Midterm Exam
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 3: Monday, September 8th: Introduction and Review of Syllabus; Introduction: What is Astrobiology?; Week 4: Monday, September 15th: What is Life?; Week 6: Monday, September 29th: How Did Earth and Its Biosphere Originate? (PART I); Week 7: Monday, October 6th: How Did Earth and Its Biosphere Originate? (PART II); Week 8: Tuesday, October 14th: How Have Earth and Its Biosphere Evolved? (PART I); Week 9: Friday, October 24th: How Have Earth and Its Biosphere Evolved? (PART II)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
the study of life in the universe that investigates the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life on Earth, combines knowledge and information from astronomy, chemistry, geochemistry, biochemistry, biology, space technology, geology, and planetary sciences
astrobiology

This Greek philosopher proposed natural explanations for natural phenomena; he proposed that the universe consisted of water and that Earth was a flat disk on an infinite ocean
Thales
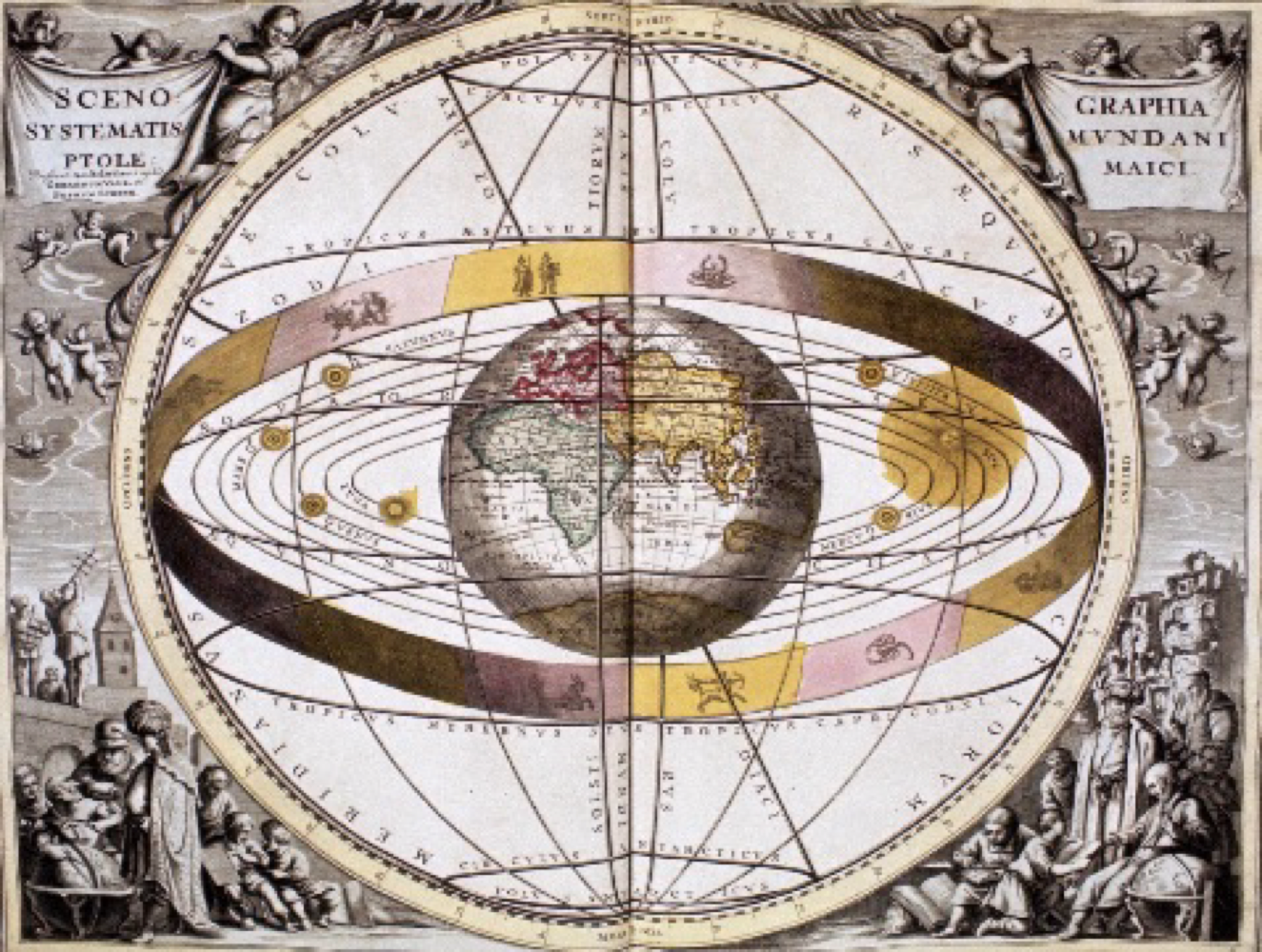

the early Greek model depicting a central earth surrounded by the celestial sphere
Geocentric Revolution

This Greek philosopher proposed an alternative idea to the geocentric revolution to explain the retrograde motion of planets
Aristarchus
this idea, proposed by Aristarchus, depicts the earth revolving around the sun
the heliocentric idea

the revival of Aristarchus’s idea of a sun-centered system by Nicolaus Copernicus, who worked out the math to support it
Copernican Revolution
astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher who made major contributions to the scientific revolution, and to the telescope—wich led to astronomical observations and support for copernicaism
Galileo Galilei
this individual debunked Copernicus’s belief that “heavenly motion” must occur in perfect circles, thus discovering that planetary orbits are elliptical (oval). his model was then developed into three laws
Johannes Kepler
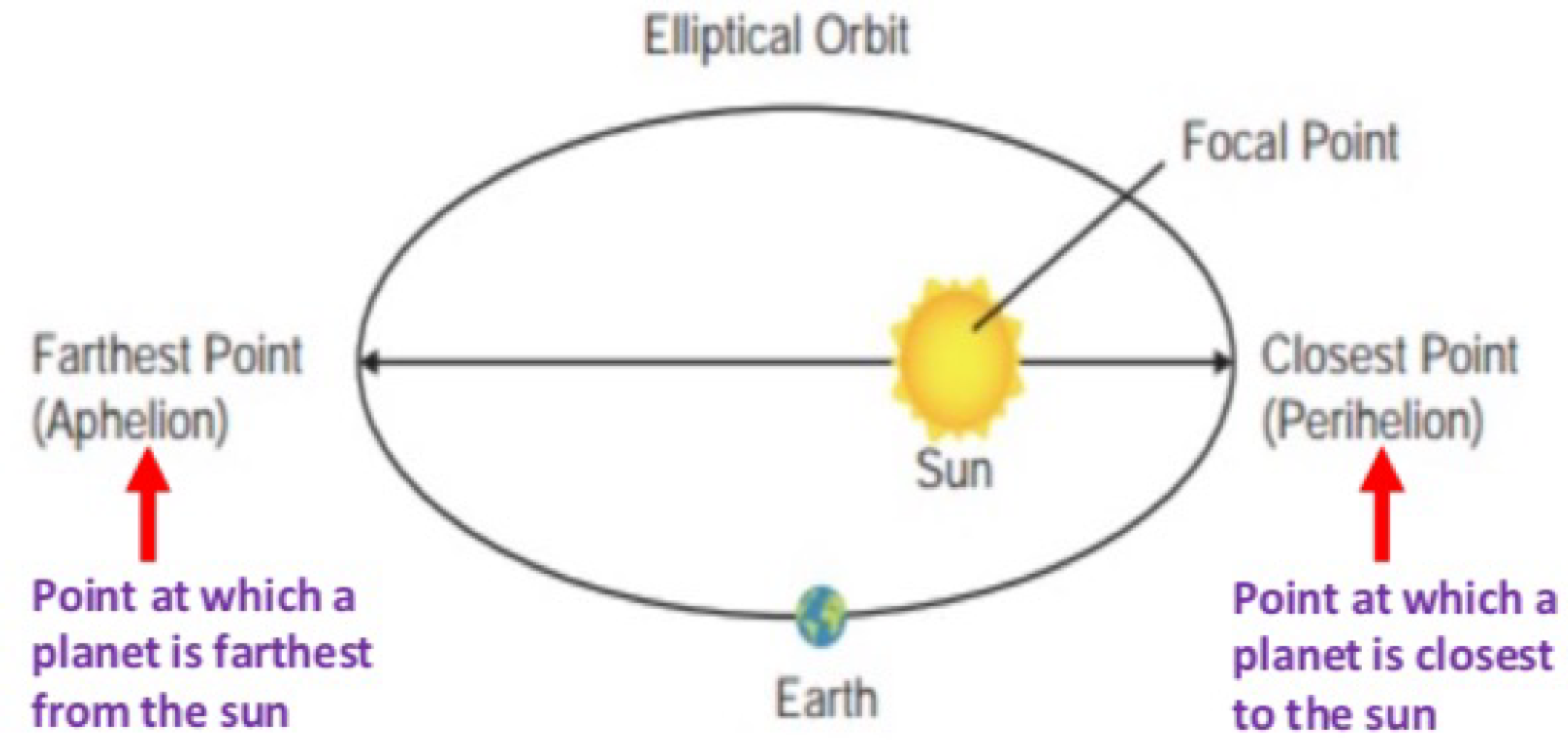
“the orbit of each planet about the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus” describes Kepler’s _______
Kepler’s first law
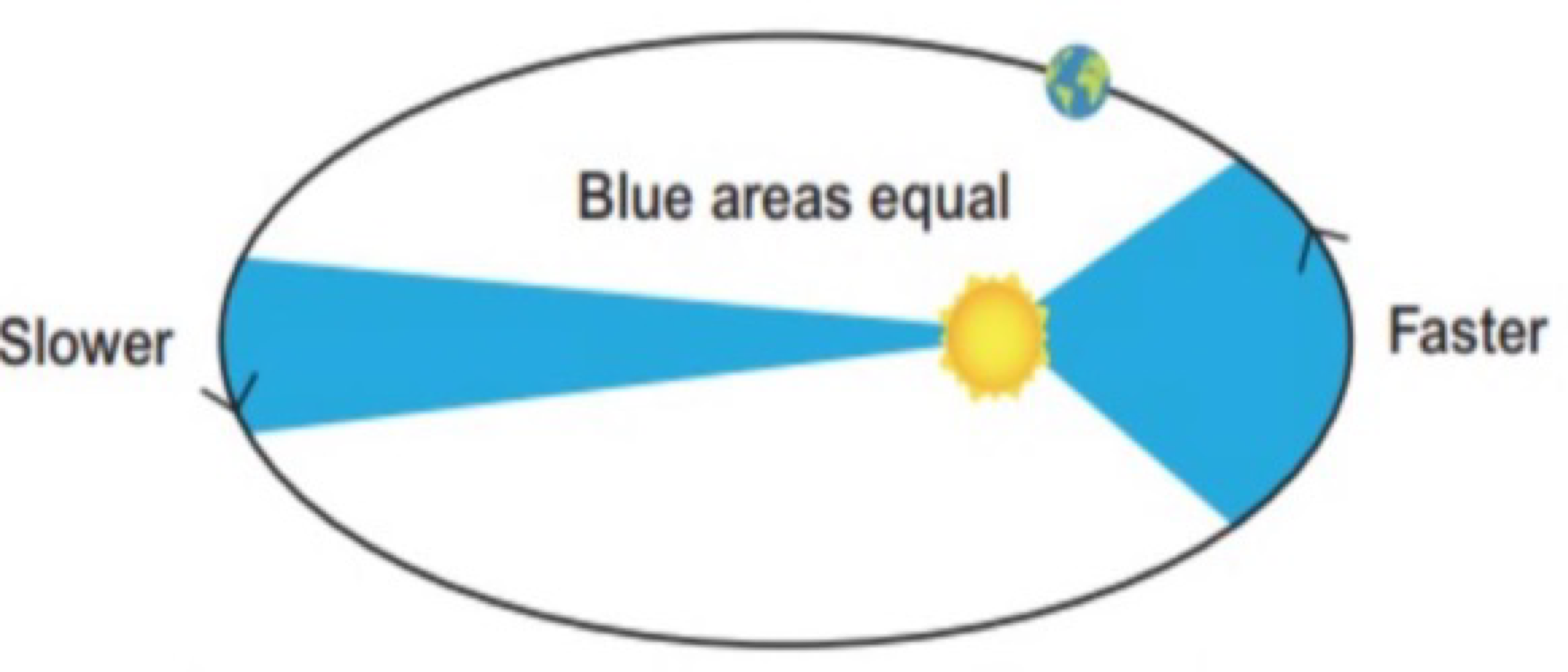
“as the planet moves around its orbit, it moves faster when closer to the sun than when farther away” describes Kepler’s _______
Kepler’s second law
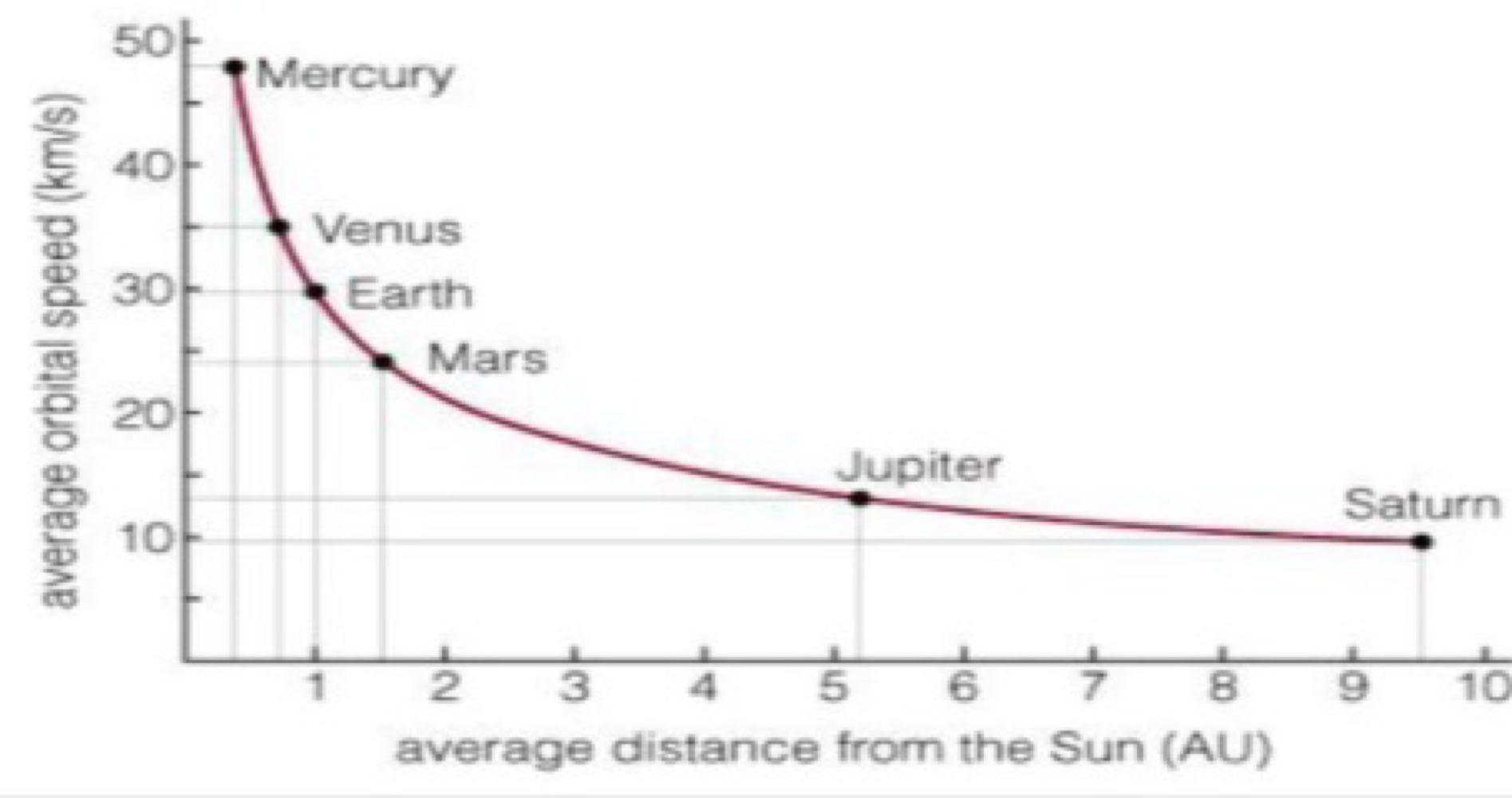
“more distant planets orbit the sun more slowly” describes Kepler’s _______
Kepler’s third law
_______ invented calculus to explain and discovered many fundamental principles of physics
Issac Newton
true or false: Issac Newton explained why the planets should move in elliptical orbits at varying speeds
true
Newton’s publication of Principia included precise mathematical descriptions of how motion works in general, and is now called _______
Newton’s Laws of Motion
“an object in motion stays in motion at the same velocity in a straight line unless a force acts to change its speed/direction” describes Newton’s _______ of motion
Newton’s First law
“force = mass x acceleration” describes Newton’s _______ of Motion
Newton’s Second Law
“for any force, there is always an equal and opposite reaction force” describes Newton’s _______ of Motion
Newton’s Third Law
true or false: Newton’s laws still apply to concents such as black holes and gravitational waves
false. Newton’s laws break down when you get to concepts like black holes and gravitational waves
Issac Newton expressed the force of gravity mathematically with his law of _______, which states that every mass attracts every other mass through the force (gravity)
universal gravitation
Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that the greater the mass of an object, the greater is its _______
force of gravity
Newton’s law of universal gravitation states that the force of gravity depends on the _______ (smaller distance = greater force of gravity)
distance between two objects
true or false: Issac Newton’s theory of gravity led to predictive advances, such as Halley’s comet return
true
the physicist who developed the General Theory of Relativity, which states that all objects reside in a fourth-dimensional spacetime
Albert Einstein
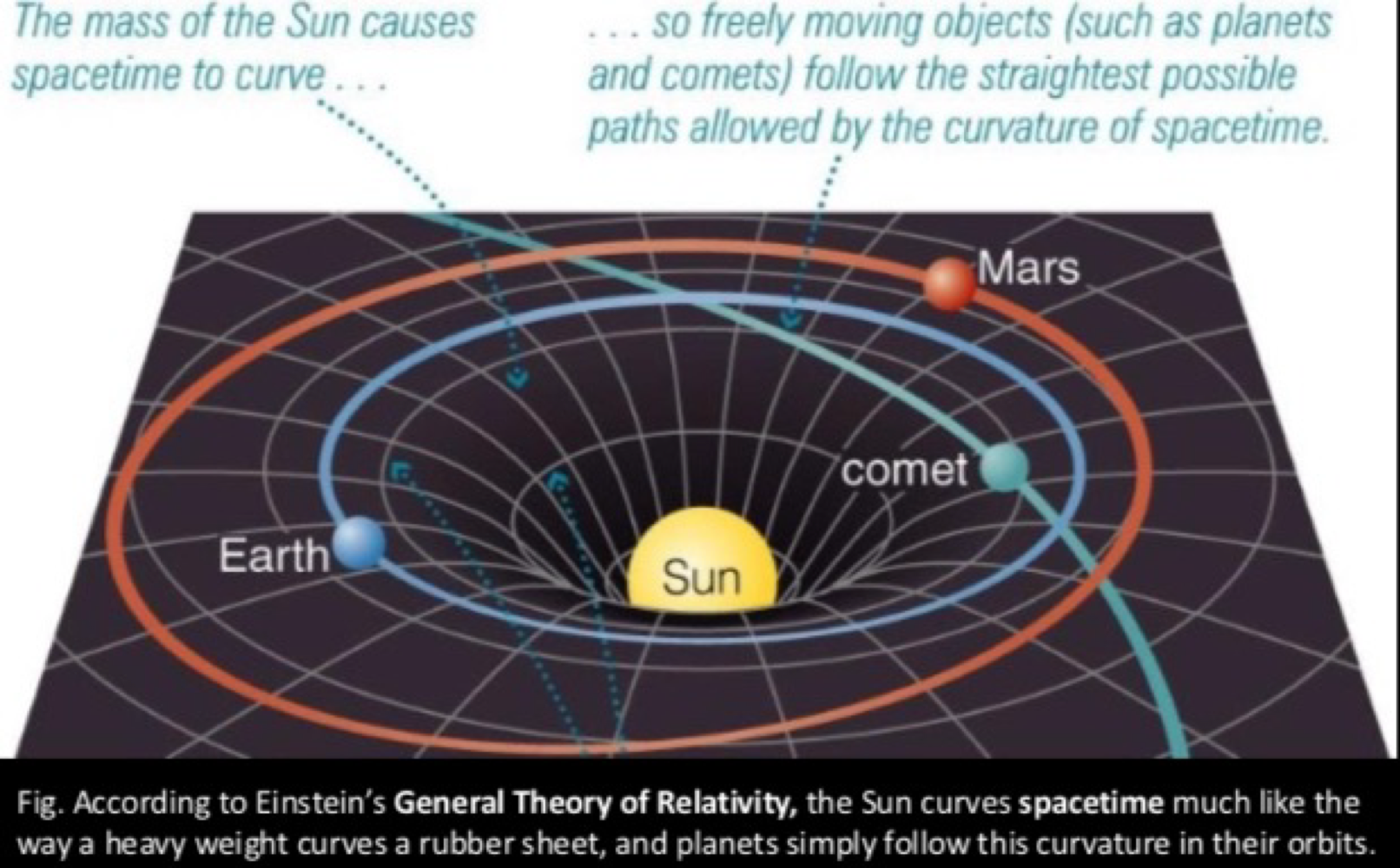
Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity states that spacetime is curved by massive objects (the sun), and other objects (the planets) _______
follow the curvature
Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity predicts the existence of what type of suns?
black holes
10-5 million years ago, _______ developed, which is a physical characteristic of the way Homo erectus walk
Bipedalism
4.2-4 million years ago, _______ emerged; they used simple tools (sticks and stones)
Australopithecus
2-1.5 million years ago, _______ emerged and had the following characteristics:
They used more advanced stone tools
known as handymen
Homo balilis
2-0.1 million years ago, _______ emerged and had the following characteristics:
1. “upright men”
first to evolve a human-like body plan and gait
used large advanced stone tools (spears)
first hominid to use fire (warmth, cooking, defense)
homo erectus
400,000-40,000 years ago, _______ emerged and had the following characteristics:
closest extinct human relative
lived in Europe/Central Asia
large nose for humidifying/warming cold, dry air
short/stocky
used sophisticated tools
controlled fire
lived in shelters
fashioned clothing
skilled hunters
buried their dead
made ornamental objects
homo neanderthalensis
the _______ were Sumerian sky dieties, depicted in Akkadian cylinder seal around 2,300 BC
Anunnaki
_______ were Mayan sky gods during the classical period
Itzamna
_______ (Nevada) and _______, New Mexico are alleged UFO crash sites in the U.S. since 1940
Area 51 and Roswell
The Native American _______ was known to predict alien arrival (“star beings”) who come from the sky to teach mankind
Hopi Dancer
the _______ people of Mali in West Africa impart wisdom from the cosmos: eppiptical orbit of Sirius B around Sirius A
Dogon
_______ and _______ are neolithic monuments reflecting ancient Druid cosmology with significant alighments with celestial events like solstices, suggesting their use in observatories or calendars
Stonehenge and Newgrange
order is a property of life that can be broken down into _______ and _______
bilateral symmetry and radial symmetry
_______ is a property of life in which reproductive success results from inherited traits
evolutinary adaptations
_______ is a property of life in which organisms respond to stimuli in the environment
responses to the environment
_______ is a property of life in which reguation of internal levels in relation to the outside occurs
homeostasis
_______ is a property of life in which energy is obtain and processed
energy processing
_______ is a property of life in which organisms experience gradual changes from embryo to adult
growth and development
_______ is a property of life in which organisms pass genes onto offspring
reproduction
true or false: viruses are considered alive because they can reproduce/replicate without a host
viruses aren’t considered alive because they can’t reproduce/replicate without a host
_______ claimed evolution occured through _______, adapting to different lifestyles, developing traits that are best suited for inheritance
Charles Darwin, nautural selection
true or false: plants have a cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and chlorophyll for pigment
true
carbon molecules associated with life are _______, and form bonds with _______
organic molecules, hydrogen
_______ have two sugar molecules attached
glycosidic bond
_______ has a phosphate group attached to a pentose sugar
phosphodiester bond
_______ has 2 or more amino acids bound together
peptide bond
_______ has a glycerol group and 3 fatty acids and triglyceride bound together
ester bond
_______ makes up oxygenic photosynthetic species
bacteria domain
_______ are organisms that can survive extreme environments
extremophiles
_______ are extremeophiles that are bacteria and can survive dryness and radiation
deinococcus radiodurans
_______ are extremophiles that cause anthrax, and can survive lack of water, extreme heat/cold, and toxins
bacteria subtilis
_______ are extremophiles that are animals and can survive a wide range of environments (extremotolerant)
tardigrades
the _______, proposed by Georges Lemaitre in 1931, describes how the uniiverse expanded from high density and temperature compressed matter about 14 billion years ago
big bang theory
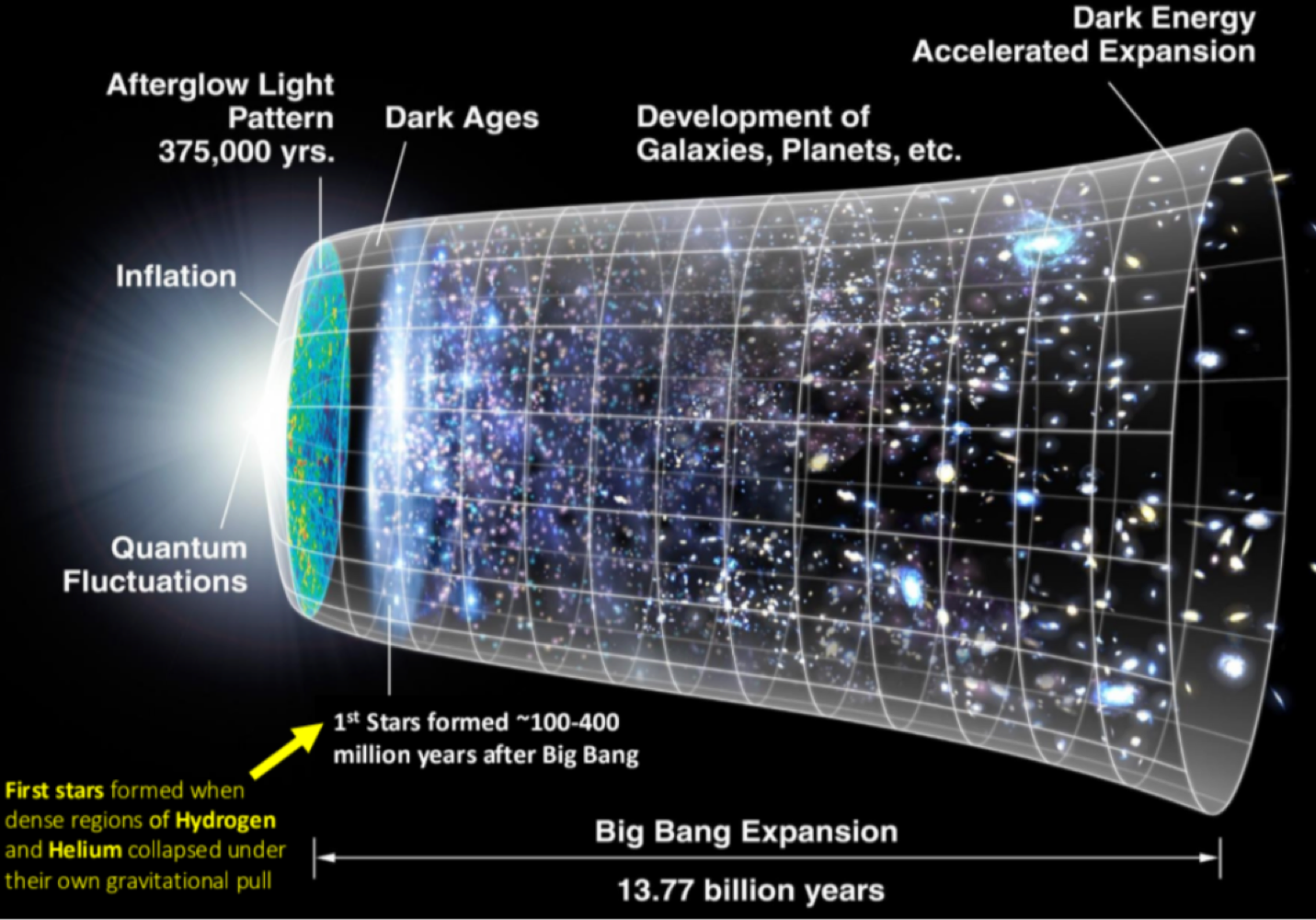
_______ is composed of the sum of all matter and energy, superclusters, voids, and everything within it
the universe
planets are within a _______, which is the sun and its orbiting objects (planets, their moons, smaller objects [asteroids, comets])
solar system
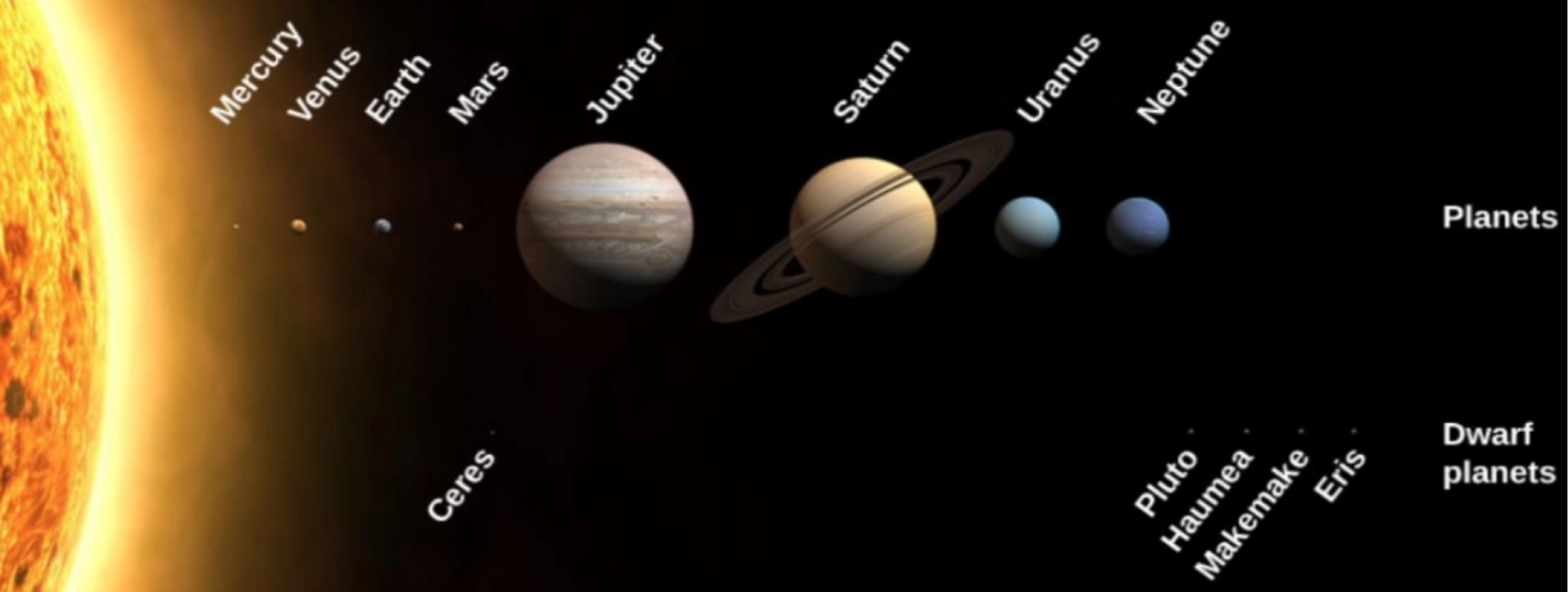

mercury, venus, earth, and mars are _______ planets, whereas jupiter, uranus, and neptune are _______ planets
terrestrial/rocky, jovian/gas
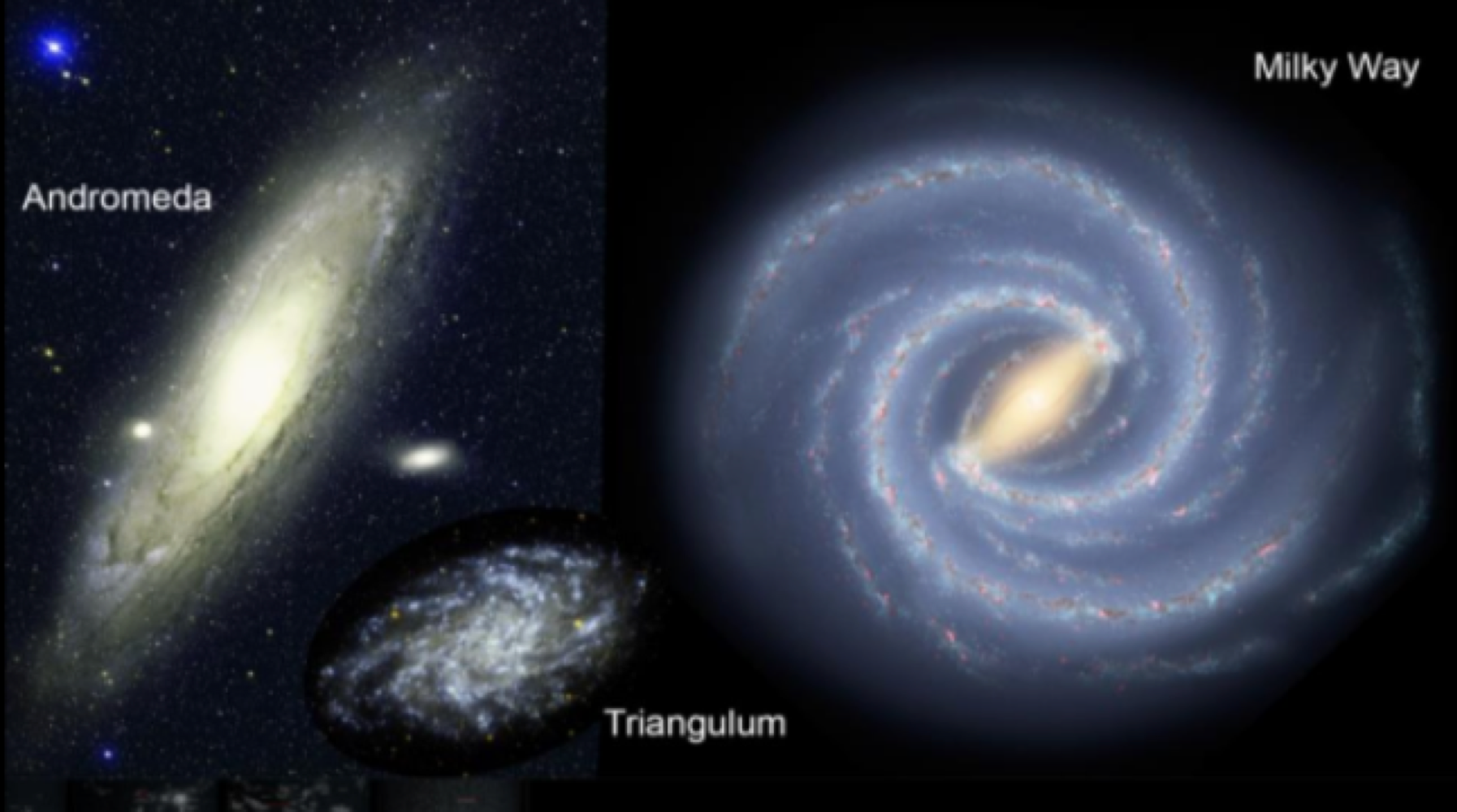
_______ contain solar systems, gas, dust, and billions of stars, which are located in the local galactic group
galaxies

_______ are large groups of galaxies bound together by gravity
local superclusters
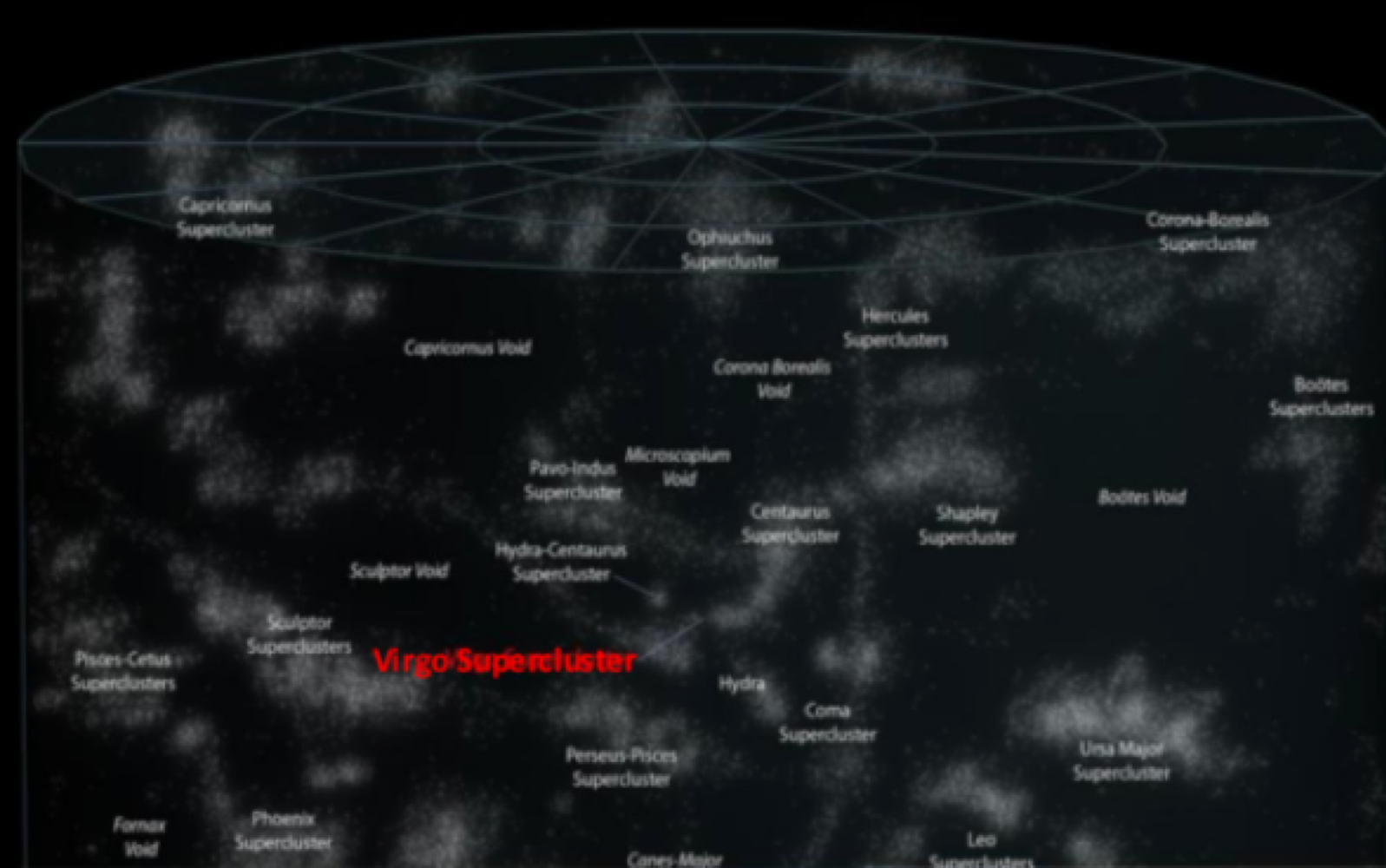
the _______ is the shpherical region of the universe (all matter) visible from earth
observable universe

interstellar distances are measured in light years; 1 light year = the distance that light can travel in 1 year, which is _______
10 trillion kilometers (km)
_______ is the closest star system to our planet, and is 4.4 light years away
Alpha Centauri
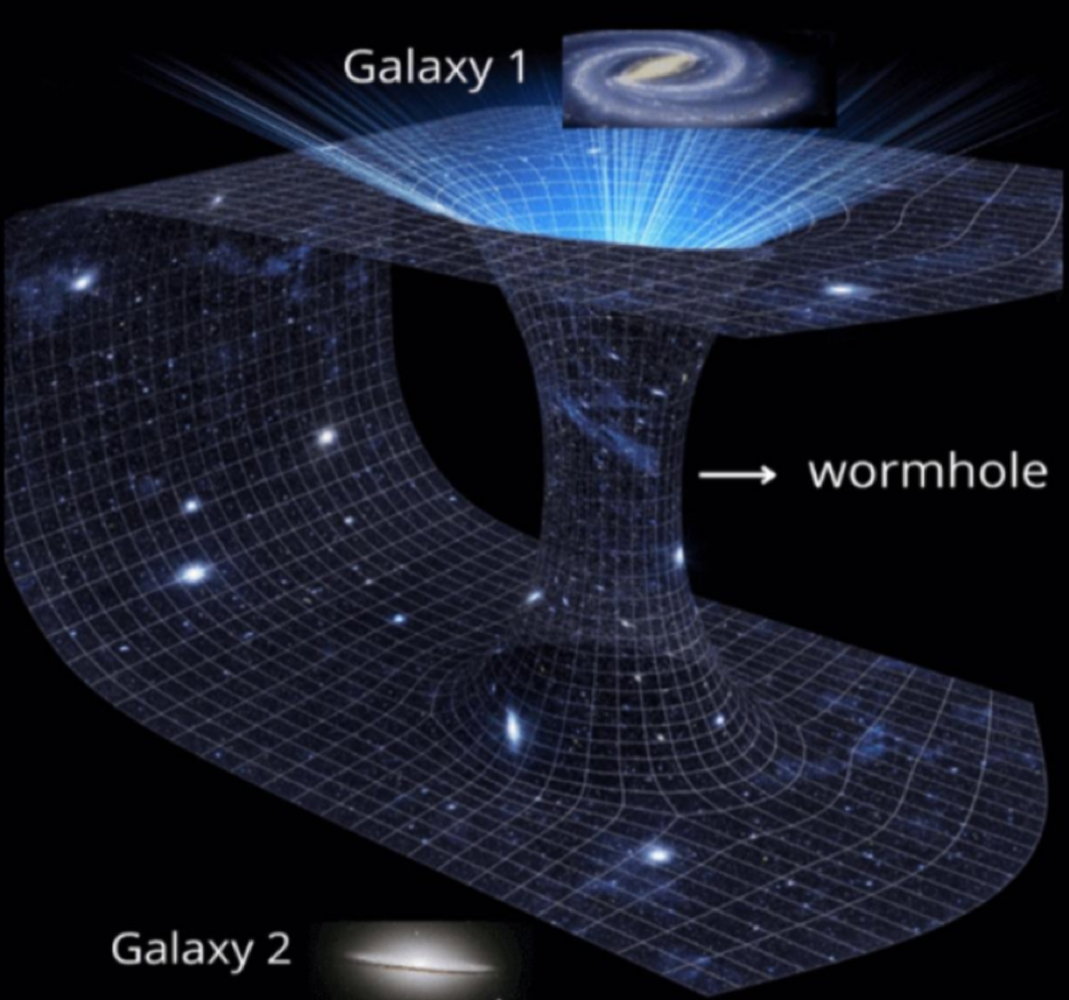
a _______ is a shortcut to travel the interstellar space
wormhole
_______ are leftover icy bodies that releasese gases as it orbits the sun
comets

_______ are leftover rocky bodies smaller thana planet that orbits the sun
asteroid

_______ are leftover rocky/metallic fragments of an asteroid, comet, or planet
meteoroid

_______ are streaks of light seen when a meteoroid hets up in the atmosphere
meteor

_______ are leftover meteor fragments that reaches the ground
meteorite

_______ is between Mars and Jupiter, and contains most of the ateroids in our solar system
asteroid belt
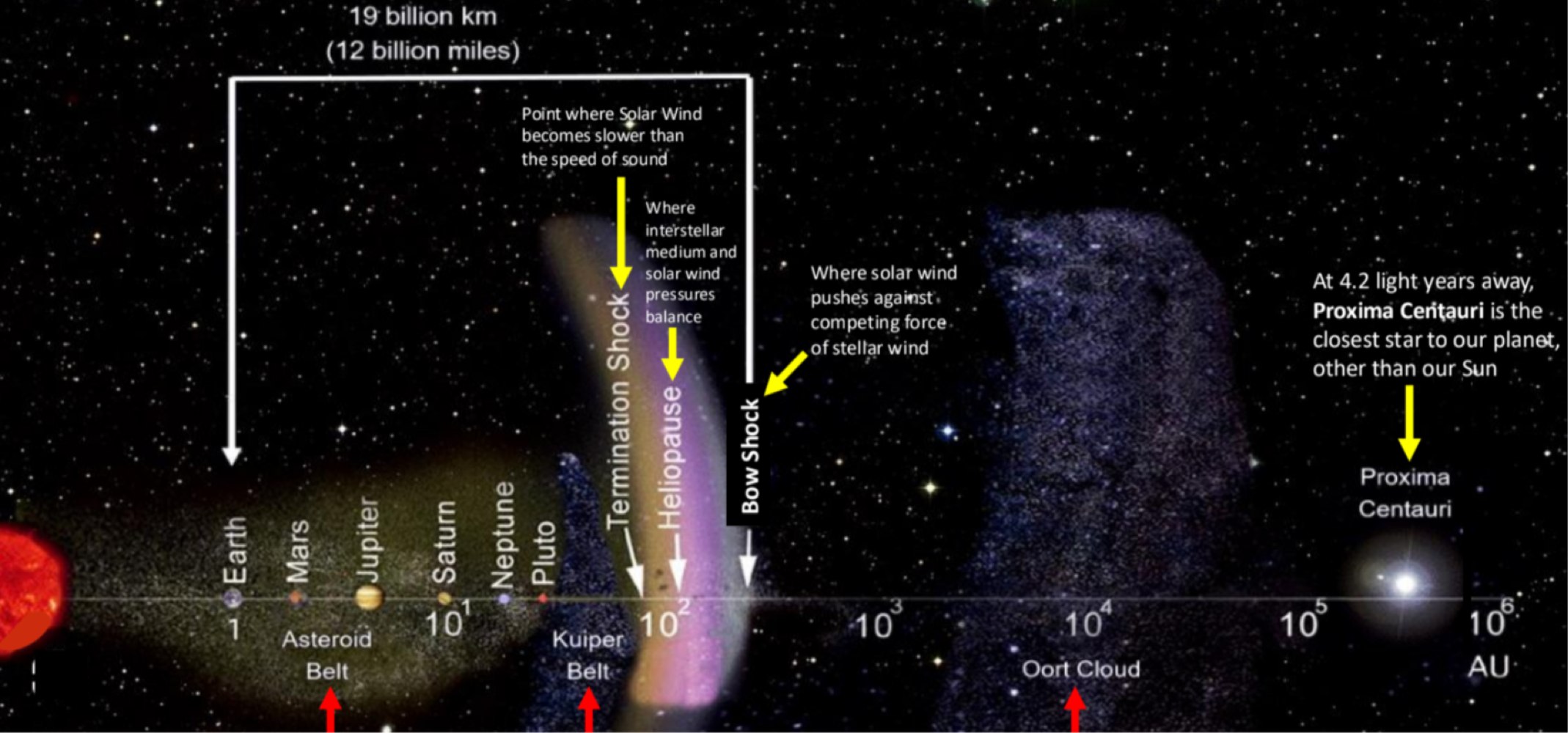
_______ is between pluto and the termination shock (where solar winds are slower than the speed of sound)
Kuiper Belt
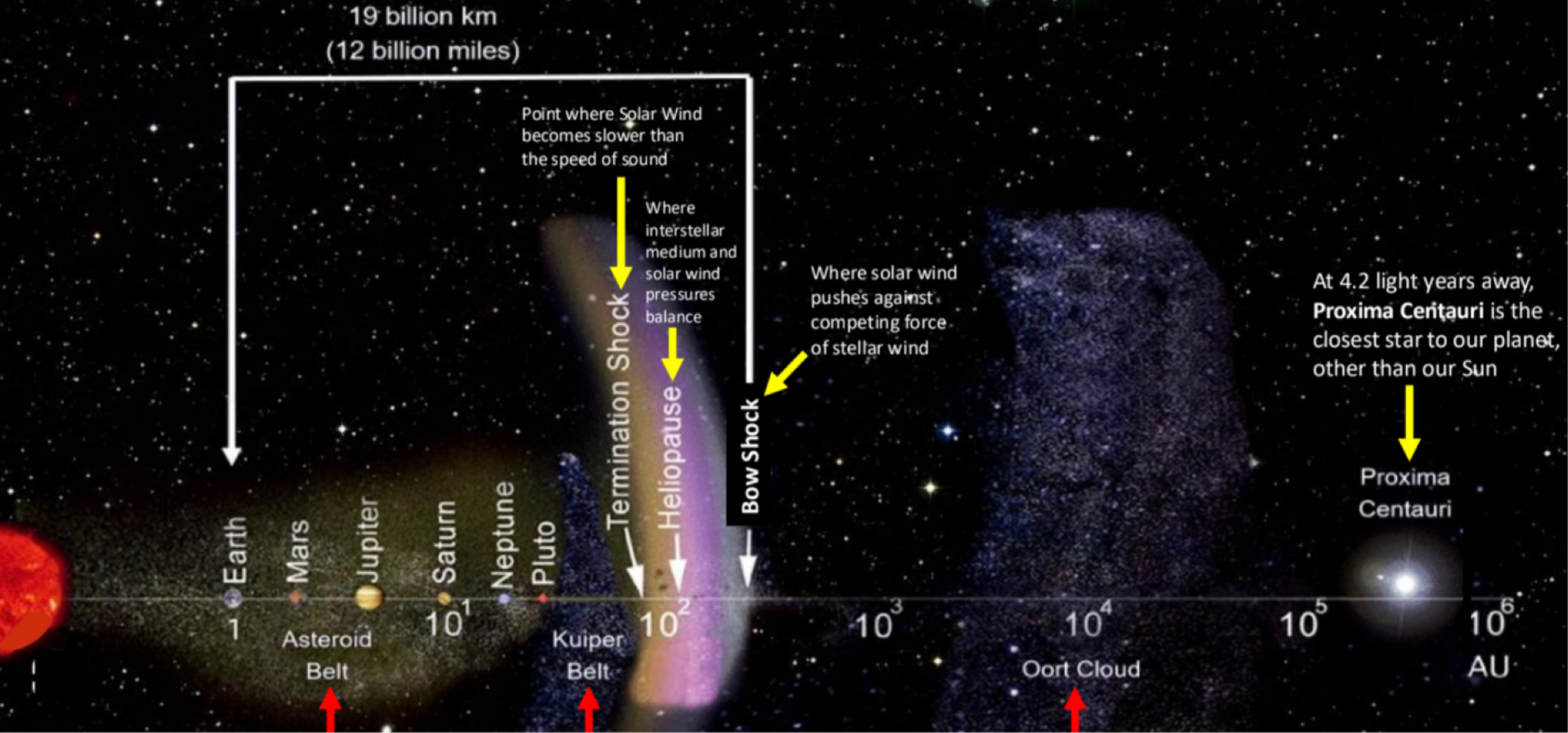
_______ is beyond Pluto’s orbit where comets come from
Oort Cloud
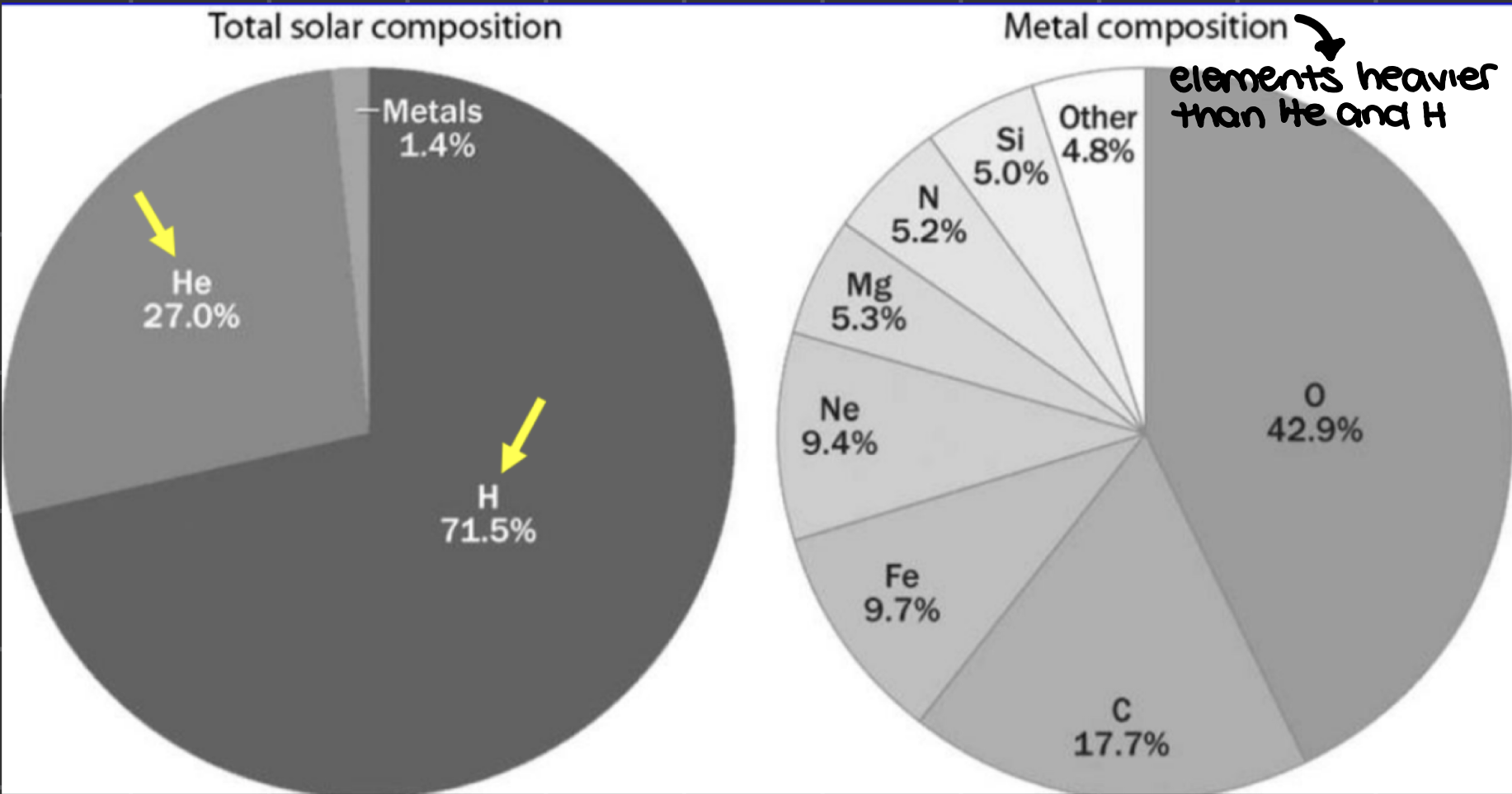
all chemical elements ae formed in _______, the addition/removal of nucleons (protons/neutrons)
nucleosynthetic processes
earliest element synthesis occurred during the _______, which produced most of the universe’s hydrogen and helium
Big Bang nucleosynthesis
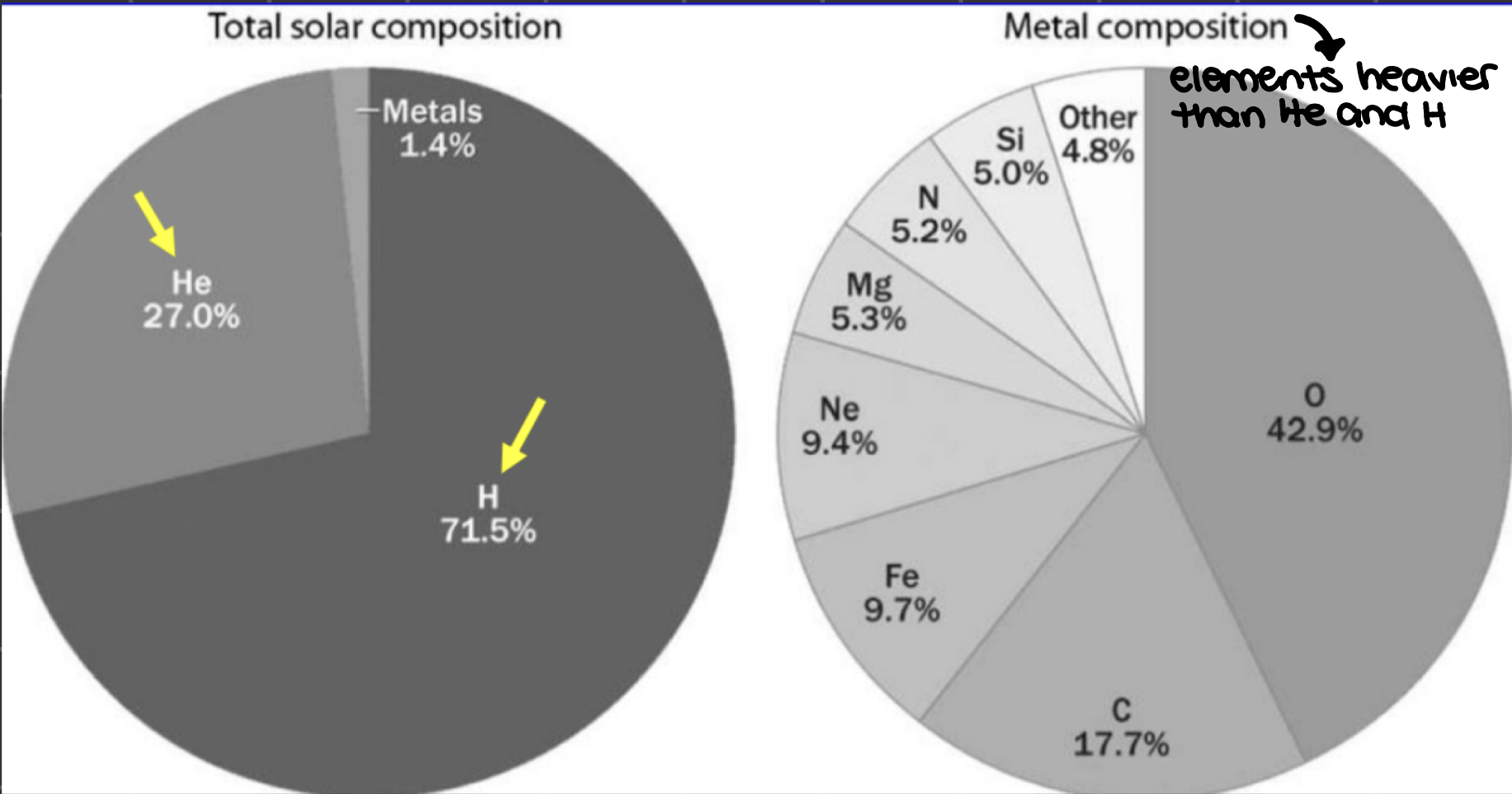
_______ in stars produced the majority of other nautrally occurring elements
stellar nucleosynthesis
stars are formed by _______, gravitational collapse of giant dust and gas clouds made of hydrogen and helium
nebula

gravity will pull hydrogen into a nebula, then it starts to spin and heat up, eventually forming a _______, the result of a nebulae
protostar
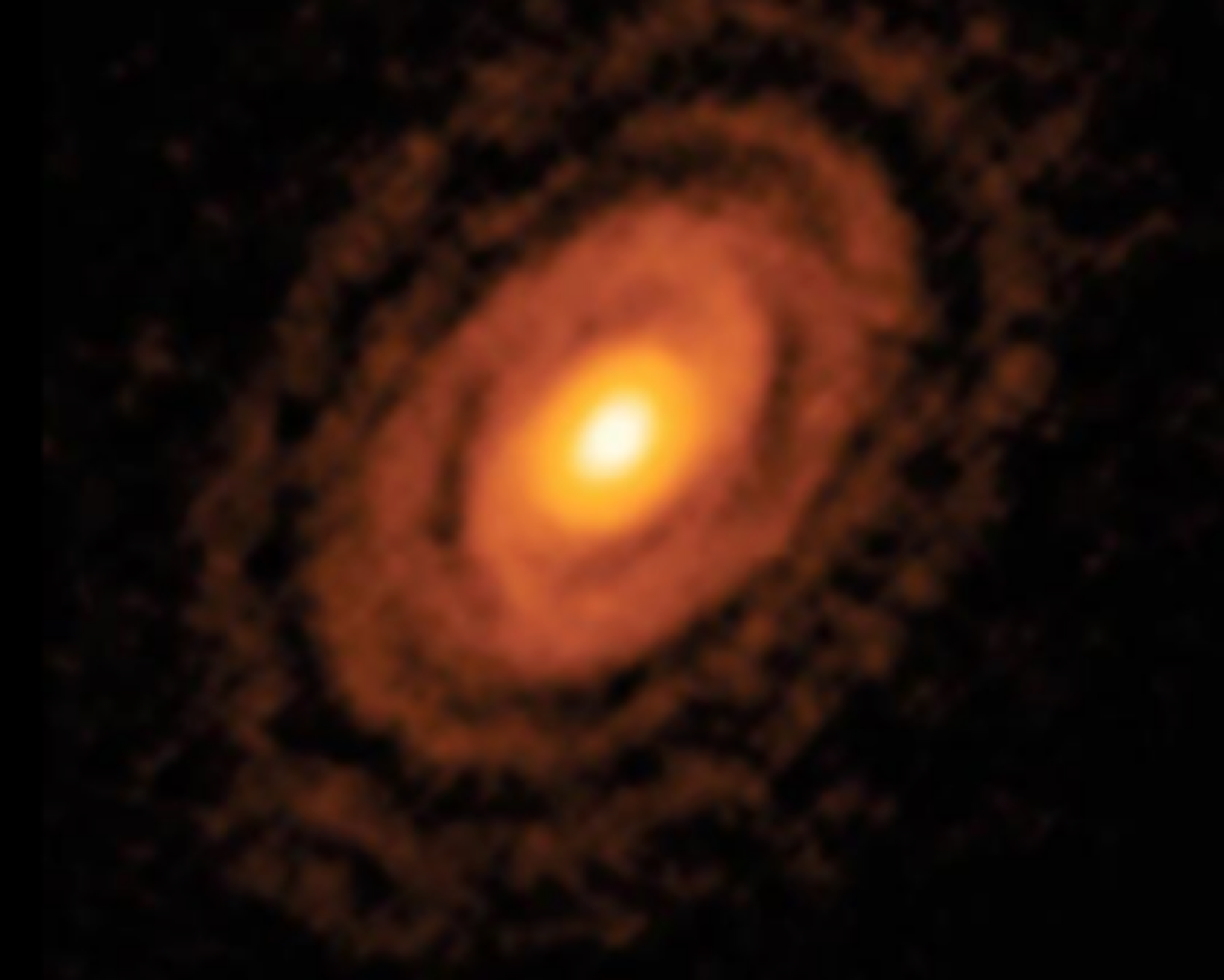

a protostar moves in to the _______ (pre-main sequence; still forming), the transform into a _______ (like ours) or a _______ (Sirius)
T-Tauri Phase, low/medium mass star, higher mass/massive star

low/medium mass stars transform into _______ → _______ (can birth planets) → _______ → _______ (emits no heat or light)
red giants → planetary nebula → white dwarf → black dwarf

higher mass/massive stars transform into _______ → _______ (death of a large star) → _______ or _______
red super giants → supernova → neutron star or black hole
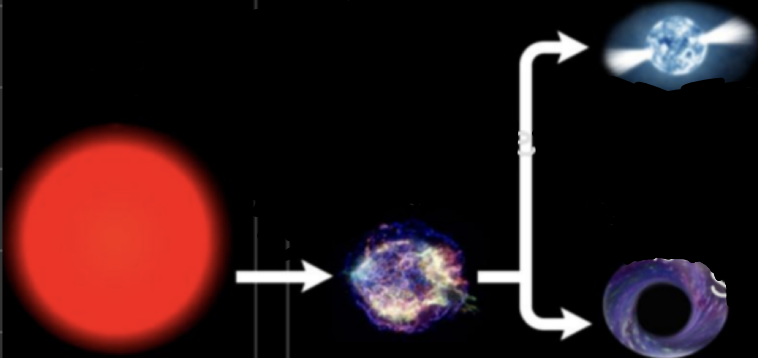
a _______ is a dense city-size ball of neutrons
neutron star
a _______ is an enourmous star that emits no light and has such a strong gravity that prevents the fastest particles in the universe from escaping
black hole
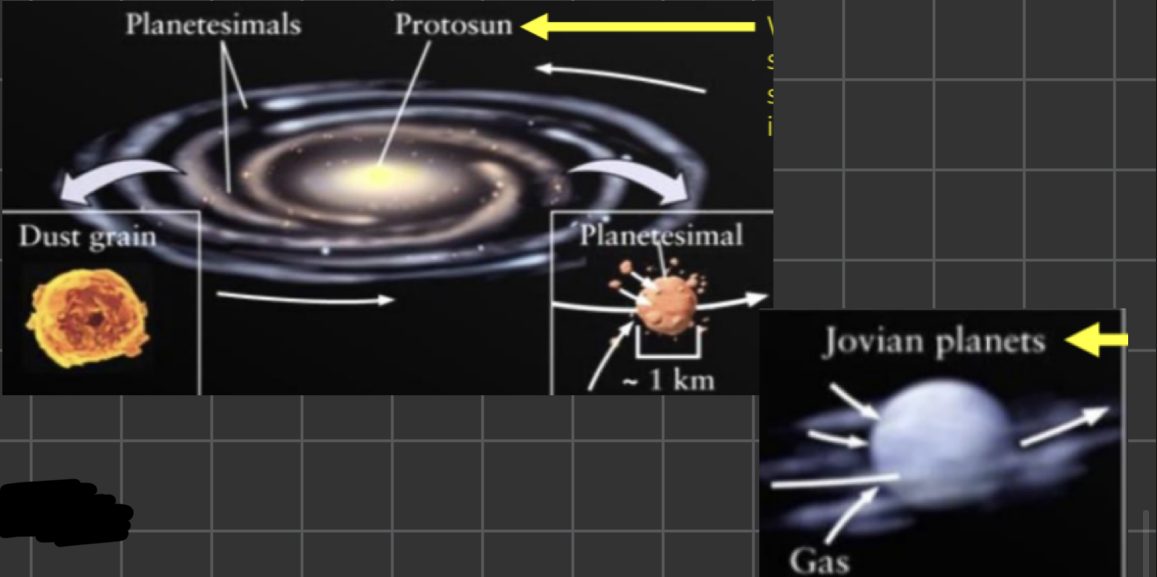
planets start of as dust grains and emerge from _______, giant donut-shaped disk of gas and dust that circles young stars
protosuns
terrestrial planets form from collisions and the accretion of _______ by gravitational attraction, whereas jovian planets are formed by _______
planetsimals, gas accretion
the last giant impact that formed earth was the _______, which threw rock, gas, and dust into space to form the moon
moon-forming impact
the _______ of the protosun is where metals and minerals condense into planets
central region
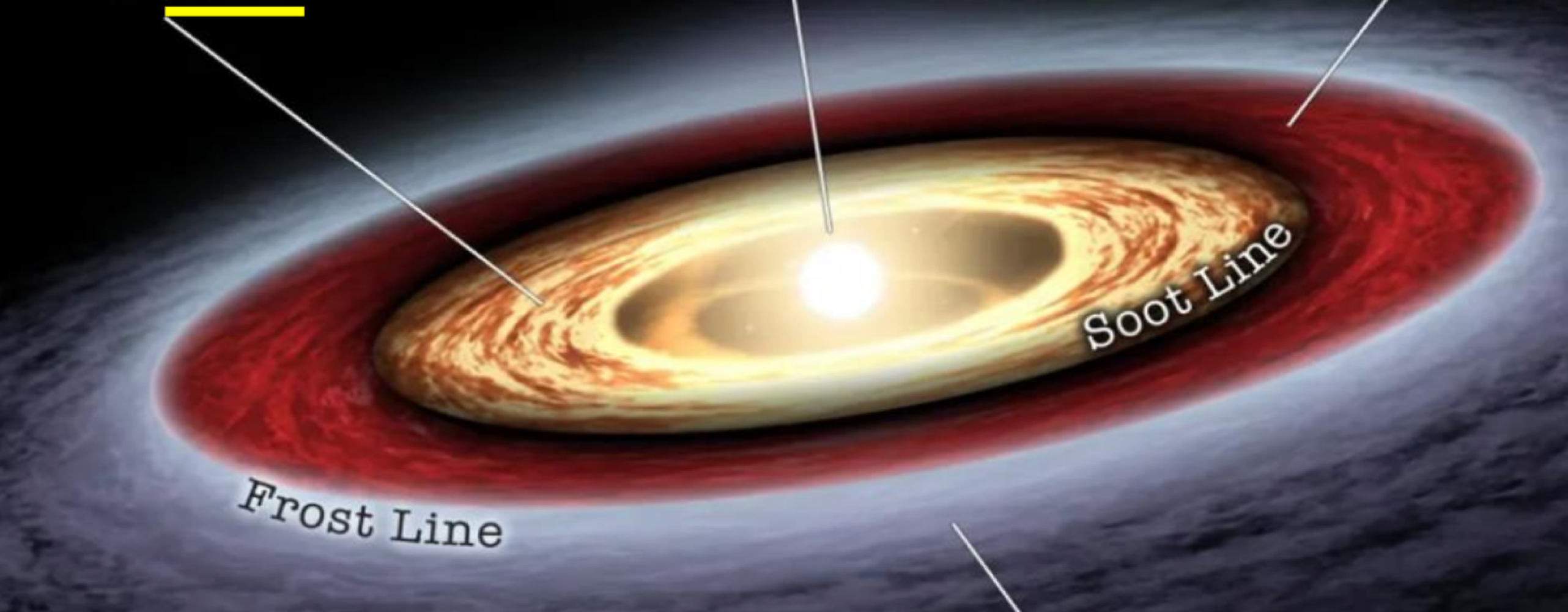

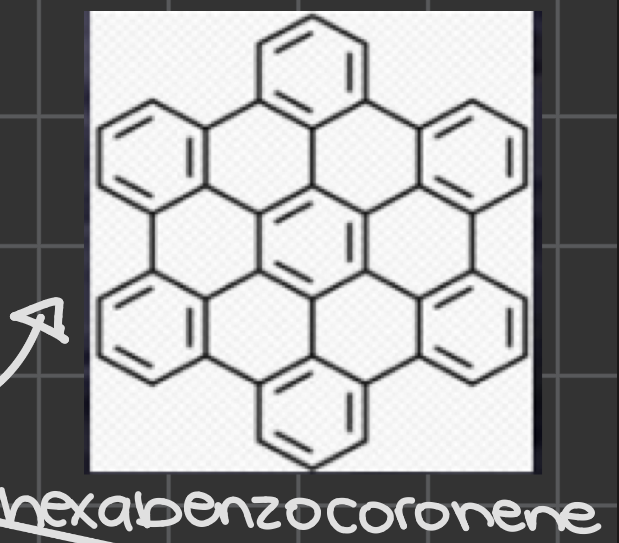
outside the _______ of the protosun is where polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) exist, allowing forming planets to include condense carbon compounds
soot line
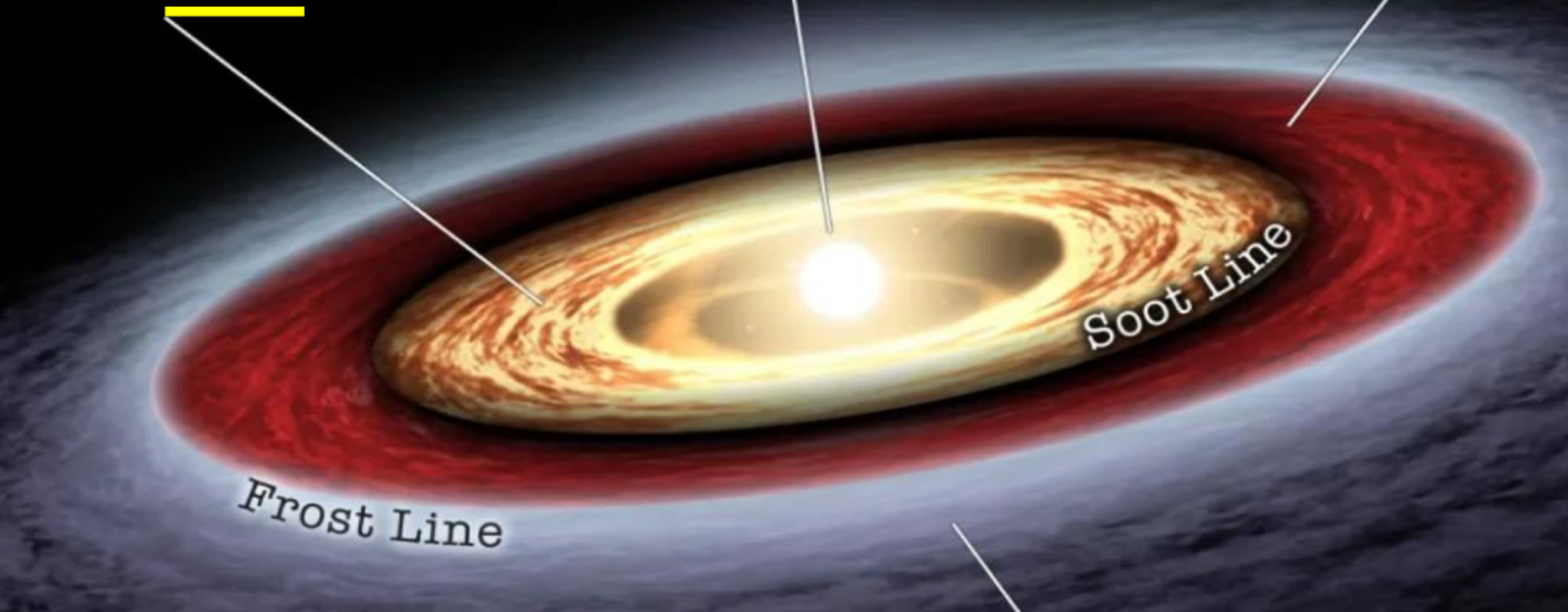

_______ of the protosun is where low temperatures allow condensing planets to include volatile molecules such as water, ammonia, and methane
outside the frost line
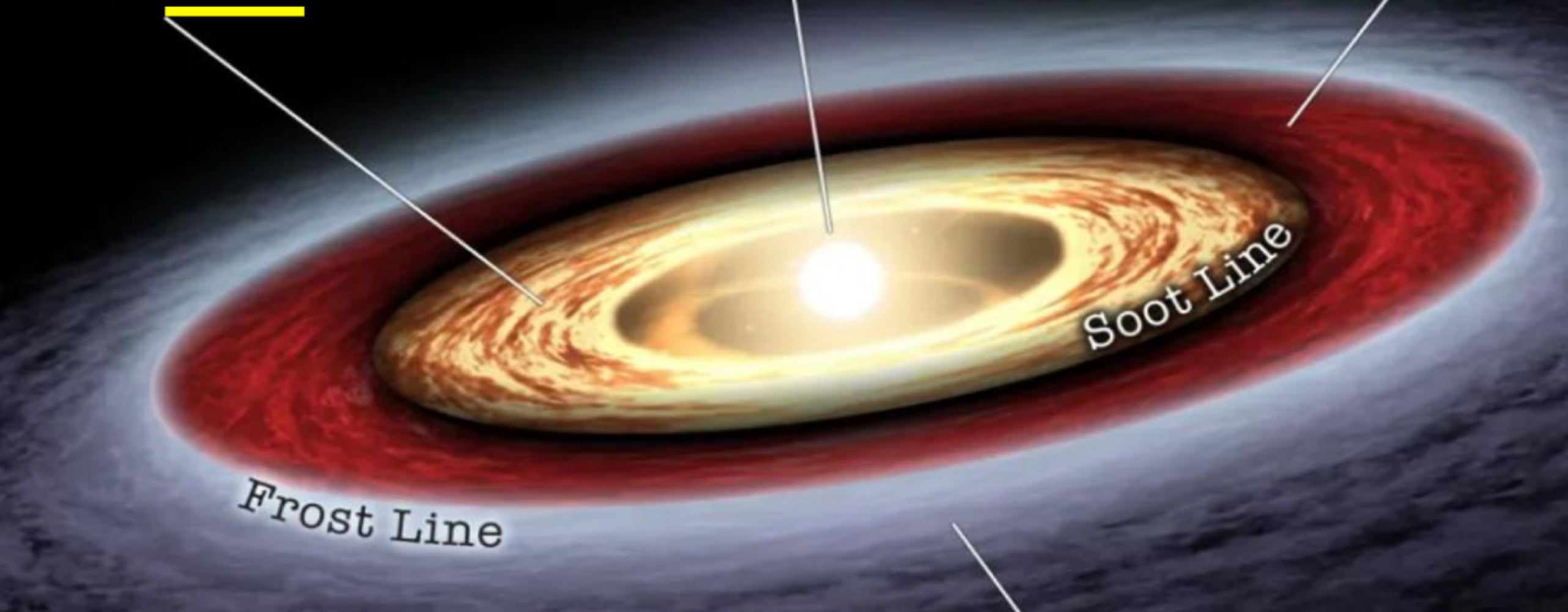

the biosphere formed from _______ and _______ (chondrites), both of which brought volatile elements (hydrogen and oxygen; mostly water), carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus (dissolved salts/gas)
comets, primitive meteorites (chondrites)
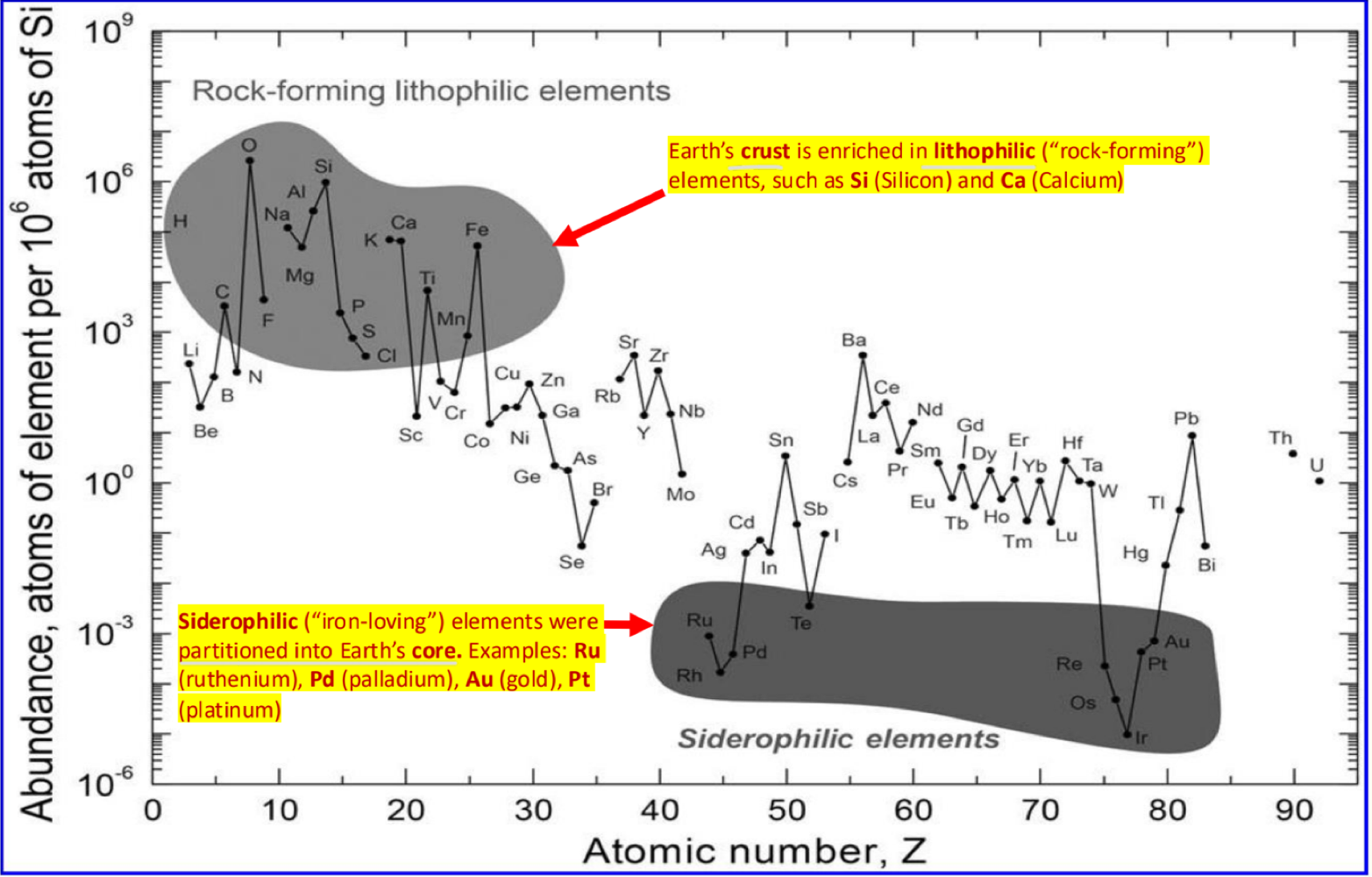
_______ elements compose the surface dn crust of earth, while _______ elements compose the core
lithophilic (rock-loving), siderophilic (iron-loving)
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, partitioning in to different sections
differentiation
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, impact from other objects (comets, asteroids)
cratering
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, low land areas filled with water and magna
flooding
like other terrestrial planets, Earth went through 4 developmental stages, such as _______, active geology, tectonic plates, mountain ranges, recyclation of minerals, weathering, erosion
slow surface evolution (habitability)
_______ explains how life began from a “prebiotic soup”
prebiotic evolution
_______, _______, and _______ helped synthesize and develop essential biomolecules
volcanic activity, lightning, and hydrothermal vents
_______ supports the idea that organic molecules can form from early Earth conditions
Miller-Urey Synthesis
_______ is a stage of earth’s atmosphere defined as mostly hydrogen adn helium from the protosun, both of which were stripped away by solar winds
primordial atmosphere