Informatics Chapter 5 Organizing and storing data
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
relational (another name for a table) database
is a series of related tables, stored together with a minimum of duplication to achieve consistent and controlled pool of data
is a type of database that stores data in structured tables (relations) consisting of rows and columns.
Each row is called a record (or tuple).
Each column is called a field (or attribute).
Relationships between tables are defined using keys (primary key, foreign key).
Data can be queried, updated, and managed using SQL (Structured Query Language).
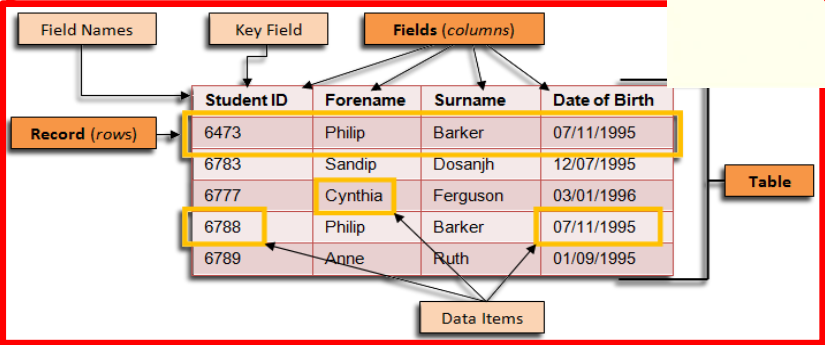
entity
A person, place or thing about whom or about which an organization wants to store data.
records
A row in a table; all the data pertaining to one instance of an entity.
fields
A characteristic or attribute of an entity that is stored in the database. ( column headings)
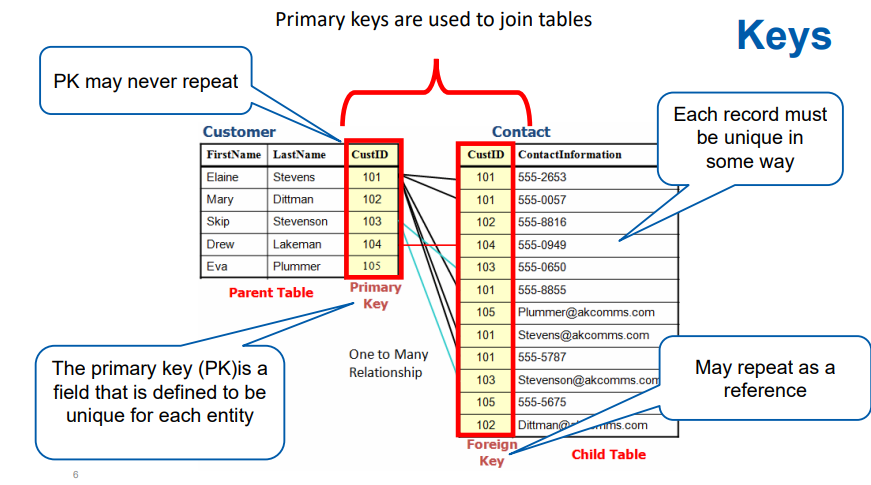
primary key
A field in a table that is unique – each record in that table has a different value in the primary key field. The primary key is used to uniquely identify each record and to create relationships between tables.
foreign key
when a primary key is posted into another table to create a relationship between the two.
is a field (or a set of fields) in one table that refers to the primary key of another table.
It is used to establish and enforce a link between the data in the two tables.
Ensures referential integrity, meaning that relationships between tables remain consistent.
Database design
is the process of structuring a database to efficiently store, organize, and manage data while minimizing redundancy and ensuring data integrity.
A well-designed database supports easy data retrieval, updates, and reporting.
It involves planning tables, fields, relationships, and constraints.
The approach has four stages
1 Identify all entities.
2 Identify all relationships between entities.
3 Identify all attributes.
4 Resolve all relationships.
Database Management Systems
is software that allows users to create, manage, and interact with databases.
It provides a systematic way to store, retrieve, and manipulate data.
Ensures data integrity, security, and efficiency.
data manipulation language (DML)
is a subset of SQL used to manipulate the data stored in a database.
Unlike DDL, which deals with database structure, DML deals with the actual data inside tables.
Commonly used by database users and developers to query and update data.
data definition language (DDL)
collection of instructions and commands used to define and describe data and relationships in a specific database
is a subset of SQL used to define, modify, or remove database structures such as tables, indexes, and schemas.
It does not deal with the data inside the tables (that’s DML’s job).
It is used by database administrators (DBAs) and developers to design the database structure.
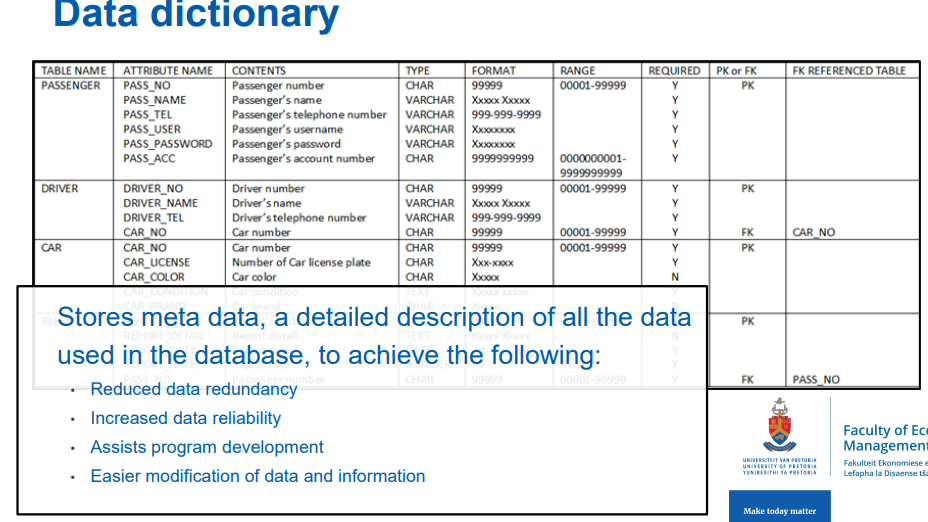
data dictionary
A detailed description of all the data used in the database
is a central repository of information about the data in a database.
It contains metadata, which is data about the data—describing the structure, relationships, and rules of the database.
Used by database administrators (DBAs) and developers to manage, understand, and maintain the database.
concurrency control
A method of dealing with a situation in which two or more people need to access the same record in a database at the same time.
data manipulation language (DML)
The commands that are used to manipulate the data in a database
database administrator (DBA)
The role of the database administrator is to plan, design, create, operate, secure, monitor and maintain databases.
data administrator
A non-technical position responsible for defining and implementing consistent principles for a variety of data issues.
Important characteristics of databases to consider
■ Database size. The number of records or files in the database.
■ Database cost. The purchase or lease costs of the database.
■ Concurrent users. The number of people who need to use the database at the same
time (the number of concurrent users).
■ Performance. How fast the database is able to update records.
■ Integration. The ability to be integrated with other applications and databases.
■ Vendor. The reputation and financial stability of the database vendor.
A DBMS can act as a front-end application or a back-end application
front-end application is one that directly interacts with people or users.
A back-end application interacts with other programs or applications; it only indirectly interacts with people or users.
Big Data Applications
Are software systems or platforms that analyze, process, and manage extremely large and complex datasets (big data) to extract meaningful insights, patterns, or predictions.
data warehouse
is a database or a collection of databases that holds business information from many sources in the enterprise, covering all aspects of the company’s processes, products and customers.
data mining
The process of analyzing data to try to discover patterns and relationships within the data.
Data Collection → Gather large amounts of structured or unstructured data.
Data Cleaning → Remove errors, duplicates, or irrelevant data.
Data Integration → Combine data from multiple sources.
Data Selection → Identify relevant data for analysis.
Data Transformation → Convert data into a suitable format.
Pattern Discovery / Mining → Apply algorithms to find relationships, trends, or anomalies.
Evaluation and Interpretation → Assess the results and extract actionable insights.
business intelligence (BI)
The process of gathering enough of the right information in a timely manner and usable form, and analyzing it to have a positive impact on business strategy, tactics or operations.
competitive intelligence
is the process of gathering, analyzing, and using information about competitors, market trends, and the business environment to make better strategic decisions.
One aspect of business knowledge limited to information about competitors and the ways that knowledge affects strategy, tactics and operations.
counterintelligence
The steps an organization takes to protect information sought by ‘hostile’ intelligence gatherers.
Distributed Database
Database in which the data may be spread across several smaller databases connected via telecommunications devices
replicated database
A database that holds a duplicate set of frequently used data.
online analytical processing (OLAP)
Software that allows users to explore data from a number of perspectives.