measuring sleep
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
How can sleep be investigated and measured
By investigating and measuring consciousness through physiological responses or behaviour, since states of consciousness cannot be directly observed
Why can't states of consciousness be directly measured
Because they are internal and must be inferred from physiological responses or behaviour
What are two main types of data used to study sleep
Objective physiological changes and qualitative information about changes during sleep
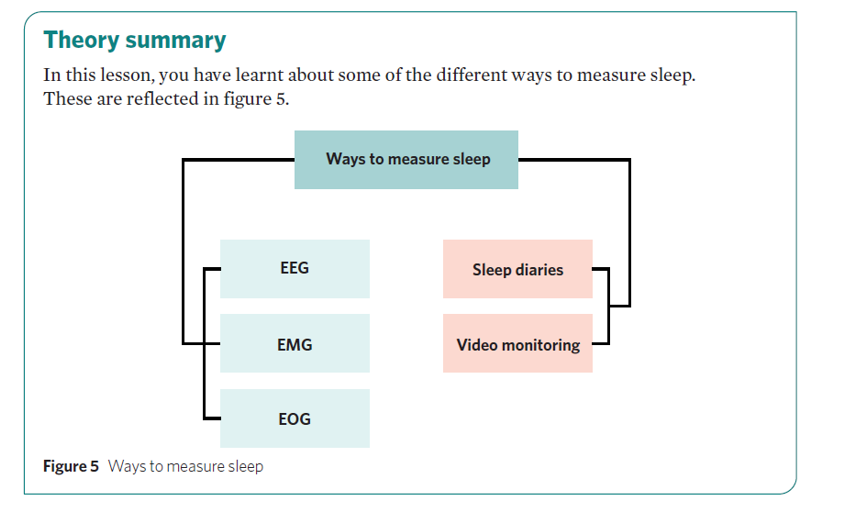
What are some measures used to investigate consciousness and sleep
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
Electromyograph (EMG)
Electro-oculograph (EOG)
Sleep diaries
Video monitoring
What does the EEG measure in relation to sleep
Electrical activity in the brain
What does the EMG measure in relation to sleep
Muscle activity or tension
What does the EOG measure in relation to sleep
Eye movements
What is the purpose of a sleep diary
To record qualitative, self-reported information about sleep patterns and experiences
What does video monitoring provide in sleep studies
Observational data on sleep behaviours and movements
What does an electroencephalograph (EEG) do
It detects, amplifies, and records the electrical activity of the brain
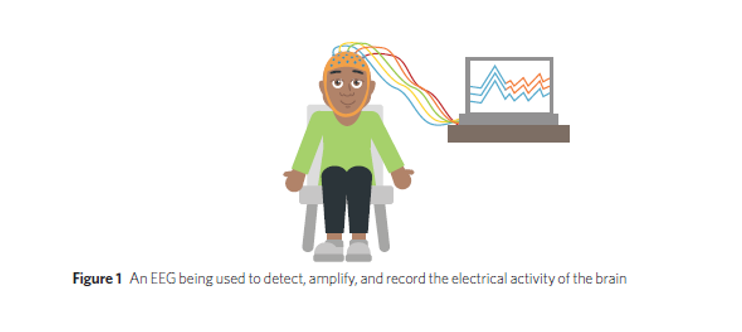
What causes the electrical activity detected by an EEG
Electrical impulses emitted by neurons when they communicate
How is brain activity displayed by an EEG
As brain wave patterns
How can brain waves help assess a person's state of consciousness
Different brain wave patterns correlate to different states of consciousness.
What device records brain wave patterns to identify sleep stages
The electroencephalograph (EEG)
What two key features of brain waves are used to distinguish between states of consciousness
Frequency and amplitude
What is brain wave frequency
The number of brain waves that occur per second
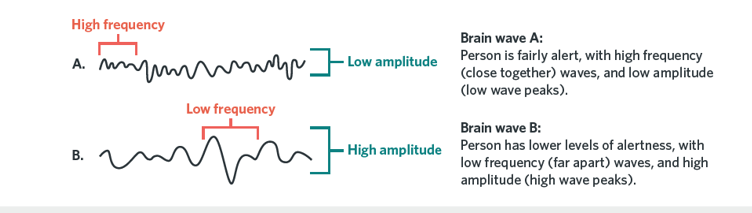
What is brain wave amplitude
The intensity and height of the brain waves
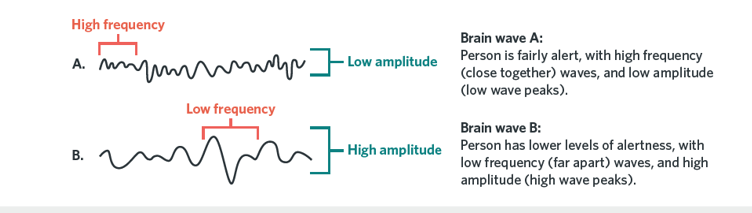
What is the amplitude and frequency of brain waves during normal waking consciousness
what brain wave and diagram of EEG recording
Low amplitude and high frequency

What does high frequency and low amplitude brain activity indicate
Normal waking consciousness or REM sleep (an altered state of consciousness)

What brain wave characteristics are associated with a deeply relaxed or meditative state
what brain wave and diagram of EEG recording
Low–medium amplitude and medium–high frequency

What type of brain wave pattern is typically seen in early or light sleep
what brain wave and diagram of EEG recording
Medium–high amplitude and low–medium frequency

What are the EEG characteristics of deep sleep
what brain wave and diagram of EEG recording
High amplitude (highest of all) and low frequency (lowest of all)
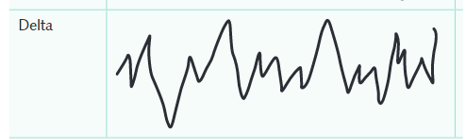
How do EEG wave characteristics change from being awake to deep sleep
Frequency decreases and amplitude increases
What does an electromyograph (EMG) do
It detects, amplifies, and records the electrical activity of the body’s muscles
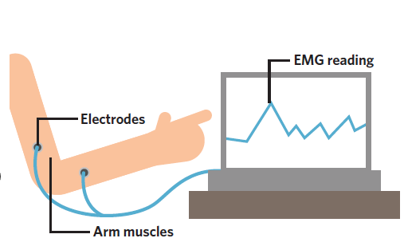
How is muscle activity recorded using an EMG
Electrodes are attached to the skin above the muscles under investigation
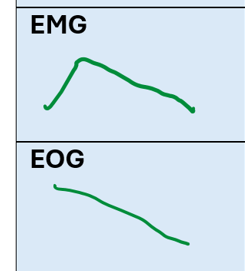
What does an EMG reading show during REM sleep
Low muscle activity due to low physiological activity
What does an EMG reading show during NREM sleep
Medium to moderate muscle activity due to some physiological activity
How do EMG readings change as NREM sleep stages progress
Muscle activity tends to decrease as movement becomes less likely, though it can still occur
What does an electro-oculograph (EOG) do
It detects, amplifies, and records the electrical activity of the muscles responsible for eye movement
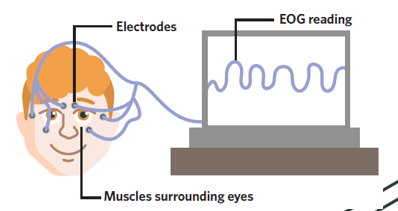
How does an EOG measure eye movement
By using electrodes attached to the skin above the eye muscles
What do EOG readings show during REM sleep
High activity due to rapid eye movement
What do EOG readings show during NREM sleep
Low activity, as there is no rapid eye movement
What are the EEG characteristics of REM sleep
diagram of brain activity
High frequency, low amplitude

During REM sleep, what is the level of muscle (EMG) and eye (EOG) activity
diagram of brain activity
EMG: No–low activity (lowest)
EOG: High activity
What are the EEG characteristics of NREM Stage 1
diagram of brain activity
Medium frequency
Medium amplitude
Which stage of sleep has the highest muscle (EMG) activity
diagram of brain activity
NREM Stage 1 (medium/moderate activity)
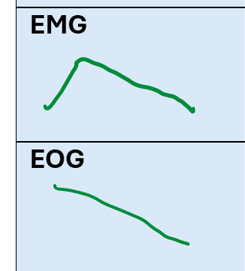
What are the EEG characteristics of NREM Stage 2
diagram of brain activity
Medium-low frequency
Medium-high amplitude
What is the level of eye movement (EOG) in NREM Stage 2
diagram of brain activity
Medium-low activity
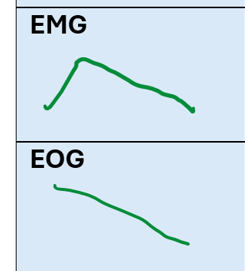
What are the EEG characteristics of NREM Stage 3
diagram of brain activity
Low frequency
High amplitude

What is the level of EMG and EOG activity during NREM Stage 3
diagram of brain activity
EMG: Low activity
EOG: Low activity
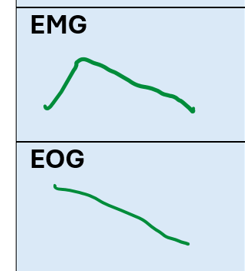
Which sleep stage is associated with high eye activity but minimal muscle tone
REM sleep
What is a key strength of objective sleep measures like EEG, EMG, and EOG
They provide reliable, unbiased, quantitative data that can indicate a person’s state of consciousness
What is a limitation of objective sleep measures like EEG, EMG, and EOG
They do not provide qualitative detail about the personal experience of sleep
Why might findings from EEG, EMG, or EOG sometimes lack validity
Because changes in physiological responses may be due to factors other than a change in consciousness
What is a sleep diary
A self-reported record of an individual’s sleep, including estimated sleep time and judgments about the quality and nature of their sleep
What types of data can a sleep diary include
Both qualitative and quantitative information
What are some examples of information recorded in a sleep diary
Duration of sleep
Quality of sleep
Thoughts and feelings before sleep
Thoughts and feelings after waking
Behaviours before sleep
Behaviours after waking
Number of sleep disruptions
What is a key disadvantage of sleep diaries
They are subjective and may not be accurate; they also require interpretation by a third person
What is a key advantage of sleep diaries
They provide qualitative information and detailed descriptions of the sleep experience
What is video monitoring in sleep studies
The use of camera and audio technology to record an individual while they sleep, tracking sleep and wake periods, movements, activities, and sounds
What is one advantage of video monitoring
It provides data specific to the individual and is useful for observing behaviours in people with sleep disorders
How can video monitoring increase the validity of physiological data
By confirming events recorded by devices (e.g., a spike in EMG can be validated by observing bodily movement on video)
What is a disadvantage of video monitoring
Interpretation can be subjective, such as not knowing if a person getting out of bed is awake or sleep-walking
Why can measuring sleep be difficult
Some techniques can be disruptive, invasive, or require sleeping in a laboratory setting
How can changes in an individual’s regular sleep patterns affect sleep measurements
Recording sleep or attaching electrodes can influence the quality and quantity of sleep
What is a consequence of sleep measurement methods on data accuracy
They may not provide a true reflection of an individual’s usual sleeping patterns
Theory summary