Core practical 5- light microscopy
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
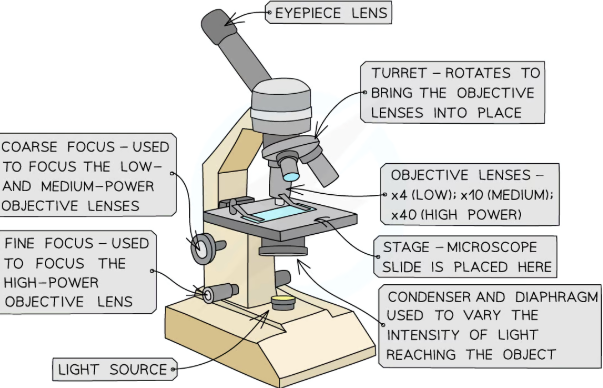
The key components of an optical microscope are
The eyepiece lens which often has a magnification of x10
The objective lenses each with a different magnification
The stage
The light source
The coarse and fine focus
Other tools that may be used
Forceps
Scissors
Scalpel
Coverslip
Slides
Pipette
Staining solution
method for preparing a slide using a liquid specimen with wet mount
add a few drops of the sample to teh slide using a pipette
cover the liquid/smear wiht a coverslip at an angleand gently press down to remove air bubbles
wear gloves to ensure there is no cross-contamination of foreign cells
how squash slides made
for soft spcimens
wet mount squashed between slide and coverslip
eg root cells to look at cell division
how smear slides made?
for body fluid specimens
the edge of the slide is used to smear the sample, creating thin even coating
eg blood smear to view erthrocytes
methods of preparing a microscope slide using a solid specimen
Take care when using sharp objects and wear gloves to prevent the stain from dying your skin
Use scissors or a scalpel to cut a small sample of the tissue
Use forceps to peel away or cut a very thin layer of cells from the tissue sample to be placed on the slide
The tissue needs to be thin so that the light from the microscope can pass through
Apply a stain to make cells more visible
Gently place a coverslip on top and press down to remove any air bubbles
Some tissue samples need to be treated with chemicals to kill cells or make the tissue rigid. How is this done?
This involves fixing the specimen using the preservative formaldehyde, dehydrating it using a series of ethanol solutions, impregnating it with paraffin or resin for support and then cutting thin slices from the specimen
The paraffin is removed from the slices and a stain is applied before the specimen is mounted and a coverslip is applied
To calculate the tensile strength of the fibre, the cross-sectional area has to be determined. (i) Devise a method to determine the cross-sectional area of a fibre, using the following equipment:
• a sharp blade
• a microscope
• a microscope slide and coverslip
• an eyepiece graticule • a stage micrometre
a (transverse) section/layer/slice of the fibre is cut, ensure section is flat,
graticule calibrated (with stage micrometer)./ calibrate eyepiece graticule
diameter measured/found using eyepiece graticule ./ count number of eyepiece gratiucle units over the cell
convert eyepiece graticule units to microns using calibration data
area calculated using πr2
measure diameter at different positions/orientation
describe procedure for accurate determinaiton of diameter
answer that includes the following points
• (using a light microscope find cell) under low power (1)
• then view under high power (1)
• calibrate eyepiece graticule / use of stage micrometer
• count number of (eyepiece) graticule units over the cell (1)
• convert eyepiece graticule units (to microns using calibration) (1)
• measure diameter at different positions / orientations (1)
Describe a safe method to prepare and examine the structure of human cheek cells.
bud into disinfectant/sterile/fresh bud/toothpick/
wear gloves/ goggles/safe use of microscope/slides/careful use of bud/stain to prevent injury
use of cotton bud, followed by use of stain/dye, place cells (on slide) under coverslip
use of high power of microscope
n.
it involves {enzymes / (chemical) reactions} and enzymes / (chemical) reactions are affected by temperature
Describe a safe method to observe the stages of mitosis in roots
Why is a low power and then a high power microscope is used?
Using a low power microscope to locate the specimen and a high power microscope to magnify
helps prevent damage to lens of coverslip in case the stage has been raised too high
how to prevent the dehydration of tissue
Adding a drop of water to the specimen beneath the coverslip can prevent the cells from being damaged by dehydration
what to do if you see unclear or blurry images
Switch to the lower power objective lens and try using the coarse focus to get a clearer image
Consider whether the specimen sample is thin enough for light to pass through to see the structures clearly
There could be cross-contamination with foreign cells or bodies
limitations of optical miroscope
The size of cells or structures of tissues may appear inconsistent in different specimen slides
Cell structures are 3D and the different tissue samples will have been cut at different planes resulting in this inconsistencies when viewed on a 2D slide
Optical microscopes do not have the same magnification power as other types of microscopes and so there are some structures that cannot be seen
The treatment of specimens when preparing slides could alter the structure of cells
what is magnification
Magnification is how many times bigger the image of a specimen observed is in comparison to the actual, real-life size of the specimen
what is total magnification
total magnification = eyepiece lens magnification x objective lens magnification