Unit 4 | APHUG
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
neocolonialism
powerful country controlling weaker country indirectly through economy
relic boundary
used to exist but no longer a boundary
ex. berlin wall
superimposed boundary
drawn by external powers WITHOUT considering differences
ex. scramble for africa
antecedent boundary
boundaries drawn BEFORE a territory was populated
ex. canada, USA (49th parallel)
ex. boundary between Chile & Argentina was seperated by mountains

delimit
to draw boundaries on map
demarcated
boundary is marked with physical object

demilitarized zone
area between 2 states that agreed to no military presence
allocational boundary dispute
valuable natural resource in both sides
redistricting
redrawing boundaries of voting districts after a census
state fragmentation
country divided into distinct regions
state disintegration
countries into 2 or more distinct countries
state
area with a permanent population
defined borders
sovereign government
recognized by other states
nation
group of people with shared culture & history
self determination
right/desire for a nation (group of people) to govern themselves
nation-state
a sovereign state that has one nation (ethnic group) within its borders
ex. south korea (many south koreans)
multinational state
state that has more than one nation within its borders
ex. United States
multistate nation
nation spread across multiple sovereign states
ex. Burques live in Spain & France
Kurds live in Iraq, Turkey, Iran
What do stateless nations lack?
control over political boundaries
government with sovereignty
control over affairs
recognition from other states
autonomous regions
geographic area in a state with higj degree of autonomy from the state
ex. native america reservations in U.S
semi-autonomous regions
area controlled by another state
moderate degree of self-governance
ex. Hong Kong, China
colonialism
acquiring territories and settling there to exert control
Berlin Conference
European powers colonized Africa and drew political borders that benefited them without considering existing ethnic borders
devolution
power is broken up and spread between lower organizations
shatterbelts
region caught between stronger conflicting forces, leading to instability and political fragmentation.
ex. west & east germany, korean war
chokepoint
narrow passageway to another place which is difficult to pass through
countries in charge hold a lot of political power
subsequent boundary
drawn after people had already settled in the area
ex. Protestants in the north (Northern Ireland) and Catholics in the south (Republic of Ireland).
consequent boundary
boundary drawn with consideration of different cultural landscapes
(type of subsequent boundary)
ex. border between pakistan and india due to religious differences
frontier
no state has direct power over

definitional boundary dispute
disagree over interpretation of legal documents/original plan

locational boundary dispute
original boundary moves
ex. Mississippi river shifting
operational boundary dispute
borders are clear
function of border causes conflict
ex. Mexican/U.S border
United Nations Conference on the Law of The Seas (UNCLOS)
sea boundaries
extends 12 miles into territorial sea
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
country has rights to natural resource extraction to zone that extends 200 naval miles from coast
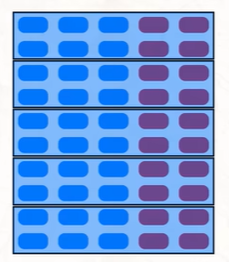
cracking
Splitting a group of voters so they’re too small to win in any district.
🧩 “Break them up!”
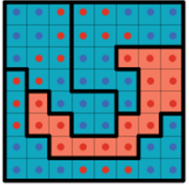
packing
Putting a group of voters all into one district so they can’t influence others.
📦 “Stuff them all in one place!”
win there, but no influence elsewhere.
unitary state
centra/national government has power
policies are made by central government and funneled down to regional units
ex. China, France
advantages of unitary state
fewer government agencies
less corrupt at local level
efficiency
disadvantages of unitary state
central government favoring the dominant group (ignoring minority groups)
disconnection from local areas (slow to respond to their issues)
federal state
power is shared between central government & regional government
decisions are made both local and national level
advantages of federal state
allows for diversity of opinions
allows for multiple political parties to be in power
can tend to local needs
disadvantages of federal state
takes longer to make policy changes
inefficiency
devolution
irredentism
when a country wants to reclaim land it believes belongs to it.
russia’s claim over crimes
disintegrate
when a state or region breaks apart into smaller parts, often due to conflict or division.
Example:
Yugoslavia disintegrated into several independent countries.
Soviet Union
South Sudan & Sudan
Supranational Organizations that revolve around political or military goals
United Nations
African Union (eradicate forms of colonialsm)
Supranational Organizations that focus on military
North Atlantic Treaty Org (NATO) (collective defense/allies)
Economic Supranational Organizations
European Union
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (accelerate economic growth)
Enviromental Supranational Organizations
Arctic Council
Examples of Nation-State
Japan, Denmark, Poland
Examples of Stateless Nation
Kurds
Basques
Palestinians
Multinational state
Former USSR
Lebanon
Multistate nation
Kurds
Koreans
Balkanization
states fragmenting into smaller states
ex. former yugoslavia