POL 235 Midterm: Marxism and Command Economics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is Marxism
work of Karl Marx + ppl who built on his ideas. many diff schools of thought and divisions within Marxism. when we talk abt communism/socialism we are referring to political systems that embody key Marxist theory ideas
MarxKarl
German. studied law and philosophy. spent 3 successive periods of exile in capital cities of France, Belgium, England. most known for critical engagement with contemporary capitalist society (raising issues abt morality, ideology, politics) and his predictions of a communist future
What did Marx's world look like
he was responding to the economic conditions of his time -- first era of globalization. industrial revolution in 1800s produced profound changes + social disruptions: development of industrial manufacturing, terrible working conditions, little gov regulation.
Marxist source of political conflict
all conflict is class conflict. the history of all hitherto existing societies is history of class struggle. contrast to liberals who believe there's essential harmony of interest b/w social groups. marxists believe society is systematically prone to conflict. axis of conflict between bourgeoisie (capitalists) and proletariat (workers)
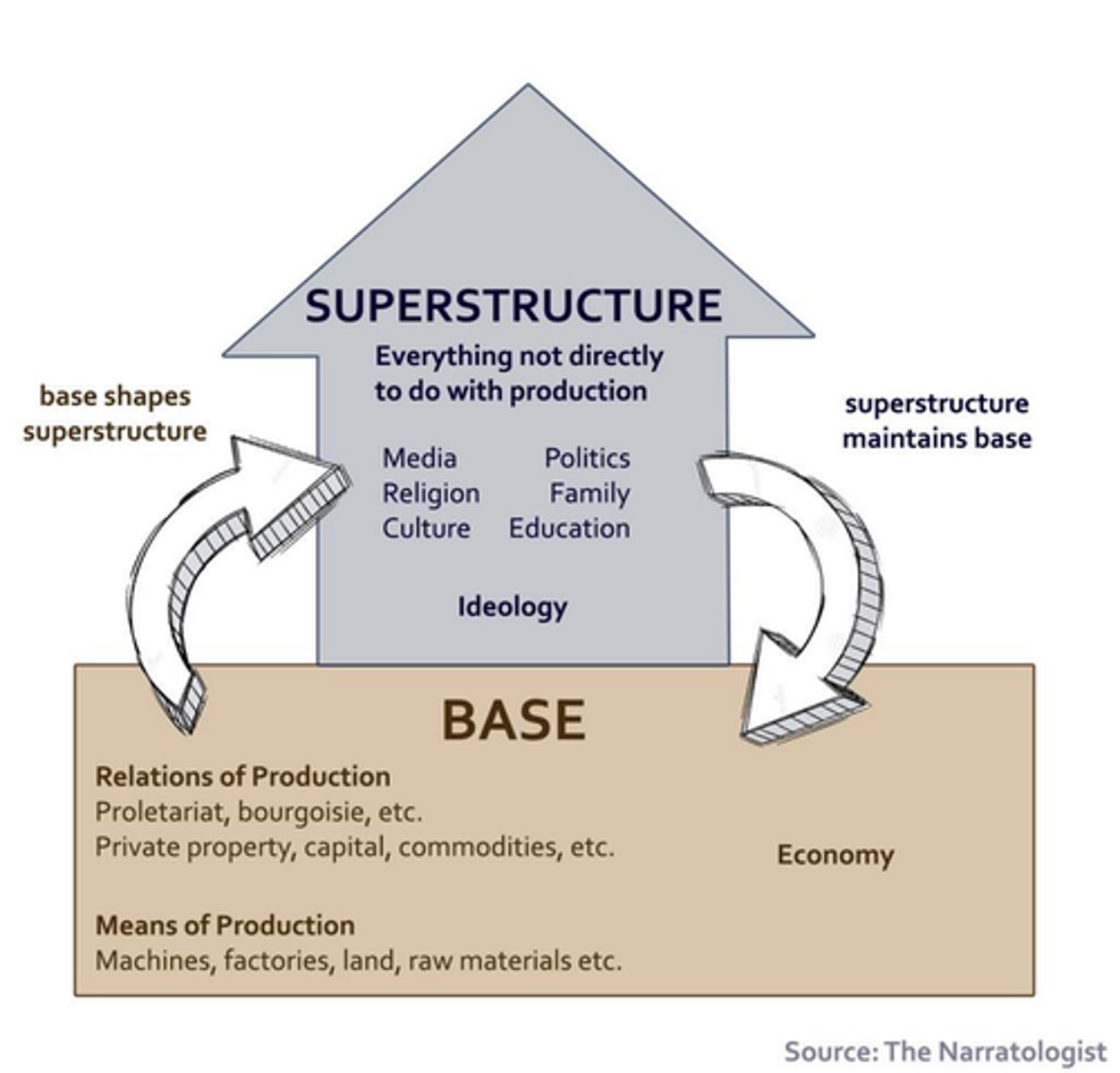
means + relations of production
politics reflects relationship b/w means and relations of production which forms base
means of production: economic activity which can change over time
relations to production: diff economic activities will underpin diff types of social relations.
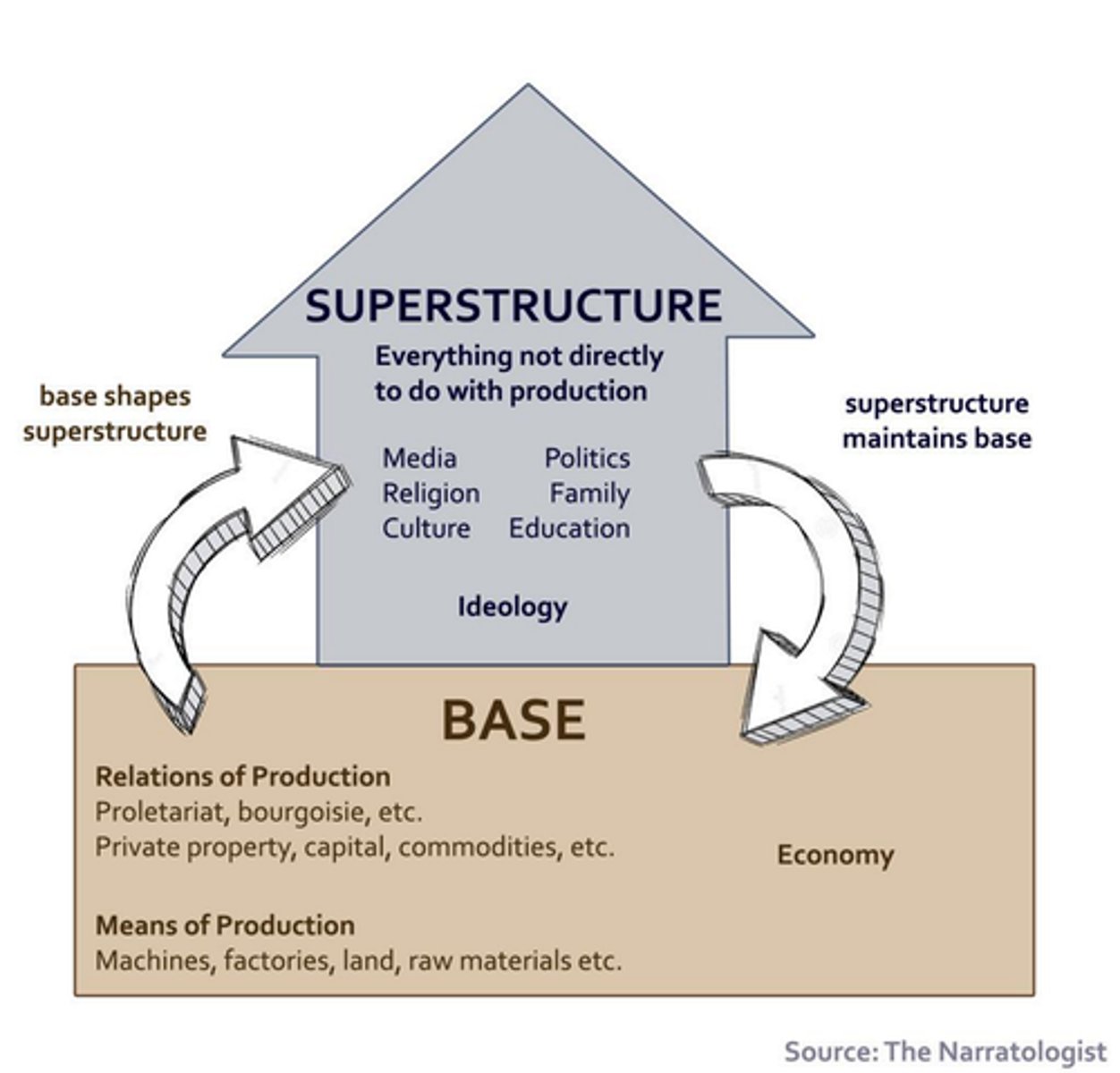
Superstructure
legal, political, cultural institutions and practices of a society that reflect and reinforce the pattern of power and control in the society
alienation + human flourishing
marx was interested in human labor. how can ppl be connected to their labor (pottery vs. assembly line). how can injustices of capitalism be addressed (building class consciousness + working class mobilization). why is capitalism doomed (insatiable need for growth)
class consciousness
the awareness of one's rank in society. essential for proletariat to overthrow capitalism and establish socialism
Marxism informed political movements + systems throughout 20th century
Marxism+Leninism as base of Soviet Union
Maoism in China
Marxism +Leninism in Cuba
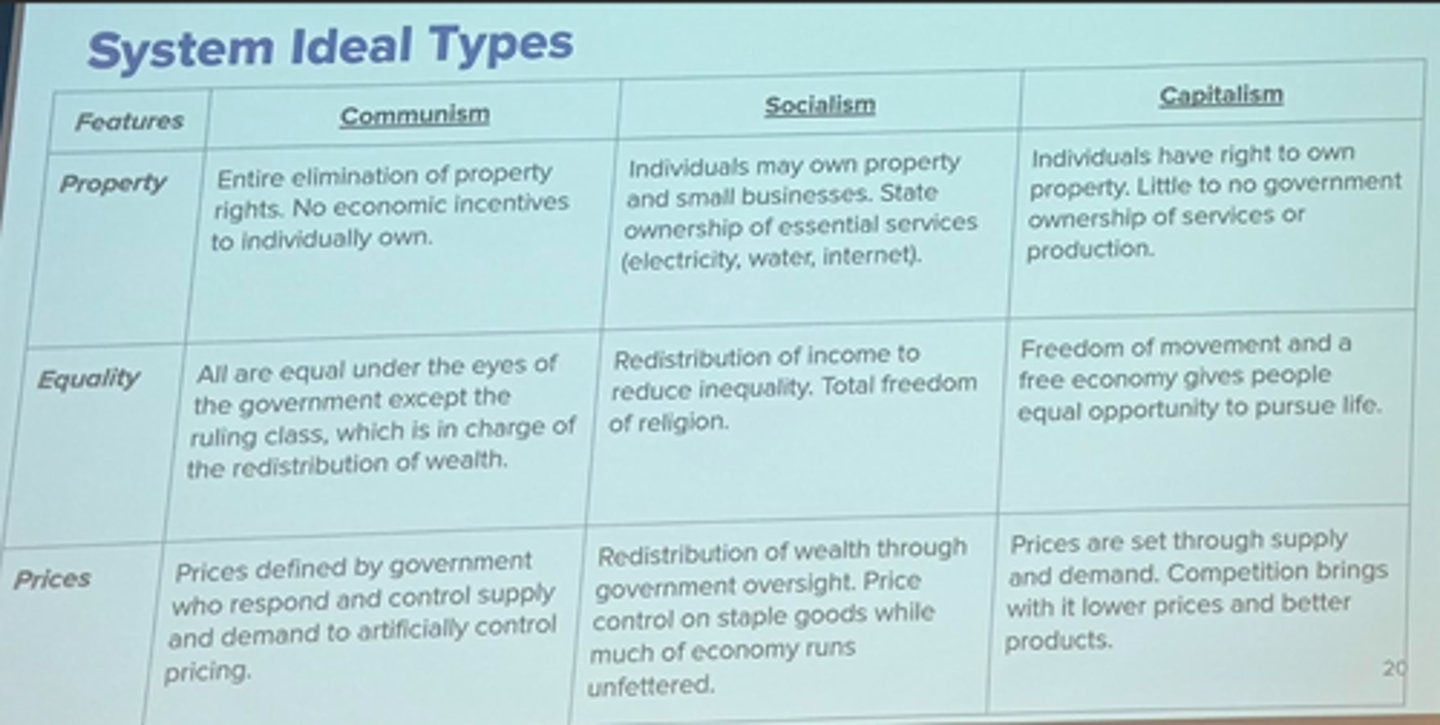
System (communism v. socialism v. capitalism) idea types (property, equality, prices)
3 real world impacts of Marxism
democratization, welfare state development and Universal Basic Income (UBI), climate change mitigation strategies
democratization
many countries went through it in 19th century. involved choices abt suffrage and electoral systems. elites wanted to democratize without losing power. choice between Majoritarian and Proportional Representation (PR). electoral system design part of strategy used by right parties to protect shared interest in minimizing influence of working class mobilization and socialism
Majoritarian
winner take all system. country divided into districts. politicians compete in their districts for seat. the candidate who receives highest vote share wins election and represents district
Proportional Representation (PR)
citizens vote for political parties instead of individual candidates. seats in legislature are then allocated in proportion to vote shares (ex: 23% of votes = 23% of seats)
Elite strategy to minimize power of working class through electoral system
Scenario 1: working class = weak. elite strategy = containment through majoritarian
scenario 2: working class = strong but ideologically moderate. elite strategy = containment through majoritarian
scenario 2: working class = strong and radical. elite strategy= competition through PR
welfare state
the state plays a key role in the protection and promotion of the economic + social well being of citizens. public provision of unemployment insurance, anti poverty programs, basic education, health services, etc.
Universal Basic Income (UBI)
regular, unconditional cash payment by gov that is given on a monthly or annual basis
Welfare state development in 20th century
strongly informed by interventionist approaches. Keynes, Depression, unemployment, New Deal, etc. political dynamics of Cold War. Soviet Union (enemy) known as workers paradise. rose fears that failure to provide adequate support for workers would incentivize them to support more radical labor unions, workers parties, maybe even Soviet Union.
Soviet Union as workers paradise in Cold War era
claimed to be society based on Marxist-leninist principles, where workers supposedly held the power and were free from capitalist exploitation. highly contested label, mostly in propaganda
UBI and welfare state
in its early days UBI put forward as aligning w/ goals of Marxist perfectionism. UBI enables individuals to practice inherently rewarding work since they're freed from need to work to live. now UBI resonates w/ diff + conflicting ideological views. Milton Friedman (neoliberalism) endorsed form called negative income tax (NIT)
Milton Friedman's Negative Income Tax (NIT)
income tax system changed a bit to include exemption based on family size. only earned income above that point is taxed. if you make less than the exemption amount, you receive a subsidy
climate mitigation
capitalist global economy where there's pressure to incr. growth/production yearly-- not sustainable. Marx thinks this is resource hungry+wasteful. climate change single biggest health threat facing humanity.
degrowth
strategy to stabilize economies and achieve social and ecological goals. called to transform the goals that guide economic and political systems. de-globalization, greater state intervention, scale down/eliminate harmful sectors, services, products. not getting traction
green growth theory
argues climate change can be mitigated through capitalism. tech change will allow us to decouple GDP growth from resource use and carbon emission