4.1.3.6 The interrelationship between markets
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
How does a competitive market work?
operates through the interaction of demand and supply
As demand for G&S changes ~~> it has an impact on other markets
Firms will move away from markets where demand has fallen and into markets that have seen an increase in demand
This leads to an increase in supply —> firms move into new markets
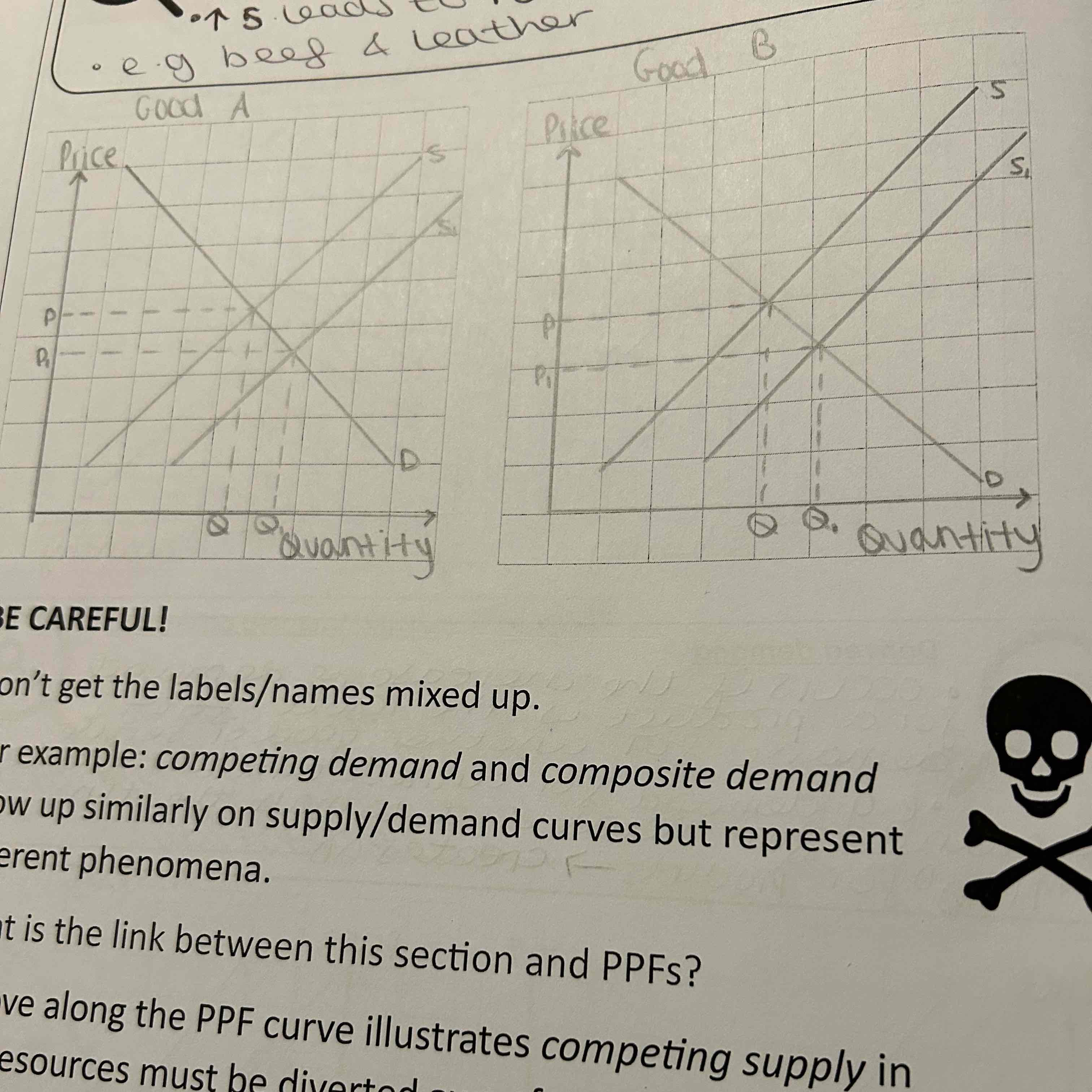
What does joint demand mean?
occurs when an increase in Demand for one good will see an increase in demand for a complementary good
What do the graphs for joint demand show?
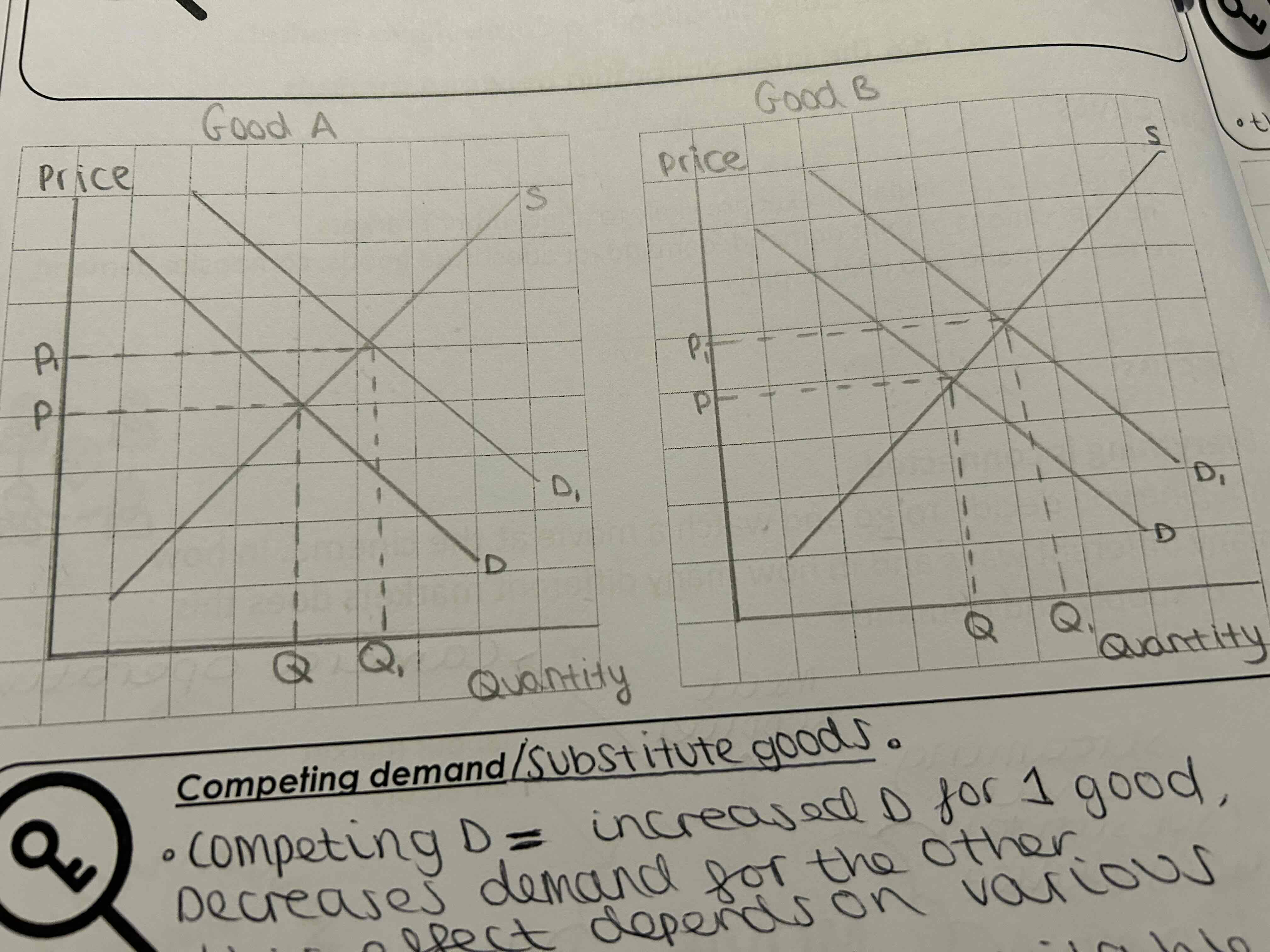
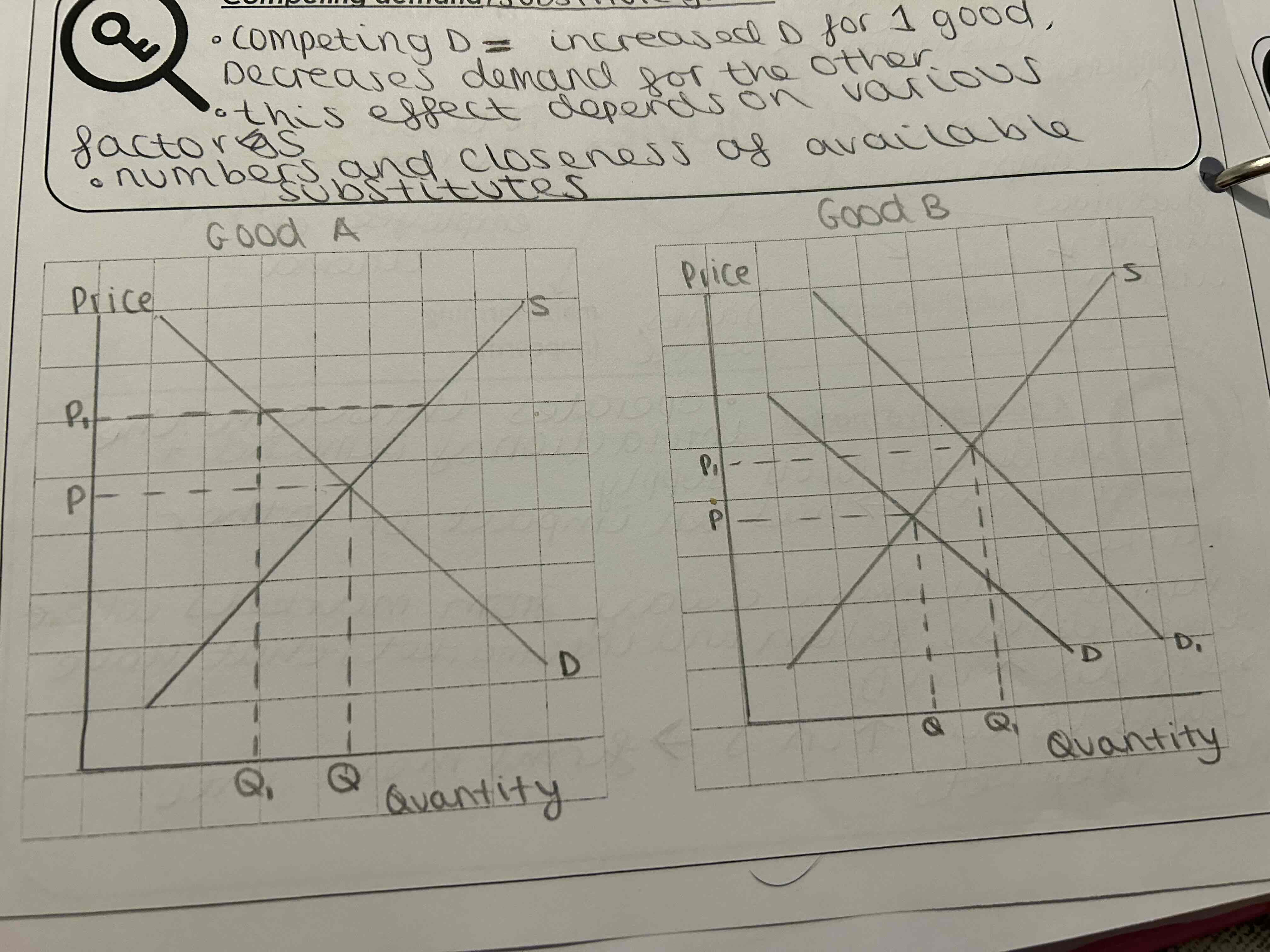
What does competing demand/ substitute goods mean?
competing demand is when an increase in demand for one good decreases demand for the other
This effect depends on various factors
Number and closeness of available substitutes
What does the graph for competing demand look like?
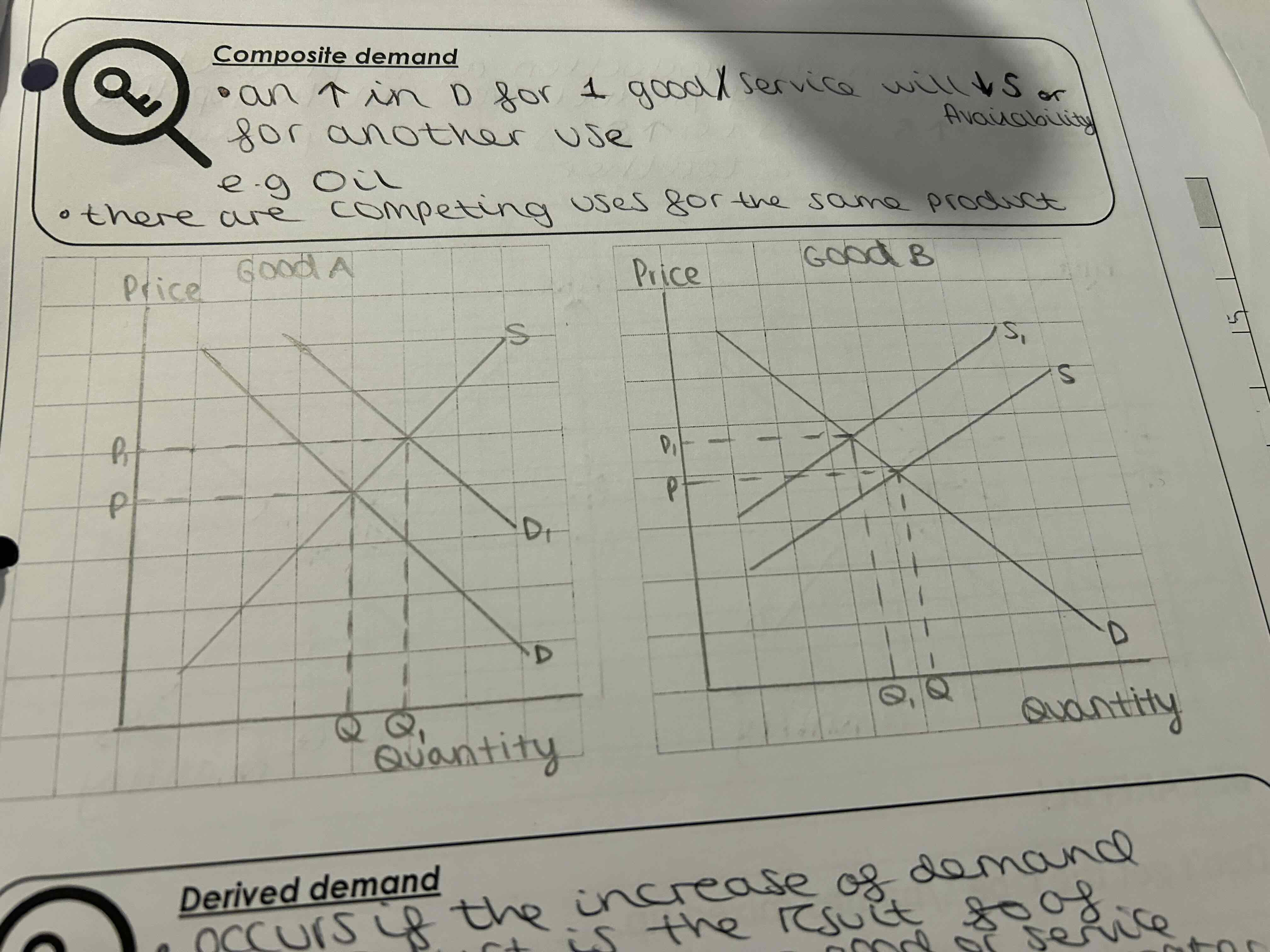
What does composite demand mean?
an increase in demand for one good/service will decrease supply or availability e.g oil
There are competing uses for the same product
What do the composite demand graphs look like?
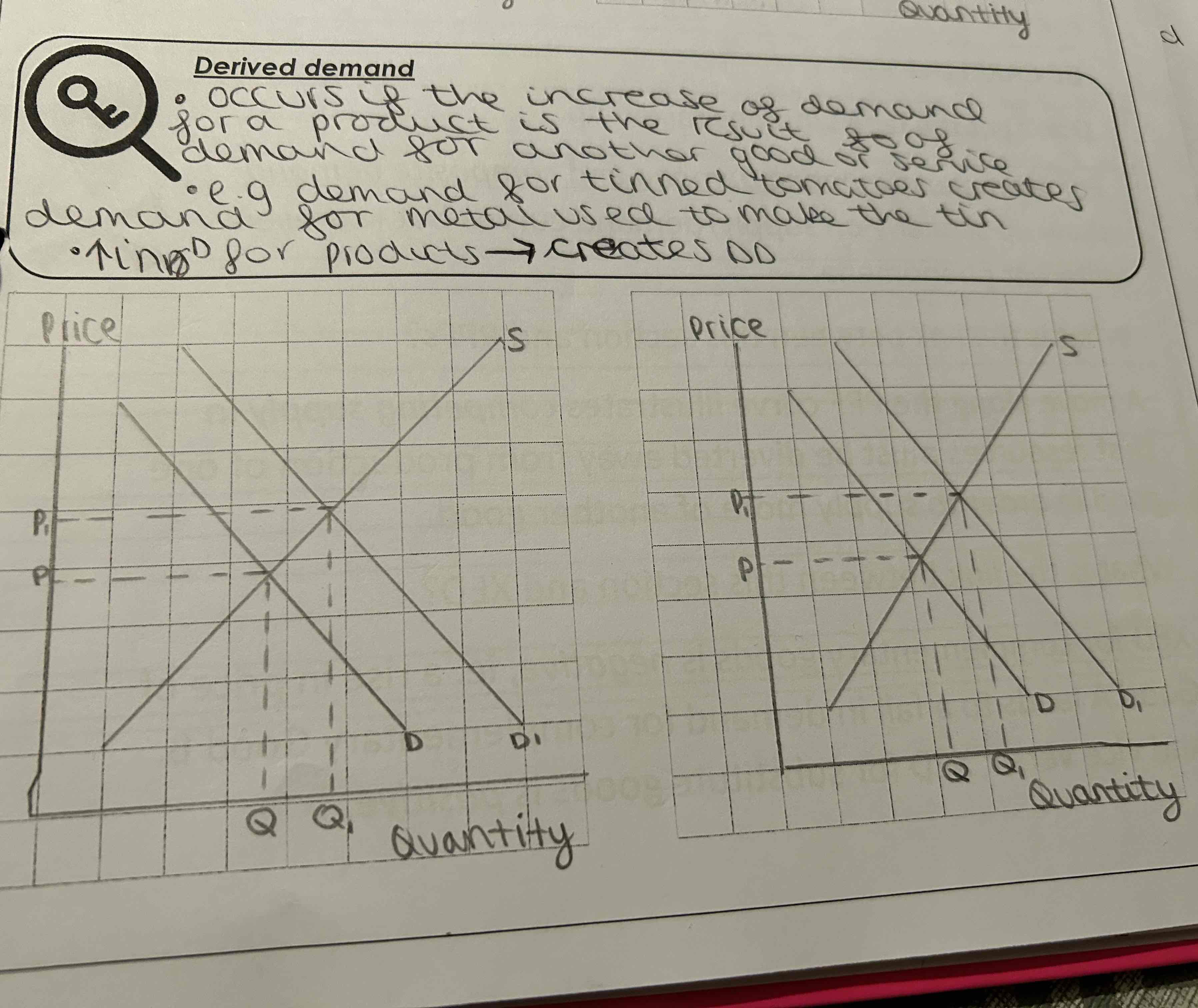
What does Derived Demand mean?
increase of demand for a product is the result of demand for another good or service
E.g demand for tinned tomatoes creates demand for metal used to make the tin
Increasing demand for products creates double demand
What do the graphs for derived demand look like?
What does joint supply mean?
production of a product creates a by product that can be supplied
What do joint supply graphs look like?