COMP1860 Lecture 2.2 Virtual Machines: Stack
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to virtual machines, stack architecture, and the Hack VM language, based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Virtual Machine Abstraction
An abstraction layer that allows code to run on different hardware platforms by providing an intermediary layer between the code and the hardware.
Hack VM Language
A low-level language used for virtual machines, utilizing arithmetic and logical operations to manipulate data on a stack-based architecture.
Stack Pointer (sp)
A pointer that indicates the next available position on the stack, not the top element, used for managing data flow in stack-based operations.
Push Operation
A fundamental stack operation that adds an element to the top of the stack.
Pop Operation
A fundamental stack operation that removes the top element from the stack.
Stack Arithmetic
Performing arithmetic operations by popping operands from the stack, evaluating the result, and pushing the result back onto the stack.
One tier compilation
High level programming language is compiled directly into machine level instructions.
Pros
1. Generates efficient code
2. Can take full advantage of hardware
Cons
1. Requires one compiler per target platform
2. Porting and maintaining software is time consuming
Two-Tier Compilation
High-level language is first compiled to an intermediate code (VM commands/bytecode), and then a VM translator converts this to machine code.
Pros
1. Compile once, run everywhere
2. Maximum portability
Cons
1. Requires VM translator per target platform
2. Generates less less efficient machine code
Memory Segments
Designated areas in memory used to store different types of data, such as constants, static variables, local variables, arguments, and pointers.
Constant Segment
A memory segment used to push constant values onto the stack; pop operations are not permitted from this segment.
Local Segment
A memory segment used to store a function's local variables, typically used for function calls.
Argument Segment
A memory segment used to store a function's arguments, commonly used for function calls.
This Segment
A variable memory segment that starts at pointer[0] and is commonly used to point to objects or arrays.
this i means: "the i-th element of the array starting at the address held in this"
That Segment
A variable memory segment that starts at pointer[1] and is commonly used to point to objects or arrays.
that i means: "the i-th element of the array starting at the address held in that"
Pointer Segment
The starting point for 'this' and 'that' memory segments.
Temp Segment
A memory segment containing eight temporary variables for short-term storage.
VM Emulator
A software tool that simulates the execution of virtual machine code, allowing developers to test and debug their programs.
LCL (Local)
Base address of local segment.
ARG (Argument)
Base address of the argument segment.
THIS
Base address of this segment, used for objects/arrays
THAT
Base address of that segment, used for objects/arrays
True/false
True = -1
False = 0
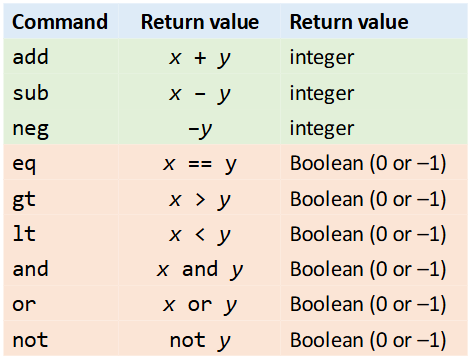
Arithmetic and logical operations
Difference between static and temp
Static variables retain their value between function calls and are stored in the data segment (have a fixed memory location).
Temp (temporary) variables are typically stored in registers or stack, used only during a short computation, and are not preserved after use (only exist during a specific function).