Rate of reactions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Factors that affect reaction speed
1. Catalyst
2. Concentration
3. Temperature
4. Size of the particles surface area
5. Nature of reactant (ionic or covalent)
Rate in relation to concentration
They are directly proportional when one is increased the other will increase.
They produce a straight line graph through the origin
Ionic bond
Give or take of electrons is a force of attraction between ions
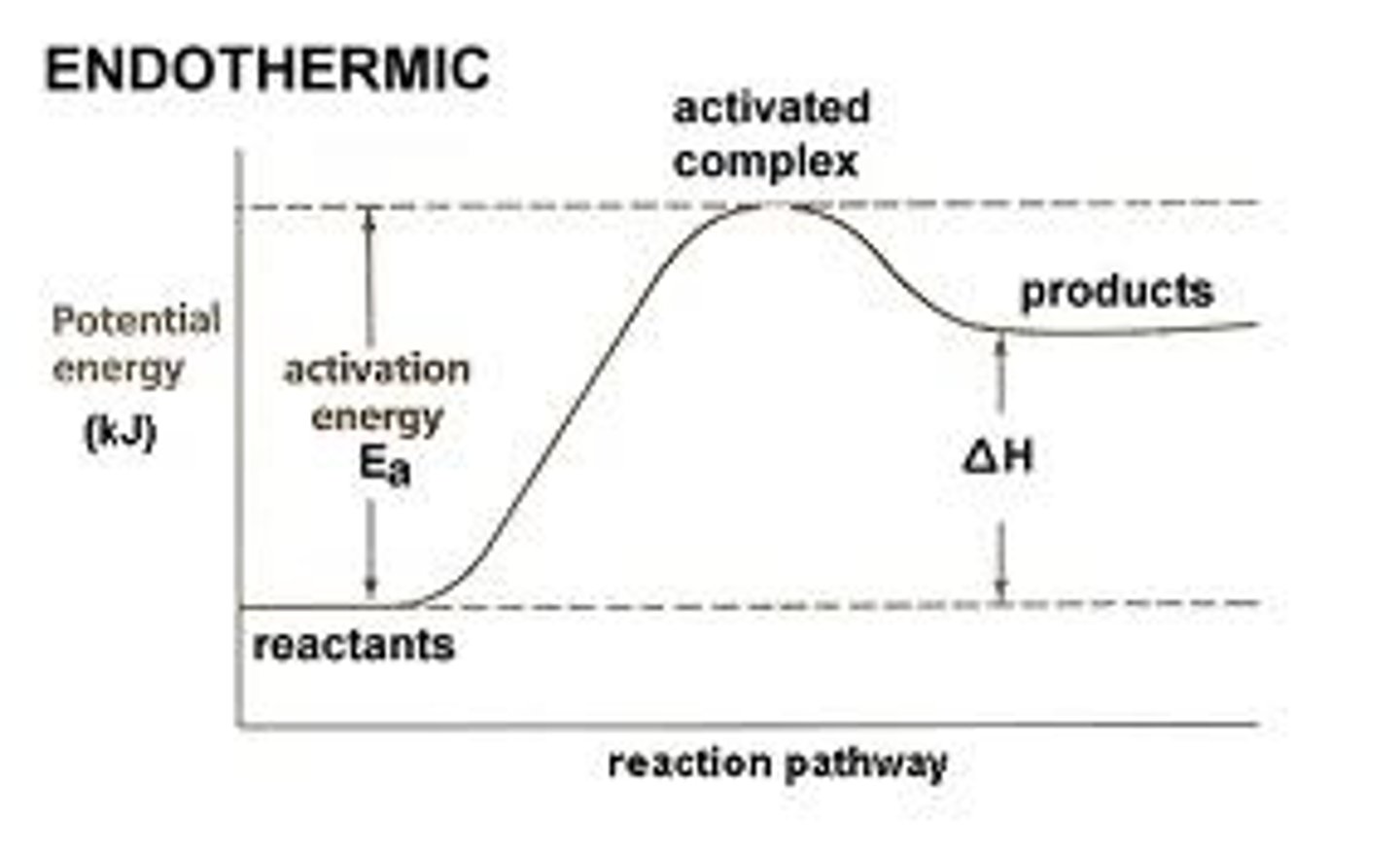
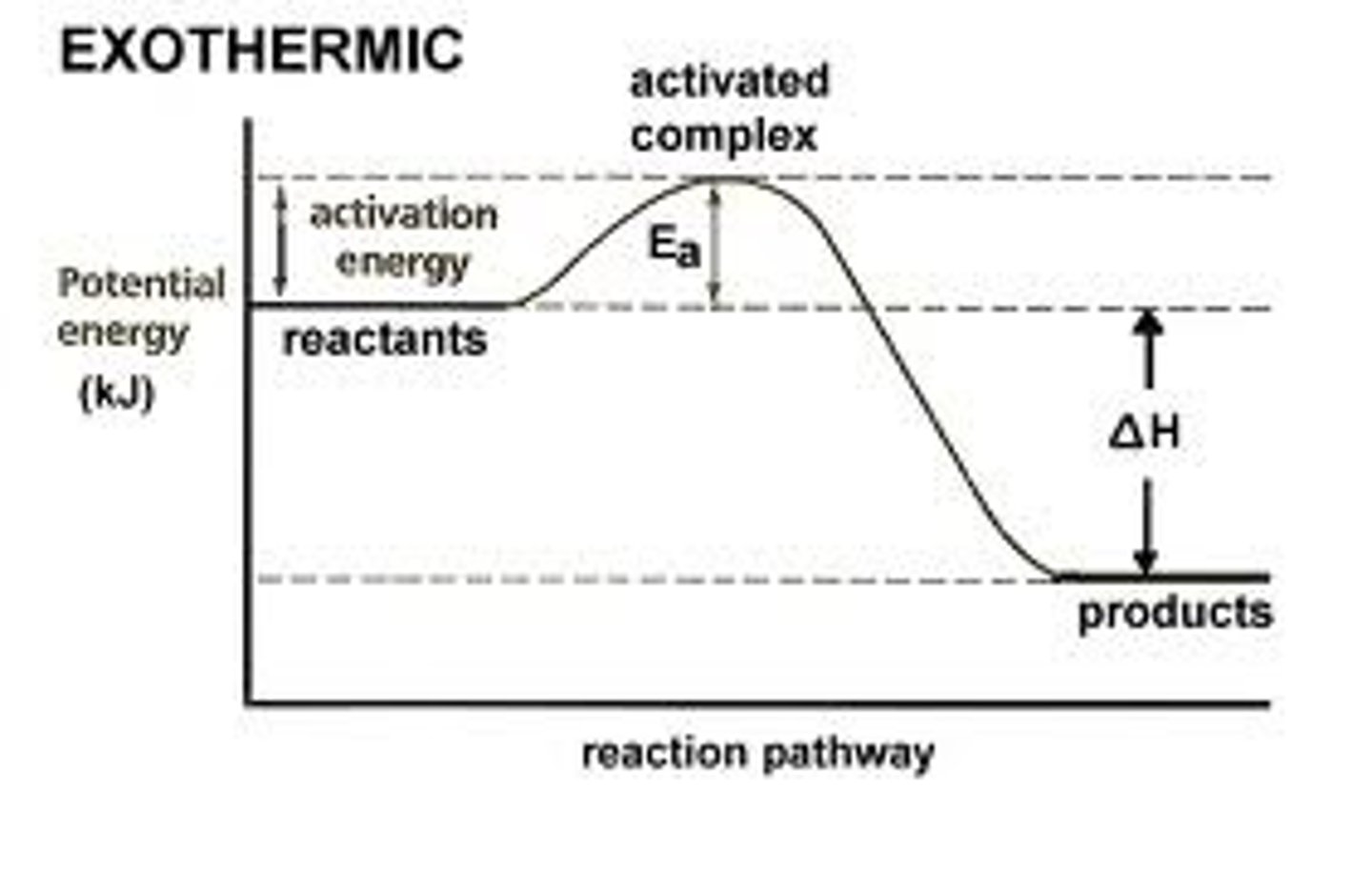
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must have for effective collisions and therefor the reaction to occur
Collision theory
1. For a reaction to occur the particles must collide
2. A collision will only form products if it has a certain amount of energy is present called the activation energy
3.Such a collision is called an effective collision
Effective collision
A collision that results in the formation of products
Endothermic
it results in a positive delta h value
Exothermic
Results in a negative delta h value
rate of reaction
the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time
instantaneous rate of change
slope of the tangent at a point in time. It is the change in concentration at a specific moment
average rate of change
Total volume
---------------
Total time
Rates relation to time
1
Rate = -------
Time
Time is inversely proportional to both rate and concentration
If rate is doubled time is half
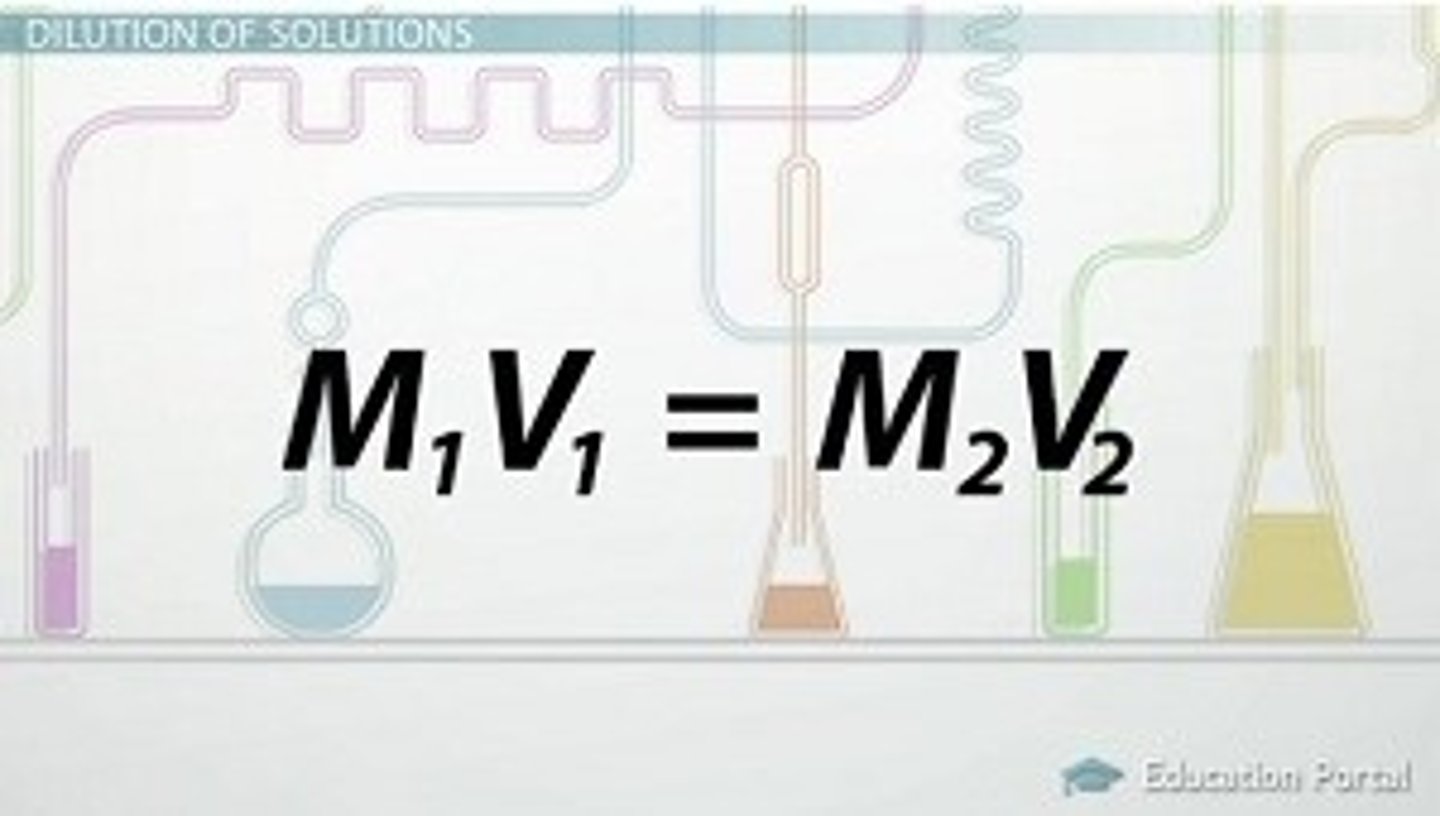
dilution formula
(Vc) X (Mc) (Vd) x (Md)
------------ = ------------
1000 1000
C= concentration
D= Dilute
Relationship between Rate and Temperature
Rate increases exponentially with temperature because more collisions reach the activation energy needed
Effervescence
Fizing created when gas is produced
Conditions for a dust explosion
1. Combustible particles
2. Source of ignition
3. Oxygen
4. Confined space
Catalyst
A substance that alters the rate of reaction but it is not used up in the reaction itself
Properties of a catalyst
1. Specific
2. Chemically unchanged at the end of reaction
3.Increased the mass of catalyst has no effect
4.Powered is faster then lumps due to surface area
5. Catalysts can be poisoned
Heterogeneous Catalysis
This is when the catalysts and reactants are in different phases ( Eg one is solid one is liquid)
Eg 2H2O2 catalyst- MnO2 (solid) 2H2O +O2- product
Homogeneous catalysis
A reaction in which the catalyst and reactants are in the same physical state
2H2O2-reactant catalyst-KI(Liquid) 2H2O+O2- product
Auto-catalysis
this is when one of the products of the reaction is also a catalyst for the reaction
This increases the reaction speed over time
*use example from copy
Mechanisms of catalysts
1. surface adsorption theory
2.Intermediate compound formation theory
Adsorption
the collection of one substance on the surface of another
The surface absorption theory
*Only applies to Heterogeneous Catalysis
1. The reactants hydrogen and oxygen are absorbed onto the surface of platinum. They are held onto the surface by temporary bonds
2.The increased concentration on the surface makes it more likely that a reaction will occur. Bond
3.The water molecules are released from the surface of the catalyst allowing more reactants to approach the surface
The intermediate compound formation theory
1. Consider this reaction
W+X results in Y+Z
2. Add a catalyst c one of the reactants combines with the catalyst to form an intermediate compound which is short lived. This is a fast reaction
W+C results in WC (this is the intermediate compound)
3. The intermediate compound then reacts with the other reactant to give a final product and regenerate the catalyst
[WC] + X Results in Y+Z+C (fast - C is the regenerate catalyst)
Overall