2.06 Measuring detection thresholds
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
4 stages of perception

What do we need to detect something
Need light to be reflected off an object and into our eyes
List natural sources of light

What does light sources emission spectrum mean
Different light sources emit different wavelengths of lignt
This influences what we see
What is the visible spectrum
The range of wavelengths that the human eye is sensitive to/can see
Between 400-720nm
How is radiation from the sun controlled
Most of it is eliminated by atmospheric scatter (low wavelengths) and absorption
Ozone layer (O3) absorbs UV
Why do we need to limit sum radiation/UV
UV causes skin cancer
Global warming
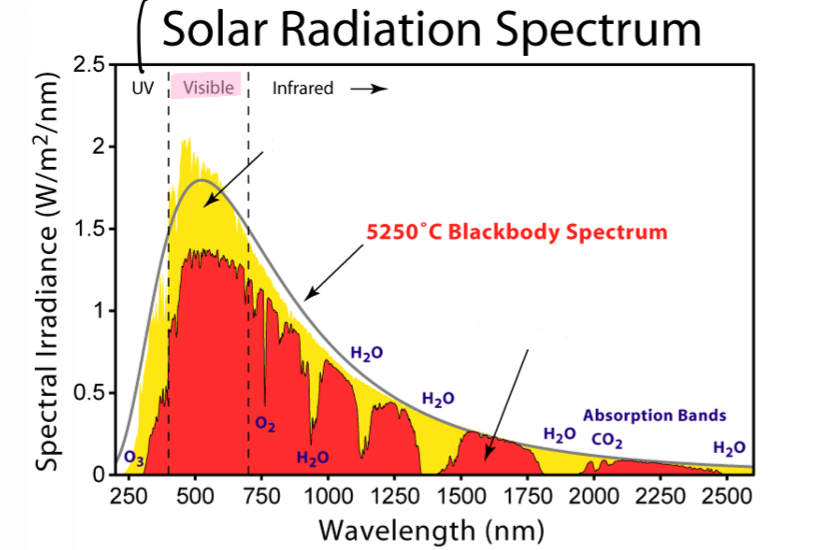
What do the yellow and red curve represent
Yellow - sunlight at the outermost/top of the atmosphere
Red - radiation at sea level (eg bfd)
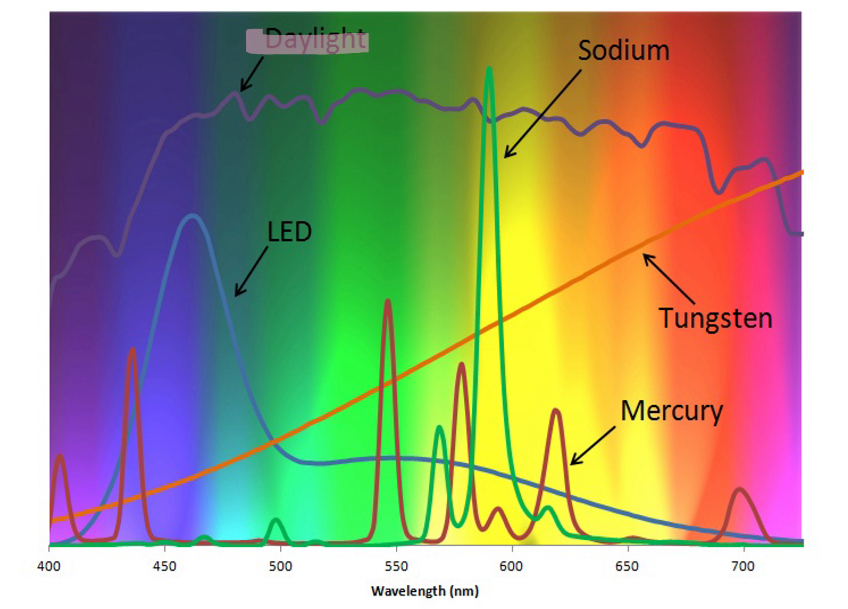
What is this showing
Artificial/man made light sources have very different spectra compared to natural sources (daylight)
Daylight is quite flat it has lots of different wavelengths so shows lots of different colours
Other artificial sources usually peak betwen a small range of wavelengths and that determines their colour
Eg sodium lamps show mainly yellow light

What does the colour of an object depend on
Which wavelengths of light as absorbed and reflected by an object
How does the eye protect the retina from UV rays

What are the 4 things retinal image quality is dependent on

What 3 things reduce retinal image quality
Spherical abberations
Chromatic abberations
Diffraction patterns
What are spherical abberations
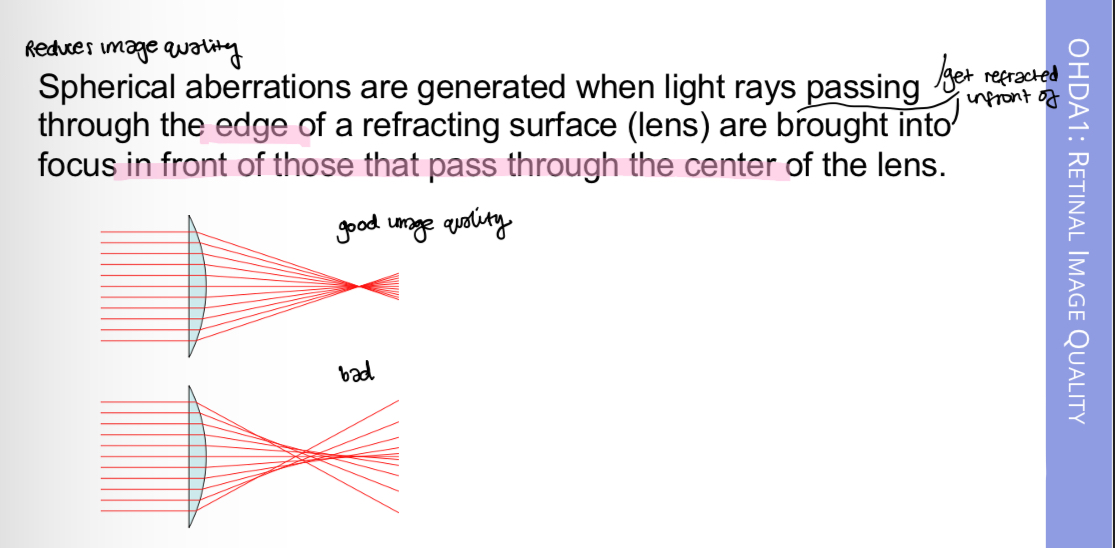
How does the eye counteract spherical abberations

What is a chromatic abberation

How does the eye counteract chromatic abberations
Yellow pigment at the fovea absorbs maximally at 460nm (absorbs short wavelengths)
What is the wave theory of light

What is a diffraction pattern
The bright central disc contains about 84% of the light and is called the airy disc

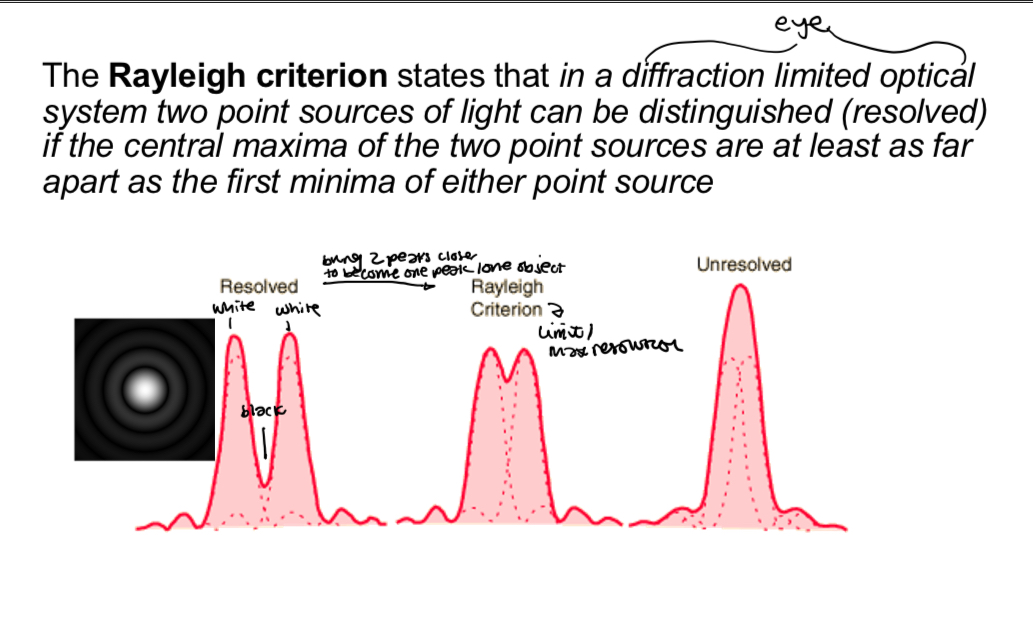
What is the Rayleigh criterion
Can be used to estimate the resolving power of an optical system
What is psychophysics
The direct quantification of our sensory performance
What is the detection threshold

What is the absolute theshold
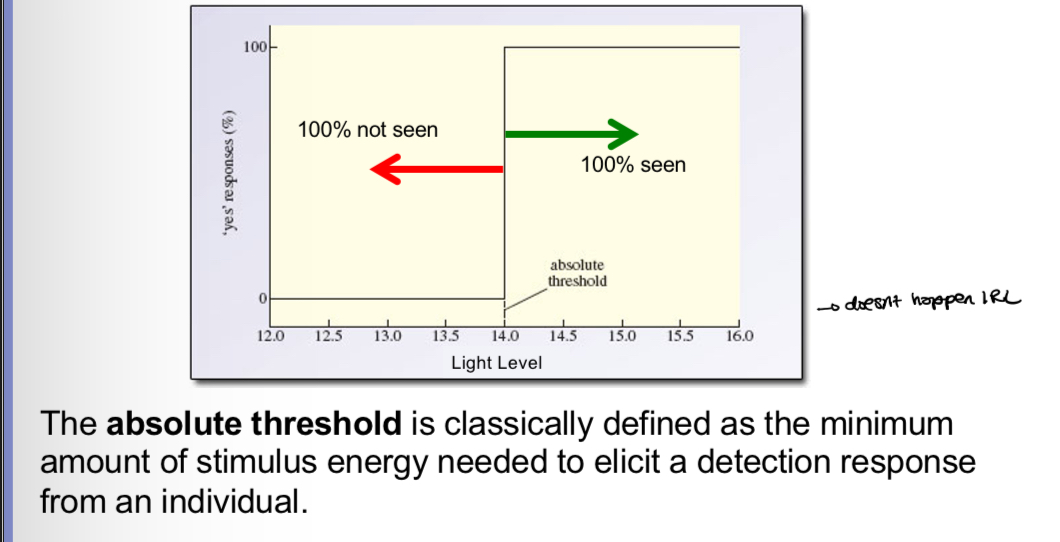
Why is the absolute threshold only theortical

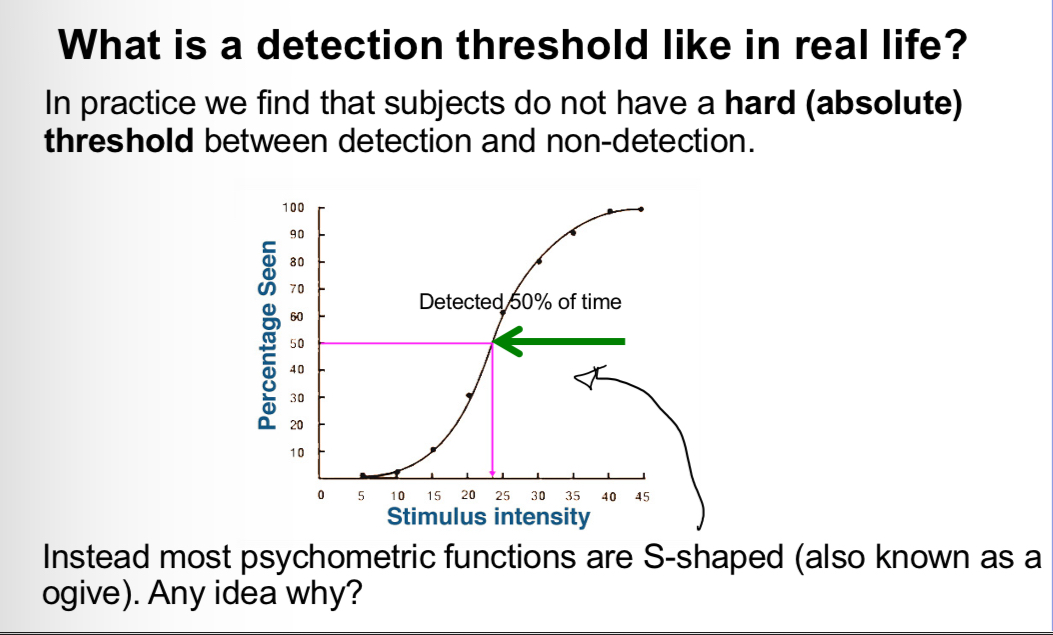
What shape are most psychometric functions
S shaped,
What are the 6 methods to measure detection threshold

Method of limits
Procedure
Advantages
Disadvantages
Stimui are presented in ascending or decending order eg increasing light intensity
Patient reports if they see the stimulus or not
Repeat a few times and find average
+ quick
- patients anticipate the threshold if each trial starts at ths same level
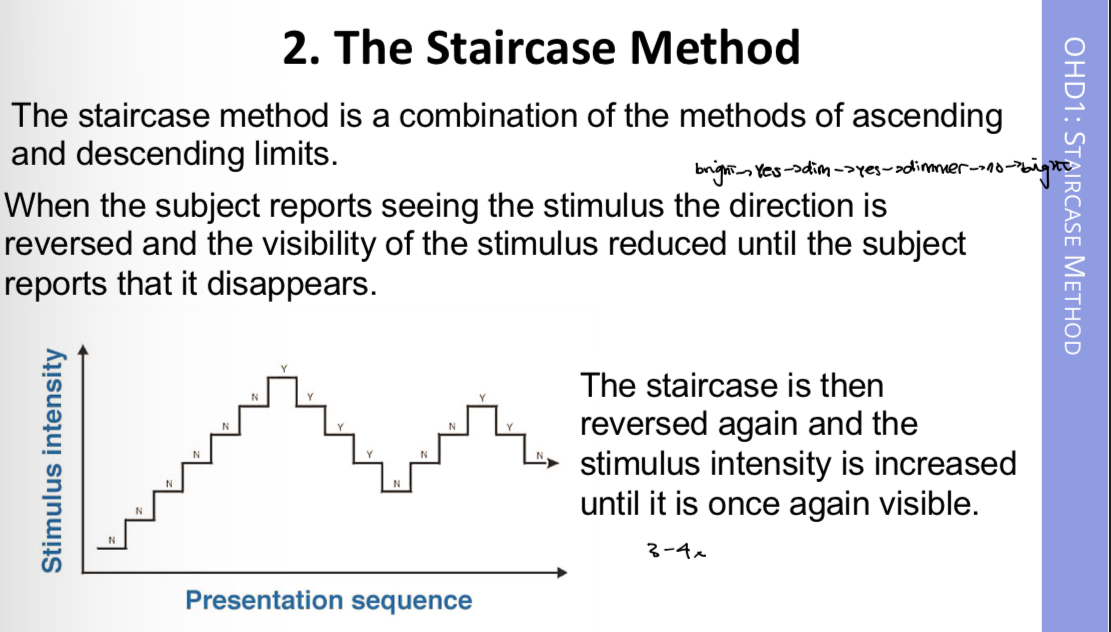
The staircase method
Procedure
Advantages
Disadvantages
The threshold is defined as having occured after 3 or 4 reversals
+ it is quick and reliable
- patienr can anticipate the threshold
The method of constant stimuli
Procedure
Advantages
Disadvantages
+ patients cannot anticipate the visibility of each stimulus
- time consuming

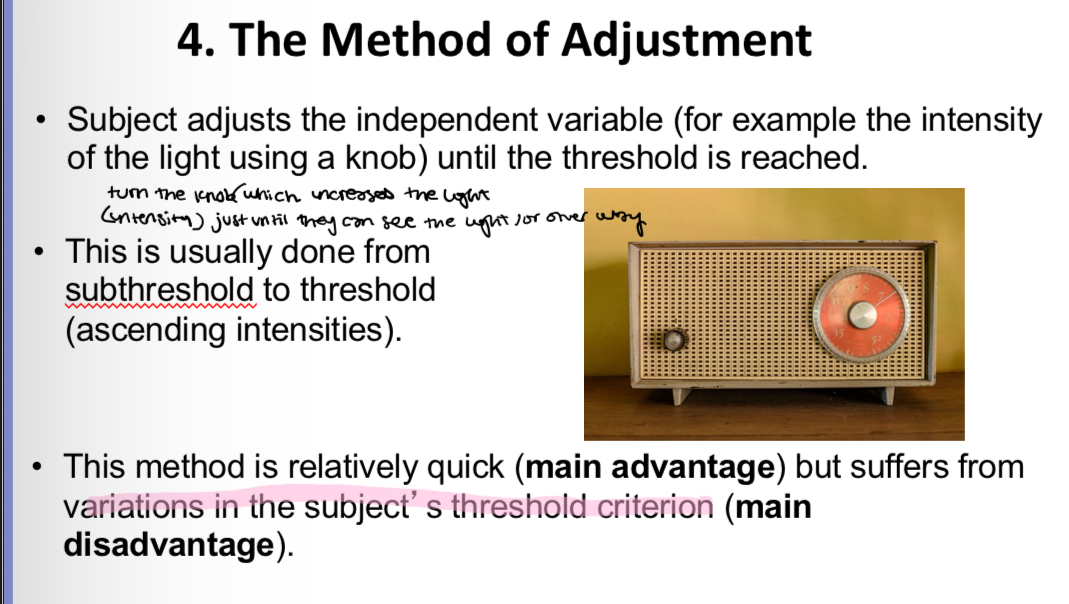
The method of adjustment
Procedure
Advantages
Disadvantages
Forced choice procedure
Procedure
Advantages
Disadvantages
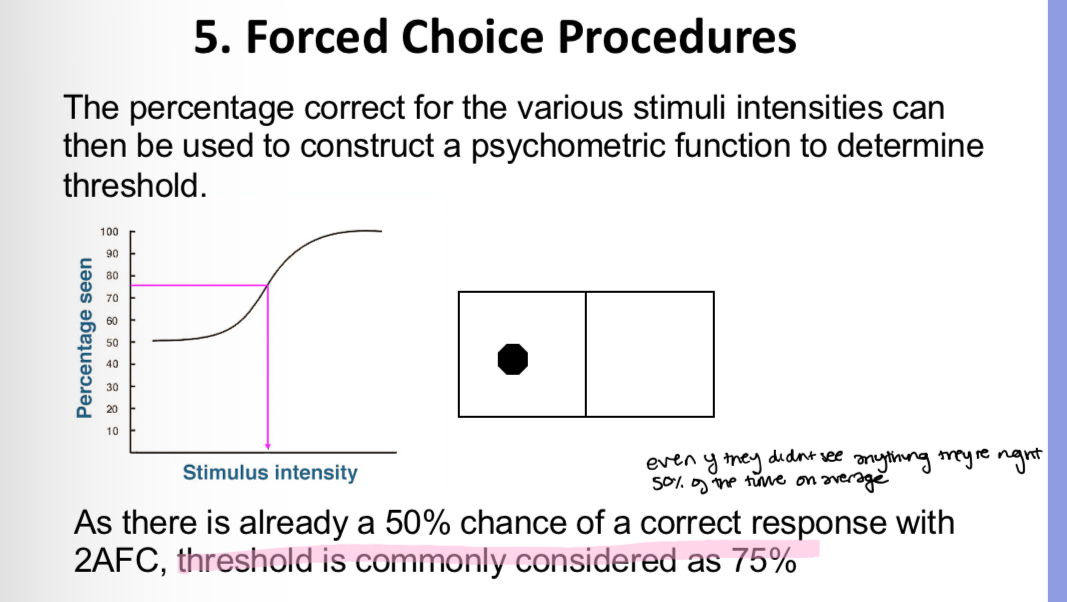
The patient is forced to choose from a number of alternative choices, one of which contins the stimulus (can have 2AFC, 4AFC, 6AFC) (AFC - alternative forced choice)
The threshold is calculated by 100 divided by however many AFCs there are, then the threshold is halfway between that number and 100 eg 4AFCs - 100/4 =-25 25% , halfway from 25 to 100 is 62.5% so thats the threshold. The ogive starts at 25% because theres already a 25% chance of a correct response with 4AFC
+ eliminates subjects response criterion
- subject may not be able to see anything but still have to choose
Advanced adaptive methods
- procedure
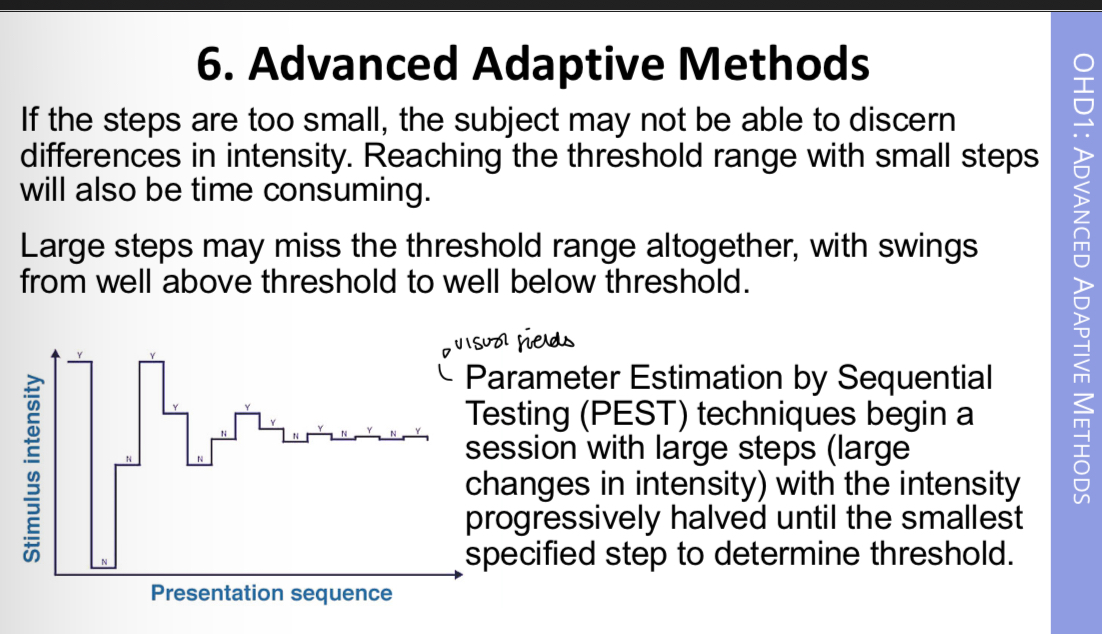
Advanced Adaptive Methods involve presenting signals based on the subjects previous responses (like the staircase method).
Three correct responses, intensity decreased by one step.
An incorrect response, one step increase in intensity.
In the initial methods the size of the steps remain the same throughout the session.
Session ends when a narrow range of stimuli is reached
Threshold is taken as the average of the intensity levels within the period of stable tracking
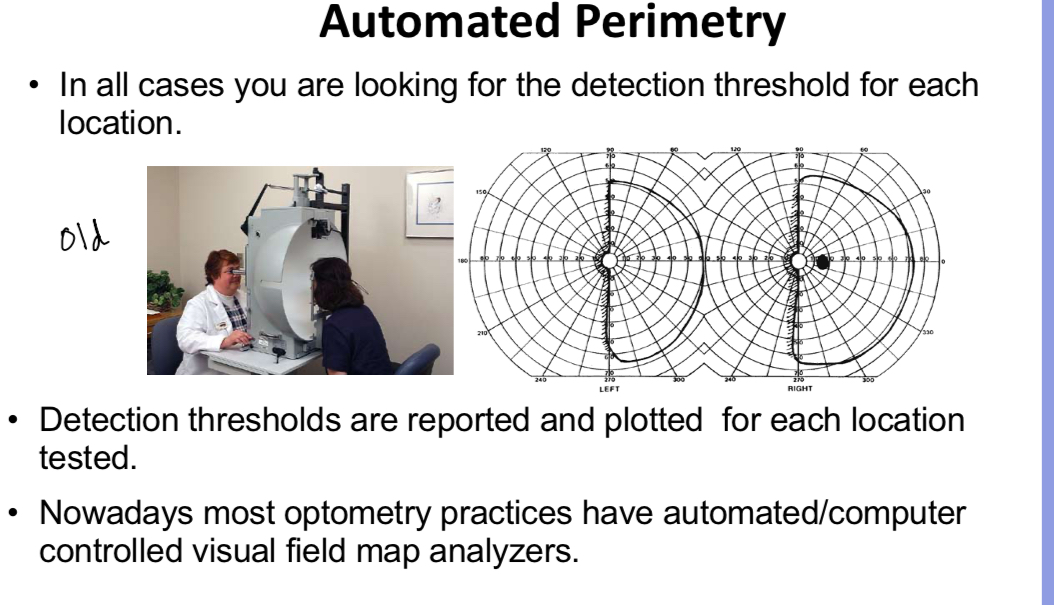
Automated perimetry
procedure
•Subjects are positioned inside a white dome and a fixation light is presented then small target lights are displayed inside the dome.
modern systems operate using the same psychophysical principles and produce a print-out of the visual field test results. - dark areas om the mop are where theres a loss in VF
What is signal detection theory

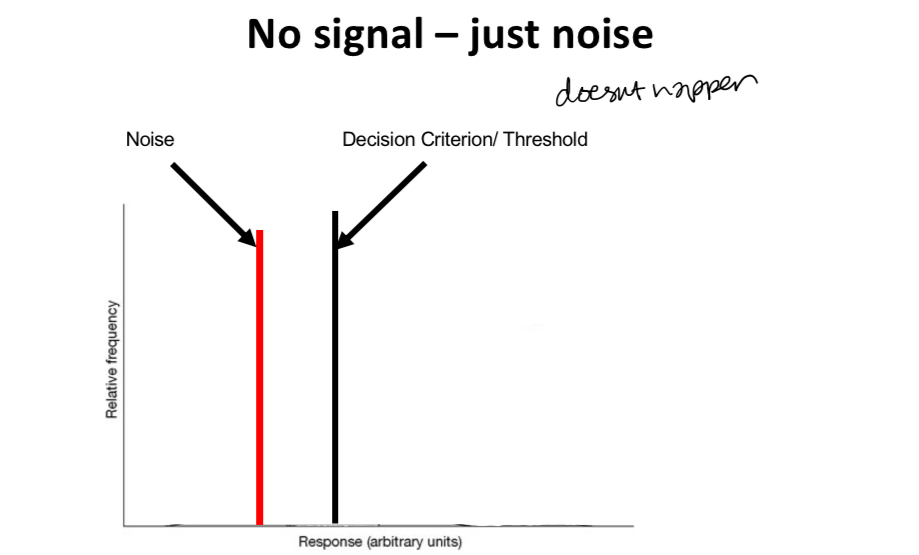
Explain the graph
if the noise was simply at one level (as indicated by the red bar) then if you chose a decision criterion or detection threshold that is above this level of activity you would never mistake noise for a signal and would always respond that there is no stimulus present when there is no stimulus present.
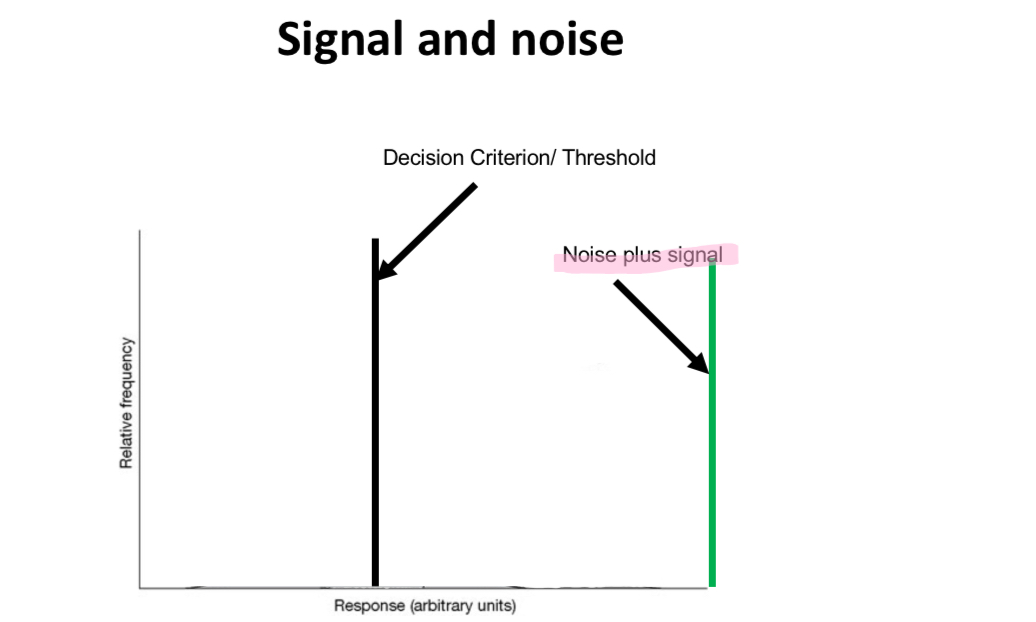
Explain the graph
If noise was always the same and a signal was added, we could set a threshold below the noise level to detect the signal every time. This means we would never miss detecting a signal when it is actually present.
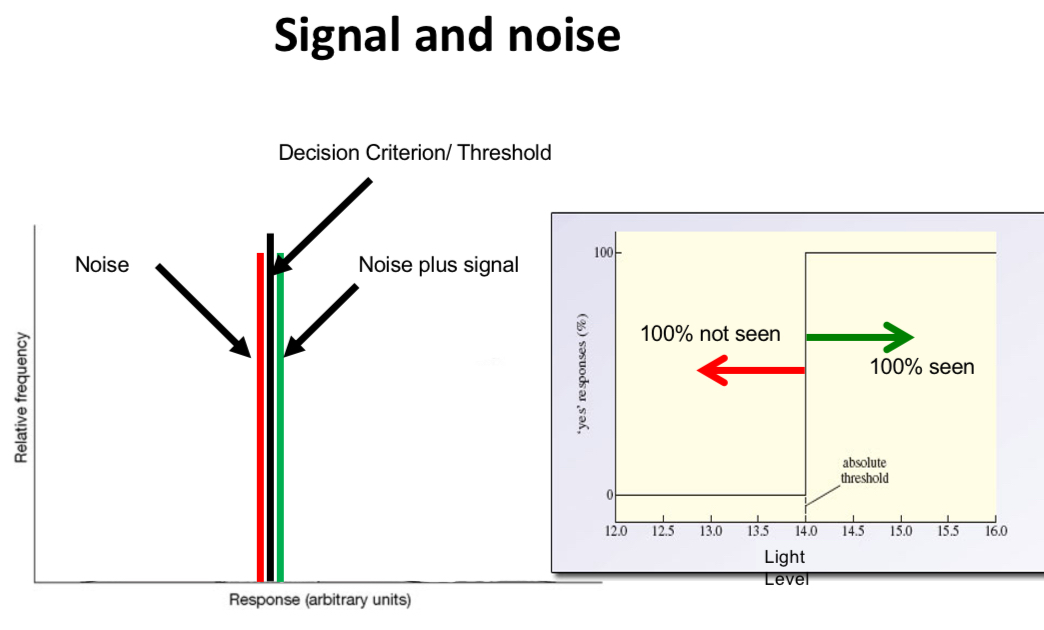
Explain the graph
If this were the case then you would generate a hard threshold also known as an absolute threshold as shown above but as we know this is not how the visual system works.
Explain the graph
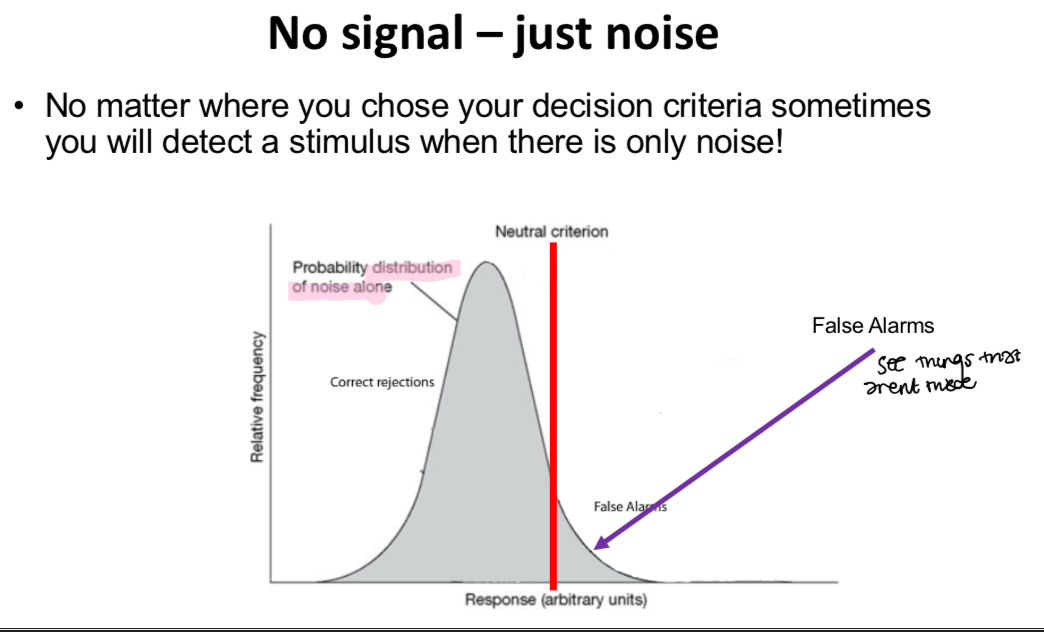
This figure depicts what is actually happening in the visual system when no stimulus is present just the noise. The noise is not a single value but rather has a distribution of possible values– if the noise is great enough you may see something that is not these – we often call this a hallucination if this was for example a covid test then this would be a false positive! While an error and can be serious (for example an incorrect cancer diagnosis) you would often run further tests (or a second covid test if you felt fine and didn’t believe it) before enaging with invasive treatments.
Explain the graph
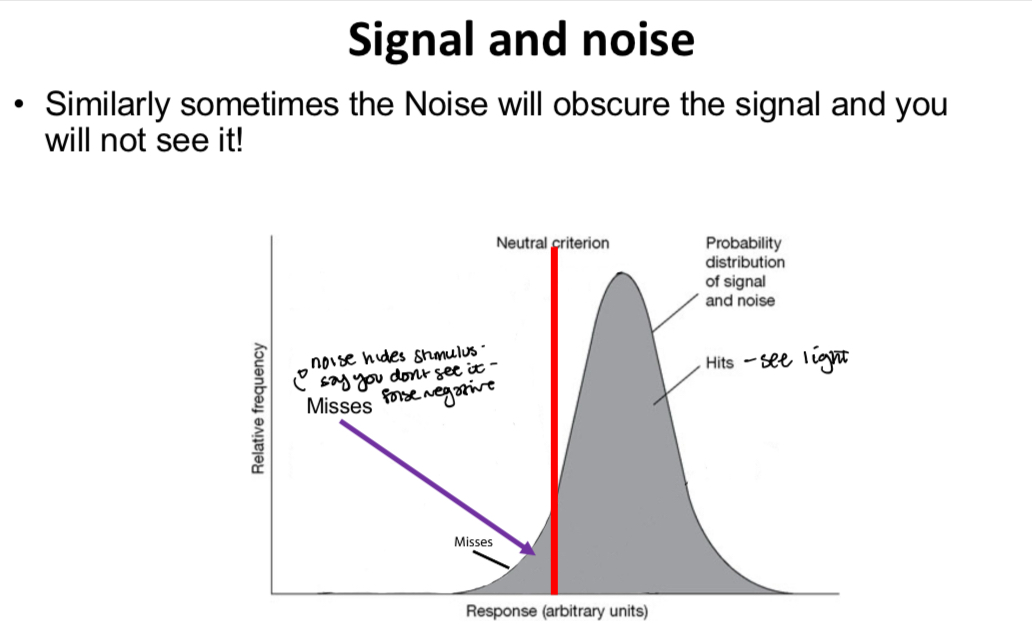
In this case there is a signal present as well as the same internal noise. In this case, most of the time we see the stimulus, but sometimes the noise is so great that it hides the stimulus and we would miss it - this is usually referred to as a MISS as you should have seen the light or can also be called a false negative as you reply incorrectly that you don’t see the light – again with a covid test this would be if for some reason the test did not detect your covid antibodies even though you did have covid. In terms of medical tests this is more serious than a false positive as thepatient would be unaware they had covid or cancer or AMD for example and would not seek appropriate treatment.
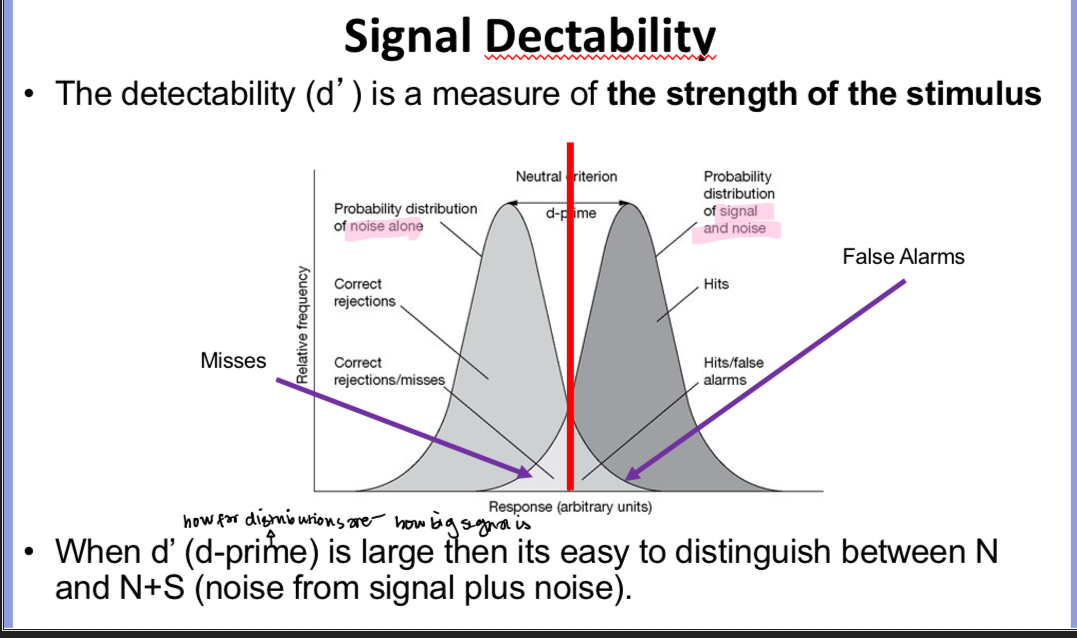
Explain the graph
If d prime is large then there will be very little overlap between the distributions so very few misses and very few false alarms. If however detectability is small then you will have poor discrimination between a positive and a negative result with lots of overlap and lots of misses and false alarms so it would not be a very reliable test.
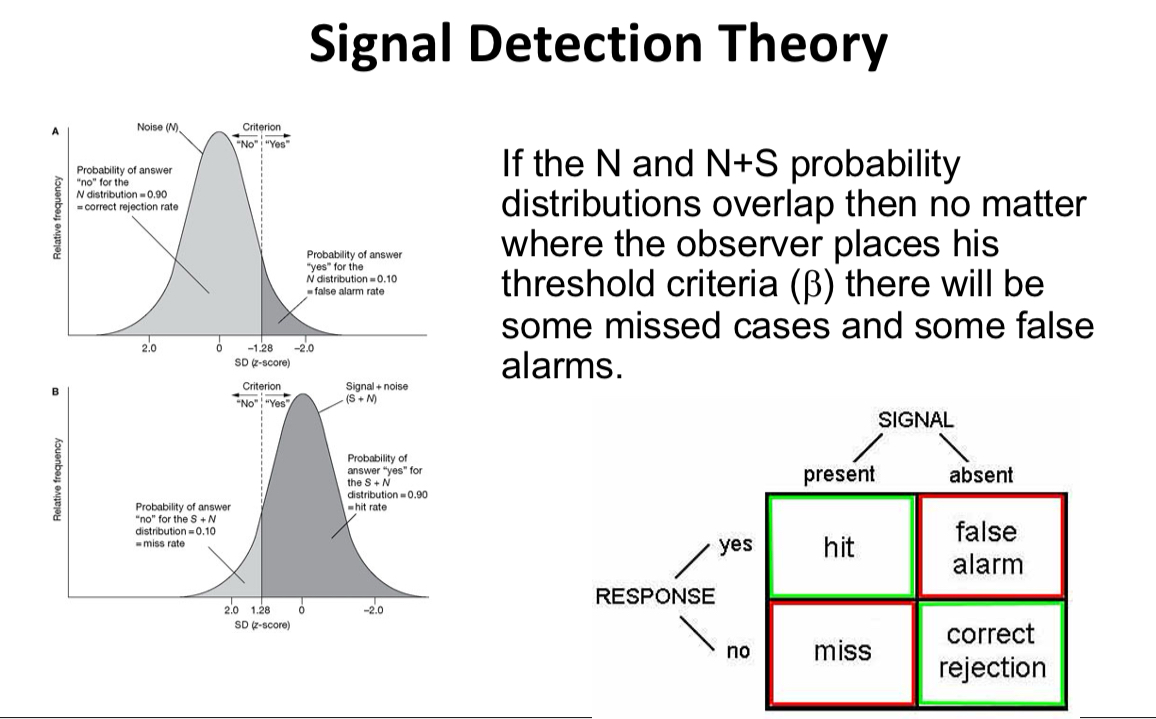
Explain the graphs
There are 4 possible outcomes 2 when the stimulus/signal is there – you either detect it or you don’t (hit or miss) and 2 when the stimulus/signal is NOT there – a correct rejection or a false alarm. We want to maximise the hits and correct rejections while minimizing the misses and false alarms.
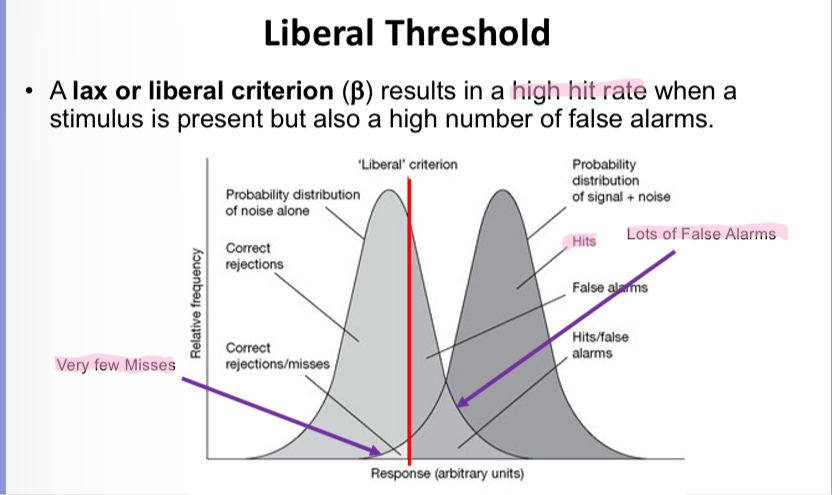
Explain the graph
they are more likely to respond that they see the light if they think they might have indeed seen the light – their decision criterion/threshold moves to the left
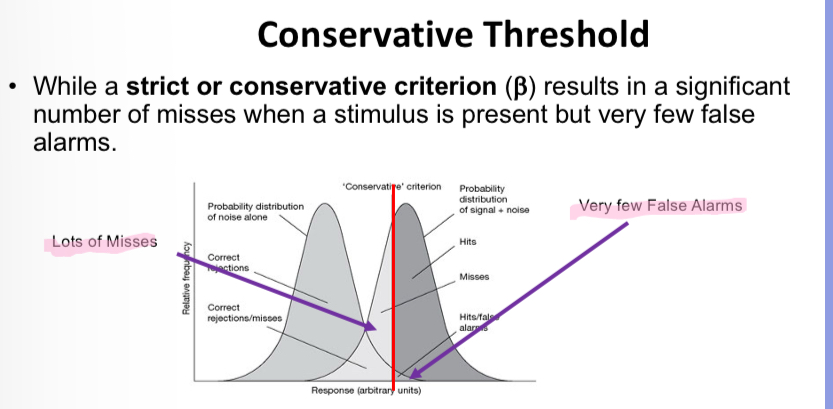
Explain the graph
they are only likely to respond that they see the light if they are sure that have indeed seen the light – their decision criterion/threshold moves to the right versus the neutral person
How to calculate sensitivity of a test

A very sensitive test will have..
A sensitive test will have very few misses BUT it could have a lot of false positives.
You can think of this as a sensitive test will indicate a hit if there is even a slight hint of something being present. (Lots of Hits, very few misses but a lot of false hits!). So it has a very liberal criteria.
How to calculate specificity of a test
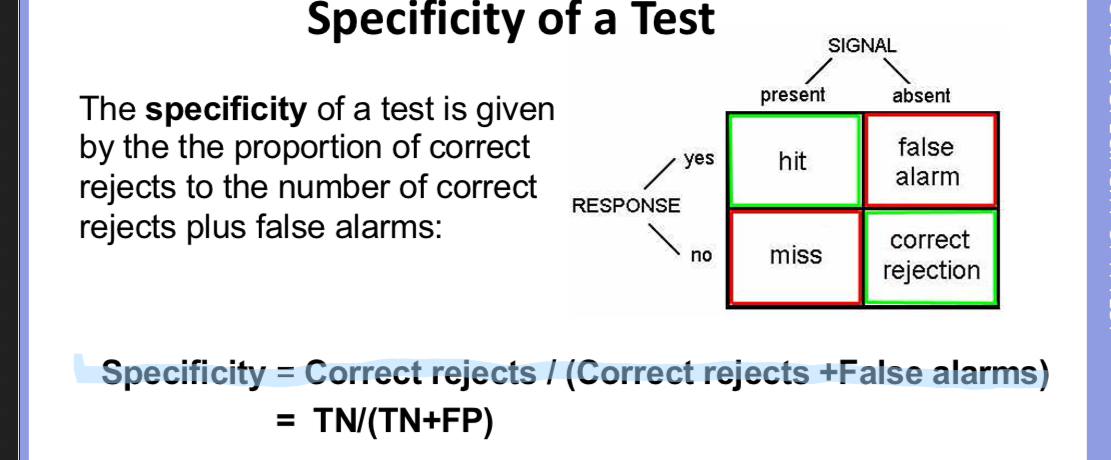
A very specific test will have…
A very specific test will have very few false alarms however it may miss a number of cases