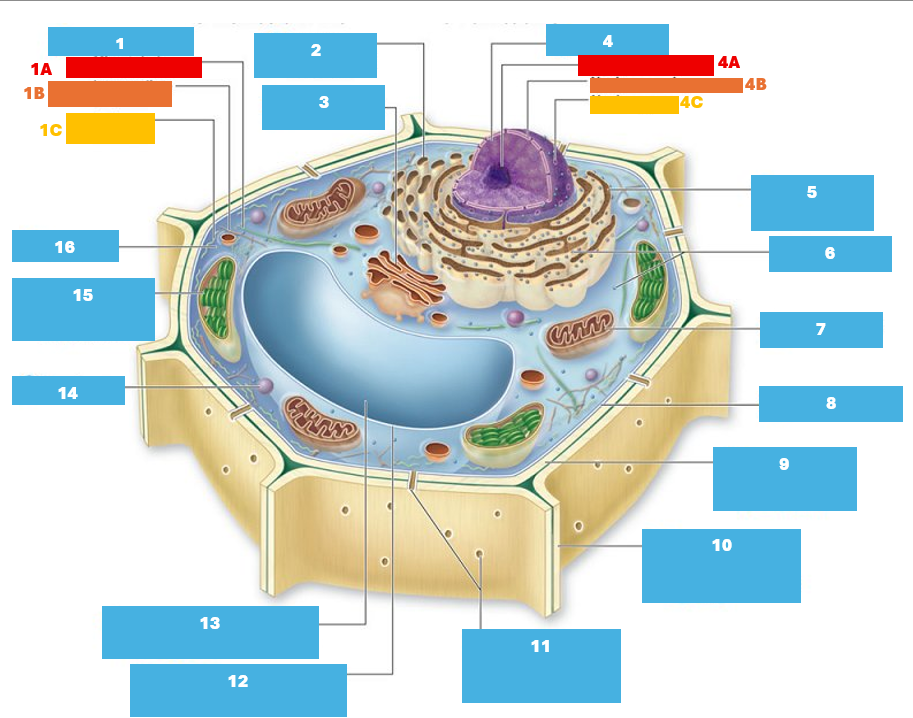
12
Tonoplast
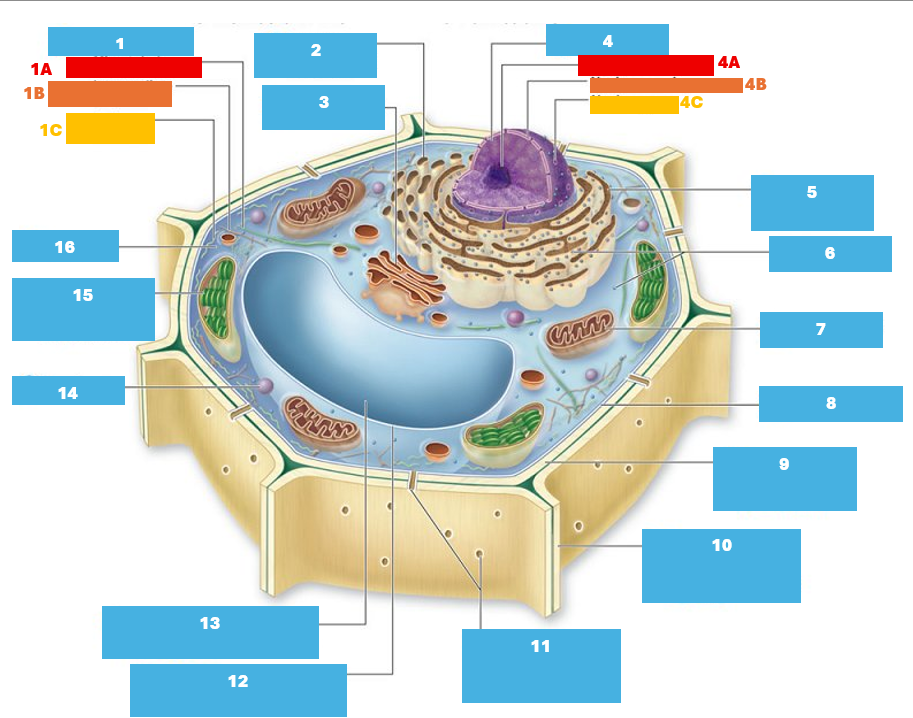
13
Central Vacuole
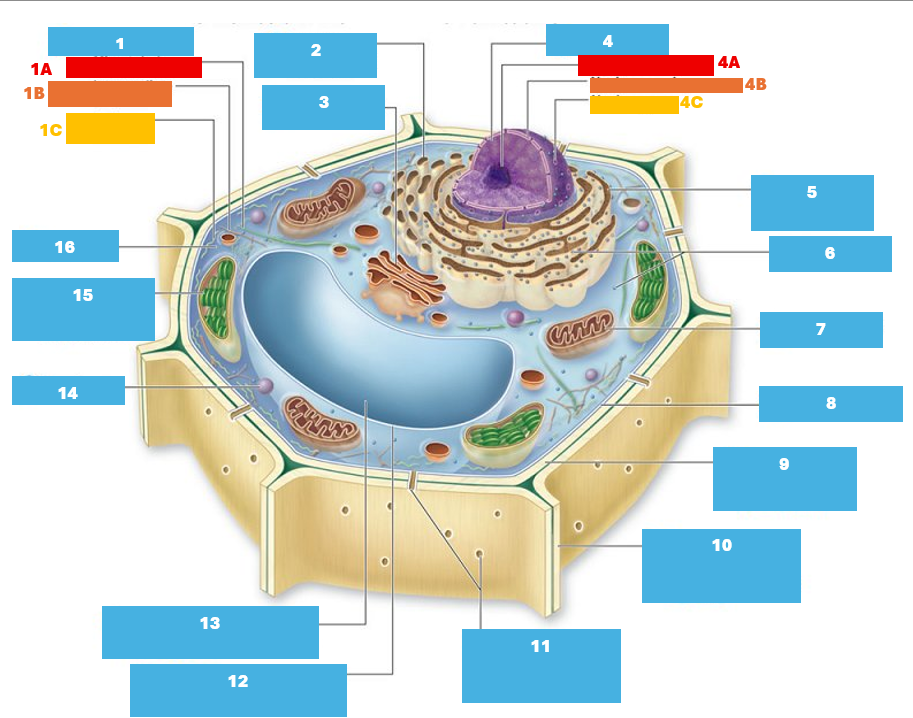
14
Peroxisome
15
Chloroplast
16
Cytoplasm