Pentose Phosphate Pathway of Glucose Oxidation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Pentose phosphate pathway
pathway that oxidizes glucose 6-phosphate, producing pentose phosphates and NADH
Cells and Tissues that use the pentose phosphate pathway
- rapidly dividing cells use ribose 5-phosphate to make RNA, DNA, and coenzymes
- tissues that carry out extensive FA synthesis require the NADPH provided in this pathway
- tissues that actively synthesize cholesterol and steroid hormones require the NADPH provided by this pathway
Lactonase
catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactone to the free acid 6- phosphogluconate
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
catalyzes the oxidation and decarboxylation of 6-phosphogluconate to form ribulose 5-phosphate and NADPH
Overall equation for the pentose phosphate pathway
glucose 6-phosphate + 2NADP+ + H2O ----> ribulose 5-phosphate + CO2 + 2NADPH + 2H+
Ribulose 5-phosphate epimerase
epimerizes ribulose 5-phosphate to xylulose 5-phosphate
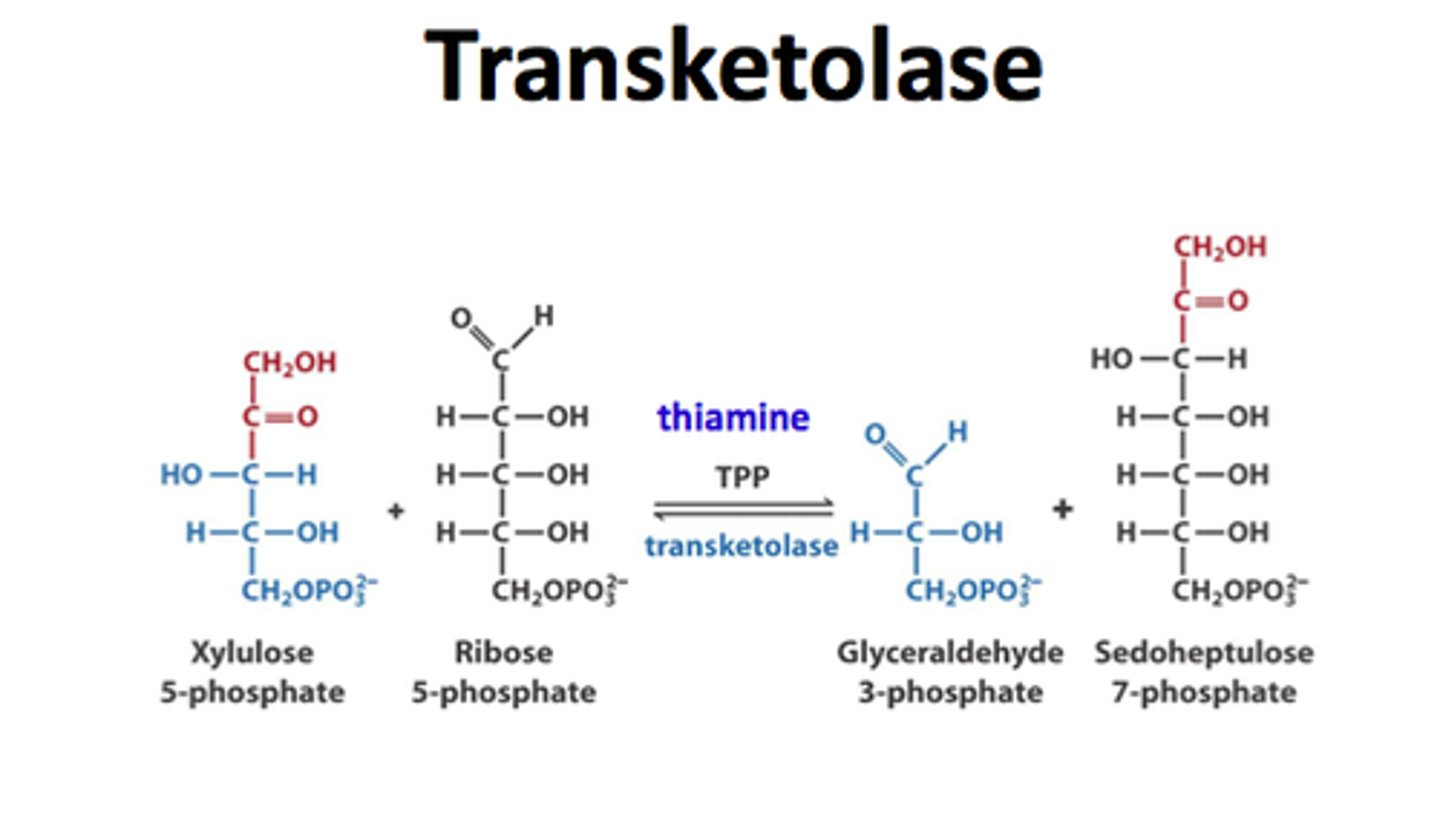
First step in the pentose phosphate pathway
transketolase catalyzes the transfer of a two-carbon fragment from a ketose donor to an aldose donor
- yields sedoheptulose 7-phosphate
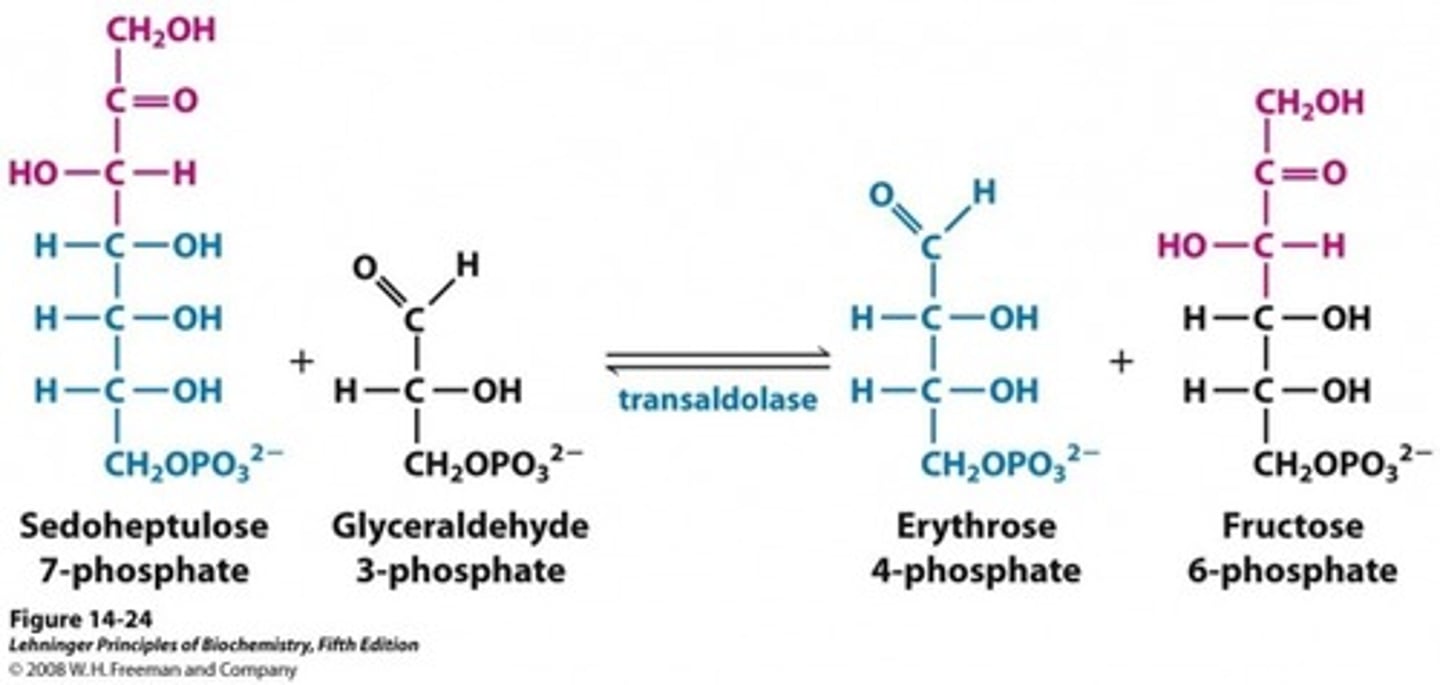
Second step in the pentose phosphate pathway
transaldolase catalyzes the condensation of a three-carbon fragment from sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, forming fructose 6-phosphate and the tetrose erythrose 4-phosphate
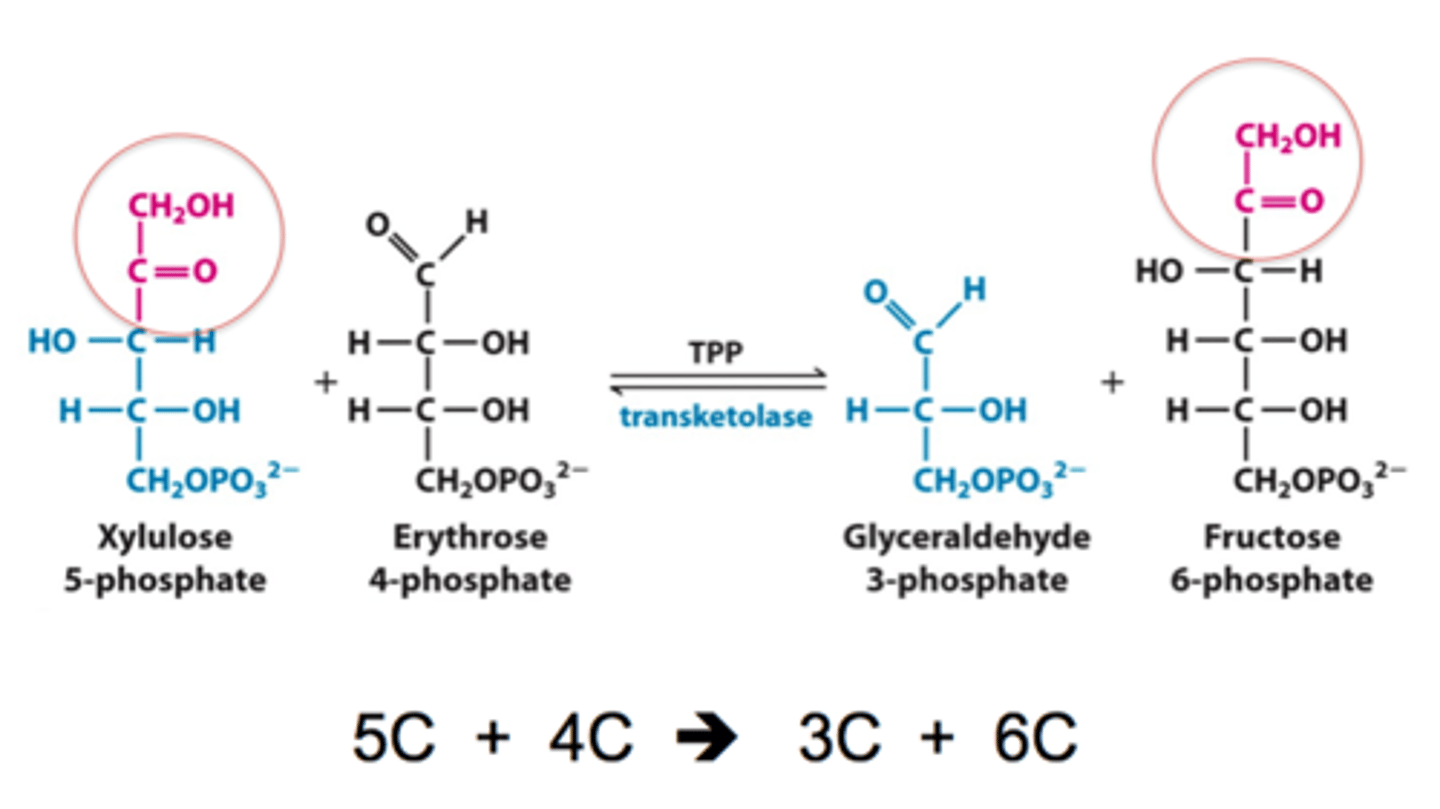
Third step in the pentose phosphate pathway
the second transketolase rxn forms fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate from erythrose 4-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate
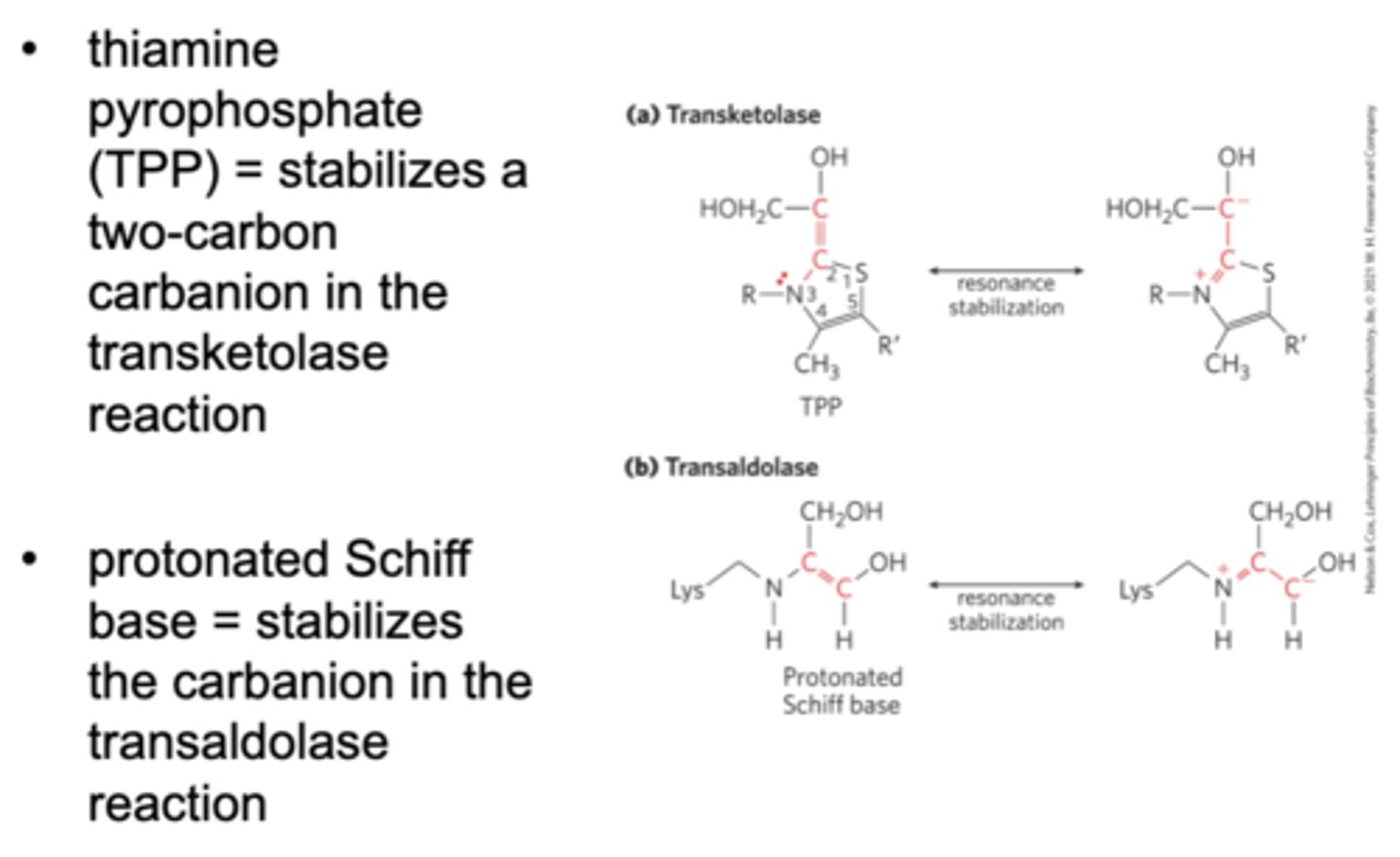
Fourth step in the pentose phosphate pathway
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) stabilizes a two-carbon carbanion in the transketolase rxn, and a protonated Schiff base stabilizes the carbanion in the transaldolase rxn
reductive pentose phosphate pathway
converts hexose phosphates to pentose phosphates