Quantum mechanics of atoms - Q2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
He integrated the contributions of various researchers
into the Quantum Mechanical Model of the atom.
Erwin Schrödinger
He developed complex mathematical equations known as “wave
functions” to estimate where electrons in an atom are likely to be
found, 95% of the time.
Erwin Schrödinger
He referred to these regions as “______”. It is a
three-dimensional space where there is a greater than 95%
chance of locating an electron, and it can hold a maximum of two
electrons.
orbitals
Unlike orbits, which precisely define an object's path, these do not specify an exact location for an electron but rather a probable area where it can be found 95% of the time.
Orbitals
He further divided Bohr’s principal
quantum levels (n) into sub-levels, each
containing a specific type of orbital (s, p, d, f,
etc.).
Erwin Schrödinger
The principal quantum level and sub-level (type
of orbital) together indicated what?
The distance of the electron from the nucleus and its energy.
The energy levels are numbered 1, 2, 3, etc. the ________ the number, the closer the energy level is to the nucleus. The Letter ‘‘n’’ is used to represent the energy level.
Smaller
Each energy level can only hold a certain number of?
Electrons
The first energy level can only hold 2 electrons, the second can only hold 8, and the third can only hold how much?
18
2n2 is the what?
Equation for the max # of electrons per energy level.
Number of electrons in the first shell
2
Number of electrons in the second shell
8
Number of electrons in the third shell
18
Within each energy level are what?
Energy sublevels
These are labeled as s, p, d, and f.
Energy sublevels
Notice that the number of sublevels in an energy level is?
equal to the number of the energy level.
Within each sublevel, there are?
Orbitals.
This is the final location where the electrons reside.
Orbitals
Each of these may contain 1 or 2 electrons that spin on their axis.
Orbitals
If two electrons occupy an orbital, they must spin in?
The opposite directions.
Electron configurations,
orbital diagrams and quantum numbers to
describe which of the following statement?
The energy and motion of electrons
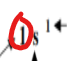
What does this represent in an electron configuration.
Principal quantum level (n)
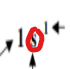
What does this represent in an electron configuration.
Orbital shape (sub-level)
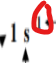
What does this represent in an electron configuration.
Number of electrons in sub-level
These are visual representations of electron configurations.
Orbital diagrams
They also show individual orbitals and the spin of electrons within those
orbitals.
Orbital Diagrams
The lowest energy orbitals are filled before the
higher energy orbitals. this is the?
(Aufbau Principle)
Each orbital gets one electron first, before adding
the second electron to the orbital, this is the?
(Hund’s Rule)
Only 2 electrons, of opposite spins, can occupy
each orbital, this is the?
(Pauli Exclusion Principle)
describe the properties of atomic orbitals and the electrons in
them. There are four quantum numbers.
Quantum Numbers
The symbol of this quantum number is n (symbol n)
Principal Quantum Number
The values of this quantum number are: Positive integers (1, 2, 3, 4)
Principal Quantum Number
The significance of this quantum number indicates the energy level and size
of the orbital. Higher n values correspond to
higher energy levels and larger orbitals.
Principal Quantum Number
Higher n values (Principal Quantum Number) correspond to
_______ energy levels and _______ orbitals.
higher and larger
The symbol for this quantum number is 1 (Symbol: 1).
Angular Momentum Quantum Number
The significance of this quantum number indicates the shape of the orbital.
Angular Momentum Quantum Number
l=0: s orbital (spherical)
l=1: p orbital (dumbbell-shaped)
l=2: d orbital (cloverleaf-shaped)
l=3: f orbital (complex shapes)
These are all examples of what quantum number?
Angular Momentum Quantum Number
l=0 shows which orbital?
s orbital (spherical)
l=1: shows which orbital?
p orbital (dumbbell-shaped)
l=2: shows which orbital?
d orbital (cloverleaf-shaped)
l=3: shows which orbital?
f orbital (complex shapes)
f orbital consists of?
(complex shapes)
d orbital consists of?
(cloverleaf-shaped)
p orbital consists of?
(dumbbell-shaped)
s orbital consists of?
(spherical)
The symbol for this quantum number is ml (Symbol: ml)
Magnetic Quantum Number
The values for this quantum number ranges: Integers from - l to +l
Magnetic Quantum Number
The significance of this quantum number Indicates the orientation of the orbital in space.
Magnetic Quantum Number
The symbol for this quantum number is ms (Symbol: ms)
Spin Quantum Number
The values for this quantum number are either: +1/2 or −1/2
Spin Quantum Number
The significance of this quantum number indicates the spin of the
electron.
Spin Quantum Number
Each energy level can only hold a certain number of electrons. The first energy level can only hold how many electrons? The second can only hold 8, and the third can only hold 18.
2
Each energy level can only hold a certain number of electrons. The first energy level can only hold 2 electrons, the second can only hold how many? And the third can only hold 18.
8